Biochem CH. 11
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
lipids are soluble in
organic solvents
5 classes of lipids
free fatty acids
triacylglycerols
phospholipids
glycolipids
steroids
free fatty acids func
common fuel
triacylglycerols
storage form of fatty acids
phospholipids are
membrane lipids
glycolipids
membrane lipids composed in part of carbohydrates
steroids
polycyclic hydrocarbons w/ a variety of func
fatty acids structure
chains of hydrogen-bearing carbon atoms
carboxylic acid at one end
methyl group at other end
main source of fuel
fatty acids
fatty acid carbons are usually numbered beginning with
carboxyl terminal atom
omega carbon is the
met
△9 means…
double bond between carbon 9 & 10
when double bonds present in fatty acids, what usual configuration
cis configuration
fatty acid chains usually contain what kind of number of chain
even number
usually 16-18 carbon atom
polyunsaturated acids have what separating their double bonds
methylene group (CH2)
the properties of fatty acids depend on what 2 things
chain length & degree of unsaturation
short chain length relates to temp how
low melting temp
double bonds leads to
less hydrophobic interactions
2 things that can influence fluidity of fatty acids
short chain length & presence of double bonds
(low MP + less hydrophobic interactions)
2 things that determine MP of fatty acids
shape (sat or unsat)
unsat = double bonds —> less hydrophobic interactions —> decrease MP
chain length
longer chain —> more hydrophobic interactions —> increase MP
what types of fatty acids are essential to our diet/cannot be synth by humans
cis polyunsaturated fatty acids
cis polyunsaturated fatty acids are precursors to
a variety of hormones
which type of fatty acids offer protection from coronary heart disease
cis polyunsaturated fatty acids offer protection
triacylglycerols aka triglycerides structure
3 fatty acids joined in ester linkage + glycerol backbone
C#2 ususually has unsat. fatty acids
triacylglyerols nomenclature
beginning fatty acids lose “-ic acid” —> change to “-oyl”
only last fatty acid keeps whole name
(ie: 1-hexadecanoyl-2-(9)octadecenoyl-3-hexadecanoic acid)
fatty acids are stored as
triglycerols/triglycerides
where is the major site for triacylglycerol storage in mammals
adipose tissue
soaps
sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids
how are soaps generated
triacylglycerols are treated w/ strong base
triacylglycerols components
energy rich
hydrophobic
stored when excess glucose in adipose tissue
used when no more glucose
3 types of membrane lipids
phopholipids, glycolipids, cholesterol
phospholipids structure (4)
2 fatty acids
platform (glycerol or sphingosine)
phosphate
alcohol
2 common plaforms of phospholipids
glycerol & sphingosine
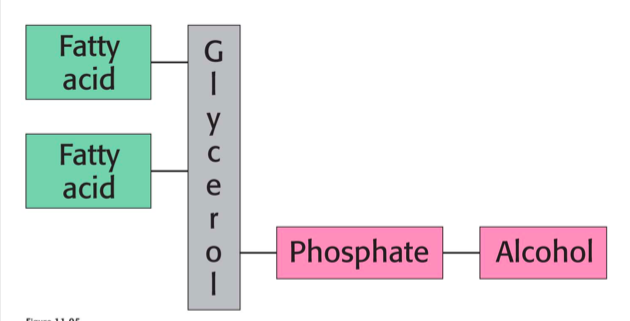
glycerophospholipids strucutre
2 fatty acids
glycerol backbone
phosphate
alcohol
glycerophospholipids features
contains polar group (@ pos. 3 instead of another fatty acid)
amphilic nature (polar/nonpolar)
glycerophospholipids are susceptible to cleavage by
phospholipases
prostaglandins & thromboxanes are involved in what
blood clotting
what inhibits blood clotting
aspirin
leukotrienes
involved in allergy attacks & asthma
phosphatidlyinositol
increases Ca2+ in cytosol
diacylglycerol
activates protein kinase
increase in Ca2+ leads to
increase in aerobic respiration enzyme activity
sphingolipids are phospholipids..
phospholipids built on sphingosine platform
sphingolipids
major membrane components of neurons for nerve sheath
can serve as signaling molecule
sphingolipids structure
contains trans double bond
sphingosine parent compound
sphingosine are more stable than ______ due to _______
glycerophosphate due to amide linkage
ceramides
simplest sphingosine; only has fatty acid
(no sugar/polar groups)

sphingomyelin
major component of nerve sheath
multiple sclerosis is caused by
destrucution of nerve sheath by autoimmune or virus
in sphingomyelin, if A has FA attached and B has phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine it can lead to
sphingophospholipid
destroys nerve sheath —> multiple sclerosis
in sphingomyelin, if A has FA attached, what does B need to have tolead to multipl sclerosis/sphingophospolipid
B has either
phosphatidylethanolamine
phosphadylcholine
cerebroside structure
has monosaccharide @ B and FA @ A
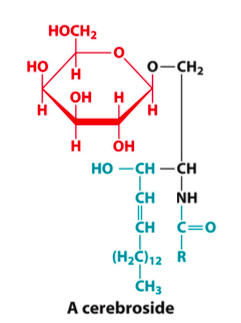
what’s the simplest glycolipid
cerebroside
ganglioside structure
3-30 sugar residues @ B
FA @ A
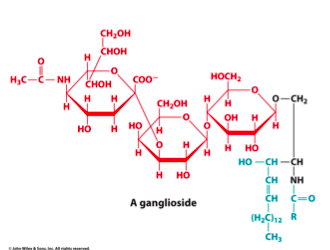
ganglioside func
receptors for pituitary glycoprotein in hormones
if ganglioside can’t be broken down —> leads to
sphingolipid storage diseases
glycolipids (def)
carbohydrate-containing lipids; also a membrane lipid
glycolipids role in cell membrane
cell-cell recognition on extracellular surface
steroids structure
built on tetracyclic platform
3 cyclohexane rings + 1 cyclopentane ring fused together
cholesterol is a precursor to
steroid hormones & some vitamins
most common steroid
cholesterol
glucocorticoids (steroid) func
carb, lipid, protein, metabolism
aldosterone (steroid) func
excretion of water + salt from kidneys
androgens & estrogens (steroids) func
sexual characteristics
3 lipid soluble vitamins
vitamin A, E, K
vitamin A func
assists in vision
vitamin E func
antioxidant —> reduces oxidizers
vitamin K func
assists in blood clotting
what parts of the membrane lipid provide hydrophilic properties
alcohol & phosphate components (polar head)