AP Human Unit One - Thinking Geographically
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
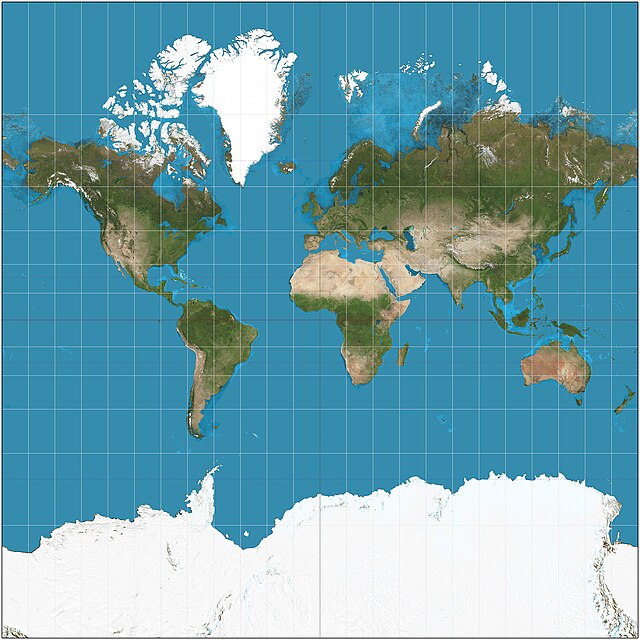
What is the Mercator projection?
A cylindrical map projection that distorts size and distance but preserves angles, commonly used for nautical navigation.
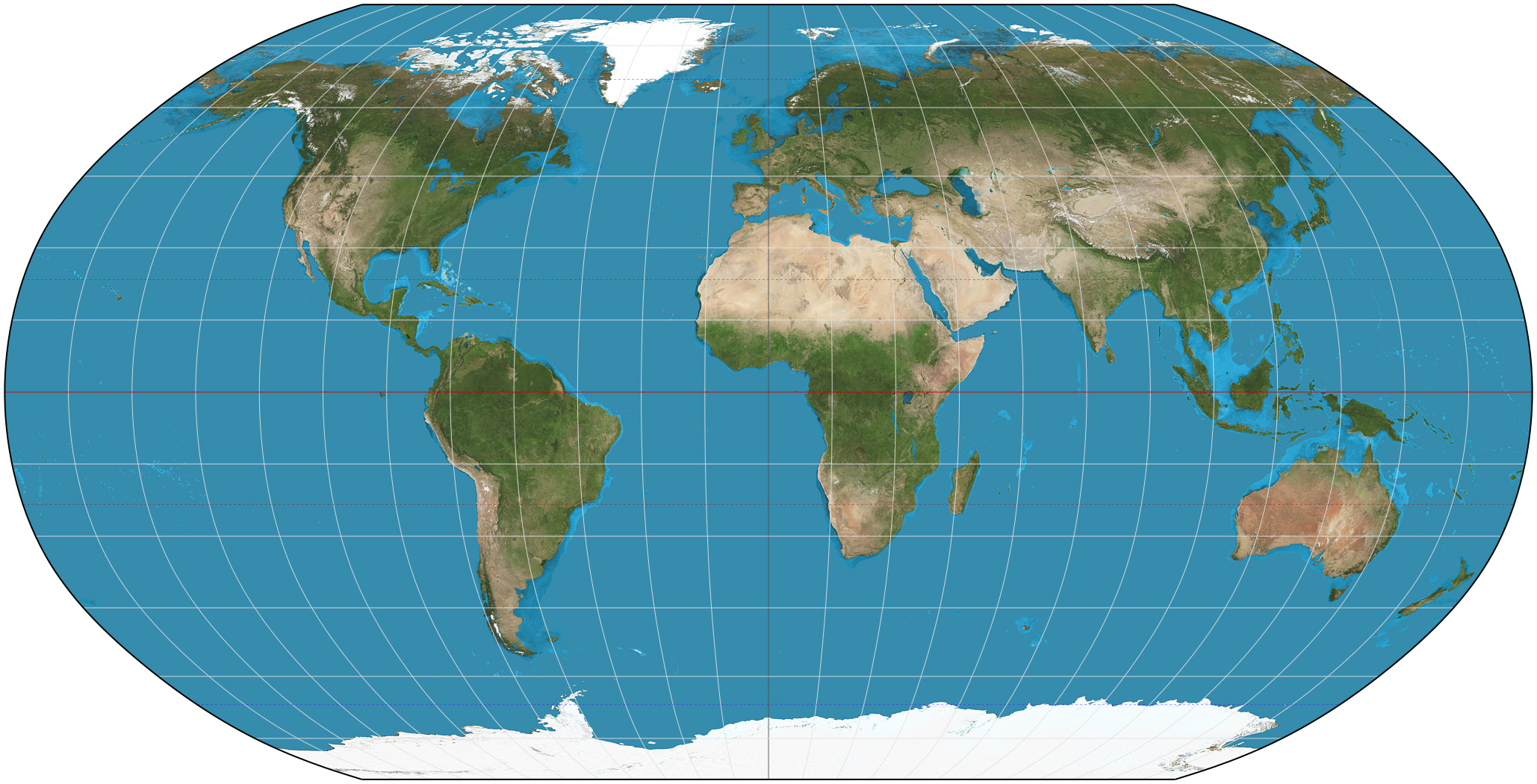
What is the Robinson projection?
