BIOL 4100 Exam 1 (Dr. Mehari - Auburn)
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
Where does DNA transcription occur?
nucleus
Where does DNA translation occur?
cytoplasm
What process synthesizes a DNA strand?
replication
What process synthesizes RNA from a DNA template?
transcription
What process synthesizes protein from RNA?
translation
What is the central dogma?
DNA -> RNA -> protein
Genetic changes followed by selection are best described as the fundamentals of what process?
a. genetic drift
b. DNA replication
c. evolution
d. reproduction
e. regeneration
c. evolution
When comparing liver cells and kidney cells within an organism, many differences can be observed and documented. Which of the following is not a difference between liver cells and kidney cells in the same animal?
a. The different cells have different roles in the body
b. The different cells produce different proteins
c. The different cells express different genes
d. The different cells are generated during the animal's development
e. The different cells have different DNA
e. The different cells have different DNA
Which structure could not be seen using an electron microscope?
a. individual cell
b. DNA
c. electron
d. plasma membrane
e. ribosomes
d. plasma membrane
What is a drawback to using light microscopy?
a. It requires the use of fluorescent probes
b. It cannot be used to view living cells
c. It can be used only to view samples that are sliced very thinly
d. It cannot be used to view a whole cell or organism
e. It cannot be used to view structures smaller than a bacterium
e. It cannot be used to view structures smaller than a bacterium
What is the smallest object that can be seen using an electron microscope?
a. individual hydrogen atom
b. individual nanometer
c. individual large organelle
d. individual molecule
e. individual electron
d. individual molecule
Is the following statement true, false, or impossible to determine?
An individual ribosome can be seen with a fluorescence microscope.
a. true
b. false
c. impossible to determine
a. true
What do eukaryotic cells have that prokaryotes lack?
a. a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
b. a means of using chemical energy
c. ribosomes
d. nucleic acids
e. a cell wall
a. a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Is the following statement true, false, or impossible to determine?
One thing all cells have in common is the ability to colonize any environment on Earth.
a. true
b. false
c. impossible to determine
b. false
What organisms commonly colonize the hot acid of volcanic springs, the airless depths of marine sediments, the sludge of sewage treatment plants, the pools beneath the frozen surface of Antarctica, as well as the acidic, oxygen-free environment of a cow's stomach where they break down ingested cellulose and generate methane gas?
a. eukaryotes
b. bacteria
c. archaea
d. all of these
c. archaea
Is the following statement true, false, or impossible to determine?
Like the differentiated cells in an individual plant or animal, all bacteria have the same DNA.
a. true
b. false
c. impossible to determine
b. false
Is the following statement true, false, or impossible to determine?
At a molecular level, the members of the two domains of prokaryotes -- the archaea and bacteria -- differ as much from each other as either does from the eukaryotes.
a. true
b. false
c. impossible to determine
a. true
Which organelle's ancestor was likely engulfed by primitive eukaryotes to help the cell survive in an oxygen-rich atmosphere?
a. mitochondrion
b. lysosome
c. Golgi apparatus
d. endoplasmic reticulum
e. peroxisome
a. mitochondrion
What is the name of the process by which eukaryotic cells engulf material captured from an external medium?
a. cytokinesis
b. endocytosis
c. exocytosis
d. endosymbiosis
e. endomitosis
b. endocytosis
Which of the following is a stack of flattened membrane-enclosed sacs that receives molecules made in the endoplasmic reticulum, often chemically modifies them, and then directs them to the exterior of the cell or to various locations inside the cell?
a. endoplasmic reticulum
b. Golgi apparatus
c. ribosome
d. lysosome
e. peroxisome
b. Golgi apparatus
Which cellular component separates the DNA of eukaryotic cells from the cytoplasm?
