Environmental Science 10
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
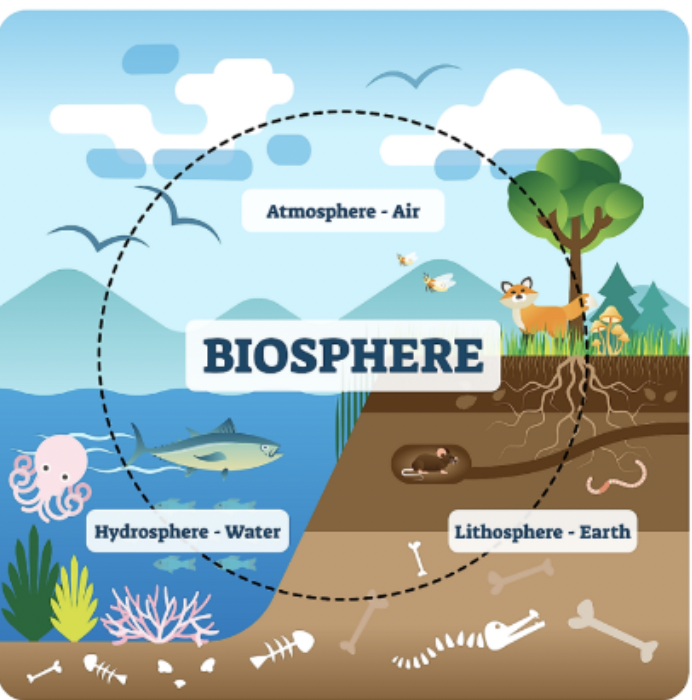
The Biosphere
The zone of the Earth that support life.
What are the 3 interacting components of the biosphere?
Hydrosphere: All water on Earth
Atmosphere: The layer of gases that surround the Earth
Lithosphere: The solid portion of the Earth
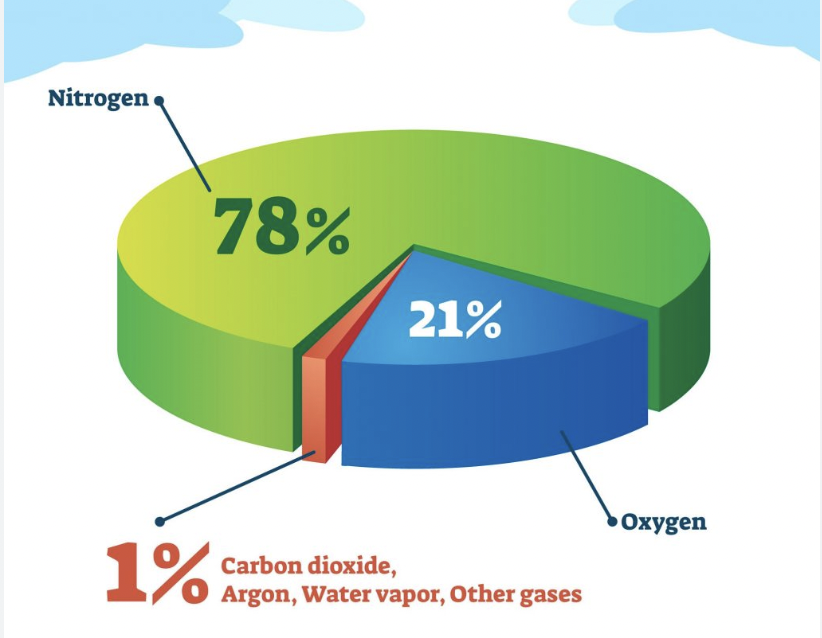
What makes up the atmosphere in percentages?
78.8% Nitrogen
20.95% Oxygen
0.97% Other gases (include argon, carbon dioxide, neon, helium, methane, and krypton
The atmosphere rises over how many kilometers?
500km
Atmospheric dust
Solid particles that can include non-living and living particles.
Nitrogen
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere.
Needed by plants and bacteria convert it into valuable forms.
Oxygen
Second most abundant gas in the atmosphere.
A central component of photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and combustion.
The atmosphere is, generally, divided into how many major layers?
4
How are the layers of the atmosphere determined?
By the average air temperature.
How long is the troposphere and what is its temperature range?
From 0 - 10km
Temperature decreases from 15 to -60 degrees C

The troposphere contains what percentage of the atmospheric gases?