A map projection that attempts to balance size and shape distortion, presenting a more visually appealing view of the world while maintaining reasonable accuracy for general use.
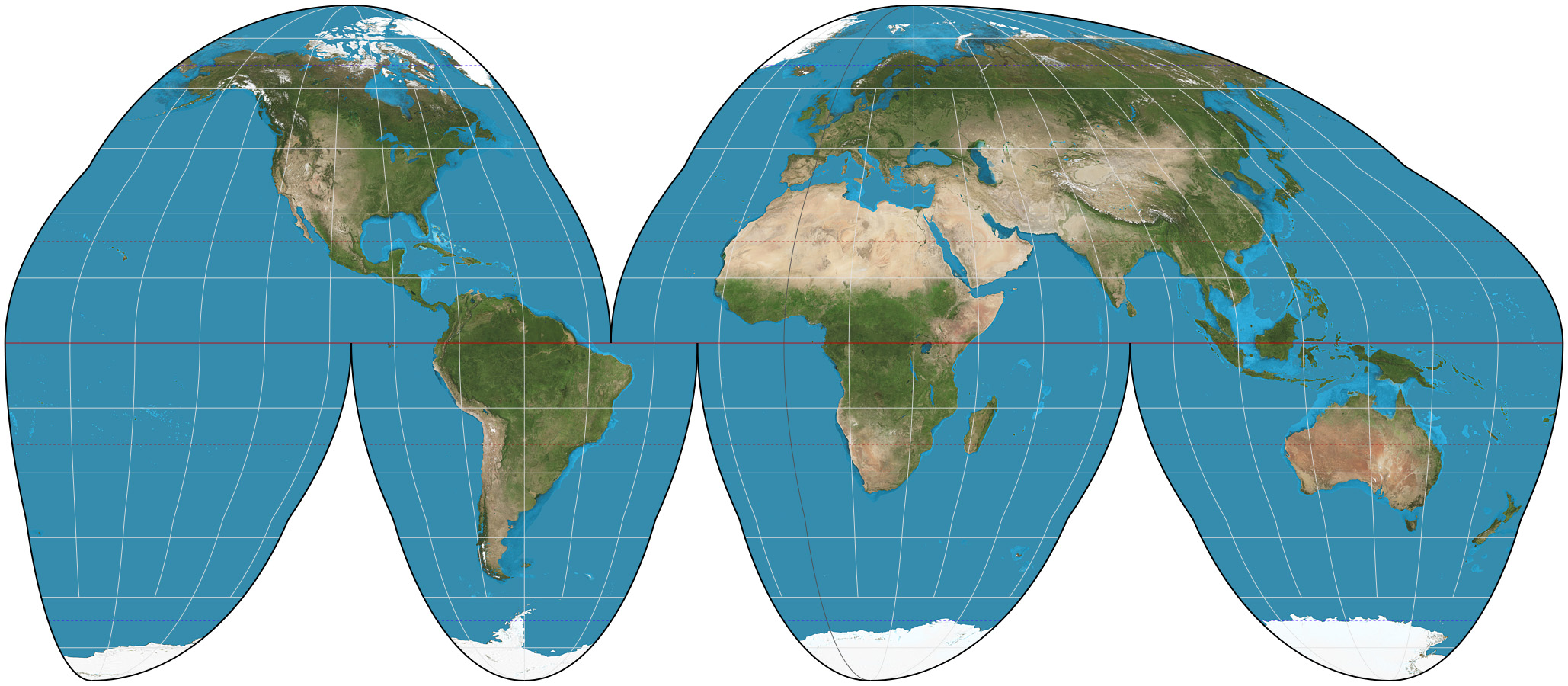
What is the Goode Homolosine projection?
