Gene Expression: from gene to protein
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Gene expression
the process where DNA directs protein synthesis, transcription + translation
Protein Synthesis
the process where cells generate new proteins, involving the translation of genetic information contained in mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids to form a protein.
Central dogma of molecular biology
describes the flow of information from DNA —> mRNA —> protein
Genes specify the sequence of mRNA which then specify the sequence of proteins
Synthesis
the process of combining different components or elements to form a coherent whole or a new entity.
Transcription
first phase in gene expression
the synthesis of mRNA using information in DNA
Translation
Synthesis of polypeptides using information in the mRNA
RNA regarding transcription and translation
The bridge between genes and the protein that they code
Ribosomes
site of translation
Transciption and translation in eucaryotic cells
nuclear envelope separates transcription from translation, they are not coupled- they don’t happen at the same time
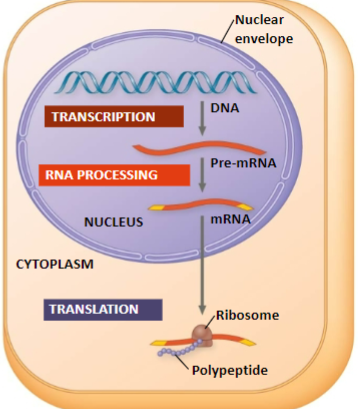
RNA processing
where eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified to make mRNA
Transcription and translation in bacteria (prokaryotes)
Translation of mRNA can begin before transcription has finished
transcription + translation are couples (happen at the same time)
No pre-mRNA/ RNA processing

Amino acids that code for nucleotide bases in DNA
adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
triplets code
a series of non-overlapping, three nucleotide words that are responsible for the flow of information from gene to protein
The words translate into amino acids forming polypeptide chains
What happens during trascription
One of the two DNA strands (template strand) provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in RNA transcript
RNA strand is complementary to DNA template strand and uses U instead of T
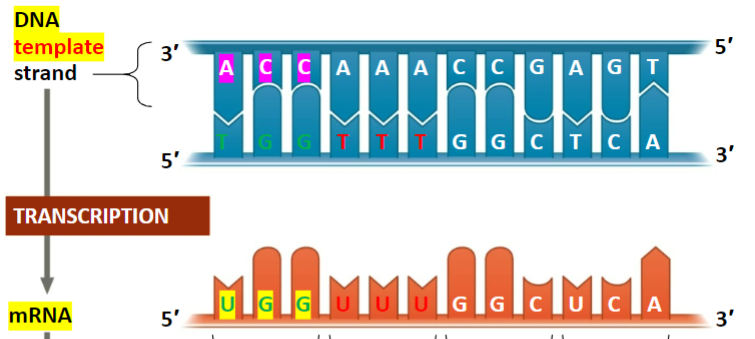
What happens during translation
mRNA codons are read from 5’ —> 3’
Each codon specifies to an amino acid to be placed in its corresponding position on the polypeptide
Stop codons
UAA, UGA, UAG
Start codon
AUG
Genetic code is redundant
Multiple codons may equal the same amino acid
UUU, UUC = Phe
can one codon code for multiple amino acids
no
what does it mean that genetic code is universal
Shard by the simplest od bacteria to the most complex animals
Non-Univeral genetic code
Mitochondria and Protists (paramecium)
RNA polymerase in transcription
Catalyze RNA synthesis, pulls DNA strands apart and joins them together with RNA nucleotides
does not require a promoter
where the DNA sequence that RNA polymerase attaches to
promoter
Transcription unit
the stretch of DNA that is transcribed
Three stages of transcription
initiation, elongation, termination
What happens at the start of initiation of transcription
Promotor signals transcriptional start point and extend several dozen nucleotide pairs from the start point
TATA box
A promoter that states the initiation complex in eukaryotic DNA
Binds to TATA binding protein, causing a bend in the DNA molecule
Determines the start point transcription
5’ → TATAAA→ 3’
Not in bacteria DNA
transcription factors
Mediates the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription
transcription initiation complex
completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase 2 bound to a promoter
Elongation of the RNA strand
RNA polymerase moves along DNA untwisting the double helix 10-20 bases at a time
Nucleotides are added to the 3’ end of the RNA molecule
Can a gene be transcribed simultaneously by several RNA polymerases