80%
Why is the troposphere an area of rapid change?
Due to natural events and human activity.
The large majority of clouds is found in?
The troposphere
Stratosphere
Area above troposphere 10 - 50km above the surface of the Earth.

What is the temperature range of the stratosphere?
Temperature increases from -60 to 0 degrees C.
The stratosphere is the area of?
Most ozone (O3) - absorbs UV light which protects living organisms.

Mesosphere
Area above stratosphere 50 - 80km above the surface of the Earth.

What is the temperature range of the mesosphere?
Temperature decreases from 0 to -100 degrees C.
Thermosphere
Area above mesosphere 80-300km above the surface of the Earth.

What is the temperature range of the thermosphere?
Temperature increases from -100 to 1500 degrees C
What layer is beyond the thermosphere?
Exosphere

Lithosphere
The solid portion of the Earth that floats above the semi-fluid (molten/clay/playdoh) portion of the upper mantle.
Outer surface of the Earth and any solid portions of the Earth’s interior.
The lithosphere is home to?
Home to many micro-organisms, plants, and animals.
What is an important difference between the oceanic and continental crusts.
The oceanic crust is much denser/heavier.
Hydrosphere
All of the water on Earth: Salt water + fresh water
Like the lithosphere, the Hydrosphere is warmed mainly by?
Incoming solar energy
However, a small degree of the hydrosphere is heated by?
Molten material in the mantle.
Water is very good at?
Retaining heat
It has the highest heat capacity.
All components of the biosphere do what?
Interact and exchange matter and energy.
Water is capable of being present in what divisions of the biosphere?
All 3 divisions.
Energy flows between what divisions of the biosphere?
Between all 3 divisions.
Water require the greatest amount of energy to?
Change state and temperature.
But also gets the most energy out of it.
Climate
The average weather conditions that occur in a region over a long period of time (30 years).
What is the average Alberta summer temperature?
14 degrees C to 20 degrees C
What is the average Alberta winter temperature?
-24 degrees C to -9 degrees C
What is the average Alberta annual precipitation?
442mm (44.2 cm)
Weather
The conditions of temperature, air pressure, cloud cover, precipitation (rain or snow), and humidity that occur at a particular place of a particular time.
Short-term
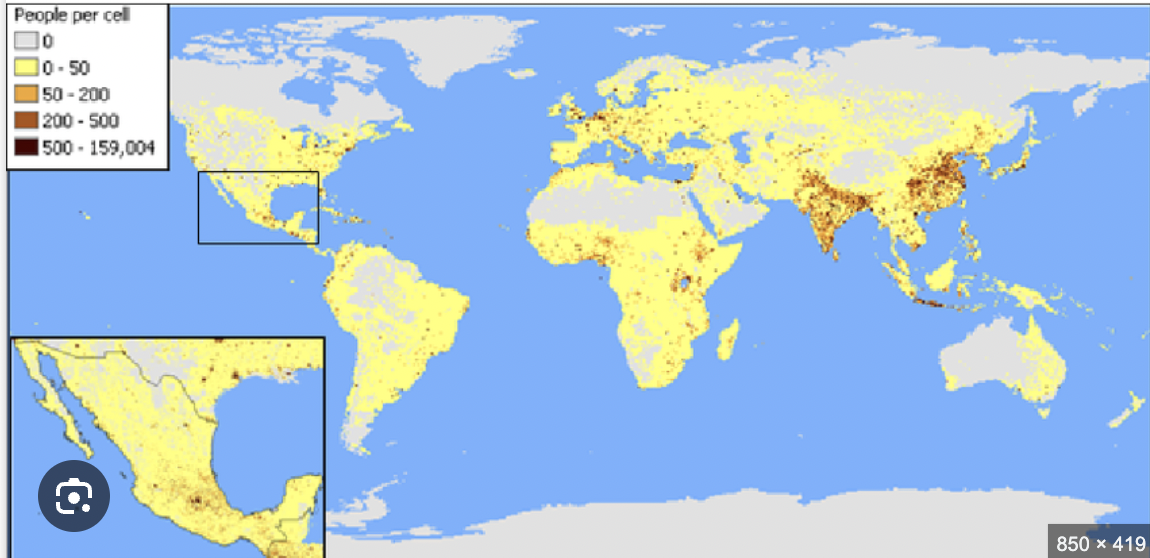
Examine the graphic, how might climate explain this image?
