Chapter 8 - Reducing balance loans, annuities and investments
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reducing balance loans, annuities and investments methods (including somehow e---ing tax ( ‵▽′)ψ)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Recurrence Relation combining Geometric Growth
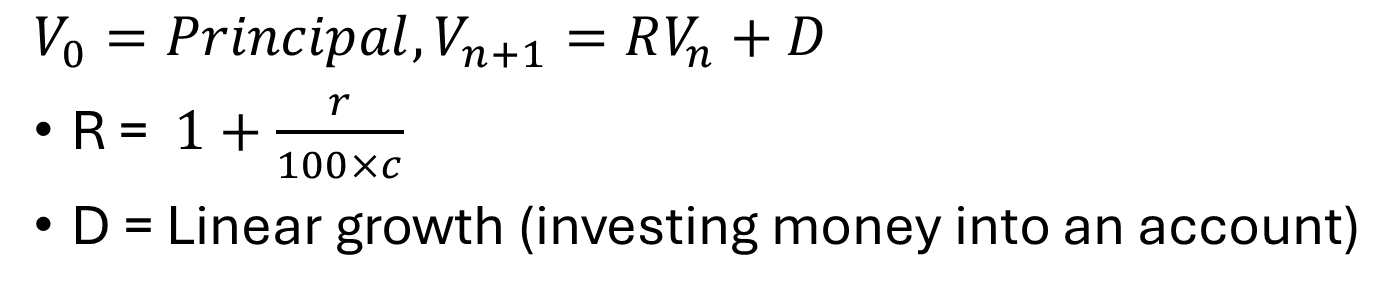
Annuity Investment
When money is invested (fixed sum) and then added to by regular payments in addition to the interest earned. Money will not be paid out to the investor until they close the account
In this situation the following process is followed:
Interest is firstly calculated on the balance of the investment at the end of each compounding period and added to the principal.
A certain amount is then deposited to further increase the balance.
Interest for Annuity Investments
Total Interest = Final value (FV) – Initial Value (PV) - Total Number of payments (PmT x N)
