KNES 337 - Unit 13 Diabetes
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
diabetes types
gestational, type I, type II
gestational diabetes
only during pregnancy
Is a resistance to insulin that develops during pregnancy, resistance is too great, so blood glucose not regulated properly → hyperglycemia
percent of gestational diabetes
5-6% of women develop gestational diabetes
higher risk for gestational diabetes
women over 35 years old
women with obesity
women from a high-risk group (African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous, South Asian)
gestational diabetes treatment
Control blood glucose levels with an individualized diet and exercise plan
Some women require daily insulin injections for blood glucose control
macrosomia
large baby more than 4 kg (8 lb. 13 oz), Issues with delivery - c-section
can be due to high blood glucose in mother → brings extra glucose to baby → high insulin in baby → causes baby to put on extra weight and body fat
infants from gestational diabetes
may have increased body fat at birth and have blood glucose control problems after delivery
May produce excess insulin which may lead to hypoglycemia - monitor closely after birth
At greater risk for diabetes later in life
6-20% will have a physical abnormality that may threaten survival or a high quality of life - e.g. cleft palate, club foot, heart defects
Can correct cleft palate and club foot with surgery, and some heart defects can be corrected
Disappears after delivery - but type II diabetes may appear later in life in the mother
Exercise, maintenance of normal weight, and a healthy diet reduce the risk that diabetes will return
type I diabetes
Autoimmune - attack on pancreatic beta cells (produce insulin)
Deficiency of insulin
percent of type I diabetes
Accounts for 5-10% of all diabetes and is increasing yearly
type I diabetes onset
Typically diagnosed in children or at least before 40 years old, onset is abrupt
Diagnosis peaks around the ages of 11-12 years
treatment of type I diabetes
Treatment is with insulin, diet, and exercise
continuous glucose monitoring
Before insulin was discovered (which was discovered in Toronto)
Starve to death - no way to get glucose into tissues from the blood
Insulin injections are life-saving
Insulin!!!! - injections, pump, islet transplant
insulin pump
Insulin is injected into the subcutaneous tissue automatically by the pump
islet transplant
done everything else, but still not enough control, get new healthy pancreatic cells - brittle diabetes
glucose monitoring
probe that constantly samples glucose levels in interstitial fluid - good indication of blood glucose
Dexcom and Libre - can see blood glucose levels over the whole day and during meals
Before, they’d have to prick their finger multiple times a day
environmental triggers of Type I
associations:
Early exposure to cow’s milk proteins - immune system may get these proteins mixed up with pancreatic beta cells (shown in mice, but not yet humans)
Vitamin D deficiency
Early exposure to gluten
Certain viruses (rubella, rotavirus, mumps, cytomegalovirus, enteroviruses)
Gut microbiota - leaky gut, immune system confused
breastfeeding
if for the first 4 months, may protect infants against type I diabetes
immune system
Expose kids to a wide variety of microbes - kids should go outside to develop their immune system well
Better at telling self vs. outside bacteria
Less allergies as well
E.g. growing up on a farm, with older siblings, with pets, even eating dirt, can be beneficial to early immune development
Certain bacteria, when present in early life can strengthen immune response and prevent T1D
glycemic index
foods that affect blood glucose are given a glycemic index value
Blood glucose elevation caused by 50 grams of food → compare to elevation caused by eating 50 g of glucose → assign a glycemic index value
foods that elevate blood glucose require more insulin to move glucose into cells
