Biology 20 - Chapter I
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/143
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
1
New cards
Nutrition
the process of taking and assimilating nutrients; the branch of science concerned with this process
2
New cards
Nutrients
a substance that provides nourishment essential for life and growth
3
New cards
Macromolecules
large, complex organic molecules. Made up of smaller subunits linked together by covalent bonds.
4
New cards
Organic molecules that make up living organisms
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, and VItamins and Nutrients
5
New cards
Assembling Macromolecules
Dehydration Synthesis - a molecule of water is removed by taking the -OH (hydroxyl) group of one subunit and a -H (hydrogen) atom from another subunit. This leaves the subunits bonded together.
6
New cards
DIsassembling Macromolecules
Hydrolysis - a molecule of water is added to the bonds between subunits breaking them apart.
7
New cards
Carbohydrates
The most important energy source for the body; produced by plants during photosynthesis.
Provide short or long term energy storage and are classified by the amount of sugars they contain.
Three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
Provide short or long term energy storage and are classified by the amount of sugars they contain.
Three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides
8
New cards
Simple sugars
1 carbon, 2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen.
Often end in “-ose”
Often end in “-ose”
9
New cards
Monosaccharides
Contain 3-6 carbons
Examples: Glucose, galactose, fructose
Examples: Glucose, galactose, fructose
10
New cards
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides
Formed by dehydration synthesis
Examples:
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Lactose = glucose + galactose
Formed by dehydration synthesis
Examples:
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Lactose = glucose + galactose
11
New cards
Polysaccharides
More than 2 monosaccharides
Formed by dehydration synthesis
Formed by dehydration synthesis
12
New cards
Starch
Polysaccharide that acts as energy storage in plants, made up of 100 - 1000 glucose units
13
New cards
Glycogen
Stored by animals as a carbohydrate, made up of 16 - 24 glucose units joined by dehydration synthesis
14
New cards
What happens to excess glucose?
Converted into glycogen by insulin and is stored in liver and muscles.
15
New cards
What happens if glucose concentration in blood decreases?
Glycogen can be converted back into glucose
16
New cards
Cellulose
Polysaccharide that makes up the cell wall of plant cells.
Made up of thousands of glucose units combined by dehydration synthesis in long chains.
The most abundant carbohydrate in nature.
Can’t be digested and used for food by humans but is an important source of fibre in our diet.
Made up of thousands of glucose units combined by dehydration synthesis in long chains.
The most abundant carbohydrate in nature.
Can’t be digested and used for food by humans but is an important source of fibre in our diet.
17
New cards
Benedict’s Test
Blue reagent turns red/orange when exposed to heat if sugars are present.
Test for Carbohydrates
Test for Carbohydrates
18
New cards
Iodine Test
Iodine (yellowish/red/brown) turns blue/black in the presence of starch.
Test for Carbohydrates
Test for Carbohydrates
19
New cards
Lipids
Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Large, insoluble molecules which are ideal for their primary role in the body.
Major component of cell membrane and many hormones.
Body’s insulation from cold.
Cushioning agent for many organs.
Carrier of vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Composed of glycerol and fatty and chain
Large, insoluble molecules which are ideal for their primary role in the body.
Major component of cell membrane and many hormones.
Body’s insulation from cold.
Cushioning agent for many organs.
Carrier of vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Composed of glycerol and fatty and chain
20
New cards
Triglycerides
Lipid composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acids.
Dehydration synthesis!
Three water molecules are formed in this process
Dehydration synthesis!
Three water molecules are formed in this process
21
New cards
Unsaturated triglycerides
double bonds, more easily broken down (oils), from plant sources
22
New cards
Saturated triglycerides
no double bonds, not easily broken down (fats), from animal sources, solids at room temperature, fats accumulate on arteries
23
New cards
Phospholipids
Lipid composed of a phosphate group attached to glycerol.
Major component of cell membranes.
Twice the energy as carbohydrates or proteins.
Major component of cell membranes.
Twice the energy as carbohydrates or proteins.
24
New cards
Waxes
Composed of many fatty acids attached to alcohols or carbon rings.
Insoluble in water
Not readily used as energy food but as a waterproofing covering of leaves, feathers, and fur.
Also used in the structuring of storage units in beehives
Insoluble in water
Not readily used as energy food but as a waterproofing covering of leaves, feathers, and fur.
Also used in the structuring of storage units in beehives
25
New cards
Translucence test
Greasy, translucent spot produced on paper.
Test for Lipids
Test for Lipids
26
New cards
Emulsions test
Milky emulsion (tiny droplets) produced by alcohol dissolved fat added to water.
Test for Lipids
Test for Lipids
27
New cards
Sudan IV
Red droplets of fat produced.