Gaps are occurring near the equator, potentially due to deserts.
Eastern dense populations (Europeans colonized attempting to find the best climate for crop growth to survive)
Give 3 examples that support the claim: “Humans modify their housing based on the climate the live in.”
Heating devices such as furnaces in Alberta.
Space heater in California results in lower fuel usage unlike Alberta (use insulation and windows)
Air conditioning in warmer climates and have to protect from excessive precipitation such as in Brazil. Steeper roofs in snowy climates (dark coloured shingles too).
Give 3 examples that support the claim: “The climate affects the economy in a particular area.”
Cost and availability of food (Florida has it easier to transport thus cheaper to give to Canada)
Cost of heating
Tourism and recreation industries
Give 3 examples that support the claim: “Plants will adapt to the climate in a particular area.”
Many plants undergo a period of dormancy during the winter.
—> Some do not in tropical regions
Deciduous trees (eg. poplars) drop leaves when dormant to protect from freezing and minimizes amount of moisture they need.
Plants in Alberta will flower and reproduce only when temperature is warmer and more moisture is available, usually.
Give 3 examples that support the claim: “Animals will adapt to the climate in a particular area.”
Grizzlies can put on as much as 200kg of fat during the summer months. Fat layer helps insulate their organs from cold of the winter. Create dens to protect from inactivity during winter.
Green iguanas are cold-blooded, so they seek out sunlight when the temperature is too cold and finds shade when temperature is too warm. Also have water-resistant skin.
Trumpeter swans only nest in wetland areas, which provides food and protection for its young.
Climate change
Change that occurs in the climate of a region over time (min 30 years).
How is climate change determined?
The average weather for a particular area over the last 30 years is analyzed to determine if climate change is occurring.
Anecdotal evidence
Reports of weather change by individual people.
Useful but can be biased.
Eg. Leonardo Dicaprio 😂
Scientific evidence
Evidence of weather change done by trained scientists using specialized equipment.
Reliable and unbiased.
Almost all of the energy on Earth initially comes from?
The Sun as solar energy
What portion of solar energy is converted to food - photosynthesis?
Only a small portion
What is the temperature for absolute zero?
-273.15 degrees C
Most of the solar energy to reach Earth’s surface is convereted to?
Thermal energy
The more thermal energy a substance has, the faster its?
Molecules move
Solar energy is? Why?
Radiant energy
Transmitted as an electromagnetic wave of various wavelengths.
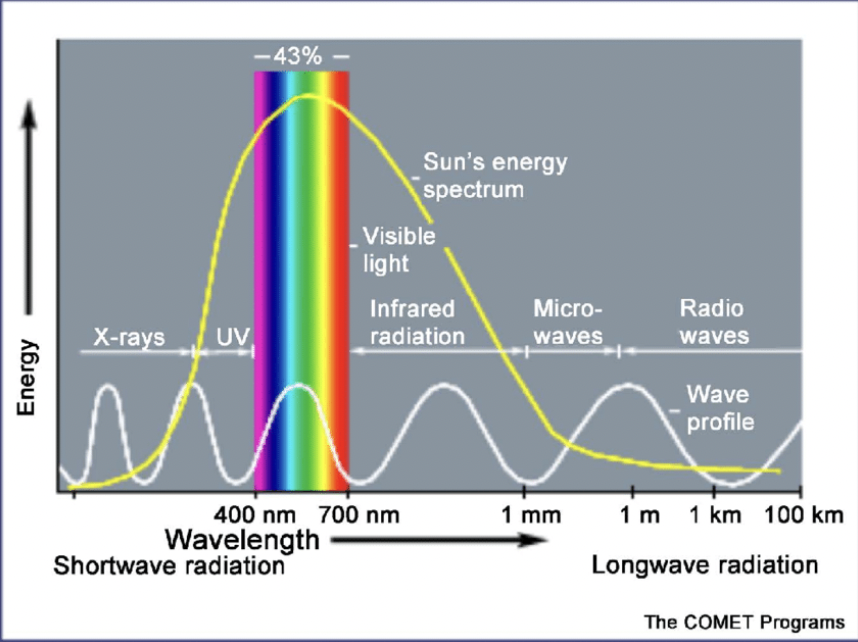
How is wavelength associated with energy?
The shorter the wavelength, the more energy the light wave contains.
