APUSH Chapters 35-37 "The Cold War Begins"
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
live, laugh, love apush <3 emphasis on the love
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Yalta Conference
General intentions! Final meeting between “Big Three”. Feb 1945. Talked and agreed ab final plans to smash Germany. Poland, Bulgaria, and Romania would have free elections (promise soon broken by Stalin). Plans for the United Nations.
Also Japan. US wanted Stalin’s help, USSR got Japanese islands and Manchuria RR and 2 ports. Blamed this was part of Truman giving up on Chinese nationalists and losing China.
“Satellite” Nations
USSR controlled nations post-WWII in Eastern Europe. “certain nations in the Cold War. These were nations that were aligned with, but also under the influence and pressure of, the Soviet Union”.
Cold War
Began from a progression of events, marked by misperceptions and genuine conflicts of interest b/w the US and USSR, wh/ led to friction throughout the world. (US stopped lend-lease to a struggling USSR-only powerful military and nuclear wise!-and refused to aid it economically). Communism vs Capitalism
Potsdam Conference, July 1945
Big Three: Truman, Atlee (replaced Churchill), and Stalin. Stalin wanted to eliminate all unfriendly regimes on Western borders and quickly establish political dominion over Eastern Europe, creating a “buffer zone”.
Third World Countries
Represented a problem of opportunities and dangers b/c in most of these nations the poor were the majority and the US worried that Communism would seem attractive to them.
Bretton-Woods Conference, 1944
Signified US taking the lead in world conferences (vs previous isolationism). Aimed to revive trade and promoting globalization. Made money acts (other flashcards).
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
To encourage world trade by regulating currency exchange rates.
World Bank
Promoted economic growth in war ravaged and underdeveloped areas.
General Agreement on Tariffs & Trade (GATT)
Reduced trade barriers among member nations.
United Nations
Created in April 1945 at a meeting of 50 nations. Made up of the General Assembly: the ultimate policy making body, and the Security Council: makes the major decisions for settling disputes among member nations. Main Goal: international cooperation to preserve peace.
Iron Curtain
A metaphor for the extreme political and ideological division that separated Western Europe from the Soviet Union and its satellite states in the east.
“Containment Policy”, George F. Kennan
Policy of keeping USSR and Communism contained.
Israel
