Genetics MT #1 - Chapter 4: extensions of mendelian inheritance
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
The type of mutation that leads to increased expression of an altered protein in a cell which does not normally express the protein is called a(n) -- mutation.
gain of function
A patient with sickle cell disease may experience a painful episode leading to tissue and organ damage because cells carrying hemoglobin S ______.
A person's specific blood type is based on (a) antibodies located on the RBC plasma membrane or (b) antigens expressed on the RBC plasma membrane?
(b) as an RBC membrane has antigens present, NOT antibodies
a trait that is expressed in only one sex is said to observe what kind of inheritance?
"sex limited"
compare and contrast sex influenced inheritance and sex limited inheritance
sex influenced refers to phenomenon in which an allele is dominant in one sex but recessive in the other sex. THIS IS NOT THE SAME as sex linked inheritance, as the genes that govern sex influenced traits are autosomal. i.e. the gene that codes for scurs present is dominant in male cattle but recessive in females, whereas the one without scurs which are absent is dominant for females and recessive for males.
sex limited refers to a trait occurring in only one sex altogether. these genes may be autosomal OR sex linked! i.e. ovaries in females and testes in males
Traits determined by genes that are found on the X or Y chromosome are called Blank______.
sex-linked
The pattern where allelic variants of two different genes affect a single trait is called
gene interaction
Two genes controlling the synthesis of different pigments are responsible for feather coloration in Australian parakeets. The dominant allele Y for one gene leads to production of psittacofulvin for yellow coloration. The corresponding recessive allele y prevents yellow pigment production. The dominant allele A for a separate gene leads to eumelanin pigment, appearing blue in reflected light. The corresponding allele a prevents blue pigment production. A bird with the Yyaa genotype will have yellow feathers, one with the yyAa genotype will have blue feathers, while one with the YyAa genotype will have green feathers. What is the interaction between these two genes?
Geneticists want to understand both inheritance patterns and the underlying molecular mechanisms that cause them to happen.
True false question.
T
Escheria coli
bacterium
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
yeast
drosophila melanogaster
fruit fly
Caenorhabdtis elegans
worm
Mus musculus
mouse
Arabidopsis thaliana
flowering plant
Suppose a genetic test shows that a woman has inherited the dominant BRCA1 allele that causes breast cancer. If she does not develop breast cancer in her lifetime, the phenomenon is called
"incomplete penetrance" a phenomenon whereby an allele that is expected to cause a particular phenotype does not always do
The following pathway is proposed to explain the inheritance of purple flower color in pea plants:
Colorless Precursor→Colorless Intermediate→Purple Pigment.
A dominant allele for Gene C provides an enzyme that converts Colorless Precursor→Colorless Intermediate.
A dominant allele for Gene P provides an enzyme that converts Colorless Intermediate→Purple Pigment.
An explanation for why plants with the ccPp genotype have white petals while plants with the CcPp genotype have purple petals is Blank______.
Which pattern is shown by a heterozygous individual that has a phenotype that is intermediate between the phenotypes of the dominant and recessive homozygotes?
incomplete dominance
According to recent microscopic evidence, round pea seeds from heterozygotes actually contain Blank______ number of starch grains compared with seeds from the corresponding homozygotes.
Blank: approx the same OR an intermediate
an intermediate
What is the name for the situation where heterozygotes have greater reproductive success than either of the two homozygotes?
"heterozygote advantage or overdominance" i.e. a heterozygote/ sickle cell carrier is unaffected and malaria resistant
A trait that is expressed in only one sex is said to observe - inheritance.
sex-limited
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A man who is color-blind:
a. must have inherited from their mother
b. could have inherited from either parent
c. can pass it along to ONLY sons
d. must have inherited from father
a.
Corn kernels can have a purple color due to the dominant allele of one gene. When the alleles of a second gene are present in the homozygous recessive genotype, the kernel color is changed to red. This is an example of Blank______.
a. overdominance
b. incomplete dominance
c. gene interaction
d. pleiotropy
c. gene interaction
incomplete dominance is a pattern observed for alleles of the SAME gene and pleiotropy is the result of the action of a single gene
The phenomenon in which an allele is dominant in males but recessive in females (or vice versa), is termed - inheritance.
sex-influenced
You have two strains of white-flowered sweet peas that, when mated, produce F1 progeny with a phenotypic ratio of 3 white-flowered plants: 1 purple-flowered plant. What are the genotypes of the parents in this mating?
a. ccPp x Ccpp
b. ccPp x ccPp
c. ccPP x ccPp
d. CCpp x ccPP
a. as only this would lead to 3 : 1 ratio
b. this cross would yield all white progeny
c. this cross will yield all white progeny
d. this cross would yield all purple
Genes that undergo segregation and independent assortment typically follow what type of inheritance?