Test for Lipids
Test for Lipids
28
New cards
Steroids
Altered lipids that are produced by the body and act as chemical messengers known as hormones.
Can have many unwanted effects
Can have many unwanted effects
29
New cards
Cholesterol
Type of steroid
Found in the body and made in the liver
An important component of cell membranes and used to manufacture certain hormones
Found in the body and made in the liver
An important component of cell membranes and used to manufacture certain hormones
30
New cards
LDL Cholesterol (Low Density Lipoprotein)
Bad cholesterol
The build up of cholesterol and fats forming plaque along the inside lining of the arteries
Can cause high blood pressure or a stroke, if the blockage is in the brain or a heart attack, if the plaque blocks thee coronary artery.
The build up of cholesterol and fats forming plaque along the inside lining of the arteries
Can cause high blood pressure or a stroke, if the blockage is in the brain or a heart attack, if the plaque blocks thee coronary artery.
31
New cards
HDL Cholesterol (High Density Lipoprotein)
Good cholesterol
Can cover the blood’s bad cholesterol
Exercise can raise it
Can cover the blood’s bad cholesterol
Exercise can raise it
32
New cards
Protein
Composed by carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. sometimes contain sulfur.
Built by combining amino acids using dehydration synthesis
amino acids → polypeptides →proteins
Built by combining amino acids using dehydration synthesis
amino acids → polypeptides →proteins
33
New cards
Polypeptide
Chain of 3 or more amino acids
34
New cards
Protein
Longer amino acid chains consisting of one or more polypeptide changes folded into complex 3D structures
35
New cards
Peptide bond
Formed when amino acids are joined
Place where the protein and later be broken down by hydrolysis and digestion
Place where the protein and later be broken down by hydrolysis and digestion
36
New cards
What happens when there is too much protein?
Kidney failure (clogs kidney with wastes)
37
New cards
What happens when there is too little protein?
Kwashiorkor (bellies swell because of water retention)
38
New cards
What do proteins do?
building and repairing cell structures
muscle fibres
enzymes
antibodies
some hormones
markers and receptors
active transport molecules
muscle fibres
enzymes
antibodies
some hormones
markers and receptors
active transport molecules
39
New cards
Primary Structure
Amino Acids are organized in linear arrangements.
Determined by DNA in the nucleus of the cell
Determined by DNA in the nucleus of the cell
40
New cards
Secondary Structure
Primary structure coils or pleated sheets
41
New cards
Tertiary Structure
Spiral chains folded upon themselves to give a globular appearance.
42
New cards
Quaternary Structure
Several globular proteins bonded together
43
New cards
Denaturation
Occurs when the bonds holding the protein molecule together are disrupted. Causes a temporary change in the protein’s shape and properties
44
New cards
Coagulation
Permanent change in protein shape
45
New cards
Biuret test
blue reagent turns violet when peptide bonds (proteins) are present
46
New cards
Nucleic Acids
Found in hereditary materials of a cell
Two main types: DNA and RNA
Made up of Nucleotides joined by dehydration synthesis
Two main types: DNA and RNA
Made up of Nucleotides joined by dehydration synthesis
47
New cards
Nucleotides
Made up of a five carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate, and a nitrogen base
48
New cards
Vitamins
Group of organic substances that help in enzyme actions
Made up by plants
Animals need them but can’t make them; thus they need to be taken in as food.
Made up by plants
Animals need them but can’t make them; thus they need to be taken in as food.