Turman formally recognized ___, even after Arab nations warned they would “lay siege to it until it dies of famine” b/c of sympathy (main reason) for survivors fo the Holocaust, to have ___ aligned w/ US instead of USSR, and to keep Jewish American votes.
German Zones
West Germany: Great Britain, France, and US. East Germany: USSR. West Berlin: GB, US, FR. East Berlin: USSR. The divide was HUGE b/w communism and “free land” like you don’t understand this was crazy!!
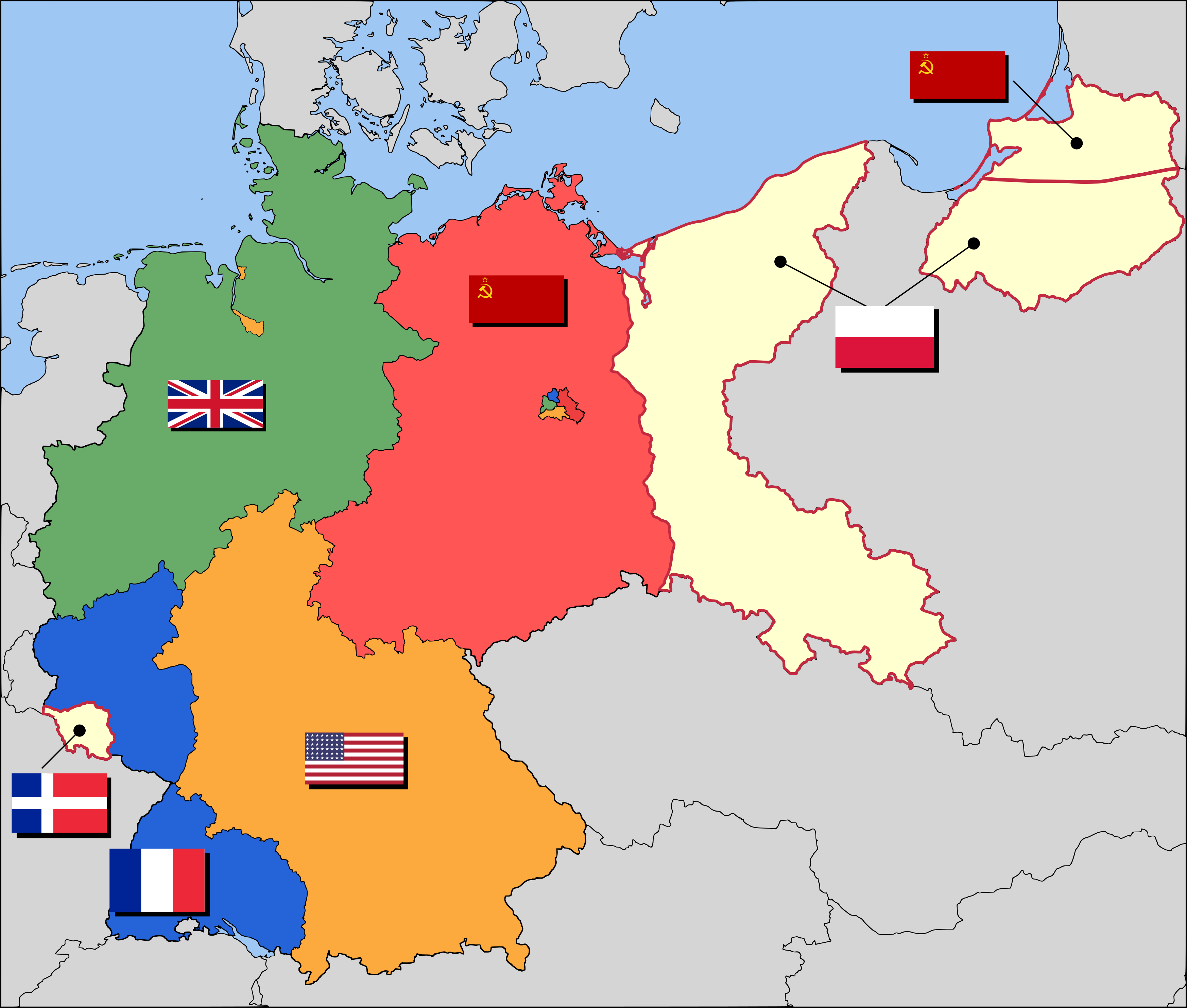
Berlin
____ became a hugely symbolic issue for both sides.
Berlin Airlift
A military operation in the late 1940s that brought food and other needed goods into West Berlin by air after the government of East Germany, which at that time surrounded West Berlin (see Berlin wall) (see also Berlin wall), had cut off its supply routes. Resulted in USSR giving up.
National Security Act
Created the Department of Defense
Secretary of Defense
Oversees Secretaries of the Army, Navy, and Air Force
National Security Council (NSC)
Assembled top diplomatic and military advisors to advise the president on security matters.
Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
Handles foregin intelliegnce gathering and covert operations
“Voice of America”
American radio broadcasts behind the Iron Curtain
H-Bomb-Hydrogen Bomb
Developed by US first, then USSR. Nuclear arms race. MUCH more powerful than the first nucelar bombs.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
US, Candad, & 10 European nations signed a mutual defensive pact. Unity!
ANZUS
Australia, New Zealand, and US
General MacArthur
In charge of demilitarizing Japan (who was willing of this change, and a major postwar victory of the US).
Chinese Civil War
Communists (Mao Zedong) vs Nationalists (Jiang Jieshi). Communists won, many thought Truman abandoned the nationalists. “losing China” = major reason for US involvment in Vietnman
38th Parallel
After WWII, Korea was divided along the ____.
North Korea
(Korea) allied w/ USSR
South Korea
(Korea) Allied w/ US
National Security Council 68 (NSC-68)
Policy that committed US to a military approach to the Cold War. Prompted by North Korea invasion into South Korea. Massive US military expansion.
The Red Scare
1945-1955 An assault on civil liberties brought on the US by an intense fear of Communism and Soviet Communist spies infiltrating US goverment.
Communist Party
In rapid decline in the US after WWII
Executive Order 9835
Established a loyalty program to eliminate “disloyal” federal employees
Loyalty Review Board
Investigated millions of federal employees, who worked under a cloud of fear
Smith Act
Made it a criminal offense to advocate for the overthrow of the US government by force. The first peacetime anti-sedition law since 1798.