a. nuclear membrane
b. smooth endoplasmic reticulum
c. cell wall
d. plasma membrane
a. nuclear membrane
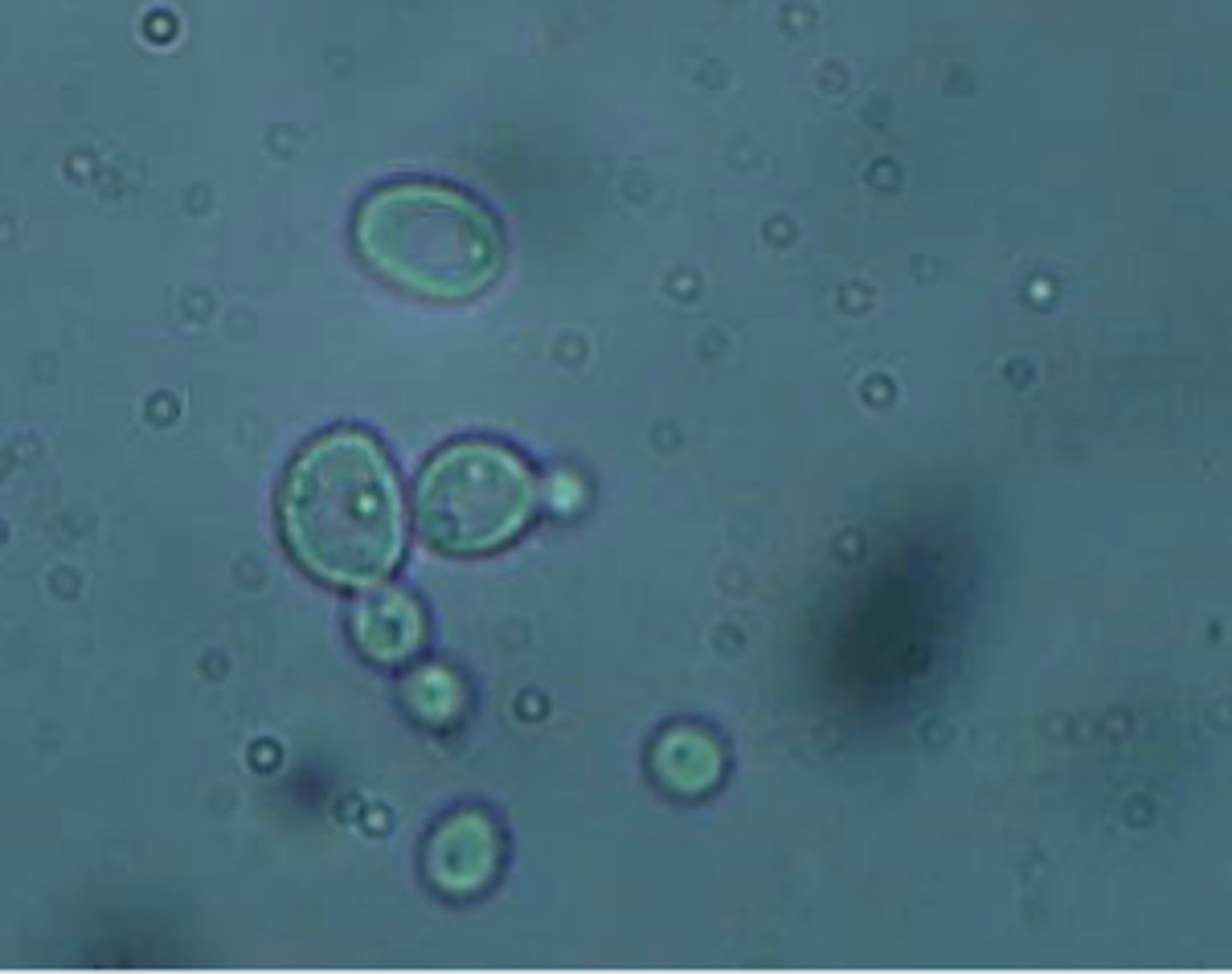
Which model organism is represented in this microscopic image?
a. Drosophila melanogaster
b. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
c. Caenorhabditis elegans
d. Arabidopsis thaliana
e. Escherichia coli
b. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Which of the following is a model plant used by scientists?
a. Caenorhabditis elegans
b. Homo floresiensis
c. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
d. Arabidopsis thaliana
e. Homo sapiens
d. Arabidopsis thaliana
Which is not a function of proteins?
a. encoding genetic information
b. catalyzing biochemical reactions
c. providing cells with structural support
d. acting as molecular motors
e. encasing certain viruses
a. encoding genetic information
Is the following statement true or false, and why?
