Introduction to microbiology and bacterial cells
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are the two cellular organism types?
Prokaroytes and eukaryotes
Prokaroyotes
1 - 5 um
Haploid
Asexual reproduction
Unicellular
No true nucleus
Cell wall
Bacteria , archae
Eukaroytes
>10 um
Diploid
Sexual reproduction
Unicellular/multicellular
True nucleus (some exceptions)
Fungi (yeasts), algae
Viruses
No cellular structure (genetic material surrounded by protein)
Prions
No nucleic acid (pieces of infectious protein e.g mad cows disease)
Bacteria
Unicellular
Huge diversity; size, shape, habitat and metabolism
Majority are harmless or even beneficial
Some cause disease and SOME are pharmaceutical contaminats
Name given to bacteria which can cause disease
Pathogenic
How do we name bacteria?
Start with genus then species, write our fill name e.g Escherichia Coli then abbrivate after E. coli
What are the 3 different ways to classify bacteria
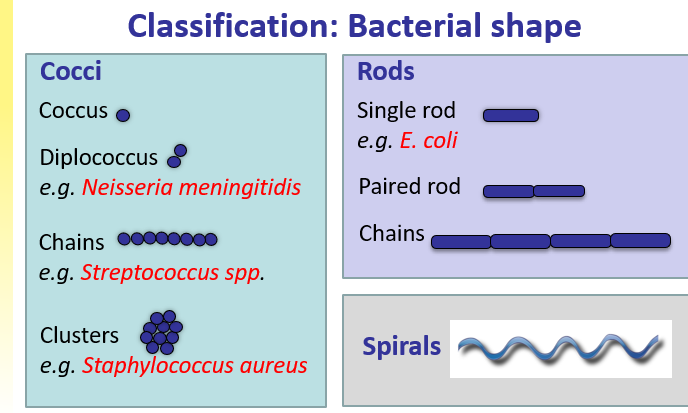
Morphology (cell shape, size, motility, spore forming)
Metabolism: use of energy/nurtients
Molecular characteristics: protein, lipid structure sequence of gene encoding 16s RNA
3 different shapes so classify bacteria
Why have we picked the 16s ribosomal RNA gene sequencing for classifcation of bacteria and archae?
Essential gene-all bacteria have ribosomes
16s genes highly conserved (similar in lots of bacteria) but contains hypervariable regions (short section of DNA which are different)
Therefore BIG variation in the hypervariable regions between species so organisms are easily idenitifed by their sequences (compare to data base)
Bacterial cell structure
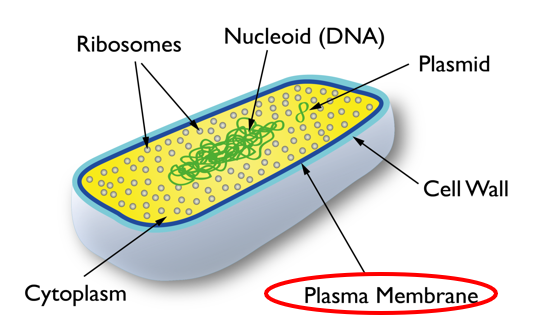
What vital component do bacterial cells not contain?
Mitchondria
No mitochondria means what in the cells?
Site of secretion, respiration and environmental response regulators occur on the plasma membrane
Why do bacteria’s ribosomes add up to 70s and not 80s?
Due to svedberg units (density), 50s and 30s subunits make 70s
Where is cytoplasm located?
Between plasma membrane and nucleoid
What does the cytoplasm contains
Ribosomes
Inclusion bodies (granules) also known as storage bodies which contain important nutrients (C, P, N, S)
High conc of dissolved solutes → high osmotic pressure
Bacterial chromosome (nucleoid-genetic material)
Double-stranded DNA (dsDNA)
Not enclosed by a nuclear membrane
Usually single closed circular chromosome
DNA is supercoild
1 copy of each gene
Plasmids (nucleoid- genetic material)
Extrachromosomal; small circular dsDNA
Replicate independently of chromosome (multiple copies)
Encode auxiliary functions e.g antibiotic resistance
Prokaroytic cell wall
Extremely important structure as it protects bacteria cells from the environment
Provides rigidity and strength
Unique to bacteria so it makes an excellent drug target
Composed of peptidoglycan; cross linked to form a mesh
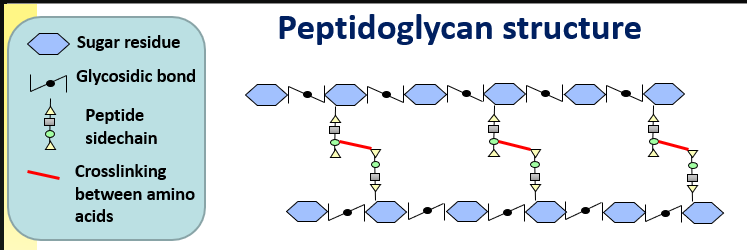
Peptidoglycan structure
Sugar back bone joined together by glycosidic bonds
Every other sugar is linked to a short peptide (chain of amino acids), which crosslink to a peptide on an adjascent glycan backbone
Strong mesh is formed so NOT a solid barrier
Why is the peptidoglycan structure beneficial?