Low-glycemic index foods decrease blood triglyceride levels and insulin requirements in type 2 diabetes
High-glycemic foods good to promote glycogen formation - but don’t want to become insulin resistant
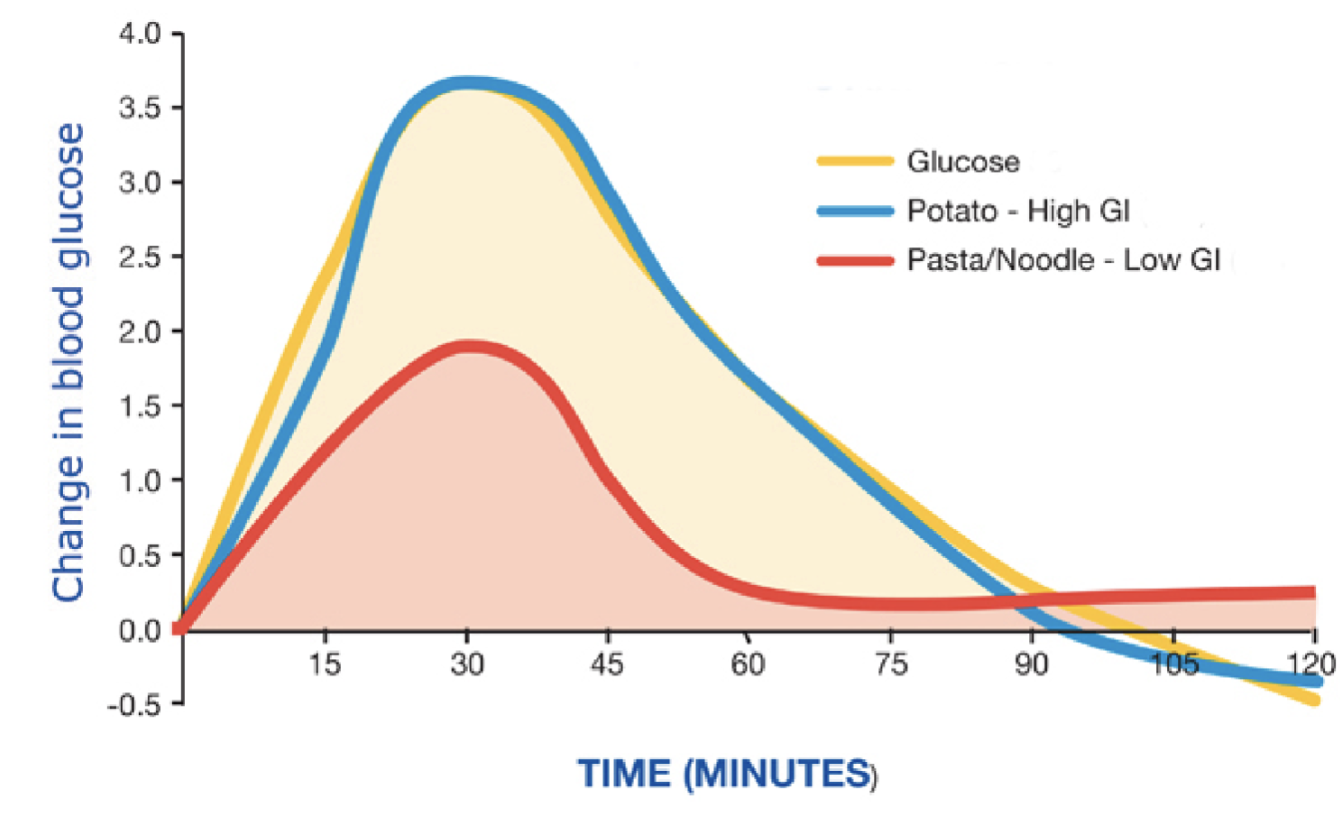
potato and glucose
overshoot the baseline (lower blood glucose after a spike) - may feel angry, shaky, not good
potatoes
Russet (baked potatoes usually) and instant mashed potatoes higher GI than red potatoes
Boiling and then cooling starches is better
pasta
low GI food
curve is gentler
Cooked al dente (slightly hard) - slower glucose absorption
Sourdough pasta - used bacterial culture to make it, good for gut microbiota - can change how body metabolizes carbs and starches
oatmeal
Instant oatmeal (rolled oats) - GI = 79 - will raise blood glucose the most
Quick oatmeal - GI = 65
Steel cut oats, large flake oats, muesli/granola (baked) - GI = 55
GI of glucose
GI = 100
GI of french bread
GI = 95
GI of rice krispies
GI = 82
Gi of sticky rice
GI = 86
GI of all-bran
GI = 42
GI of yogurt
GI = 35
GI of milk
GI = 31
GI of hummus
GI = 6
prediabetes
Elevated fasting blood glucose levels below the cut off point used to diagnose type 2 diabetes (6.1-6.9 mmol/L) = prediabetic
Prediabetes is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes
Once you have type 2 diabetes - it’s irreversible
Try and reverse it in the prediabetes stage
insulin resistance risk factors
Obesity
Low levels of physical activity
Genetics
When blood glucose levels become high, the pancreas secretes more insulin to keep glucose levels under control
Pancreas becomes exhausted from over work and insulin production slows or stops
7 mmol/L
or higher = the fasting blood glucose levels at which type 2 diabetes has developed
type II diabetes
lifestyle related, most cases, treatment is weight reduction and medications
Occurs in individuals with overweight or obesity and a sedentary lifestyle
Most common in people over 40 - but increasingly seen in young children and adolescents
Strong genetic component
Runs in families (Black, Hispanic, Indigenous, Asian), associated with apple obesity
Individuals with type 2 diabetes are insulin resistant
managing type II diabetes
Can be managed with diet and exercise - most of the time
If not, there are 8 different classes of diabetes medications that can be prescribed to manage diabetes (including Ozempic)
Manage with diet and exercise
Weight loss alone significantly improves blood glucose control - even 5% weight loss
Proper diets are crucial
Complex carbohydrates - whole-grain breads, cereals, high-fiber foods, vegetables, fruits, low-fat milk and meats, and fish (low glycemic foods)
Healthy fats
Regular meals and snacks
Protein at every meal - particularly bedtime - helps liver to not overproduce glucose during overnight fasting period
symptoms of diabetes
applies to all types if poorly controlled/untreated
High glucose levels
Frequent urination
Increased thirst and hunger
But not gaining weight
Energy trapped in blood
Unusual fatigue
Weight loss - without trying
Big sign in children - if they plateau or lose weight, immediately check for diabetes (key symptom)
Blurred vision - High glucose can affect retina
Increased susceptibility to infection
Slow healing sores - Especially on feet
health consequences
over long term
Heart disease and stroke
Kidney damage (nephropathy)
Lead to dialysis requirement
Can’t clear out waste other wise
Blindness (retinopathy)
High blood glucose → can attach to proteins (glycation) in the retina → lead to blindness
Nerve damage (neuropathy)
Loss of sensation, not healing
Can’t feel feet, if injured, you might not feel it and not know it’s there - wounds can get infected if not treated
Loss of limbs due to poor circulation
Amputations - mostly foot, toes
Alzheimer's Disease / dementia
alzheimers disease
Can be known as “type III diabetes”
May be linked to type II - common pathways of insulin resistance and inflammation
Control diabetes as best as possible to avoid developing dementia