Within a developed multicellular organism, all cells possess the ability to divide and do so regularly.
a. It is true, because all cells can always replicate their DNA in the same manner
b. It is false, because most multicellular organisms cannot reproduce at all
c. It is false, because some cells lose the ability to replicate their DNA and divide
d. It is true, because all cells can always split into two cells in the same manner
c. It is false, because some cells lose the ability to replicate their DNA and divide
What is a drawback to using electron microscopy?
a. It can be used only to view atomic details in structures larger than a ribosome
b. It can be used only to view samples that are sliced very thinly
c. It cannot be used to view a whole cell or organism
d. It requires the use of fluorescent probes
e. It cannot be used to view living cells
e. It cannot be used to view living cells
Which of these cannot be resolved with a conventional light microscope?
a. bacterium
b. cell nucleus
c. mitochondrion
d. ribosome
e. embryonic cell
d. ribosome
In 1970, Frye and Edidin published research describing the mobility of plasma membrane proteins. They fused mouse and human cells together, creating a hybrid cell, and then examined the localization of mouse and human proteins over time. Initially mouse and human proteins were each restricted to one-half of the heterokaryon, but over time the mouse and human proteins mixed, with each being present over the entire cell surface. What technique did Frye and Edidin likely use to examine the mouse and human proteins?
a. transmission electron microscopy
b. scanning electron microscopy
c. fluorescence microscopy
d. interference contrast light microscopy
c. fluorescence microscopy
Which statement represents the cell theory?
a. All cells resemble square or rectangular chambers
b. All cells require a continual input of energy to sustain life
c. All cells contain DNA
d. All cells can be seen using a microscope
e. All cells are formed by the growth and division of existing cells
e. All cells are formed by the growth and division of existing cells
Which is not evidence for the endosymbiotic origins of mitochondria and chloroplasts?
a. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have similar DNA
b. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are each surrounded by a double membrane
c. Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain their own DNA
d. Mitochondria and chloroplasts resemble bacteria
e. Mitochondria and chloroplasts reproduce by dividing in two
a. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have similar DNA
Mitochondria are essentially the same in all eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi. Based on this observation, how were mitochondria most likely acquired?
a. by an ancestral eukaryotic cell before the lines that led to animal cells, plant cell, and fungi diverged
b. from a free-living, photosynthetic bacterium
c. by a prokaryotic cell approximately 1000 years ago
d. by an ancestral eukaryotic cell and then replaced by chloroplasts in the line that led to plant cells
e. by an ancestral prokaryote and then lost in the line that led to archaea
a. by an ancestral eukaryotic cell before the lines that led to animal cells, plant cells, and fungi diverged
Which statement is not true of chloroplasts?
a. Chloroplasts are thought to have originated from bacteria
b. Chloroplasts are present in essentially all eukaryotic cells and in certain photosynthetic bacteria
c. Chloroplasts contain their own DNA
d. Each has an internal stack of membranes and is enclosed by two membranes
e. Chloroplasts absorb light and generate oxygen and carbohydrate
b. Chloroplasts are present in essentially all eukaryotic cells and in certain photosynthetic bacteria
Which statement is not true of mitochondria?
a. Mitochondria are involved in the chemical energy cycle of the cell
b. Mitochondria are thought to have originated from bacteria
c. Mitochondria are not present in plant cells
d. Mitochondria have an inner and outer membrane
e. Mitochondria contain their own DNA
c. Mitochondria are not present in plant cells
Is the following statement true, false, or impossible to determine?