Mendelian
A cell with at least one copy of a wild-type allele will typically produce Blank______.
a functional or nonfunctional version of the protein specific by this allele?
functional
When a preexisting allele is changed to a new version that no longer codes for a functional protein, the new allele is called a(n) allele.
mutant!
In fruit flies, the para mutation causes a change in a sodium channel necessary for conducting nerve signals. Mutant flies have normal movement at 22oC but become immediately paralyzed at 29oC. The paralysis is reversed when the temperature returns to 22oC. The para mutation is most likely due to a(n) - allele.
temperature sensitive
What phenomenon is observed in a population when three or more alleles can be found for a single gene?
"multiple alleles"
Which of the surface antigens related to blood type would be found on the red blood cells of an individual with the IAIB genotype?
each RBC carries both surface antigen A and surface antigen B
This occurs when the heterozygote expresses the phenotypes of both homozygotes.
codominance
Corn kernels can have a purple color due to the dominant allele of one gene. When the alleles of a second gene are present in the homozygous recessive genotype, the kernel color is changed to red. This is an example of Blank______.
gene interaction
The IA and IB alleles code for two types of the enzyme that have different structures in their active sites.
glycosyl transferase
Suppose that the covering on corn kernels can have a purple color due to the dominant allele P of gene 1. The genotype pp leads to a colorless covering. Alleles of gene 2 can mask the purple color, with the dominant allele C having no effect but genotype cc changing the purple color to colorless. Alleles of gene 2 have no effect on plants with genotype pp for gene 1.
For the cross PpCc x PpCc, what fraction of the plants are expected to have colorless covering on their corn kernels?
7/16
Note that epistatic interaction has 9:7 phenotypic ratio
For which of the following genotypes would the effects of codominance be observed in the individual's phenotype?
Multiple choice question.
IBIB
IAIB
IBi
IAi
IAIA
IAIB
The inheritance pattern in which both alleles of a gene are equally expressed in a heterozygote is called
codominance
The pattern where allelic variants of two different genes affect a single trait is called
gene interaction
Chromosomes that differ between males and females are called
sex chromosomes
When a daughter can inherit a sex-linked allele from either her mother or father, it must be located on Blank______.
the x chromosome
Which blood type results from a loss of function mutation in glycosyl transferase that prevents the enzyme from attaching a sugar to the carbohydrate tree of the surface antigen?
Multiple choice question.
Blood type O
Blood type AB
Blood type B
Blood type A
blood type O
For summer squash, the dominant allele Y for gene 1 leads to yellow color while the recessive allele y leads to green color. Alleles of gene 2 can prevent color formation, with the dominant allele W leading to white squash while the recessive allele w does not interfere with color development. For the cross YyWw x YyWw, what is the fraction of offspring that will be white?
12/16 as all offspring with at least one W allele will be white, thus that makes up the majority
Which of the surface antigens related to blood type would be found on the red blood cells of an individual with the IAIB genotype?
each RBC would carry both antigen A and antigen B
Colorblindness is due to an X-linked recessive allele. To be colorblind, females must inherit Blank______ copy(ies) of this allele and males must inherit Blank______ copy(ies).
two; one
Genes that are located on the X chromosome are called X- genes.
linked
An allele that can lead to the death of an individual is a(n) Blank______ allele.
lethal
A gene that produces a beneficial product that is not absolutely required for survival of the organism is called a(n) Blank______ gene.
a. nonessential
b. lethal
c. essential
nonessential
The pattern where one gene affects many traits is called .
pleiotropy
The white spotting phenotype in dogs is under the control of a single gene with multiple alleles. The dominant S+ allele results in full pigmentation while one recessive allele, sI, leads to white patches on the legs and belly called Irish spotting. Two fully-pigmented dogs have puppies with Irish spotting. What is the approximate fraction of offspring with Irish spotting expected from this cross?
1/4
When a daughter can inherit a sex-linked allele from either her mother or father, it must be located on Blank___
the X chromosome
Suppose that the covering on corn kernels can have a purple color due to the dominant allele P of gene 1. The genotype pp leads to a colorless covering. Alleles of gene 2 can mask the purple color, with the dominant allele C having no effect but genotype cc changing the purple color to colorless. Alleles of gene 2 have no effect on plants with genotype pp for gene 1. For the cross PpCc x PpCc, what fraction of the plants are expected to have colorless covering on their corn kernels?
