EHST Exam 1
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Define population
Refers to the same species in an area
Define community
Refers to the multiple species in a given area.
Difference between population & community.
Population refers to the same species in an area where as community refers to the multiple species in a given area.
What does a ecosystem consist of?
Consists of living organisms that interacts with non-living components of their environment
What are examples of population attributes?
Age structure, spatial distributions
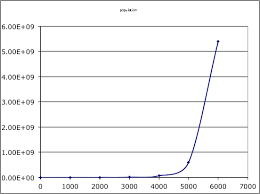
What type of curve is this?
J population curves
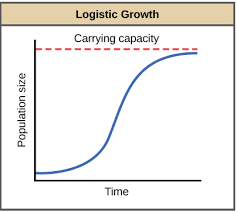
What type of curve is this?
S population curves
What is carrying capacity known as and its definition?
Equilibrium.
Described as when the number of births = the number of deaths
Red tide is an example of what type of growth curve?
J curves
What are homeostatic controls and examples?
Self-regulating factors
Examples: behavior, physiological and social responses.
What type of curve is human population growth?
J Curve
What is doubling time?
amount of time it takes a population to double in size
What did Thomas Malhus theorize?
He theorized that population growth will will always outpace the available food supply causing war, famine and disease.
Factors that created surges in population growth
Access to food, family planning, technological advancements, public health, socially economic wealth
Birth Rate =
Birth Rate = # of babies born per 1000 people per year
Death rate =
Death rate = # of deahts per 1000 people per year
Three reasons for surges in death rates?
war, famine, disease
What are modern days examples of death surges?
HIV, Covid-19
Why are some regions experiencing different growth rates?
More younger people in area than older.
What is the demographic transisition?
The decreasing of both birth and death rates at same time.
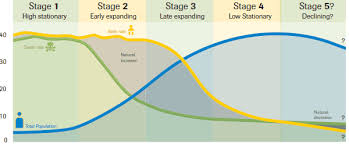
What is total fertility rate?
average # of children per mother in a reproductive timeline
Formula for Growth Rate
(Birth rate - death rate) / 10 = GR
Which of these charts is developing and developed?
What is the concern for economic and sociopolitical issues?
Global graying
Whats the term for a city with over 10 million people
mega city
What’s the minimum amount of people for a mega city?
A. 20 million
B. 15 million
C. 10 million
D. 30 million
C. 10 million
In 2001 what happened to the global population?
They resided mostly in urban areas for the first time in world history?
What happened for the first time in 2001?
People resided mostly in urban areas.
What’s a major health concern from urbanization.
safe drinking water
What’s a humane way to control population growth?
Family Planning
Early methods of birth control
withdrawal, sponge, herbal medicine
What are examples of economic and social factors?
religion, cultural preference, education, economic status
Does developing nations have more or less young people?
More young people
Does developed nations have more or less young people
Less young people
Define First Law of Thermodynamics
energy cannot be create or destroyed; only change form
Define Second Law of Thermodynamics
after each transfer of energy there is loss of that energy.
1000 → 100 →10
When is all energy is moving toward an ever less available and more dispersed state?
Entropy
Dry weight per unit area =
biomass
Does a rainforest have a more or less biomass than deserts
Yes
T/F. Energy loss occurs at every increased trophic level
True
Population growth and increased income are the largest factors for what?
Influencing food demand
Higher incomes =
Higher quality food
By 2050 72% of grain will be used for livestock feed __________ ________?
Plant-based meat
What type of meat can reduce land use requirements by 76%
plant based meat
What is basal metabolic rate (BMR) used to define.
From the FAO
Hunger
Which faces the biggest threat from hunger?
Developing nations or developed nations
Developing nations
Whos more at risk of malnutrition?
Men, Women or children
Women
What are two major causes of hunger?
Uneven distribution and poverty
Are high quality diets less or more energy efficient?
less energy efficient
What are most deaths from hunger related to?
Chronic nutritional deficiencies.
(not starvation)
What’s the leading causes of death and disease?
PEM (protein-energy malnutrition)
This protein deficiency is affecting kids in tropical areas of Africa.
Kwashiorkor
What is an overall protein-calorie deprivation.
(a deficiency of all macronutrients)
Marasmus
Which deficiency causes blindness in children
Vitamin A
What’s the most common vitamin deficiency
anemia
(iron deficiency)
Anemia in pregnant women can lead to?
Maternal death, premature delivery, stillbirth
List ways to reduce world hunger
Expanding land cultivation, increasing fish catch, aquaculture, reducing post-harvest food losses, eating lower on food chain, improving yields per acre
Why is it not practical to use more farmland
Only a finite supply of farmland and not enough water
Anchovetas, herring and mackerel are examples of?
trash fish
What impacts fish stocks
overfishing and pollution
Shrimp farming affects which ecosystem
coastal mangroves
Which law is based on: The growth of a plant is dependent on the amount of resources given to the plant
“minimum quantity”
Liebigs Law of the Minimum
What act passed in 1906
Pure Food & Drug Act
Which agency will take legal action to remove products from market?
Food Defect Action Level
FDA
What is used to boost milk production?
rBGH, BST, Bovie Growth Hormone
Can pesticides be translocated into meat milk and eggs?
Yes
Tolerance levels can also be seen as the
maximum quantity