Photosynthetic bacteria contain chloroplasts.
a. true
b. false
c. impossible to determine
b. false
The genome of the bacterium E. coli contains 4.6 million (4.6 x 10^6) nucleotide pairs, whereas the human genome contains some 3200 x 10^6 nucleotide pairs. What can be concluded based on these numbers?
a. E. coli are unicellular, whereas humans are multicellular
b. Human cells are larger than E. coli cells
c. Human cells have 700 times more genes than E. coli
d. Humans are a more complex life-form than E. coli
e. All of the above conclusions are drawn correctly
f. None of the above conclusions are drawn correctly
f. None of the above conclusions are drawn correctly
Regarding acids, bases, and pH, which of these statements is true?
a. Substances that release protons when they dissolve in water are termed acids and result in a pH lower than 7
b. Substances that release protons when they dissolve in water are termed bases and result in a pH higher than 7
c. Substances that release protons when they dissolve in water are termed acids and result in a pH higher than 7
d. Substances that release protons when they dissolve in water are termed bases and result in a pH lower than 7
a. Substances that release protons when they dissolve in water are termed acids and result in a pH lower than 7
Which of the following atoms is most likely to participate in an ionic bond?
a. carbon, with an outer electron shell filled with four of a possible eight electrons
b. chlorine, with an outer electron shell filled with seven of a possible eight electrons
c. phosphorus, with an outer electron shell filled with five of a possible eight electrons
b. chlorine, with an outer electron shell filled with seven of a possible eight electrons
Which statement is true of hydrophilic molecules?
a. They mix well with water
b. They are typically hydrocarbons
c. They form few or no hydrogen bonds
d. They are generally uncharged
a. They mix well with water
Carbon, which has four electrons in its outer shell (with a capacity of eight electrons), can form a maximum of how many covalent bonds with other atoms?
a. 8
b. 2
c. 4
d. 0
c. 4
Which bond term describes a covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally?
a. polar
b. ionic
c. hydrogen
d. nonpolar
a. polar
Which four elements make up 96% of the weight of living organisms?
a. carbon, oxygen, sodium, and hydrogen
b. carbon, phosphorus, sodium, and hydrogen
c. carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen
d. carbon, calcium, oxygen, and nitrogen
e. carbon, sodium, chloride, and oxygen
c. carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen
What type of bond is formed when two atoms share electrons?
a. hydrogen bond
b. covalent bond
c. ionic bond
d. electrostatic bond
e. electronic bond
b. covalent bond
Determine whether the statement is true or false:
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a crucially important energy carrier in cells.
a. true
b. false
a. true
Which of the following does not contain sugars?
a. steroids
b. cellulose
c. glycolipids
d. nucleotides
e. glycoproteins
a. steroids
What is not true of RNA?
a. It contains a different base than DNA
b. It is usually single-stranded
c. It cannot base-pair with other nucleic acids
d. It contains a different sugar than DNA
c. It cannot base-pair with other nucleic acids
What type of bond links two polynucleotide chains to each other in a double helix of DNA?
a. hydrogen bonds
bl disulfide bonds
c. phosphodiester bonds
d. phosphoanhydride bonds
e. glycosidic bonds
a. hydrogen bonds
What chemical group is found in a nucleotide but not in a nucleoside?
a. hydroxyl group
b. phosphate
c. nitrogen-containing base
d. sugar
e. pentose
b. phosphate
What reaction involving ATP releases a large amount of energy?
a. the release of adenine
b. the release of the sugar group
c. the release of the terminal phosphate group
d. the release of the base
e. the release of the hydroxyl group
c. the release of the terminal phosphate group
Which chemical group is found on all amino acids?
a. methyl group
b. aromatic ring
c. thiol group
d. carboxylic acid group
e. phosphate group
d. carboxylic acid group
What type of reaction is the reverse of a condensation reaction?
a. hydrolysis
b. oxidation
c. decondensation
d. reduction
a. hydrolysis
How are covalent bonds in the cell rapidly broken?
a. by enzyme catalysis that is specific between protein and substrate
b. by the large electrical force across membranes
c. by energetic molecular collisions with potassium ions
d. by energetic molecular collisions with water molecules
a. by enzyme catalysis that is specific between protein and substrate
How do protein, nucleic acid, and polysaccharide molecules polymerize (grow in length)?