7/16
In a dihybrid cross of two heterozygous individuals, you expect a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in the offspring but observe a ratio of 9:7. What is the most likely explanation?
epistatic interaction of two genes
If both copies of a gene have been rendered inactive in a diploid species, the organism is said to carry a gene Blank______.
knockout
The inheritance of purple flower color in pea plants follows this pathway:Colorless Precursor→Colorless Intermediate→Purple Pigment.A dominant allele for Gene C codes an enzyme that catalyzes the first reaction, whereas a dominant allele for Gene P codes an enzyme that catalyzes the second reaction. An explanation of why plants with CCpp and ccPP genotypes have white petals while plants with the CcPp genotype have purple flowers is:
a. complementation occurs in the CcPp plant, showing that the mutations preventing color in the white plants are in different genes.
a. complementation occurs in the CcPp plant, showing that the mutations preventing color in the white plants are in different genes.
b. the dominant allele C exerts epistasis over the recessive allele p and the dominant allele P exerts epistasis over the recessive allele c.
c. the dominant allele C exerts epistasis over the recessive allele c and the dominant allele P exerts epistasis over the recessive allele p.
d. complementation occurs in the purple-petaled plant, showing that the mutations preventing color in the white plants are in the same gene.
A gene that codes for a product that is necessary for the survival of an organism is called a(n) Blank______ gene.
essential
The Antennapedia mutation causes fruit flies to develop legs in the places on their heads where antenna would normally be found. Expression of the Antennapedia gene product in a location where it is not usually active is due to a Blank______ mutation for a Blank______ mutant allele.
gain of function; dominant
Individuals affected with sickle cell disease are homozygous for the HbS allele and produce only allele ----- S. This causes their red blood cells to deform into a sickle shape under conditions of low -- concentration
hemoglobin, oxygen
There are several forms of Mendelian inheritance patterns involving two genes. The inheritance pattern in which the alleles of one gene mask the phenotypic effects of the alleles of a different gene is termed . In addition, the phenomenon in which two parents that express the same or similar recessive phenotypes produce offspring with a wild-type phenotype is known as .
epistasis; complementation
compare and contrast the different types of mendelian inheritance patterns
a. simple mendelian inheritance obeys Mendelian's laws and follow a strict dominant/recessive relationship as well as 3:1 ratio. molecular: 50% of the protein produced by a single copy of the dominant allele in the heterozygote is sufficient to produce the dominant trait
b. incomplete penetrance; in the case of dominant traits, this pattern occurs WHEN a dominant phenotype is not expressed even though an individual carries a dominant allele. in the case of recessive traits, this pattern occurs when a homozygote carrying both recessive alleles does not exhibit the trait. molecular: eventhough a dominant alele is present or two recessive alleles are present, the protein coded by the gene may not exert its effects. This can be due to environmental effects or due to other genes that code proteins that counteract the effects of the protein coded by the dominant allele.
c. incomplete dominance occurs when the heterozygote has a phenotype that is intermediate between either corresponding homozygote. (red flower and white flower form pink flower) molecular: 50% of the protein, produced by a single copy of the functional allele in the heterozygote, is not sufficient to produce the same trait as in a homozygote making 100% of that protein.