Mesh structure = things can pass in/out
2 type of bonds make it strong and rigid
Contains other components that contribute to pathogenicity (ability to cause disease)
Dynamic structure; constantly being remodelled
Differences in PG structure divide MOST pathogenic bacteria into 2 groups
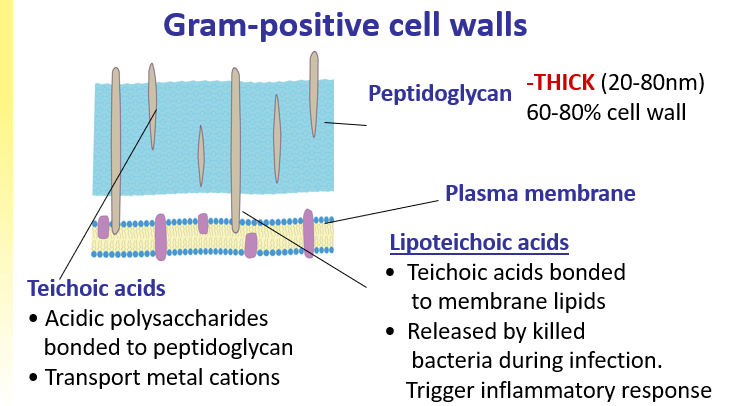
Gram positive = stain purple ; Thick PG layer cell wall and x linked to form thick mesh e.g staph
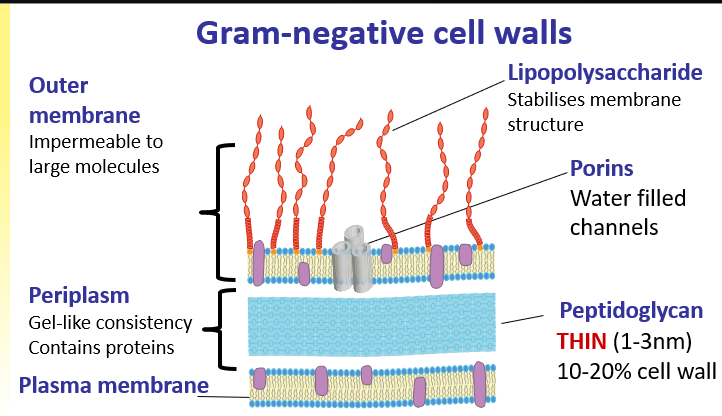
Gram negative = stain pink ; Thin PG layer surrounded by an outer membrane e.g e coli
Gram-positive cell walls
Gram negative cell wall 1
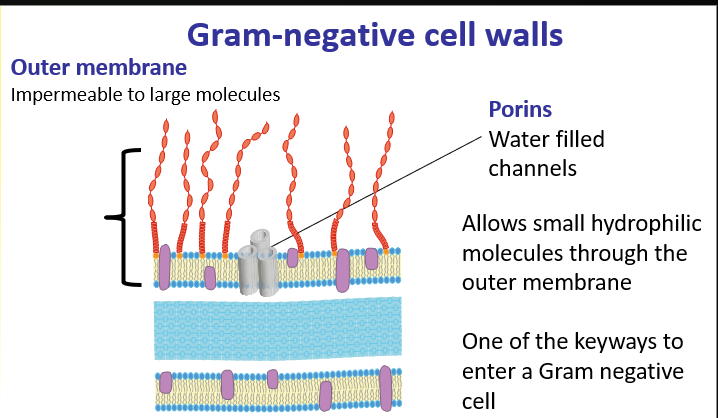
OUTER MEMBRANE IS MAIN PART
Gram negative cell wall 2
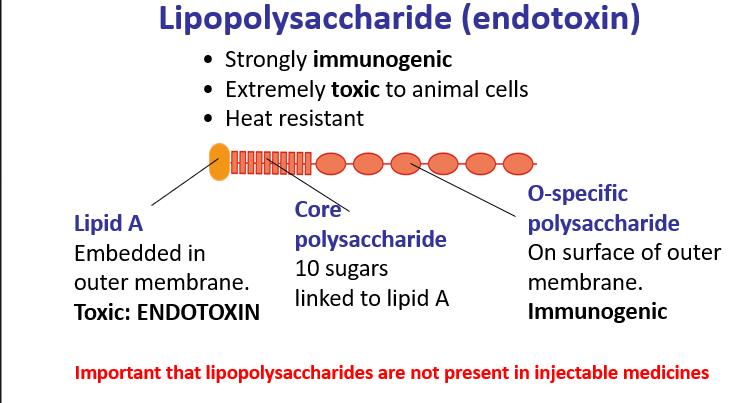
Lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin)
Pathogenic bacteria which are not classified by gram stain

What is a bacterial endospore?