Yes
Termination of transcription in bacteria
Polymerase stopes transcription at the end of the terminator and the mRNA can be translated without further modification
Termination of transcription in eukaryotes
RNA polymerase 2 transcribes the polyadenylation signal sequence; the RNA transcript is released 10-35 nucleotides past the is polyadenylation (poly A) sequence
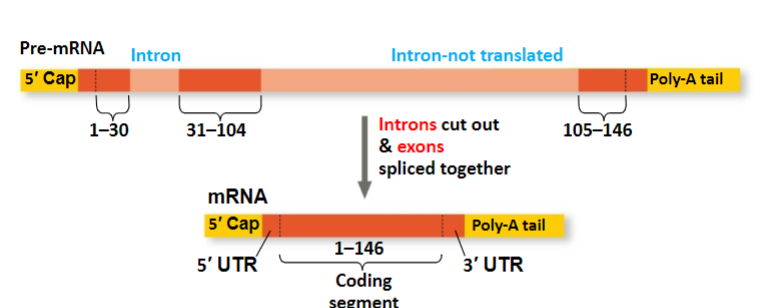
pre-mRNA
initial transcript of a gene that undergoes processing to become mature mRNA, which includes splicing, capping, and polyadenylation.
What happens to the primary transcript during RNA peocessing
modification allowing it to become mature mRNA
Capping
Poly A tail
Splicing
capping in RNA processing
the addition of a modified guanine nucleotide to the 5' end of the primary transcript, which protects the RNA from degradation and facilitates ribosome binding during translation.
polyadenylation in RNA processing
the addition of a poly(A) tail, a long stretch of adenine nucleotides, to the 3' end of the transcript, enhancing its stability and aiding in its export from the nucleus.
splicing in RNA processing
Splicing is the process of removing non-coding regions (introns) from the primary transcript and joining the coding regions (exons) together, forming the mature mRNA that can be translated into proteins.
Introns and Exons
Introns: noncoding regions
Exons: expresed region of RNA, usually translated into amino acid sequences
Function of introns
transcribed into pre-mRNA but are removed during RNA splicing. regulate genes and alternative splicing, allowing for the production of multiple proteins from a single gene.
exon shuffling
coding regions of genes, are rearranged or recombined to create new genes or protein variants. This mechanism contributes to genetic diversity and the evolution of new
What happened to the ends of pre-mRNA while its being modified in the nucleus
5’ end receives a modified 5’ cap (Guanine)
3’ end gets a poly-A tail
Function of modified mRNA ends
Facilitate the export of mRNA to the cytoplasm
Protects mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes
Help ribosomes attach to the 5’ end of mRNA
RNA cutting and splicing
Removes introns and joins exons creating an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence
Catalyze
to make a chemical reaction happen or happen more quickly by acting as a catalyst
Catalyst
a protein that speeds up biochemical reactions within cells without being consumed in the process, allowing life processes to occur efficiently
Spliceosomes
Responsible for the accurate cutting of introns
Catalyze the splicing reaction
Consist of several small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNPs) or snurps that recognized splice sites
5’ splice is bound by U1 snRNA
3’ splice site is bound by U2 auxiliary factor
Ribozymes
an RNA molecule capable of acting as an enzyme.
What properties allow RNA to function as an enzyme
Can form a 3D structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself
contains functional groups that participate in catalysis
Hydrogen bonds with other nucleic acid molecules
three binding sites of tRNA
Types of RNA
Ribosome RNA (structure)
Ribosomal protein- part of the ribosomes → structural (nothing to do with the protein making)
Pre-mRNA- genetic code → affects proteins
mRNA- processed, no introns
tRNA- bring aa to ribosomes for protein synthesis
RNA Primer- replication
snRNP- small proteins and RNAs → stabilized introns for cutting, exon junction
Mutations
Missense mutation
Sickle cell
point mutation
Frame mutation
insertion and deletion (serous mutation)
Silent mutation
chnage in condon has no effect
Nonsense mutation