A pseudo-cylindrical map projection that minimizes distortion in size and shape, separating the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
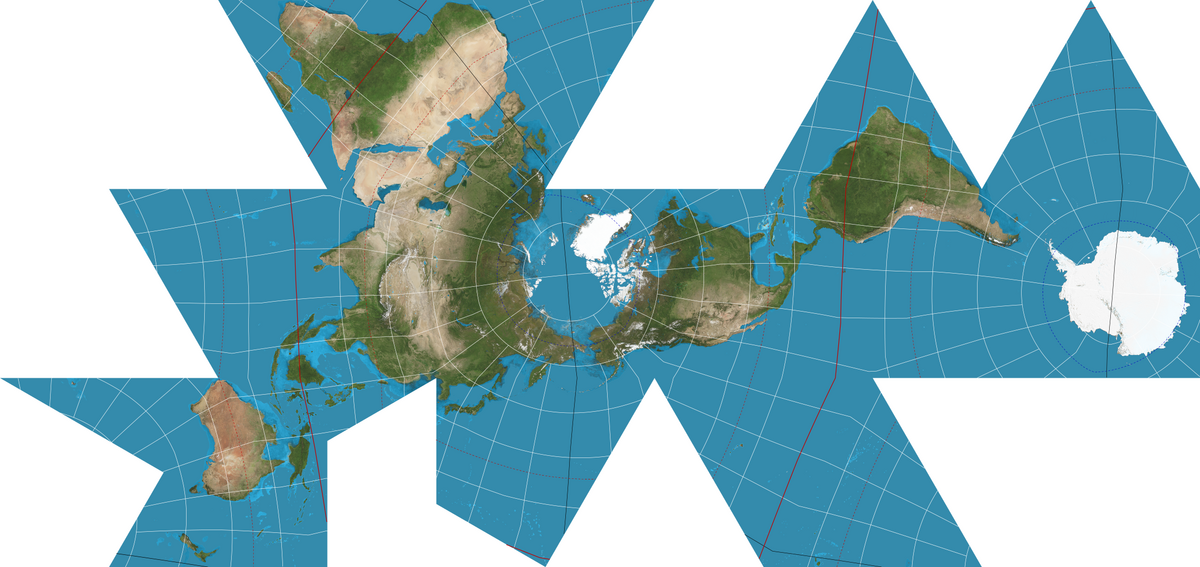
What is the Fuller Dymaxion projection?
A map projection that represents the Earth's continents with minimal distortion, displaying them in a way that emphasizes the interconnectivity of landmasses while unfolding the globe into a geometric pattern.
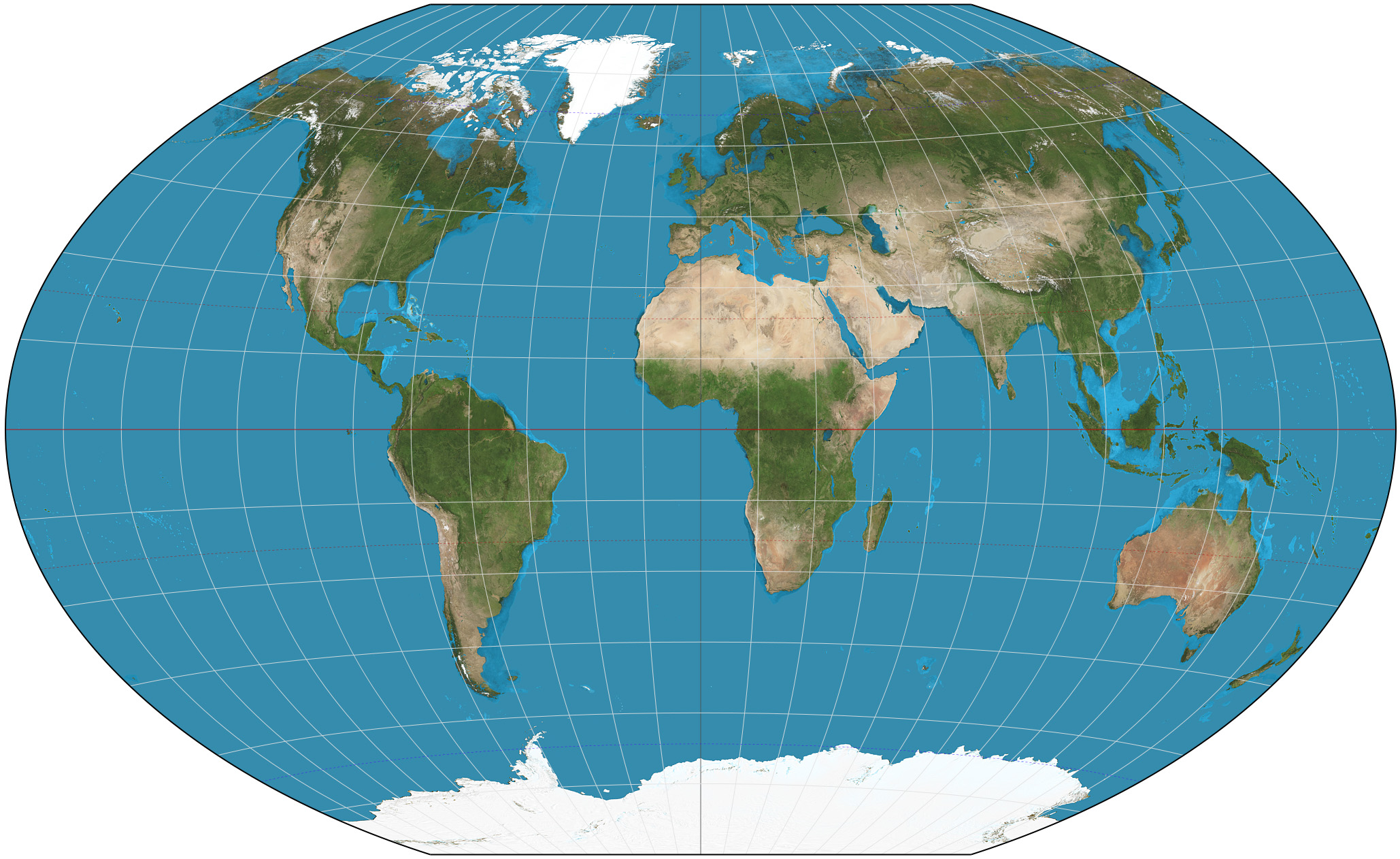
What is the Winkel Tripel projection?