We are only capable of seeing?
Visible light
What shows evidence of UV light?
A SUNBURN

All regions of the Earth do not receive?
The same amount of solar radiation.
Insolation
The amount of solar energy received by a region of Earth’s surface.
How direct the sunlight is.
Insolation is strongly dependent on?
Latitude
What does insolation stand for?
INcoming
SOLar
radiATION
Angle of inclination
The degree to which the Earth is tilted in its orbit around the Sun.
Its measure is the angle taken from the perpendicular axis.
The Earth’s angle of inclination is?
23.5 degrees
The angle of inclination gives us what?
Seasons on Earth
Draw a diagram of the Earth’s seasons.
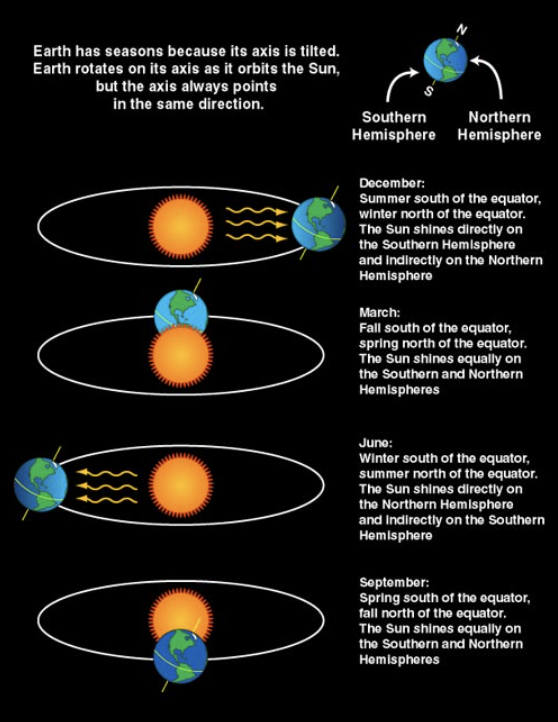
Solstice
One of two points during Earth’s orbit:
When the poles are furthest and closest to the sun.
Equinox
One of two points during Earth’s orbit:
The number of daylight hours is equal to the number of night hours.
What is the relation between latitudes and hours of sunlight?
Different latitudes receive different hours of sunlight during one of Earth’s orbits.
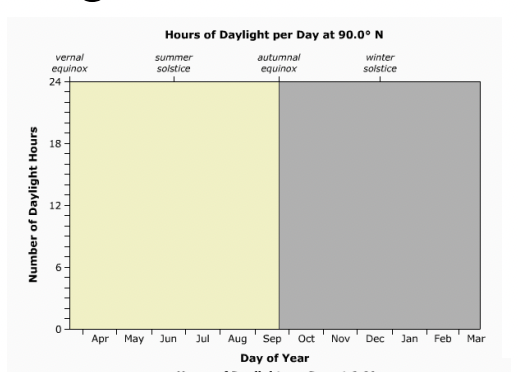
What region does this graph represent?
North Pole
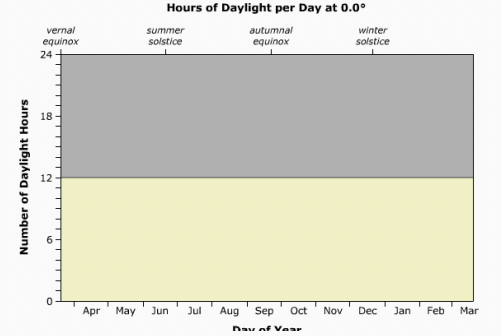
What region does this graph represent?
Equator
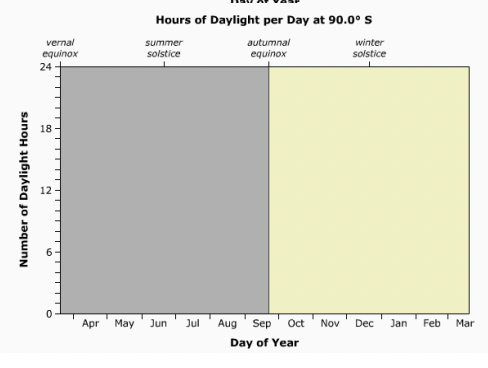
What region does this graph represent?
South Pole
Angle of incidence
The angle of a ray falling on a surface and the line of the perpendicular to that surface.