Annual Interest Rate = Interest/Principal * 100% * Compounding Period (c)
Principal Addition = Future (FV) − Present value (PV)
Total paid = Payments received each time period (PMT) × Total number of payments (N)
Modelling compound interest investments with regular additions to the principal
Let Vn be the value of the compound interest investment (i.e. annuity investment) after n additional payments have been made.
Recurrence Relation:
V0 = Principal, Vn+1 = RVn + D
R= 1+r/(100×c)
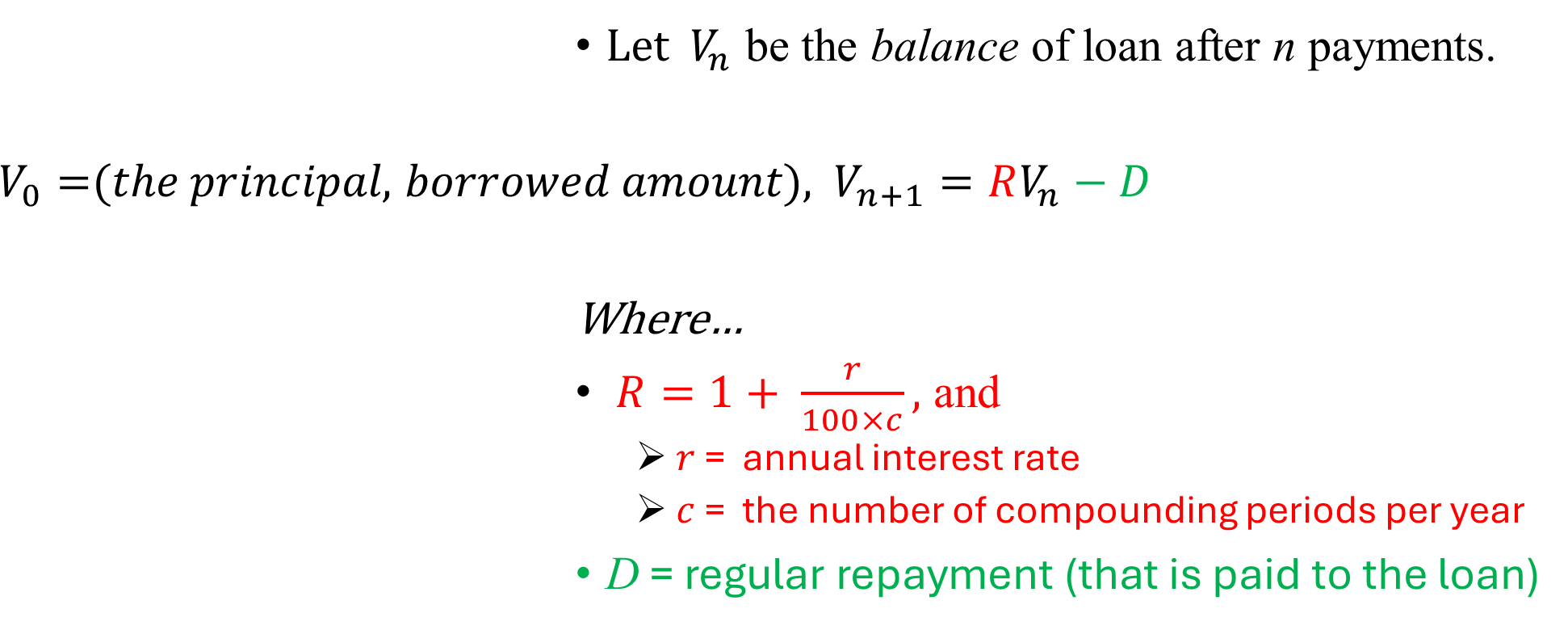
Reducing Balance Loan
A loan accrues interest on the outstanding balance at the end of each compounding period (R > 1). The borrower makes regular repayments, which cover the interest and reduce the principal balance (-D). This process continues until the loan is fully paid off.
Annuity
An investment that earns interest (grows) over time while providing a stream of income through regular payments (withdrawals) until the balance of the investment reaches $0.