a. by hydrolysis reactions
b. by oxidation reactions
c. by condensation reactions
d. none of these
c. by condensation reactions
What is the measure of disorder in a system called?
a. entropy
b. free energy
c. catabolism
d. enthalpy
e. second law of thermodynamics
a. entropy
Reactions that use energy to drive the synthesis of molecules inside the cell are most specifically considered ___.
anabolic
Which of the following represents energy in its most disordered form?
a. electromagnetic (light) energy
b. heat energy
c. chemical bond energy
d. potential energy
e. kinetic energy of a moving object
b. heat energy
Which of the following does not occur in cells?
a. the metabolism of nutrients to produce useful energy stores
b. the use of heat to burn foodstuffs and transport glucose
c. the conversion of sunlight into energy stored in chemical bonds during photosynthesis
d. the use of chemical energy to transport organelles through the cytosol
b. the use of heat to burn foodstuffs and transport glucose
Which energy conversion characterizes photosynthesis?
a. electromagnetic (light) energy -> heat energy
b. electromagnetic (light) energy -> kinetic energy
c. electromagnetic (light) energy -> CO2
d. electromagnetic (light) energy -> oxidation energy
d. electromagnetic (light) energy -> chemical bond energy
e. electromagnetic (light) energy -> chemical bond energy
Which of the following does not describe an oxidation reaction?
a. the conversion of a chlorine atom to Cl-
b. the conversion of Fe2+ to Fe3+
c. the removal of electrons from a molecule
d. the addition of oxygen atoms to a molecule
a. the conversion of a chlorine atom to Cl-
Compared to adding heat to the system, what is the advantage of using an enzyme to overcome an energy barrier?
a. An enzyme generates multiple different products using multiple pathways
b. An enzyme can catalyze a reaction in many different ways
c. An enzyme is specific for one desired pathway and end product
d. An enzyme speeds up a reaction more than heat does
c. An enzyme is specific for one desired pathway and end product
All four possible reactions in the animation are energetically favorable; the energy of the four products is lower than the energy of the original starting molecule. Why does the starting molecule not completely and quickly convert to its possible products before the addition of heat or an enzyme?
a. An activation energy barrier exists that must be overcome for conversion to products
b. The starting substrate does quickly convert to the four products
c. The starting molecule can only form some of the products quickly
d. When heat was added to the reaction, only some of the products were produced
a. An activation energy barrier exists that must be overcome for conversion to products
In thermodynamics, what does the term "free energy" refer to?
a. excess energy from a reaction that a cell does not use
b. energy that cannot be harnessed to do work or drive chemical reactions
c. energy that can be harnessed to do work or drive chemical reactions
d. energy that cells borrow from the environment
e. energy required to initiate a chemical reaction
c. energy that can be harnessed to do work or drive chemical reactions
Which statement about enzymes is not true?
a. Enzymes can help build large polymers
b. Enzymes reduce the activation energy required to initiate a spontaneous reaction
c. An enzyme can force an energetically unfavorable reaction to take place inside the cell
d. Enzymes can speed up energetically favorable reactions
c. An enzyme can force an energetically unfavorable reaction to take place inside the cell
For a biochemical reaction, ___ energy is the term for the extra energy boost required to initiate an energetically favorable reaction within the cell.
activation
For the simple reaction Y -> X, the equilibrium constant K is equal to which of the following equations?
a. [Y] x [Y]
b. [X] x [Y]
c. [X] / [Y]
d. [Y] / [X]
c. [X] / [Y]
In a cell, the rate at which an enzyme will encounter its substrate depends on which of the following?
a. the concentration of other proteins in the cytosol
b. the way that the cytosol is structured
c. the size of the enzyme
d. the concentration of the substrate
d. the concentration of the substrate
Carbon atoms cycle continuously through the biosphere. What is a by-product of cell respiration, and what does this by-product represent?
a. C6H12O6; completely oxidized carbon
b. CO2; completely oxidized carbon
c. CO2; a reduced version of carbon
d. C6H12O6; a reduced version of carbon
b. CO2; completely oxidized carbon
What is the origin of the energy that animals acquire by eating plants or other animals?
