CONSUMERISM AND PURCHASING OF FOOD
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Section 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is ‘bulk shopping’?
Bulk shopping refers to purchasing large quantities of items, typically at a lower price per unit, intended to reduce costs and minimize shopping frequency.
Who is a consumer?
A consumer is an individual or entity that purchases goods or services for personal use, rather than for resale.
What is ‘credit’ as it relates to consumerism?
The ability to purchase goods or services with borrowed money, which must be paid back with interest over time. It allows consumers to buy now and pay later, typically through credit cards or loans.
What is co-operative shopping?
Co-operative shopping involves purchasing goods or services collectively, usually through a cooperative organization, to benefit from lower prices and improved product selection.
What is comparative shopping?
The process of comparing products or services to determine the best buy in terms of price, quality, and features before making a purchase.
Who is a ‘green consumer’?
A green consumer is a person who prioritizes environmentally friendly products and sustainable practices in their purchasing decisions.
What is gross weight?
Gross weight refers to the total weight of a product, including its packaging and any additional materials.
What is impulse buying?
Impulse buying refers to the purchasing of items by a consumer spontaneously/without advanced planning.
What is unit pricing?
Unit pricing refers to the price of a product or service expressed per a standard unit of measurement.
What is a Universal Product Code (UPC)?
A Universal Product code is a barcode that uniquely identifies a product. It is used to track inventory and facilitate sales in retail stores.
State 3 details that a UPC provides
Manufacturer’s information
Brief product description
Price
Inventory Details
What is consumer education?
Consumer education is the process of informing a public about their rights and responsibilities as consumers, helping them make informed purchasing decisions.
List 4 rights of a consumer
The right to safety - Healthy environment
The right to be informed - Accurate information
The right to choose - representation
The right to be heard - Obtaining redress
List 3 responsibilities of a consumer
To use products safely - ensuring proper use
To provide truthful information - sharing accurate personal data
To seek redress - advocating for complaints or issues with products.
To provide reviews
To exercise informed choosing
To be responsible for their purchases - weighing the consequences of buying decisions.
What is the role of the Consumer Affairs Division?
The Consumer Affairs Division is responsible for protecting consumer rights and ensuring fair trade practices. It monitors businesses to enforce consumer protection laws and provides resources to assist consumers with complaints.
What is the primary role of the Bureau of Standards?
To ensure a high standard or a specific standard is met by all products and services, verifying quality and safety through regulation and testing.
The Weight and Measures Division is concerned with?
Ensuring the accuracy of measurements and weights used in commerce, promoting fairness in trading.
How do personal reasons influence a person’s purchases?
Teenagers, adults, and elderly people often buy different products.
A person's job influences what they need or can afford.
Interests, hobbies, and daily routines play a role.
Income level affects buying power and preferences.
People often buy products that reflect their identity.
How can psychological factors influence a person’s purchases?
Psychological factors, such as
Motivation: Needs (basic or psychological) that drive a person to make a purchase.
Perception: How a consumer interprets information and forms an opinion about a product.
Learning: Past experiences can shape future buying decisions.
Beliefs and Attitudes: A consumer’s values and opinions affect how they view products, perception, beliefs, and attitudes, significantly influence consumer behavior. These factors can affect preferences for certain products and overall purchasing decisions.
List 4 types of factors that influence an individual’s purchases
Personal Factors
Psychological Factors
Social Factors
Cultural Factors
State some guidelines for preparing a food budget
Shop in reasonably priced supermarkets/stores
Compare unit prices to save money
Look for discounts and sales
Shop in bulk when possible
Plan meals ahead of time to minimize waste
State 2 features to look for/avoid when purchasing fresh fruits and vegetables
Look for firmness, crispiness and good colour
There should be no signs of bruising, decaying or discolouration, worm injury or wilting
Leaves should not be yellowed
State 3 guidelines that can be followed to make more economic choices when purchasing fresh meat and poultry
Buying less tender cuts of meat is cheaper
Choosing ground meats can save money and still provide nutritional value.
Buy on a cost per serving basis rather than a cost per pound basis
Liver and organ meats are good value
Whole poultry is ready to cook and more economical
State 3 guidelines that can be followed to make good choices when purchasing fresh fish
Look for firm flesh, bright and bulging eyes, and red gills
Skin should be shiny
Free of any off odors.
Flesh should be firm to the touch
Shellfish should be alive or fresh, with a clean shell and no strong odor.
State 3 guidelines that can be followed to make good choices when purchasing frozen meat, poultry and fish
Ensure the product is fully frozen
Check that packaging is intact without any tears or ice crystals.
Look for a sell-by date that is current or future.
Choose products that show no signs of freezer burn.