49
New cards
Vitamin A
beauty vitamin (skin/hair/nails) and visual pigment (at night)
50
New cards
Vitamin B
energy metabolism
51
New cards
Vitamin C
bones/teeth, immune system, connective tissue
52
New cards
Vitamin D
calcium absorption (bones/teeth)
53
New cards
Minerals
Group of inorganic substances that have various functions:
Maintain electrolyte balance in body fluids
Act in the nerve and muscle cells
Form structures such as teeth and bones
Help in enzyme actions in other macromolecules
Example: calcium, iron, iodine, potassium/sodium
Maintain electrolyte balance in body fluids
Act in the nerve and muscle cells
Form structures such as teeth and bones
Help in enzyme actions in other macromolecules
Example: calcium, iron, iodine, potassium/sodium
54
New cards
Calcium
Growth of bones/teeth (rickets)
55
New cards
Iron
Blood hemoglobin (anemia)
56
New cards
Iodine
Part of a hormone called thyroxin (goiter)
57
New cards
Potassium/Sodium
Nerve impulse (nerve disorders)
58
New cards
Enzymes
Functional 3-D proteins that act as biological catalyst
Often end with -ase and are named for their substrates
Often end with -ase and are named for their substrates
59
New cards
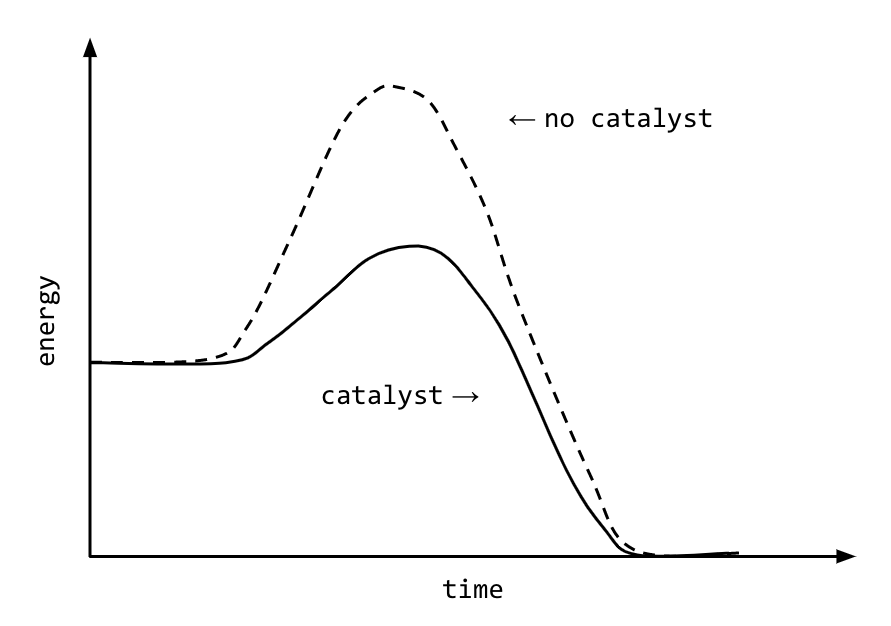
Activation energy
Needed to start a chemical reaction, usually heat.
Problem: for cells to start reactions they need to put in energy; but temperature increase can coagulate their proteins and the cells die
Solution: enzymes lower the necessary energy of activation
Problem: for cells to start reactions they need to put in energy; but temperature increase can coagulate their proteins and the cells die
Solution: enzymes lower the necessary energy of activation
60
New cards
Substrate
Molecule to which the enzyme attaches itself
61
New cards
Active site
Area of an enzyme that attaches wit the substrate molecule
62
New cards
Enzyme helpers
cofactors and co-enzymes
63
New cards
Cofactors
inorganic molecules, atoms, or ions that can help enzymes bind to substrate molecules
made up from minerals
made up from minerals
64
New cards
Co-enzymes
organic molecules that help enzymes bind to substrate molecules
made up from vitamins
made up from vitamins
65
New cards
Factors affecting enzyme activity
Temperature, pH, Concentration of Substrate, Concentration of Enzyme, Inhibitors
66
New cards
Temperature
More = faster reaction
Having a higher _____ can denature the enzyme stopping it from working - active site an no longer bind substrate molecules
Enzymes work at an optimum _____
Having a higher _____ can denature the enzyme stopping it from working - active site an no longer bind substrate molecules
Enzymes work at an optimum _____
67
New cards
pH
Enzymes work at its optimum _____
Change in acidity or basicity an alter enzyme shape
Active site can no longer bind substrate molecules
Change in acidity or basicity an alter enzyme shape
Active site can no longer bind substrate molecules
68
New cards
Concentration of Substrate
Enzymes work slowly with low _____
Usually more substrate increases reaction rate
When the enzyme is working as fast as it can, more substrate will not make it work faster, the enzyme has reached maximum velocity.
Usually more substrate increases reaction rate
When the enzyme is working as fast as it can, more substrate will not make it work faster, the enzyme has reached maximum velocity.
69
New cards
Concentration of Enzyme
Increases the reaction rate, providing there is an unlimited supply of substrate
70
New cards
Inhibitors
Competitive and Non-Competitive
71
New cards
Competitive Inhibitors
Compete with the substrate for the active site on the enzyme. If they bond to the enzyme they stop the reaction.
Loosely bound to the active site though and can be replaced by the substrate, therefore the effect is irreversible.
Its degree depends on the relative concentrations of it and the substrate
Loosely bound to the active site though and can be replaced by the substrate, therefore the effect is irreversible.
Its degree depends on the relative concentrations of it and the substrate
72
New cards
Non-Competitive Inhibitors
Attaches to the enzyme changing the shape of the active site = the substrate cannot bind.