A map projection that aims to minimize distortion in area, direction, and distance, providing a more visually appealing representation of the whole world. Is very similar to the Robinson Projection.
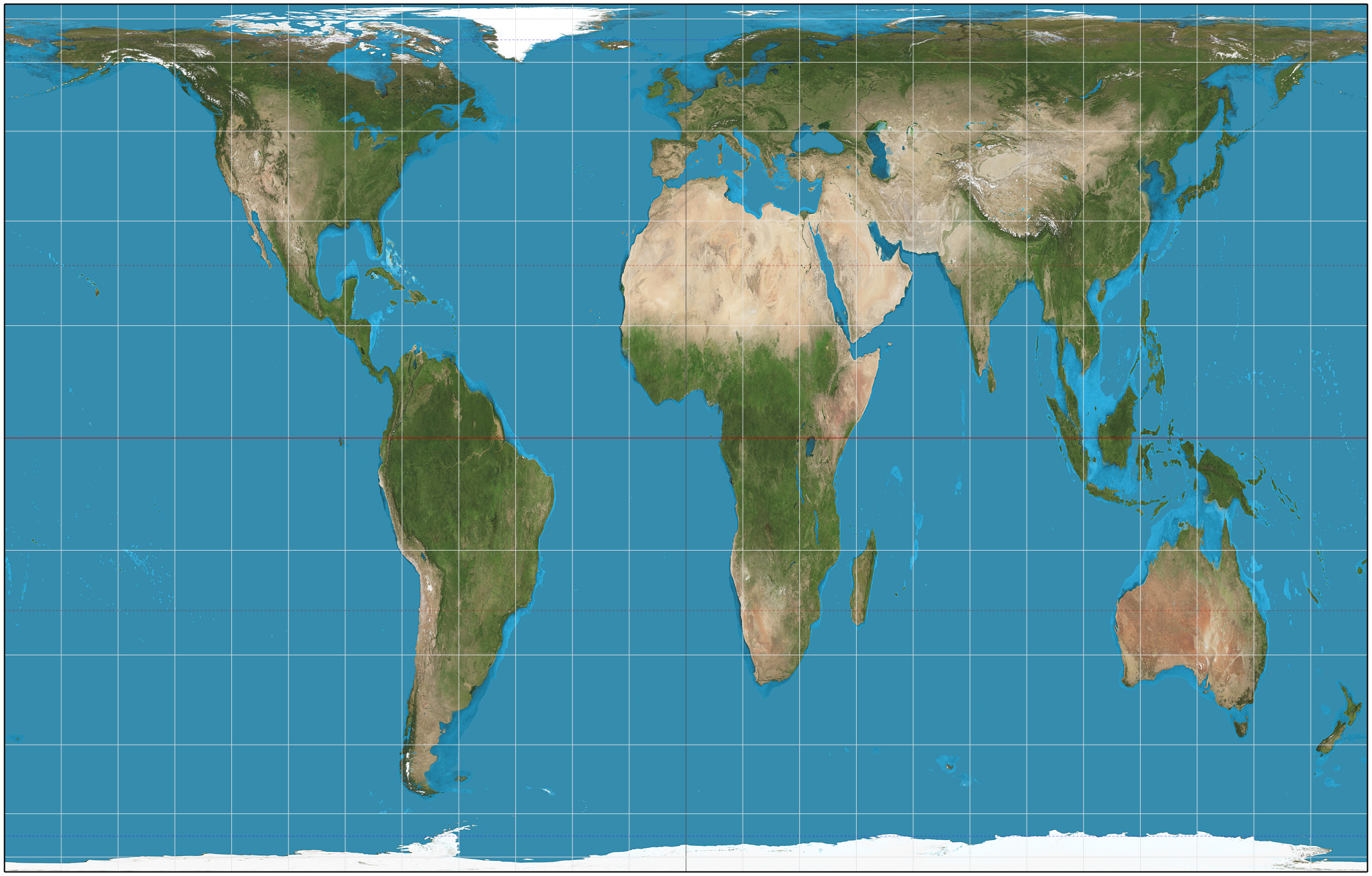
What is the Gall-Peters projection?
A cylindrical map projection that represents all areas in true proportional sizes, aiming to minimize distortion of landmass sizes.
What is a Uninterrupted map?
Map that displays entirety of earth’s surface
What is a Reference map?