Loyalty oaths
Required of many employees during the Red Scare
Dennis v. United States
Supreme Court Case that upheld the 11 convictions against those who “violated” the Smith Act
McCarran Internal Security Act
Required all communist parties to register w/ Attorney General & show member lists
House of Un-American Activities (HUAC)
Investigated “un-American propoganda” that attacked the government and “subversion” (clarification: McCarthy was never a member, he was a senator. But his rise=rise of HUAC and his decline=decline of HUAC)
“Hollywood Ten”
Refused to discuss their past political associations
blacklisted
Many targeted as Commies were ____.
Julius and Ethel Rosenberg
Exectued for passing atomic secrets. Their case sobered many Americans ab “Red Catching” bc of their sensationalist trial and the fact that their children were orphaned. The only people in US peacetime to be executed for espionage.
Alger Hiss
Accused of being in a Soviet spy ring & giving government secrets to the USSR. Chase led by Richard Nixon. Denied all charges but found guilty for perjury.
Jospeh McCarthy
The most ruthless and di the most damage to American traditions of free speech during Red Scare. Claimed State Dept. was innfiltrated w/ Communists but couldn’t back up his claims, like ever.
Army-McCarthy Hearings
McCarthy’s downfall
Executive Order 9981
Desegregated the armed forces. A major development of US democratic values in 1948. Often used as such a democratic event the US should get back to post-Red Scare. Gave more power to Civil Rights movement.
Taft Hartley Act
Aimed at large unions.
Outlawed several union tools as “unfair labor practices”
Barred the closed shop
Blocked seconday boycotts
Established cooling off periods
Required union leaders to take a noncommunist oath
CIO’s Operation Dixie
Failed efforts to unionize southern workers, couldn’t overcome racism. Like the southern workers wouldn’t cooperate bc they were racist.
Employment Act of 1946
Promoted maximum employment, production and purchasing power, and kept inflation low.
Council of Economic Advisers
Created by the Employment Act of 1946 A 3 member council to advise the President on economic policy.
Servicemen’s Readjustment Act of 1944 (GI Bill of Rights)
Provided veteran’s loans for education, homes, and businesses. Eased postwar readjustment, stimulated the economy, and helped created the postwar era.
52-20 Club
$20 a week for up to 52 weeks, for the servicemen
Veteran Administration (VA)
Enabled by the GI Bill of Rights to provide $16 billion in loans for homes, farms, and small businesses.
Whistle Stop Campaign
Truman’s campaign against Dewey. Brief appearances over a short amount of time in many towns.
Truman’s Fair Deal
Housing Act of 1949, raising the minimum wage, and the Social Security Act of 1950. Rejected to help farmers, killed permanent FEPC, and blocked national healthcare.
Housing Act of 1949
Provided money for local agencies to buy, clear, and resell land for housing. Never worked bc not enough money and poor design.
Social Security Act of 1950
Extended the benefits, covered more people, and gained broader support
The Lonely Crowd: A Study of the Changing American Character
Discusses how Americans used to be “inner directed” people, now they are “other directed” people. Individuality and innovative to conformity.
Silent Generation
Middle class America aspiring to little more than a safe life, with little concerns for outside world affairs
William Levitt and Levittowns
Mass suburban housing, caused by a mass of people moving away from the city and looking to become homeowners.