d. heterozygote advantage occurs when the heterozygote has a trait that confers a greater level of reproductive success then either homozygote has
e. codominance occurs when the heterozygote expresses both alleles simultaneously without forming an intermediate phenotype
f. x-linked inheritance involves the inheritance of genes that are located on the X chromosome. Males have one copy of X-linked genes and females have two
g. sex-influenced inheritance refers to the effect of sex on the phenotype of an individual. some alleles are recessive in males but dominant in females and vice versa
define wild-type allele
for any given gene, geneticists refer to the prevalent allele in a natural population as wild-type
define genetic polymorphism
in large populations, more than one wild-type allele may occur and this is termed genetic polymorphism
explain why loss-of-function alleles often follow a recessive pattern of inheritance
random mutations occur in populations and alter preexisting alleles - mutant alleles. since random mutations are most likely to disrupt gene function, mutant alleles are often defective in their ability to express a functional protein and are called loss-of-function alleles. they tend to be rare in natural populations
describe how traits can exhibit incomplete penetrance and vary in expressivity
incomplete penetrance results in a pattern of inheritance in which an allele that is expected to cause a particular phenotype does not always do so. variable expressivity may be explained due to environmental effects and/or one or more modifier genes may also affect phenotypes i.e. polydactyly and pedigree chart
discuss the role of the environment with regard to an individual's traits
in addition to genetic variation, environmental conditions have a great effect on the phenotype of an individual
ex 1: Siamese cats, Himalayan rabbits and Drosophila flies are all affected by temperature and thus contain temperature-sensitive alleles
ex 2: Person with PKU who follows a restricted diet may develop properly
ex 3: flies develop best at different temperatures
define 'norm of reaction'
predict the outcome of crosses involving incomplete dominance, heterozygote advantage, and codominance
incomplete dominance:
cRcR (red) x cWcW (white) form all cRcW which when self fertilized forms: cRcR (1/4) cRcW (1/2) and cWcW (1/4) (look over binomial expansion)
heterozygote advantage:
HbA HbS x HbA HbS form 1/4 HbA HbA, 1/2 HbAHbS carriers w advantage and 1/4 HbS HbS (sickle cell anemia individuals)
codominance:
two alleles are both expressed with no intermediate formed in the heterozygous individual
explain the underlying molecular mechanisms of incomplete dominance, heterozygote advantage, and codominance
incomplete dominance:
at the molecular level, the allele that causes a white phenotype is expected to result in a lack of functional protein required for pigmentation. depending on the effects of gene regulation, the heterozygote may produce only 50% of the functional protein, but this amount is not sufficient to produce the same phenotype as the cRcR homozygote, which may make twice as much of this protein. 50% of the functional protein cannot accomplish the same level of pigment synthesis that 100% of the protein can
Heterozygote advantage:
Malaria is a disease caused by Plasmodium parasites transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes. The parasite infects red blood cells, and hemoglobin is essential for its survival. In regions where malaria is endemic, individuals with the sickle cell trait (HbA/HbS) have a survival advantage over those with normal hemoglobin (HbA/HbA) or those with sickle cell disease (HbS/HbS).
The mechanism behind this advantage lies in the fact that sickle cell trait carriers have some sickled red blood cells, which are less hospitable for the malaria parasite. These cells are more likely to be destroyed by the immune system or filtered out by the spleen, preventing the parasite from completing its life cycle and reducing the severity of malaria infection. As a result, individuals with the sickle cell trait have a lower risk of contracting severe forms of malaria, which provides a selective advantage in regions where malaria is prevalent.
codominance:
The molecular level explanation of blood type groups involves the action of glycosyltransferase enzymes, which are responsible for adding specific sugar molecules (glycans) to proteins or lipids. In the context of blood type, these enzymes add specific sugar molecules to the surface of red blood cells, determining the blood type anti
predict the outcome of crosses for X-linked inheritance
X-linked inheritance refers to the inheritance pattern of genes located on the X chromosome.
Since males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome (XY), while females have two X chromosomes (XX), X-linked traits often exhibit different inheritance patterns in males and females.
Inheritance from Parents:
A male inherits his X chromosome from his mother and his Y chromosome from his father.
A female inherits one X chromosome from each parent, one from the mother and one from the father.
Males:
Since males have only one X chromosome, they will express any recessive X-linked trait inherited from their mother because they lack a second X chromosome to mask the expression of the recessive allele.
As a result, males are more likely to exhibit X-linked recessive disorders if they inherit the mutant allele.
Females:
Females have two X chromosomes, so they can be heterozygous or homozygous for X-linked traits.
For X-linked recessive traits, females need to inherit two copies of the mutant allele to express the phenotype. If they inherit only one mutant allele, they will be carriers (heterozygous) and usually won't express the trait themselves, though they can pass it on to their offspring.
For X-linked dominant traits, females need only one copy of the mutant allele to express the phenotype. In this case, males are more likely to be affected because they have only one X chromosome.