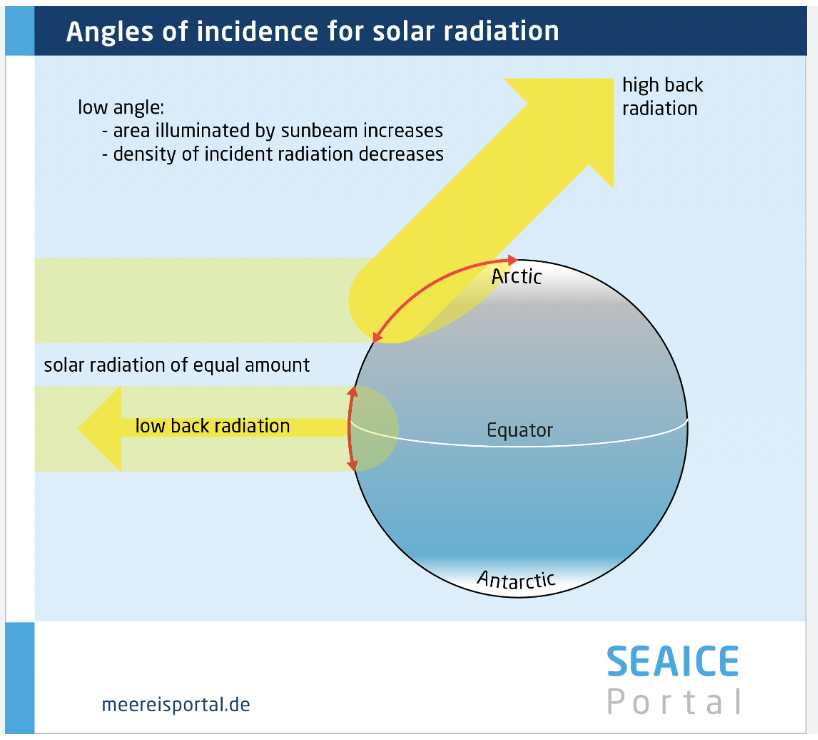
The angle of incidence at the equator is? How does it change?
0 degrees
Increases as you go North or South.
At larger angles of incidence, the sun’s rays are?
Spread out over a greater area.
They are not nearly as concentrated and thus less strong and direct.
How much solar energy do the polar latitudes recieve?
They receive less solar energy per km squared.
What is the relation between temperature and the angle of incidence?
Temperature of a location increases with the decrease of angle of incident of solar radiation.
What contributes to the creation of the Earth’s climate for various biomes?
The earth’s shape and Angle of Incidence play a large role.
Also Earth’s axial tilt.
What decreases with an increasing angle of incidence?
Insolation
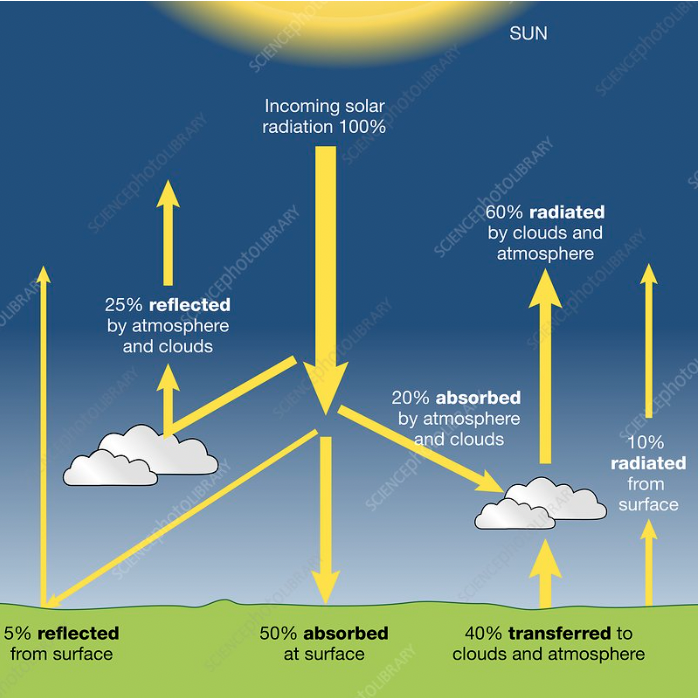
How does absorption and reflection occur in the biosphere?