“White Flight”
White middle class families leaving the inner cities for the suburbs, leaving the inner cities “black, brown, and broke”
TV
Became a huge household staple in the 1950s and had a huge impact on American society
Men
Roles:
Go to school
Support family
Find job
Maker important decisions
All in the public sphere
Women
Roles:
Housekeeping
Raising children
Left jobs wartime to return to the house
Benjamin Spock - Common Sense Book of Baby & Child Care
Advised mothers to stay at home if she wanted her children to grow up stable and secure. Highlights how this information, instead of being passed down from grandparents to parents, is in a book bc of family divides bc of massive migration movement (in sunbelt, suburbs)
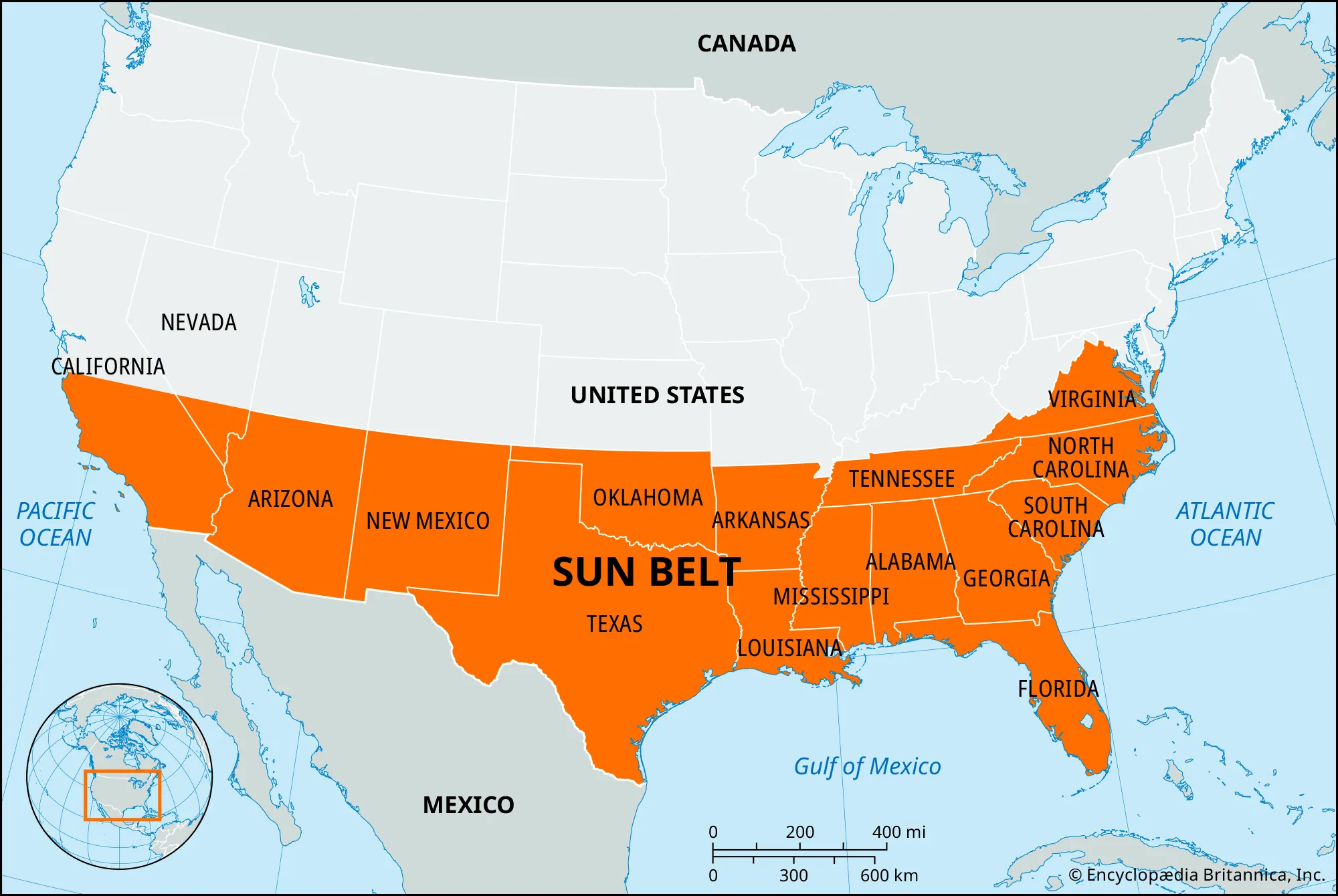
Sunbelt
15 state area (VA to CA) where a massive amount of Americans moved. The “New Frontier” of the time. Better weather, less taxes, etc.
Baby Boom
SO MANY BABIES AFTER WWII!
