Chemistry Regents Review
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Solid
Strong Forces, High Density, Low Energy
Liquid
Medium Forces, Low Density, Medium Energy
Gas
Weak Forces, Very Low Density, High Energy
Density
Color
Odor
Hardness
State of matter
No new substance
Physical Properties
fire
React
Neutralize
Combust
New substance formed
Chemical Properties
Pure Substance
matter that has uniform and definite composition
Homogeneous
pure substance distributed evenly throughout the mixture
Heterogeneous
substances not evenly mixed
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy can not be created nor destroyed, input = output
Temperature
Measure of Average Kinetic Energy
Endothermic Energy Change
Requires heat, heat on the left side of equations
Exothermic Energy Change
Produces heat, heat of the right side of equations
Heat Flow
High —> Low
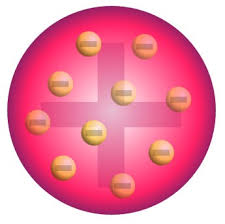
Plum Pudding
Thompson

Bowling Ball/Solid Sphere
Dalton
Gold Foil Model
Rutherford
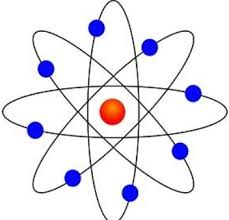
Planetary
Bohr
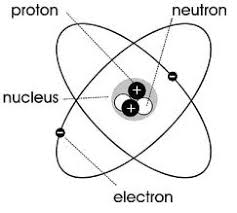
Proved existence of neutrons
Chadwick
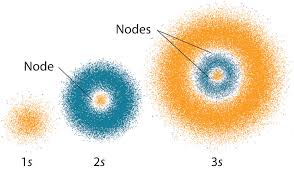
Diffuse clouds around nucleus
Quantum Mechanical Model
Nucleus
Dense, positively charged, center of atom
Isotope
Atoms with the same number of protons, different number of neutrons
Elements are defined by their number of
protons
Isotopes are defined by their number of
neutrons
Isotope similarities
Chemical properties, atomic numbers, number of electrons
Isotope differences
Number of neutrons, mass numbers
Electrons closer to the nucleus
less energy
Electrons father from the nucleus
more energy
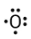
Represents number of valence electrons
Lewis Dot Diagrams
Chemical changes are caused by
competitions for valence electrons
Alkali Metals
Group 1
Alkaline Earth Metals
Group 2
Transitional Metals
Groups 3-12
Halogens
F, Cl, Br, I
Diatomic 7
N, O, F, Cl, Br, I, H
Liquids at STP
Br and Hg
Noble Gases
He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn
Gasses at STP
Noble Gases and N, O, F, Cl, H
Anion
smaller, electrons > protons, non-metals, negative
Cation
larger, electrons < protons, metals, positive
Ionic Bond
Metal and Non-Metal
Covalent Bond
Non-Metal and Non-Metal
Metallic Bond
Metal and Metal
Bond formation is
exothermic
Bond breakage is
endothermic
Ionic Naming
Metal first, non-metal becomes -ide
Ionic compounds form
ionic crystals
MP/BP: High
Crystalline Structure: Hard
Solid Conductivity: Poor
Aq/L Conductivity: Good
Ionic Compound Properties
Empirical Form
simplest ratio of elements
MP/BP: Low
Shared electrons
(Thus) Weaker Bonds
Not conductive
Overall Charge = 0
Covalent Compound Properties
Covalent Naming
Use prefixes (Table P), last ends in -ide
2 elements
Metal and Non-Metal
-ate, -ite, -ium
Table E
Binary Ionic
3+ elements
Attraction of ions of opposite charge
Covalent bonds inside Polyatomic ion
Ternary Ionic (Polyatomic)
Law of Conservation of Mass
Matter can not be created nor destroyed
1 mol
6.022 × 1023
Amu
Mass of one element in grams
Assume 100g or 1000g sample
g —> mol (dimensional analysis)
Divide moles by smallest # of moles
Empirical formula
Determine molecular mass of empirical formula (multiplier)
Empirical and Molecular Formula
Plug both given values in to get desired value
Lesser desired value is limiting reagent
must use this value
also theoretical value
Limiting Reagent
((amount you got) / (given or value you should have gotten/theoretical value)) * 100
Percent Yield
Coefficients of a substance are equal to the
number of moles of that substance
Fastest Particles @ STP
Gas, Liquid, Solid
“Fluid” Substances
Gases and Liquids
Only compressible particles
Gas particles
Heat is dependent on
sample size (mass)
Faster moving particles mean
higher temperatures
(Temperature) particle motion is
random
Sample size/mass has no effect on
temperature
Intermolecular Forces
Attraction between particles/molecules
Viscosity
resistance to flow
As heat is removed from a gas
avg KE decreases, particle attraction increases
As heat is added to a gas
avg KE increases, IMFs decrease
Melting a substance
weakens IMFs
Boiling a substance
completely breaks IMFs
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
Random, continuous motion
No attractive forces
elastic collisions
volume is negligible
Ideal Gases
Have mass
Have attractive forces
Real Gases
Real Gases behave like Ideal gases under these conditions:
High Temp
Large Volume
Low Pressure
Vapor Pressure
A measure of the tendency of a material to change into gaseous or vapor state
Increases with temp
Strong IMFs when low
Weak IMFs when high
A + B —> AB
Synthesis
AB —> A + B
Decomposition
AB + C —> AC + B
Single Replacement
AB + CD —> AD + CB
Double Replacement
Equilibrium
Forward and backward process rates are the same/equal. Must be a reversible, closed system. Amounts of products and reactants must be constant.
Reactions require
effective collisions
More collisions
faster reactions
increased reaction rate
decreased reaction time
Less collisions
slower reactions
decreased reaction rate
increased reaction time
Other collision factors
frequency of collisions
how hard they collide
angle of impact
High Temp
High Surface Area
High Concentration
Catalyst
Straightens out collision
Reactant Nature (fast —> slow)
Ionic
Gases
Liquids
Solids
Ideal Conditions for Collisions
Free Element
Oxidation state of 0
Compound charges always add to 0
Group 1 metals always +1
Group 2 metals always +2
Fluorine always -1
Hydrogen +1
Oxygen -2
Cl, Br, I in Binary Ionic Compound: -1
Polyatomic Ions add to their charge
Assign Oxidation #’s
Did #’s change during reaction
Yes: Redox
No: Not Redox
Who gained (red) and who lost (ox)
Redox Reaction Steps
What catalysts do (PE + Enthalpy)
Lowers the activation energy (flattens the curve)
+ Delta H
PEP > PER
Not fun roller coaster
A + B + heat —> C + D
Endothermic PE Curve
- Delta H
PEP < PER
Fun rollercoaster
A + B —> C + D + heat
Exothermic PE Curve
S —> L —> A —> G
More particles/moles
Increase temp
How to increase entropy
Entropy
the disorder created by everything
Solute
dissolved particles in a solution
Solvent
the dissolving medium in a solution
Saturated
a solution containing the maximum amount of solute for a given amount of solvent at constant temperature and pressure
must be soluble in water
forms ions in solution by disassociation
Conducts electricity in liquid and aqueous states
B/c ions are mobile in water
Must be charged
Electrolytes