Solar radiation can either be reflected or absorbed by all 3 levels of the Earth’s biosphere.
What are infrared waves (heat) absorbed by?
CO2, H2O, and CH4 (methane), AKA Green House Gases.
Green house gases absorb what two types of heat?
Ingoing and outgoing.
They trap it if it X escape.
Cloud Cover
Can both reflect incoming solar radiation and absorb thermal energy released from the Earth.
With what does a cloud cover help?
This helps to keep our planet both cool (reinforced) and warm (absorption).
Albedo
A measure of the percentage of solar radiation that a surface reflects.
The amount of solar radiation that is reflected or absorbed depends on?
The type of surface encountered.
What contribute to a Northern high Albedo?
Snow and ice cover.
Explain the temperature of the colours in relation to albedo.
Darker (Black + Blue) = Lower albedo, higher absorption, higher temperature
Lighter (White) = Higher albedo, lower absorption, lower temperature
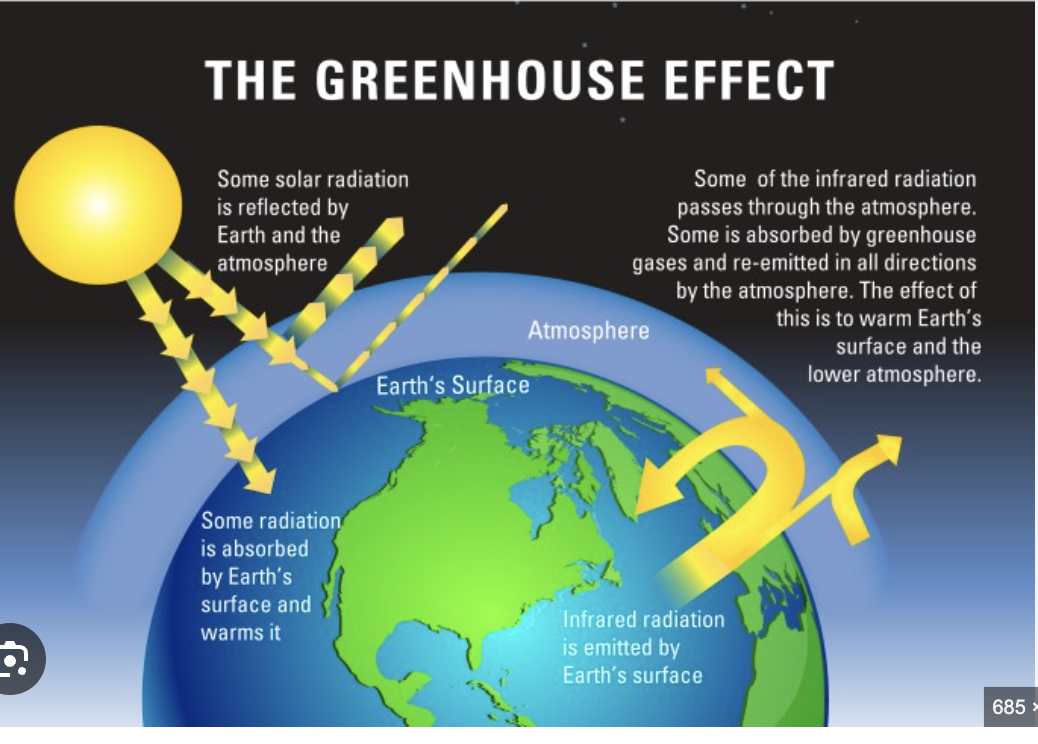
How does the natural greenhouse effect work?
Solar radiation that is absorbed by the earth's surface is often remitted as infrared radiation (thermal energy).
Gases in the atmosphere absorb the thermal energy and keep the earth warm.
Greenhouse gases. Give examples.
The gases in the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect:
Water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O)
Draw the natural greenhouse effect.