(and then they grow up and this huge age population changes and shifts and affects cultures as they move through the stages of their lives like! As babies, huge increase in baby supplies and the industry, as teens they’re part of the rock and roll atmosphere and shaped the teen rebellion of the time, and now they’re completly wreaking havoc on Social Security… you win some you lose some)
Rock and Roll
Huge market and a love all teenagers shared as part of a “youthful rebellion”
Elvis Presely
Buddy Holly
Religion
Many Americans turned to what during the Cold War? bc pastors grappled tv, sturggle agnst “Godless Communism”, and to go along w everyone else
Checkers Speech
Saved Nixon’s spot on the ticket but also spotlighted a fundamental change in US politics, where politicians could appeal directly to the people
“dynamic conservatism”
Eisenhower’s policy
Operation Wetback
Government program to round up and deport illegal Mexican migrant workers in the US
Federal Highway Act of 1956
Created a national system of interstate and defense highways. 41,000 miles of highway built with the purpose of moving supplies for war or attack.
Policy of Boldness - Sec of State John Dulles
Called for Massive Retaliation. More than just containment, intimidating and liberating.
Massive Retaliation
Build up our nuclear power and relegate the army and navy to the backseat.
Hungarian Uprising
Hungary rose up against the USSR and felt betrayed when the US didn’t help. Showed that the huge tool of nuclear power doesn;t work in small crises, wh/ are still important in stopping communism.
Shah Pahlevi
CIA staged a coup in Iran when the country started to resist Western Oil Companies control and put this guy in charge as a basically dictator…
Suez Crisis
Egypt’s President Nasser wanted to build a dam on the Nile for irrigation and power. US withdrew their promise to fund it when Egypt started chatting with the USSR. GB and FR attacked,b ut didn’t tell US so Eisenhower was pissed and didn’t give them any oil. Attack failed.
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
Countries resolved to reap the benefits of their own oil and not Western countries.
Sputnick
USSR sent first satellite up into space. Shocking and scared the US bc what the hell are you gonna hit us with if you sent that into space?? and now we’re unconfident in our space abilities
National Aeronautics Space Administration (NASA)
space organization, set up after sputnick
National Defense Education Act
Expanded college and post grad education which promoted research and teaching in math, science, engineering, and foregin languages.
Cuban Revolution, 1959
Fidel Castro came in as an unknown & claimed he wasn’t married to any one idea. Seized power over a largely poor Cuba who was frusturated with Batistia, a dictator enable by the US bc he encouraged US investment. Quickly turned Cuba into a Communist country (USSR satellite). US cut diplomatic relations & trade w/ Cuba. ~1 million Cubans fled to the US.
Military-Industrial Complex
The economic ties b/w arms manufacturers, elected officials, and US armed forces that created self-sustaining pressure for high military spending.
In his Farewell Speech, Esisenhower warned that this powerful combination left unchecked could endanger our liberties & democratic procces favoring defense concers over more peaceful goals that balanced security and liberty.
Kitchen Debate
Nixon won praise for his staunch defense of capitalism against Khrushchev, helping him to secure the Republican nomination.
Election of 1960
Rep: Nixon/Henry Cabot Lodge Jr.
Dem: JFK & LBJ
Kennedy’s obstacles: Young, Catholic, and little experience
TV
Played a big role in the 1960 election, reinforced the importance of image over substance
The “Great Debates”
Nickname for the debates b/w JFK and Nixon
JFK’s “New Frontier”
JFK’s Domestic Program. Four focuses: Economy, education, aid to the poor, space program
Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy
Shifted focus from internal security work to organized crime and civil rights enforcement
Sec. of Defense Robert McNamara
JFK’s Sec of Defense
New Frontier - Economy
JFK wanted to cut taxes to end the economic slump and help the poor
Believed extra money in tax payers’ wallet would stimulate the economy
New Frontier - Education
JFK introduced a federal aid to education bill, hoping to make education equal in all states
New Frontier - Aid to the Poor
The Other America by Micheal Harrington: about how the poor half of the country lived
New Frontier - Space Program
Congress increased funding for NASA
JFK promised a man on the moon by the end of the decade
Apollo
July 1969: 2 NASA astronauts landed on the moon and planted the America flag. “One small step for man, one huge leap for mankind”
The Peace Corps
Main goal was to work with and help the sick and poor of Third World Nations. Largely volunteer based —>
Flexible Response
Military strategy of supplementing nuclear weapons with conventional forces to respond to flare ups around the world.
European Economic Community (EEC)
Helped promote free trade Western Europe. Helped pave the way for the European Union. GLOBALIZATION!
Trade Expansion Act
Related to the EEC, promoted trade with EEC countries and promoted globalization