Predicting the outcomes of crosses for X-linked inheritance involves understanding the genotypes of the parents and the probabilities of their offspring inheriting certain alleles. Punnett squares are often used to visualize these probabilities
explain pseudo autosomal inheritance
One example of pseudoautosomal inheritance is the gene responsible for the production of a protein called steroid sulfatase (STS). Mutations in this gene can cause X-linked ichthyosis, a skin disorder characterized by dry, scaly skin. Because the STS gene is located within the PARs, inheritance follows an autosomal pattern rather than typical X-linked inheritance. Both males and females can be affected by X-linked ichthyosis, and carrier females can pass the condition on to their offspring.
pseudoautosomal inheritance involves the inheritance of genes located within the pseudoautosomal regions of the sex chromosomes. These genes follow Mendelian inheritance patterns similar to autosomal genes, rather than exhibiting the typical sex-linked inheritance observed with genes located on the non-pseudoautosomal regions of the X and Y chromosomes.
predict the outcome of crosses involving sex-influenced inheritance
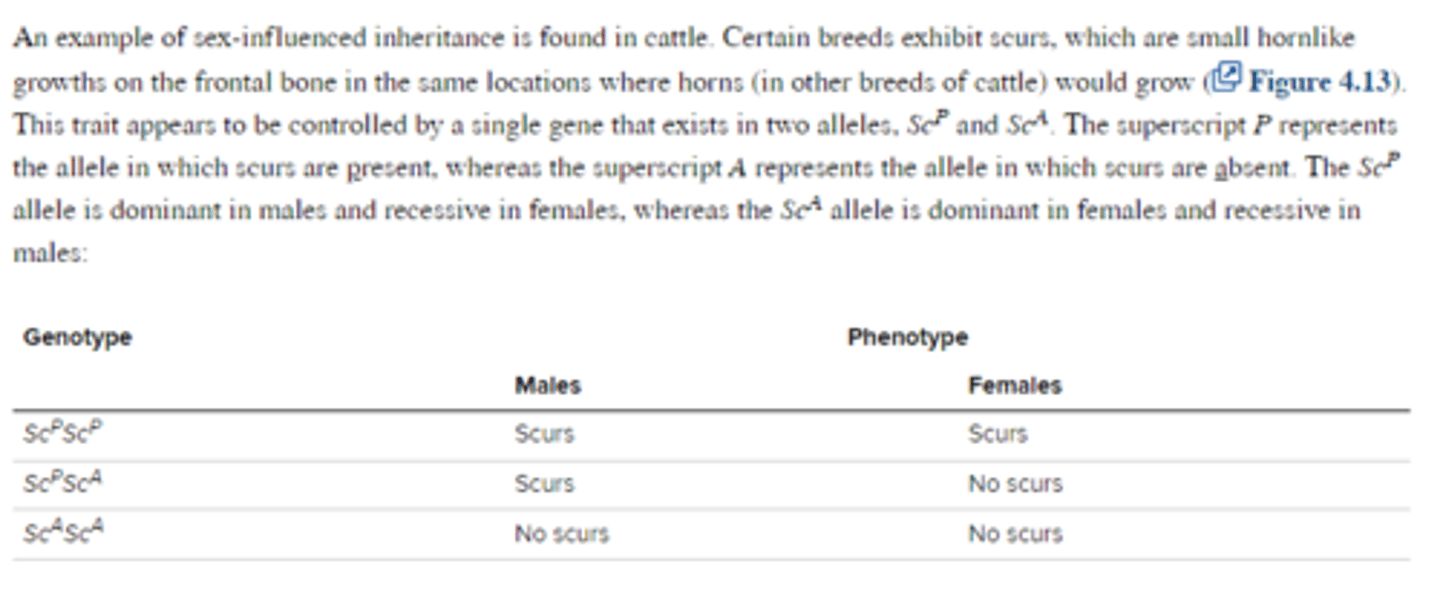
describe the different types of lethal alleles
predict how lethal alleles may affect the outcome of a cross
essential and nonessential
conditional lethal alleles (some conditional lethal alleles cause an organism to die only in a particular temp range): an allele that is lethal only under certain environmental conditions
temperature sensitive lethal alleles (optimal temp needed): an allele that is lethal only in a certain environmental temperature range