This is an irreversible event. Adding more substrate will not reactivate the enzyme
This is an irreversible event. Adding more substrate will not reactivate the enzyme
73
New cards
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
(Negative Feedback/Feedback Inhibition)
(Negative Feedback/Feedback Inhibition)
Enzymes participate in a metabolic pathway where the substrate is modified by a number of enzymes before producing a final product.
As the final product accumulates within the cell, it binds to the regulatory site of an enzyme in the pathway, changing its shape, and thus preventing the substrate from binding.
The final product is no longer produced until concentrations are reduced.
As the final product accumulates within the cell, it binds to the regulatory site of an enzyme in the pathway, changing its shape, and thus preventing the substrate from binding.
The final product is no longer produced until concentrations are reduced.
74
New cards
Precursor
Accumulation of substrate molecules causes these molecules to attach to the regulatory site of one of the enzymes in a pathway, which improves fit between enzyme and substrate - increases reaction rate
75
New cards
Digestion
Breaking down of food into materials needed by the body:
polymers → monomers → absorbed into mitochondria → ATP
polymers → monomers → absorbed into mitochondria → ATP
76
New cards
Materials needed by the cells
Monosaccharides
Amino Acids
Fatty Acids and Glycerol
Amino Acids
Fatty Acids and Glycerol
77
New cards
The Process of Digestion
Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Assimilation, and Elimination
78
New cards
Ingestion
The intake of the nutrients
79
New cards
Digestion
Breaking down of large organic compounds into smaller ones
80
New cards
Absorption
Transferring the small useful compounds from the digestive system into the circulatory system
Happens in the stomach, the small intestine, and the large intestine
Happens in the stomach, the small intestine, and the large intestine
81
New cards
Assimilation
Use of nutrients by the cells of the body
82
New cards
Elimination (egestion)
Passing left over wastes out of the digestive tract
83
New cards
Physical or Mechanical Digestion
Physically breaking down ingested food
Chewing (mouth) and churning and mixing (stomach)
Chewing (mouth) and churning and mixing (stomach)
84
New cards
Chemical Digestion
Breaking down ingested food by enzymes and other digestive secretions
85
New cards
Alimentary Canal
A continuous, coiled, and hollow muscular tube that food passes through
86
New cards
Accessory Organs
Makes chemicals needed for digestion and send them into the alimentary canal: Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
87
New cards
The Mouth
Site of ingestion of food
Chemical and Physical Digestions
Chemical and Physical Digestions
88
New cards
Saliva
Contains salivary amylase enzyme
Breaks down starch ( a polysaccharide ) → maltose (disaccharide)
Allows for the formation of a bolus (ball of food) for ease of swallowing
Secreted by the salivary gland
Composed by water, mucus, salt, and salivary amylase
Breaks down starch ( a polysaccharide ) → maltose (disaccharide)
Allows for the formation of a bolus (ball of food) for ease of swallowing
Secreted by the salivary gland
Composed by water, mucus, salt, and salivary amylase
89
New cards
Water
Lubricates food, makes it easier to swallow
Dissolves food, so it can be tasted
Moistens lips and tongue for speech
Cleans mouth of debris
Dissolves food, so it can be tasted
Moistens lips and tongue for speech
Cleans mouth of debris
90
New cards
Mucus
Lubricates food and protects wall of the stomach
91
New cards
Salts
Provides basic pH, approx 7.6, for action of amylase
92
New cards
Salivary amylase
Digestion of starch → maltose
93
New cards
Pharynx
Swallowing moves materials to the throat
Intersection that leads to the trachea (respiratory) and the esophagus (digestive).
The epiglottis prevents food from entering the trachea
Intersection that leads to the trachea (respiratory) and the esophagus (digestive).
The epiglottis prevents food from entering the trachea
94
New cards
Esophagus
Muscular tube that moves food from the mouth to the stomach
Not a digestive organ
Not a digestive organ
95
New cards
Peristalsis
Waves of muscular contraction moves food down the esophagus to the stomach
96
New cards
Stomach
Site of both chemical and mechanical digestion
Can hold food for 30 minutes to several hours depending on the type of food
Can hold food for 30 minutes to several hours depending on the type of food
97
New cards
Physical Digestion of the Stomach
Churning (breaks up food)
98
New cards
Chemical Digestion of the Stomach
proteins → polypeptides-milk proteins → coagulation
99
New cards
What is absorbed by the stomach?
Water
Salts
Aspirin
Alcohol
Salts
Aspirin
Alcohol
100
New cards
Sphincter muscles
It seals the stomach by both ends
Regulates the flow of food
Two types:
esophageal (esophagus to stomach)
pyloric (stomach to duodenum)
Regulates the flow of food
Two types:
esophageal (esophagus to stomach)
pyloric (stomach to duodenum)