a. sunlight
b. carbohydrates
c. heat
d. fats
e. sugar
a. sunlight
Which of the following statement is not true?
a. When a sugar molecule is oxidized to CO2 and H2O, the O2 molecules involved in forming the H2O are reduced
b. Oxidation and reduction reactions always occur simultaneously
c. When a carbon atom in a C-H bond has somewhat more than its share of electrons, it is said to be reduced
d. Hydrogenation reactions are oxidations, and dehydrogenation reactions are reduction
d. Hydrogenation reactions are oxidations, and dehydrogenation reactions are reduction
Your company has developed an organic molecule with commercial potential and you know how to produce it in the lab. You want to increase production and make as much of the molecule as possible, but the reaction has a positive ΔGº. What can you do to try to drive the reaction toward your desired product?
a. add some products initially to get the reaction primed
b. continually remove products
c. add an enzyme that does not couple to another reaction
d. increase the concentration of reactant
b. continually remove products, and d. increase the concentration of reactants
Throughout the 1920s, Otto Meyerhof, A. V. Hill, and colleagues investigated how cells use energy to power muscle contraction. They determined that during muscle contraction, glycogen is broken down into lactic acid, a product of fermentation. Originally Meyerhof thought that the conversion of glycogen into lactic acid directly powered muscle contraction. This idea was overturned by experiments performed by Einar Lundsgaard. What evidence did Lundsgaard provide to suggest that glycogen breakdown and lactic acid production did not directly power muscle contraction?
a. A pulse of electricity caused muscle contraction in isolated frog muscle tissue
b. Inhibition of fermentation immediately halted muscle contraction
c. Creatine phosphate infusions into muscles inhibited muscle cell contraction
d. Muscle contraction could continue for some time after inhibition of fermentation
d. Muscle contraction could continue for some time after inhibition of fermentation
What is the difference between NAD+ and NADH?
a. NADH carries an extra phosphate group
b. NADH is an electron acceptor, whereas NAD+ is an electron donor
c. NADH is the oxidized form, while NAD+ is the reduced form
d. NADH carries an extra proton and two high-energy electrons
e. NADH is involved in biosynthetic reactions
d. NADH carries an extra proton and two high-energy electrons
When NADH or NADPH transfers electrons to a recipient molecule, the recipient becomes reduced and the activated carriers are oxidized (to NAD+ or NADP+, respectively). What else happens during this reaction?
a. A proton is take up by the carrier
b. A phosphate group is transferred to the recipient molecule
c. A proton is taken up by the recipient molecule
d. A molecule of water is released into the solution.
e. A proton is released into the solution
c. A proton is taken up by the recipient molecule
Sort the following secondary structure characteristics into the correct categories.
Categories: alpha helix only, beta sheet only, or both alpha helix and beta sheet
Characteristics:
- side chains alternating above and below the structure
- cylindrical structure
- formed by hydrogen-bonding between backbone atoms
- one full turn every 3.6 amino acids
- can be formed by many sequences
- consists of antiparallel or parallel strands
alpha helix only:
- cylindrical structure
- one full turn every 3.6 amino acids
beta sheet only:
- consists of antiparallel or parallel strands
- side chains alternating above and below the structure
both alpha helix and beta sheet:
- can be formed by many sequences
- formed by hydrogen-bonding between backbone atoms
Mutations in the nucleic acid sequence of a gene can sometimes direct the substitution of one amino acid for another in the encoded protein. Which amino acid substitution would be most likely to severely disrupt the normal structure of a protein?
a. alanine to glycine
b. methionine to arginine
c. tryptophan to phenylalanine
d. leucine to isoleucine
e. asparagine to threonine
b. methionine to arginine
To identify genes coding for essential proteins, researchers can create temperature-sensitive mutations. These mutations allow proper protein folding and cell proliferation at the permissive temperature of 22ºC, but they cause protein misfolding and reduced cell proliferation at a higher restrictive temperature, such as 37ºC. Which of the following mutations might increase protein flexibility and lead to a temperature-sensitive phenotype?