semilethal alleles: lethal alleles that kill some individuals but not all
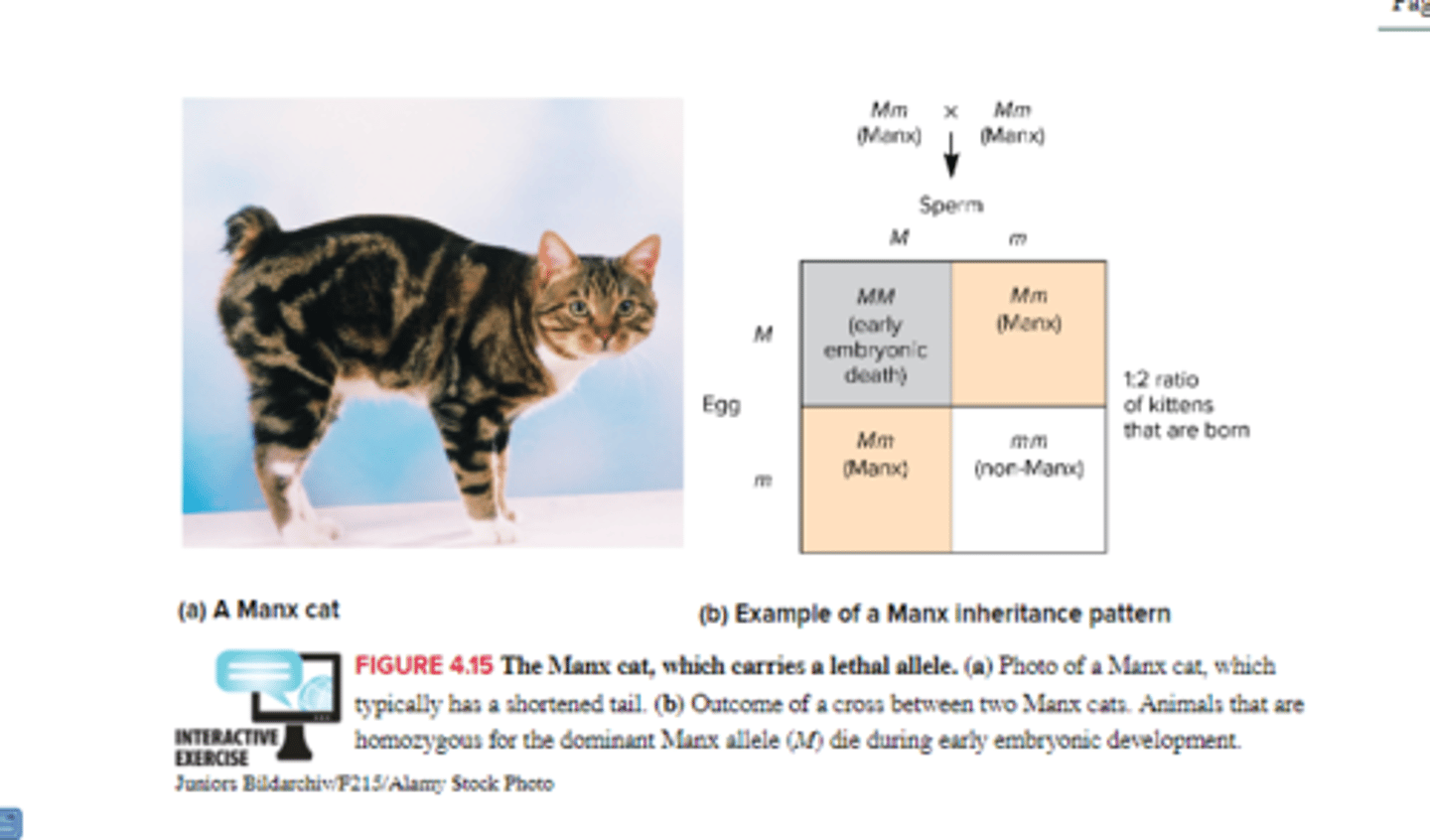
explain the phenomenon of pleiotropy
the multiple effects of a single gene on the phenotype of an organism
describe how embryonic development determines certain coat patterns in animals
embryonic development determines coat patterns in animals through the intricate regulation of gene expression, cellular interactions, and tissue differentiation. Pleiotropic genes play a significant role in this process by influencing multiple traits simultaneously, contributing to the diversity of coat patterns observed in different animal species.
i.e. In domestic cats, the gene responsible for coat color, the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene, also affects other traits such as immune function and behavior, illustrating pleiotropy. Mutations in this gene can result in various coat colors and patterns, ranging from solid black to tabby stripes or spotted patterns.
Similarly, in dogs, the extension (E) locus contains the melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) gene, which regulates eumelanin (black pigment) production. Mutations in this gene can lead to a wide range of coat colors and patterns, including solid colors, merle patterns, and piebald patterns
define gene interaction
the phenomenon in which two or more different genes influence the outcome of a single trait
predict the outcome of crosses involving epistasis, complementation, gene modifiers, and gene redundancy
describe examples that explain the molecular mechanisms of epistasis, complementation, gene modification, and gene redundancy