A structure which forms inside a bacteria in response to adverse conditions (nutrients/oxygen)
2 characteristics of bacterial endospores
Dormant: survive without water and nutrients
Non reproductive: single endospore forms within a bacteria. Reactivates in response to more favourable conditions
What are bacterial endospores tough against?
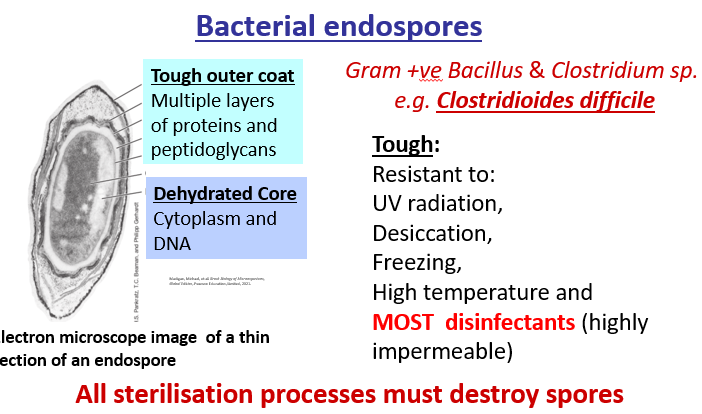
What is C.diff?
Causes hosptial associated diarrhoea
Obligate anaerobic leading to spore-forming bacteria
Naturally resistance to many antibiotics
Can progress causing bloody diarrhoea, inflamed intestine and toxic magacolon leading to death
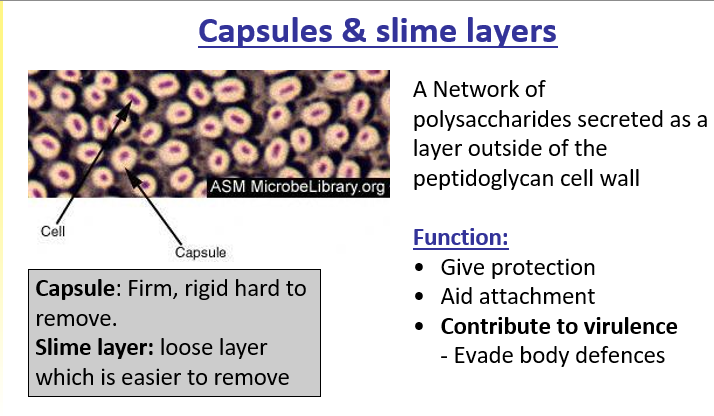
Capsules and slime layers
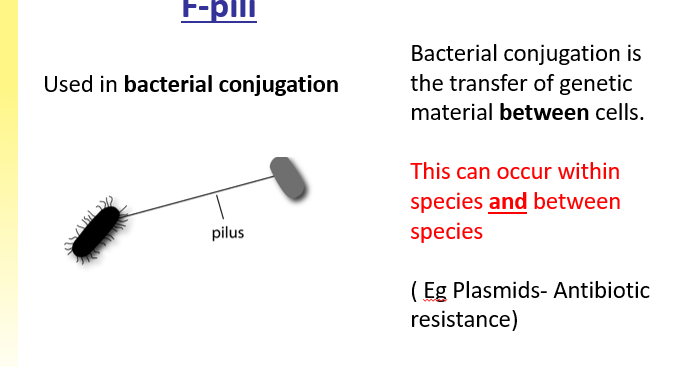
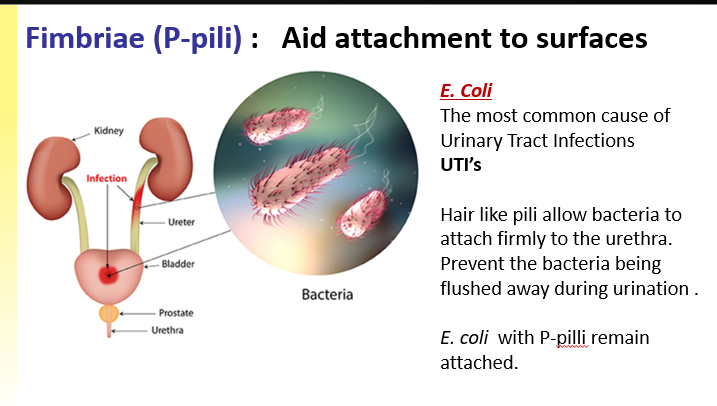
P- pili (Fimbriae) and F-pili
Morphologically and chemically similar
Hair liked structures composed of protein subunits
P- pili (Fimbriae)
F-pili