A type of insurance contract designed to turn your money into future income payments e.g. gap year.
An annuity is the investment equivalent of a reducing balance loan!!! (same formula)
Recurrence Relation for Reducing Balance Loan / Annuity
*loan/balance of annuity
Formulas for Annuity
Total Interest = Total paid – Principal Reduction
Principal Reduction = Present Value – Future Value
Total Paid = Payment made each time period * Number of payments per year.
Future value of an annuity
Total value of the investment at the end of the specified term
Present value of an annuity
Lump sum (amount paid all at once) that is deposited at the beginning of the annuity term, at the same interest rate and with the same compounding period.
Amortisation
The repayment of a loan by making regular payments; used to regularly and gradually lower the book value of a loan or investment over a period of time with regular payments.
Amortisation Table for Reducing Balance Loan and Annuitites
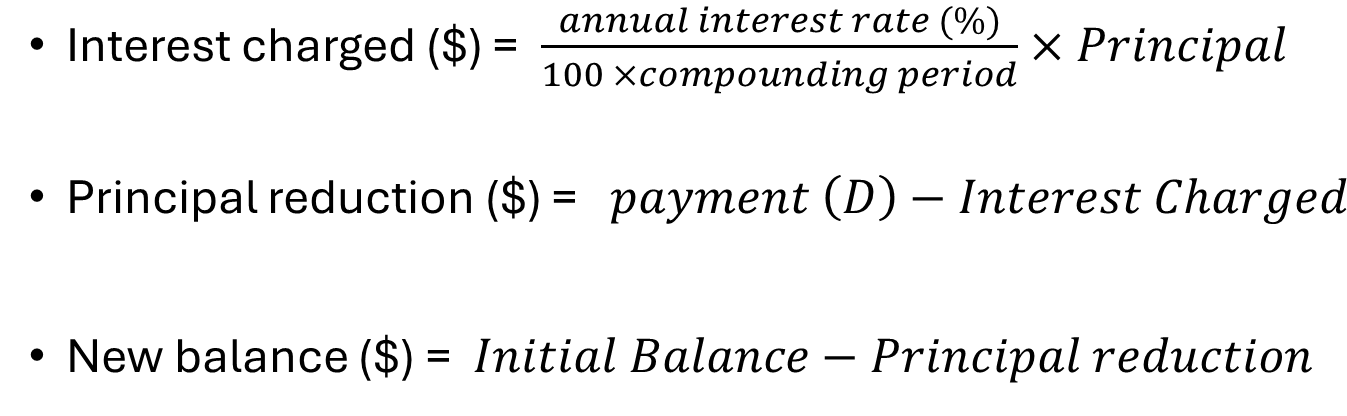
Program: REPAY
Interest Charged = LIST 2
Principal Reduction = LIST 3 - LIST 2
If Balance < Payment → Principal Reduction = Balance, recalculate Interest
Interest Rate → Use previous rows to calculate if not given
Principal Reduction ↑ → Interest ↓
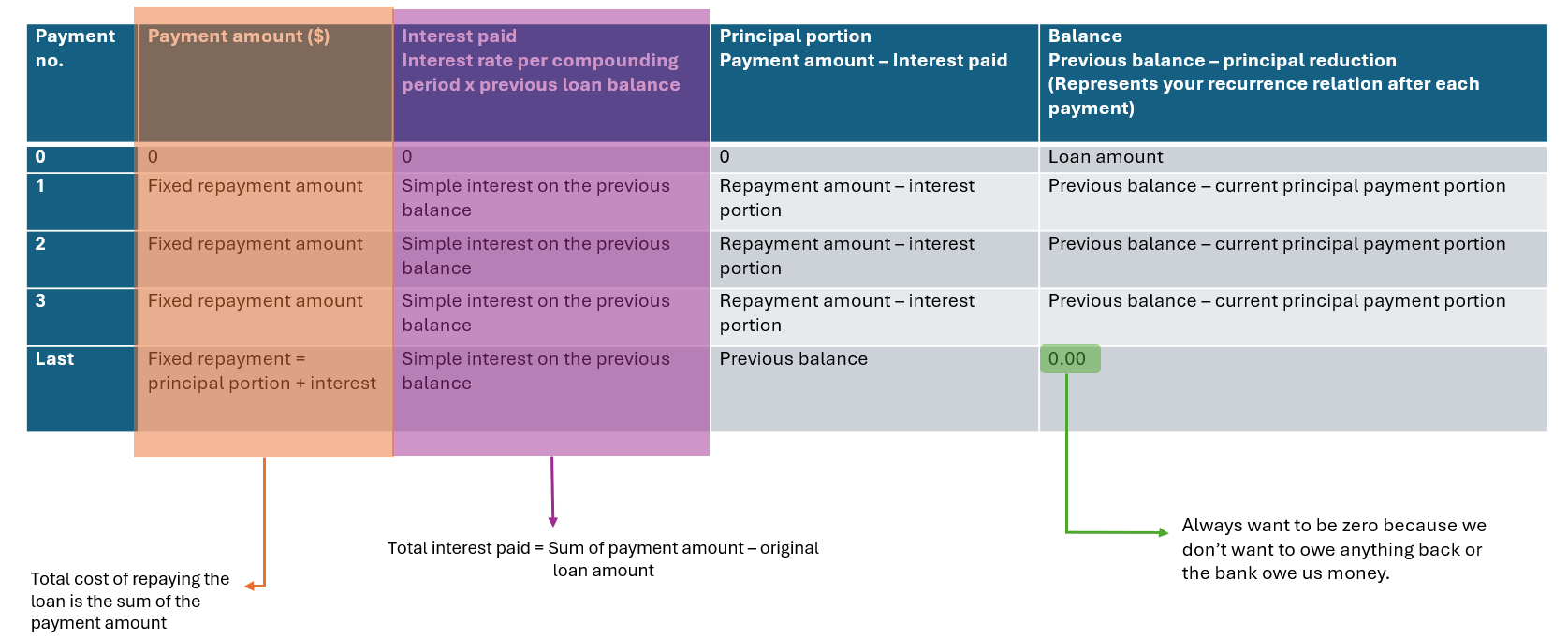
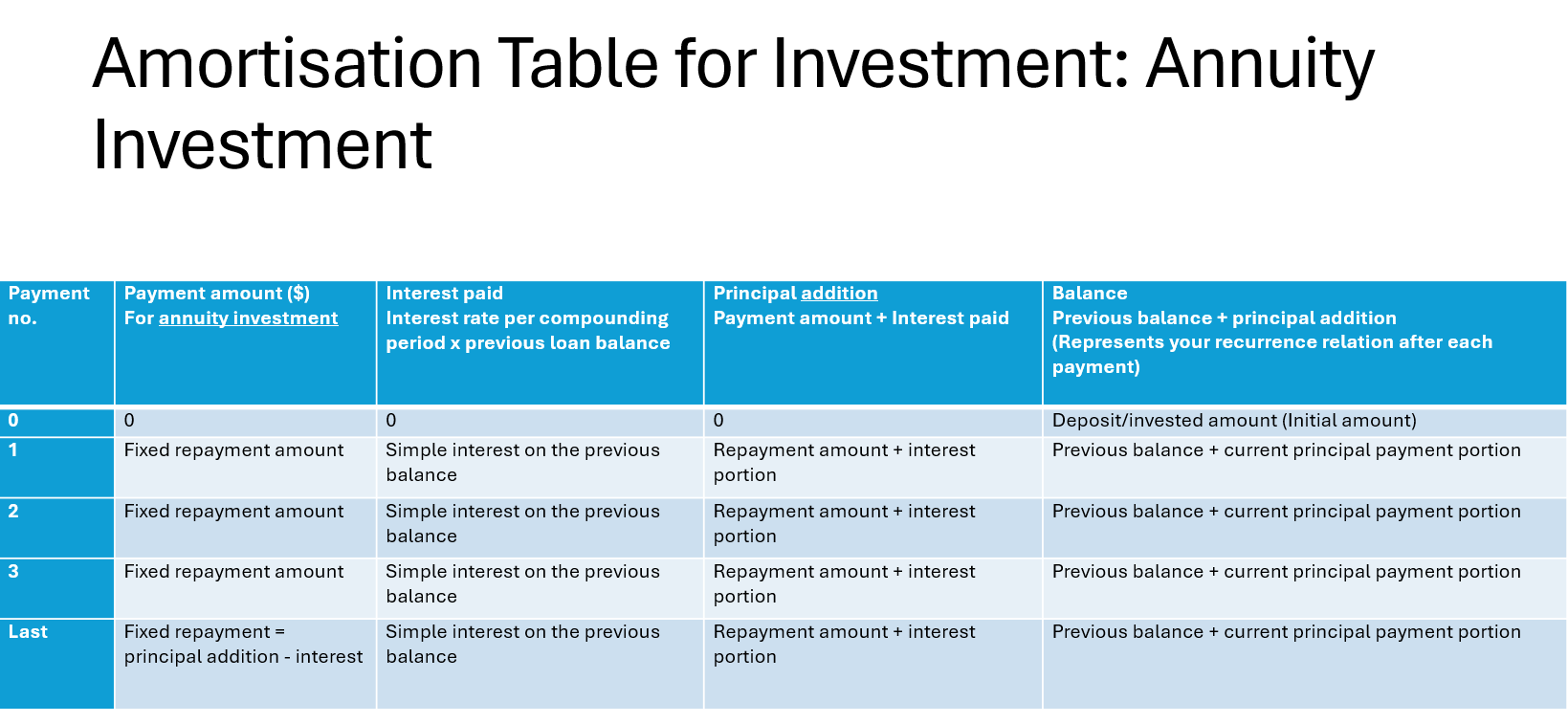
Amortisation Table for Annuity Investment

Program: Use saving
Interest Charged = LIST 2
Principal Addition = LIST 3 + LIST 2
Interest Rate → Use previous rows to calculate if not given
Principal Addition ↑ → Interest ↓
Entering Information on Finance Solver
N - Total number of payments
I(%) - annual interest rate
PV - Present value of loan/investment
PmT - Amount paid per payment
FV - Future value of loan/investment
P/Y - Payments per year
C/Y - Compounding Periods per Year
Value of Pronumerals in Finance Solver: ±?