They are maps used for informational purposes and are used to find the boundaries of a place, look at different geographic features, or be able to be used for directions.
What are some examples of a reference map?
Political maps, road Maps, topographic maps, etc.
What is a thematic map?
focuses on the spatial variability of a specific distribution or theme (such as population density or average annual income)
What are some examples of thematic maps?
Choropleth, graduated symbol, dot density, etc.
What is absolute direction?
It is the exact direction you are going in
What is relative direction?
using surrounding areas or factors for directions
What is a clustered pattern?
Little space between data
What is a Dispersed pattern?
Data is spread out
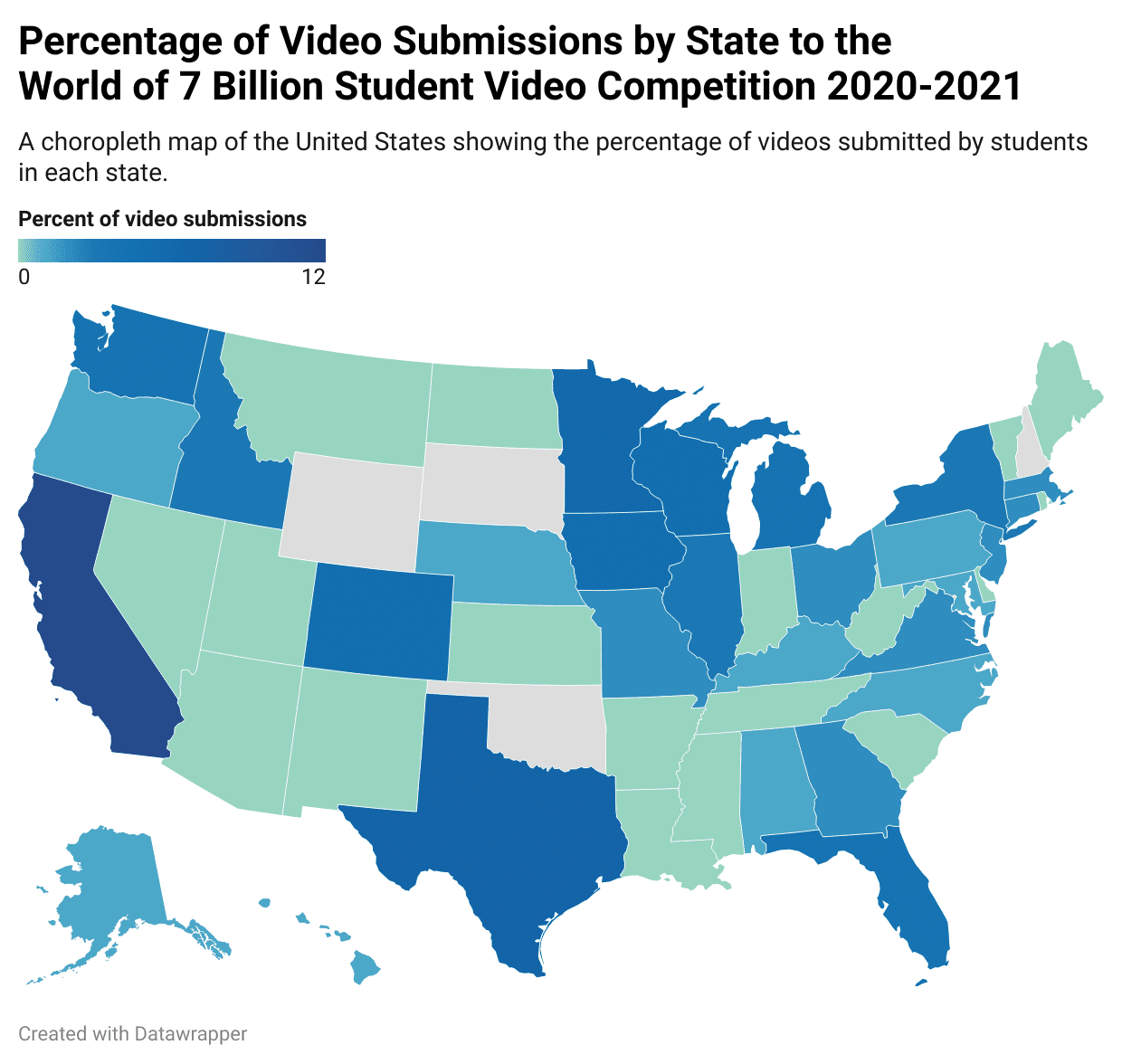
What is a Choropleth map?
Uses color to display data
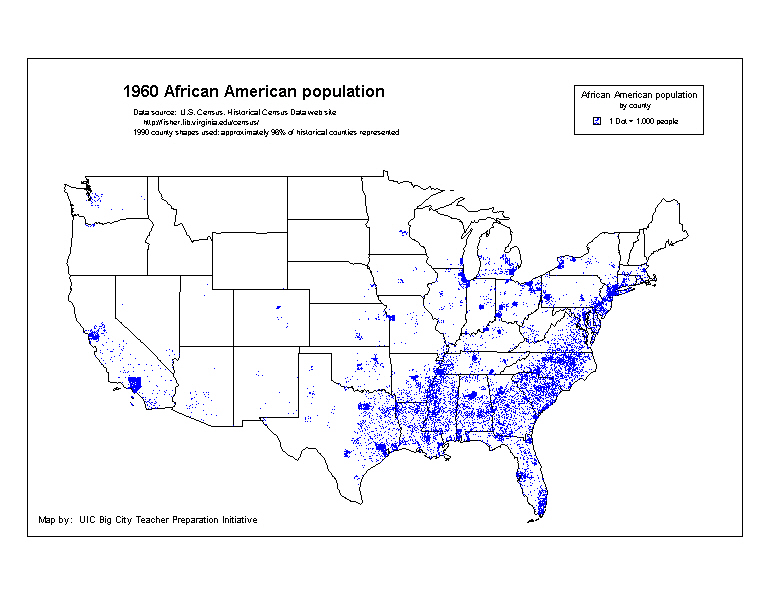
What is a dot density map?
Shows data using concentration of dots, good for showing spatial distribution
What is a graduated symbol map?