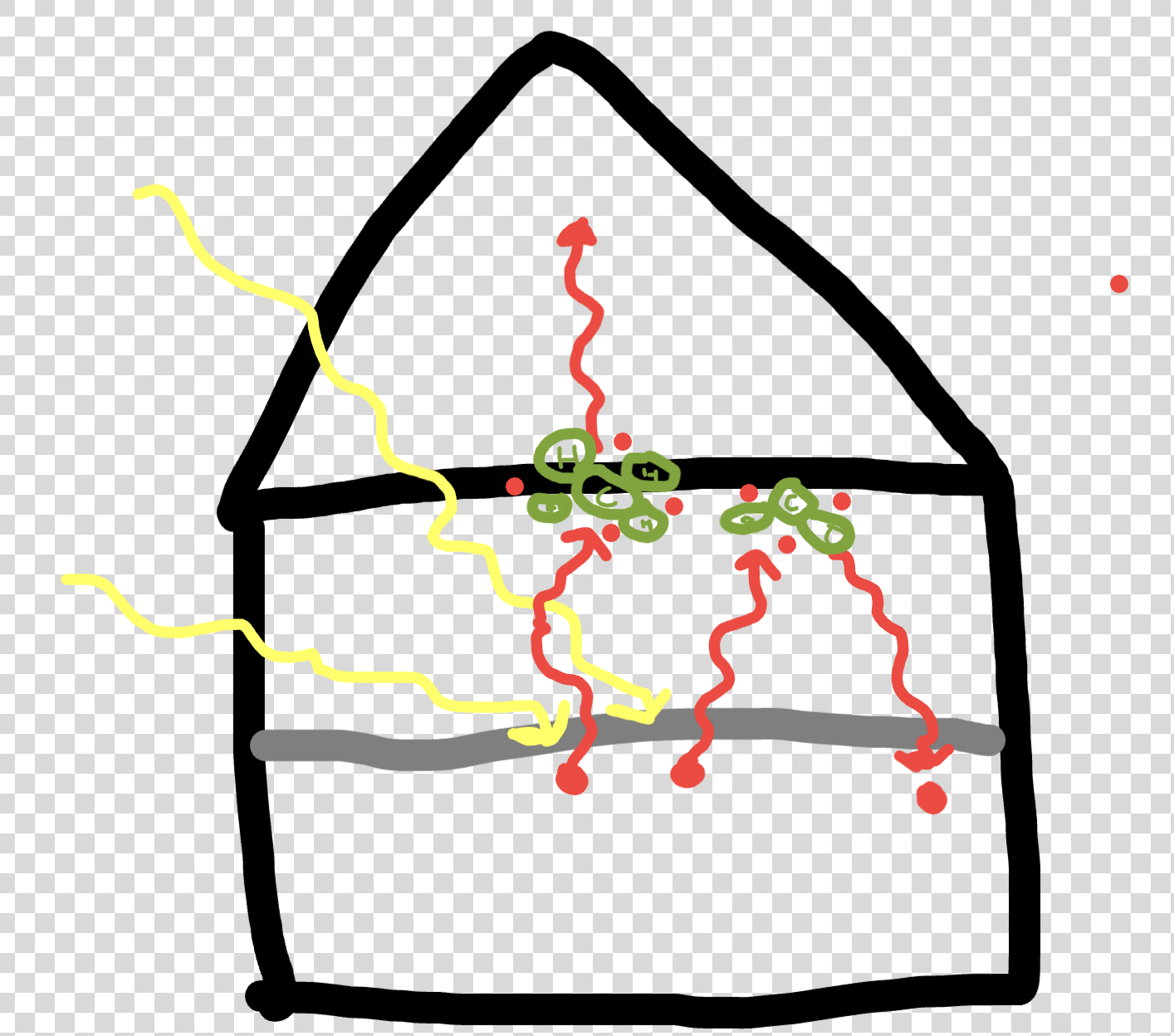
What will happen to the heat if a lamp is pointed at an empty bottle?
Some heat will be absorbed while some will be reflected. Thus, the temperature in the bottle will increase.
Net radiation Budget
The difference between the amount of incoming solar radiation and of outgoing solar radiation re-emitted from the Earth's surface and atmosphere.
What is the general equation for net radiation budget?
Net Radiation Budget = Incoming Radiation - Outgoing Radiation.
What will the equation look like if the net radiation budget is a cool temperature?
Cool = decreased IR - increased OR
What will the equation look like if the net radiation budget is a warm temperature?
Warm = increased IR - decreased OR
What will the equation look like if the net radiation budget is a stable temperature at equilibrium?
Stable/equilibrium = same IR - same OR
Can the Earth re-emit all incoming solar radiation?
In general, the Earth as a whole is able to re-emit all of the incoming solar radiation (eventually).
What is the question that is raised by the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Is there enough time for the planet to adjust?