Avoid meat,fish/poultry with signs of discolouration
State 3 guidelines that can be followed to make good choices when purchasing egg
Choose eggs with clean, uncracked, rough shells.
Check the expiration or sell-by date for freshness.
Choose appropriate sizes based on your needs, such as large or extra-large.
State 3 guidelines that can be followed to make good choices when purchasing breads, cakes, cookies
Check the sell-by and best before dates
Look for well sealed packaging
Ensure there are signs of freshness - aroma, softness (depending on type)
Fresh fish should not be refrigerated for more than __ days
2
Poultry should not be frozen for more than ____ months
three
State 2 guidelines to follow when storing poultry
Fresh poultry should be refrigerated immediately after purchased and used within 2 days
Remove store wrapping before storing and replace w, wax paper or saran wrap
If the whole bird is not required, cut into portions and freeze them
State 3 guidelines to follow when storing meat
Refrigerate meat at 40 degrees farenheit for no more than 2 days.
Store meat in a meat draw in the refrigerator or on the highest shelf
Meat which is to be kept for longer then one or two days should be frozen
Use airtight containers or wrap tightly to prevent freezer burn.
It is best to store meat in portions
Defrosted meat should not be refrozen
Frozen meat can be kept longer than 3 months in a deep freezer
What part of the refrigerator stores fresh fruits and vegetables?
The crisper drawer, designed to maintain proper humidity and temperature for fresh produce.
State 3 guidelines to follow when storing fruits for short periods
Ripe fruits stored for short periods should be wrapped and put in a covered container/placed in a cool temperature/set apart from those already rotting
Unripe fruits should be kept at room temp and refrigerated when ripe
State 3 guidelines to follow when storing fruits for LONG periods
Remove water by dehydration
Cook and bottle in syrup
Make jam and jellies
Freeze
State an appropriate place for storing cereals, dried herbs & spices etc,.
A cool, dry pantry or cupboard away from direct sunlight.
How should dairy products & fats and oils be stored before opening?
Keep them Cold, Clean and Covered in the refrigerator or appropriate cool storage
How should dairy products & fats and oils be stored AFTER opening?
Store in airtight containers in the refrigerator to maintain freshness. (Usually in original packaging)
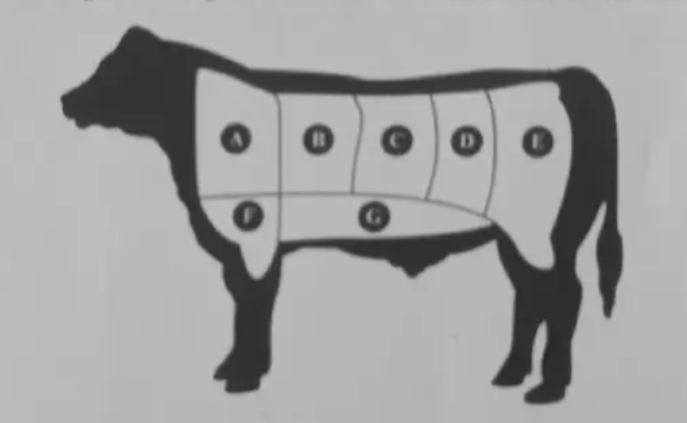
Label the parts A-G
A - Chuck
B - Rib
C - Short Loin
D - Sirloin
E - Round
F - Brisket
G - Flank
Where is the ‘Ham’ located in a pig
The ham is located in the hind leg of the pig, specifically the rear quarter.
What is poultry?
Poultry refers to domesticated birds that are raised for their meat, eggs, etc. This includes chicken, ducks, pigeons and turkey.
List 4 market forms of poultry
Thigh
Drumstick
Breasts
Wings
Whole Leg
Whole Bird
State 4 market forms of fish
Fillet
Drawn Fish - entrails removed
Whole Fish - freshly caught
Steak - crossed section of dressed fish
Butterfly Fillet - two boneless sides cut away
Cutlets
Dressed Fish - head, tail, entrails, fins removed
What are the two categories of fish?
Finfish and Shellfish
List 3 market forms of milke
Dried, Sweetened/Condensed, Evaporated, Reconstituted
List the THREE market forms of eggs
Dried, Liquid and Whole
What does the ‘sell by’ date do?
Tells stores how long to display the product
What is a health claim?
A statement that links food/nutrient to a reduced risk of a disease or health condition. They are based on scientific guidelines and are used to guide consumers to make healthy choices
List 2 health claims that can be made on a product about sugar
‘sugar free’ ‘no added sugar’ ‘reduced sugar’
Differentiate between the terms ‘enriched’ and ‘fortified’
A food is enriched when the nutrients lost during processing are added back to the end product while fortifying is adding extra nutrients to a product whether it originally had it or not.