Unit 6: Oscillations
5.0(1)Studied by 99 people
0%Unit 6: Oscillations Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:53 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
1
New cards
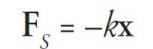
Simple harmonic motion
A type of periodic motion in which the restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium position and acts in the opposite direction to the displacement.
2
New cards
Hooke’s Law
The force required to extend or compress a spring is proportional to its displacement from its equilibrium position.
3
New cards
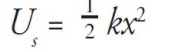
a spring with spring constant k, the elastic potential energy it possesses—relative to its equilibrium position
4
New cards
Oscillation
The back-and-forth motion of an object about its equilibrium position.
5
New cards
Amplitude
The maximum displacement of an oscillating object from its equilibrium position.
6
New cards
Period
The time taken by an oscillating object to complete one cycle of motion.
7
New cards
Frequency
The number of cycles per unit time of an oscillating object.
8
New cards
Restoring force
The force that brings an oscillating object back to its equilibrium position.
9
New cards
Spring constant
The constant that relates the force exerted by a spring to its displacement from its equilibrium position.
10
New cards
Angular frequency
The rate at which an oscillating object completes one cycle of motion in radians per unit time.
11
New cards
Phase angle
The initial angle of an oscillating object at the start of its motion.
12
New cards
Resonance
A phenomenon in which an object is forced to vibrate at its natural frequency due to the application of an external force at the same frequency.
13
New cards
simple pendulum
Consists of a weight of mass m attached to a massless rod that swings, without friction, about the vertical equilibrium position.
14
New cards
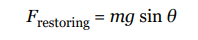
the magnitude of the restoring force when the bob is θ to an angle to the vertical