If the amount of radiation re-emitted into space was less than the incoming:
The Earth’s average global temperature would increase.
If the amount of radiation re-emitted into space was more than the incoming:
The Earth’s average global temperature would decrease.
Average temperature is?
LONG-TERM
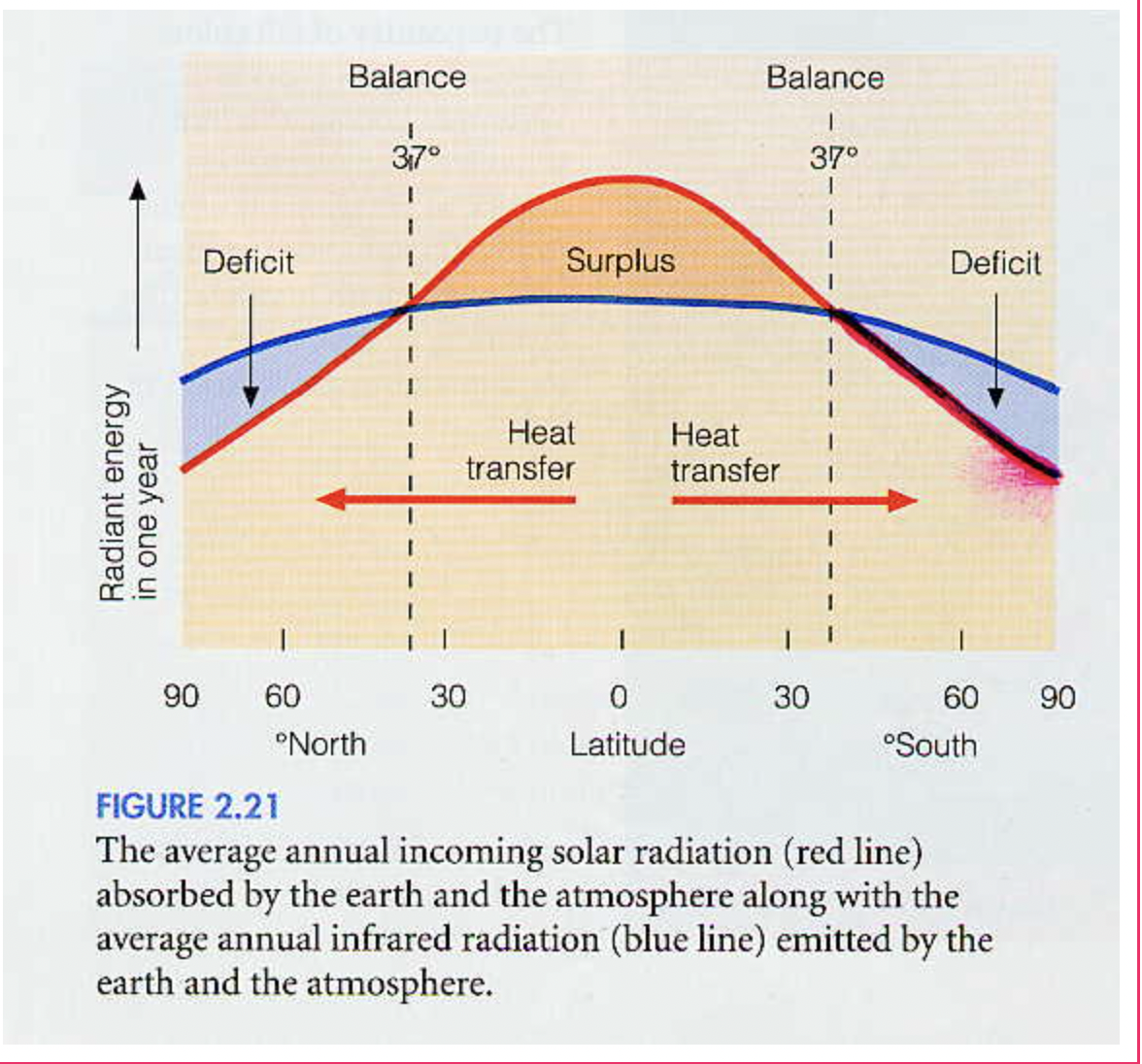
What is the relation between the net radiation budget and latitude?
The net radiation budget is generally balanced for the Earth.
Some latitudes have an unbalanced radiation budget.