Uses shapes, items, or symbols to show location or amount of data
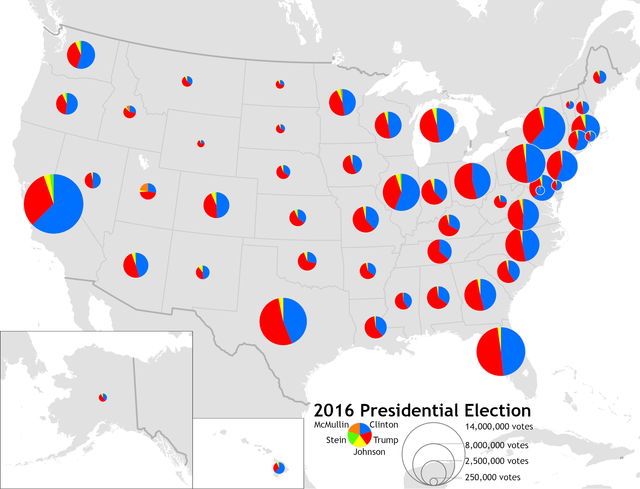
What is a flow map?
A type of thematic map that illustrates the movement of people, goods, or information between different locations, often using arrows to represent the direction and volume of flow.
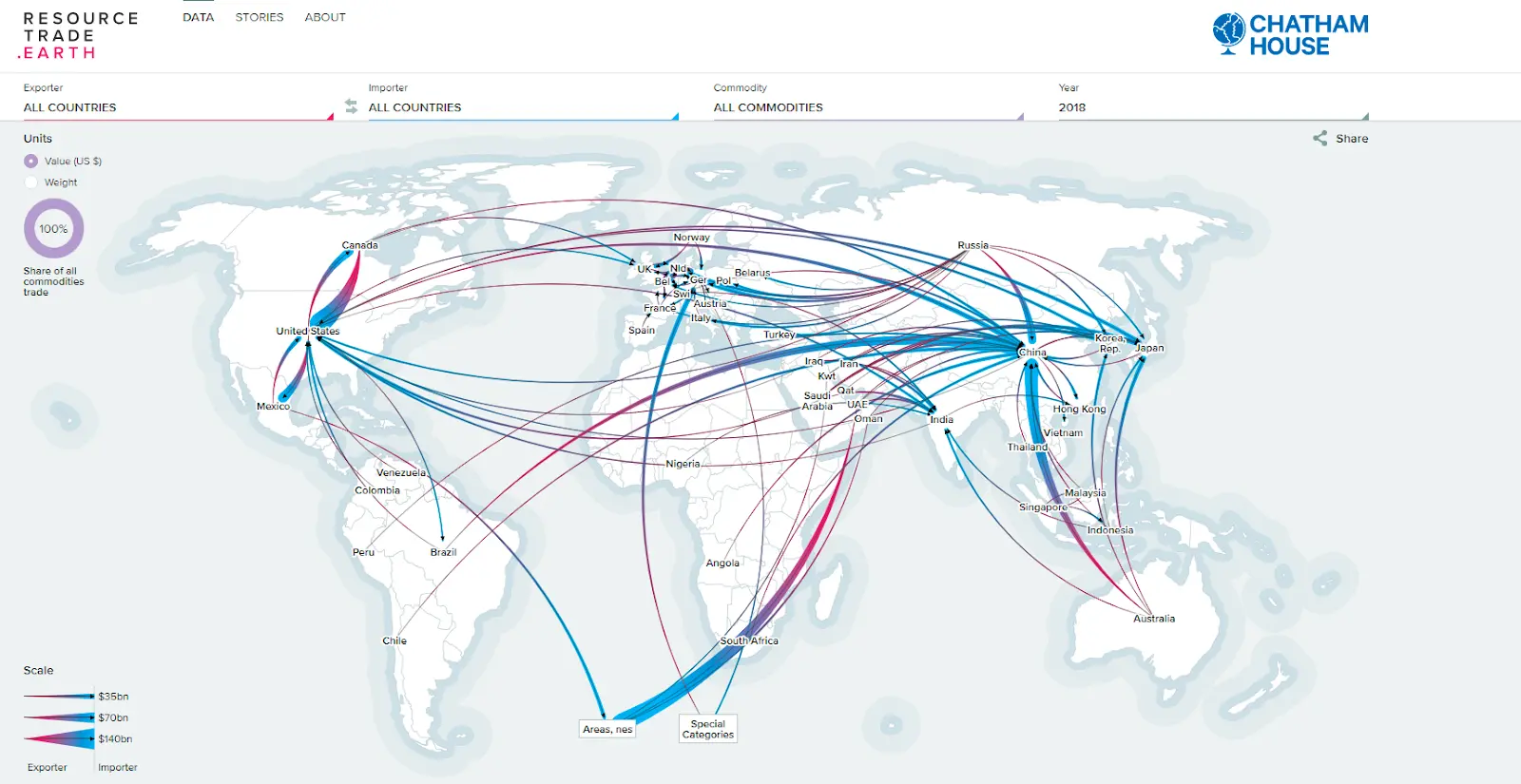
What is a isoline map?