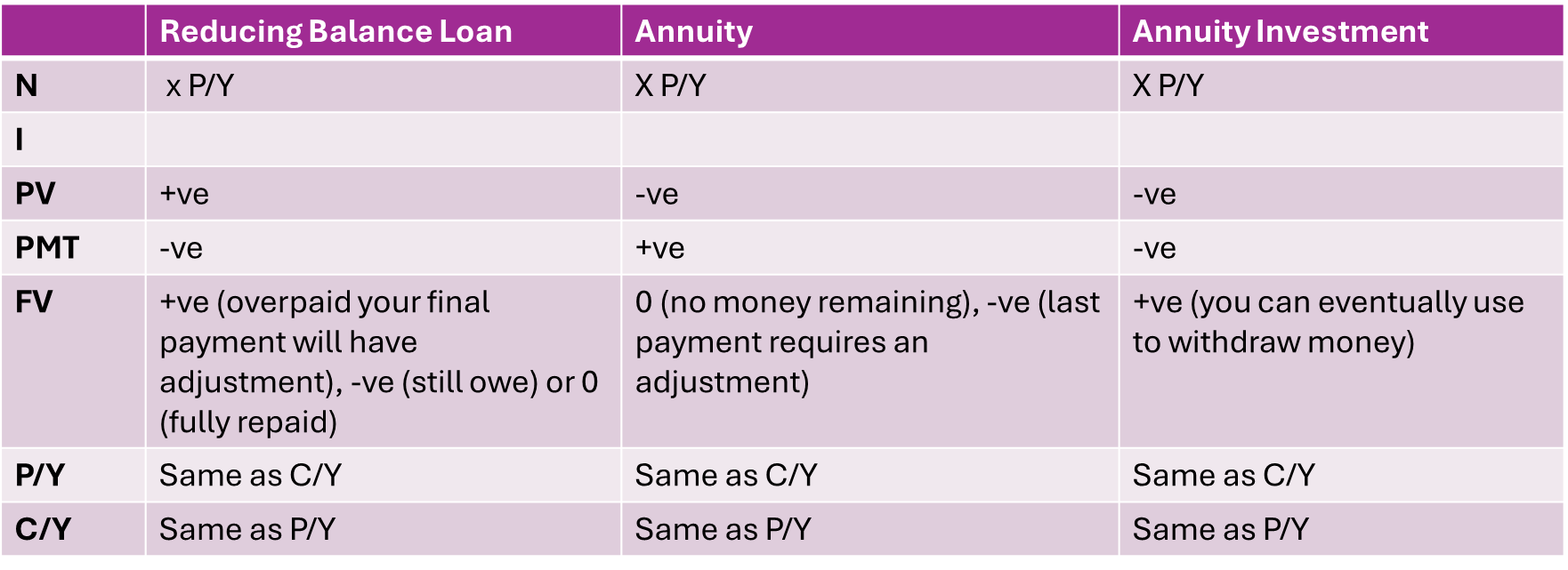
+ Value: bank gives person money
- Value: person gives bank money
Total interest earned/paid equations
For a reducing balance loan/annuity:
I = FV - PV + (PmT*N) (I = Interest, FV - Final Value, PV - Initial Value)
For a compound interest investment with regular additions (Annuity Investment):
I = FV - PV - (PmT*N)
Changing Conditions
Changes of loans and annuity midway period are centered around:
Payments made each period (often pay more/faster);
Interest rates (e.g., home loans);
Addition of a lump sum.
Important Equations to Remember

Note: Avoid early rounding where possible for these questions! Copy and paste info to keep unrounded answers. (E.g., copy from FV, paste in PV and change the sign.)
Interest - Only Loans
Borrows repays only the interest changed (NOT BALANCE).
Value of loan remains the same for duration of loan because the loan is made when asset is likely to increase in value.
Perpetuity
Type of annuity (payment) that never runs out. Able to provide a continuous payment indefinitely. Requires permanently invested money for money forever!
Interest earned = payment (because we are withdrawing interest each time). Value of investment doesn’t change.
Recurrence Relation for Interest - Only Loans & Perpetuity
V0 = Principal, Vn+1 = RVn - D
R = 1 + r/100c
D = r/100c * V0
Effect of something on interest rate, etc.
Annuity/Reducing Balance Loan | Annuity Investment | |
Effect on interest rate | •Higher interest rate increases duration of the loan due to increase in interest earned/charged. | •Higher interest rate earn more interest which makes you reach savings goal sooner |
Effect on compounding period | •Increase in compounding period will pay off a loan quicker (if interest rate remains the same) | •Greater compounding period earn more interest which reduces time to reach savings goal |
Effect on payment (if compounding period remains the same) | •Lower payment will ensure the loan/annuity lasts longer. •Increase in payment will decrease duration of loan/annuity | •Increase in payment will allow for savings goal to be reached quicker. •Btw you can use CAS to determine |