a. a premature stop codon that truncates a protein 10 amino acids from the amino terminus
b. mutation of a bulky isoleucine that was buried in the protein interior to a glycine (side chain = H)
c. mutation of a lysine (that was involved in an ionic bond with a glutamic acid) to a glycine
d. mutation of an alanine to a cysteine, leading to the formation of a new disulfide bond
b. mutation of a bulky isoleucine that was buried in the protein interior to a glycine (side chain = H), and c. mutation of a lysine (that was involved in an ionic bond with a glutamic acid) to a glycine
Determine whether the following statement is true or false:
In cells, electrostatic attractions are stronger than covalent bonds. This statement is ___.
false
In an alpha helix, hydrogen bonds form between which of the following?
a. the peptide bonds and DNA
b. nonpolar amino acid side chains
c. every fourth amino acid
d. acidic and basic amino side chains
e. every other amino acid
c. every fourth amino acid
Which parts of amino acid are involved in a peptide bond?
a. carboxyl group of one amino acid and side chain of the other
b. amino groups of both amino acids
c. carboxyl groups of both amino acids
d. amino group of one amino acid and side chain of the other
e. side chains of both amino acids
f. amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of the other
f. amino group of one amino acid carboxyl group of the other
Is the following statement true, false, or impossible to determine?
At present, it is possible to predict the precise folding pattern of any protein.
a. true
b. false
c. impossible to determine
b. false
Is the following statement true, false, or impossible to determine?
The relatedness of proteins aids the prediction of protein structure and function.
a. true
b. false
c. impossible to determine
a. false
Which parts of amino acids are involved in a peptide bond?
a. amino groups of both amino acids
b. amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of the other
c. amino group of one amino acid and side chain of the other
d. side chains of both amino acids
e. carboxyl group of one amino acid and side chain of the other
f. carboxyl groups of both amino acids
b. amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of the other
Which part of an amino acid gives it its unique properties?
a. carboxyl group
b. side chain
c. alpha-carbon
d. amino group
e. peptide bond
b. side chain
What is the best type of model for visualizing the surface of a protein?
a. ribbon
b. wire
c. space-filling
d. backbone
c. space-filling
What are the two types of beta sheets?
a. primary and secondary
b. helical and pleated
c. parallel and antiparallel
d. soluble and insoluble
c. parallel and antiparallel
What does the primary structure of a protein refer to?
a. the linear amino acid sequence of the protein
b. the locations of the peptide bonds that form the protein's backbone
c. the structure that forms first as the protein folds into its most stable forms
d. the localizations of the protein's alpha helices and beta sheets
e. the overall three-dimensional shape of the protein
a. the linear amino acid sequence of the protein
A protein domain is another phrase describing what type of structure of a protein?
a. primary
b. secondary
c. tertiary
d. quaternary
e. none of these
e. none of these
What determines the specificity an antibody has for its antigen?
a. polypeptide loops of its heavy chains
b. polypeptide loops in its variable domains
c. polypeptide loops of its light chains
d. its Y-shaped, bivalent structure
e. polypeptide loops in its constant domain
b. polypeptide loops in its variable domain
Consider the thermodynamic properties of chemical reactions. Even though enzymes do not affect the overall energy of the reactants or the products (i.e., the thermodynamics), they alter the speed of the reaction. Enzymes accomplish this by doing which of the following?
a. increasing the activation energy of a reaction
b. not altering the activation energy of a reaction
c. supplying the activation energy for a reaction
d. reducing the activation energy of a reaction
e. eliminating the activation energy of a reaction
d. reducing the activation energy of a reaction
For a given protein, hydrogen bonds can form between which of the following?
a. atoms in the polypeptide backbone
b. atoms of two peptide bonds
c. atoms in two side chains
d. a side chain and water
e. all of the above
f. none of the above
e. all of the above
Which statement concerning feedback inhibition is false?
a. Feedback inhibition is difficult to reverse
b. Feedback inhibition can work almost instantaneously
c. Feedback inhibition regulates the flow through biosynthetic pathways
d. Feedback inhibition is a feedback system for controlling enzyme activity
e. In feedback inhibition, an enzyme acting early in a reaction pathway is inhibited by a later product of that pathway
a. Feedback inhibition is difficult to reverse
How does an allosteric inhibitor work?