A type of map that uses lines to connect points of equal value, such as elevation or temperature, effectively illustrating gradient patterns.
What is GIS (Geographic Information System)?
Computer systems that can collect, analyze, and display geometric data.
What is GPS or Geographic Positioning Systems?
Network of satellites used to determine the location of something on the earth’s surface. Usually used to visualize geographic data.
What is qualitative data?
Information presented in word form that is often up for interpretation or debate
What is quantitative data?
Information that can be counted and presented in number form.
What is the census?
Conducted every 10 years and is the official count of all individuals in the population
What is a supply chain?
A network of people, organizations, resources, and activities that work together to create and sell different products.
What is time-space compression?
Advancements in technology and communication that lead to increased networking and connection between places and people that are geographically further apart. Makes the world feel “smaller.”
What is distance decay?
The principle that states the interaction between two locations decreases as the distance between them increases.
What is spatial distribution?
Is the density, concentration, and pattern of an area.
What is sense of place?
A strong feeling or perception people associate or have for a place.
What is placelessness?
A place that does not invoke any strong response from individuals due to a lack of unique identity.
What are situation factors?
Situation factors refer to the locations surrounding a place, emphasizing the relationships and connections between that place and others. These include geographic, economic, and social factors that influence accessibility, transportation, and communication, which can affect the development and interaction of regions. For example, the proximity of a company to suppliers, customers, and transport infrastructure are key aspects of its situation.
What are site factors?
Characteristics at a specific location that affect its suitability for a particular use or development. Site factors include physical aspects such as terrain, soil quality, climate, and natural resources, as well as human-made features like infrastructure, building codes, and access to amenities.
What is desalinization?
Removing salt from water to make it drinkable
What is environmental possibilism?
The idea that the environment puts limits on society, but people have the ability to adjust and modify their environment to overcome these limits
What is Environmental determinism?
The belief that the environment Sets the possibilities for humans and society
What is scale of analysis?
It refers to the level of detail or scope at which data is collected, analyzed, and presented, such as local, regional, national, or global.
What is scale?
What you see at face-value on a map
What is a functional or nodal region?
A functional region is an area defined by a particular set of activities or interactions that occur within it, often centered around a node or focal point. Transportations systems like subways and bus routes are good examples of functional regions
What is a Perceptual or vernacular region?
A region defined by people's perceptions, feelings, and attitudes about an area, often lacking clear boundaries. These regions can often change over time.
What is a formal region?
A formal region is an area defined by specific, measurable characteristics, such as political boundaries, physical features, or cultural traits that are uniform or homogenous across the region.
What is a hearth?
A point of origin or place of innovation where culture, ideas, or technology come from
What is expansion diffusion?
Diffusion that originates in a central place and then expands outward in all directions to other locations.
What is hierarchical diffusion?
Diffusion that originated in a first order location and then moves to second order locations and from each of these to subordinate locations at increasing scales (from big city to smaller area)
What is contagious diffusion?
Begins at a point of origin and then rapidly moves outward to other locations, nearby or not.
What is stimulus diffusion?
A general or underlying principle diffuses and then stimulates the creation of new products or ideas
What is relocation diffusion?
begins at a point of origin and then crosses a significant physical barrier, such as an ocean, mountain range, or a dessert, and then relocates on the other side. Often the journey can influence and modify the items being diffused.
What is the Gravity Model and what is it’s purpose?
It is a mathematical model that is used in a number of different types of spatial analysis. Gravity models are used to calculate transportation flow between two points, determine the area of influence of a city’s business, and estimate the flow of migrants to a particular place.

What is a mental map?
It is a cognitive image of a landscape in the human mind
What is arithmetic density?
Number of things per square unit of distance
What is physiological density?
Number of people per square unit of arable land, meaning land that is either actively farmed or has the potential to be.
What is agricultural density?
Number of farmers per square unit of arable land
How are time-zones divided?
They are divided up into 15-degree wide longitudinal zones around the world, with some exceptions
What is space?
The geometric surface of the earth
What is place?
An area of bounded space of some human importance
What is a toponym?
It is a place-name