a. It binds to a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme that makes the active site less accommodating to the susbtrate
b. It outcompetes the substrate molecule and binds to the active site, preventing substrate molecules from binding there
c. It binds to a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme that forces the product to leave the active site
d. It interacts covalently with the substrate, preventing it from fitting into the enzyme's active site
a. It binds to a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme that makes the active site less accommodating to the substrate
How does phosphorylation control protein activity?
a. The phosphate group, with its positive charges, temporarily relieves feedback inhibition
b. The phosphate group induces a change in the protein's conformation
c. The phosphate group, with its negative charges, prevents other negatively charged molecules from interacting with the protein
d. The phosphate group alters the primary structure of the protein
e. The phosphate group serves as an added source of energy for a protein
b. The phosphate group induces a change in the protein's conformation
What kind of enzyme adds a phosphate group to another protein?
a. kinase
b. phosphatase
c. GTPase
d. phosphorylase
e. ATPase
a. kinase
What kind of enzyme removes a phosphate group from a protein?
a. GTPase
b. phosphorylase
c. ATPase
d. phosphatase
e. kinase
d. phosphatase
Enzymes can have both active and regulatory sites. What is the purpose of these sites?
a. The binding of CTP at the active site on the protein causes decreased production of carbamoyl aspartate
b. The binding of CTP at a regulatory site on the protein causes decreased production of carbamoyl aspartate
c. The binding of CTP at a regulatory site on the protein causes increased production of carbamoyl aspartate
d. The binding of CTP at the active site on the protein causes increased production of carbamoyl aspartate
b. The binding of CTP at a regulatory site on the protein causes decreased production of carbamoyl aspartate
Electrophoresis separates proteins on the basis of what factor(s)?
a. the protein's size
b. the protein's net charge
c. the protein's cell of origin
d. the protein's affinity for a ligand molecule
a. the protein's size, and b. the protein's net charge
Which of the following are methods for isolating a protein of interest?
a. electrophoresis and nuclear magnetic resonance
b. nuclear magnetic resonance and crystallography
c. chromatography and electrophoresis
d. chromatography and mass spectrometry
e. electrophoresis and crystallography
c. chromatography and electrophoresis
Which of the following is true regarding protein structure determination?
a. Determination of a protein's structure by X-ray crystallography does not require prior knowledge of its amino acid sequence
b. A protein's three-dimensional structure can be reliably predicted from its amino acid sequence by computer algorithms that access the vast quantities of structural information archived in public databases
c. Mass spectrometry can be used to determine the amino acid sequences of a complex mixture of different proteins
d. Nuclear magnetic resonance can be used to determine the structure of proteins that are too large to crystallize
e. Mass spectrometry is the fastest way to determine the three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide or protein, regardless of its size
c. Mass spectrometry can be used to determine the amino acid sequence of a complex mixture of different proteins
Ras is a GTP-binding protein involved in cell proliferation (division). In its active form, with GTP bound, Ras activates cell signaling pathways that promote cell division. Mutations in the gene that encodes Ras can lead to cancer. How might mutations in the gene encoding Ras lead to the uncontrolled proliferation characteristic of cancer cells?
a. They increase the protein's affinity for GDP
b. They increase the rate at which Ras hydrolyzes GTP
c. They prevent Ras from being made
d. They decrease the rate at which Ras hydrolyzes GTP
e. They decrease the protein's affinity for GTP
d. They decrease the rate at which Ras hydrolyzes GTP
How do most motor proteins ensure their movements are unidirectional?
a. They couple a conformational change to the hydrolysis of an ATP molecule
b. They hydrolyze their bound GTP, effectively preventing movement in the reverse direction
c. They couple a conformational change to a thermodynamically unfavorable reaction
d. They couple a conformational change to the formation of an ATP molecule from ADP and Pi
e. Their asymmetrical structures support movement in only one direction
a. They couple a conformational change to the hydrolysis of an ATP molecule