Grade 9 - Environmental Chemistry
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Nutrients
a chemical in food, used for energy, growth, body building, or cell repair
carbohydrates
an organic nutrient made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; the starches and sugars present in foods
lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; does not dissolve in water
proteins
Nutrients the body uses to build and maintain its cells and tissues; composed of a chain of amino acids
vitamin
organic molecule that helps enzymes function in the body
macromineral
A mineral needed in the diet in amounts of 100 or more milligrams each day in order to maintain health; calcium, potassium, sodium
trace element
a mineral that the body requires in the amount of less than 100 mg/day in order to maintain health; zinc, copper, selenium
enzyme
A type of protein that regulates chemical reactions in a living thing
herbicide
a substance for killing plants, especially weeds
insecticide
substance that kills insects
fungicide
substance that kills fungi or inhibits their growth
acid
a chemical that produces an acidic substance, having a pH value of less than 7
acidic
pH less than 7
base
a chemical that produces a basic substance, having a pH value of more than 7
basic
pH greater than 7
indicator
A compound that changes color in the presence of an acid or a base

litmus
a substance used to detect the presence of an acid or a base. Acid: blue litmus turns red. Base: red litmus turns
blue.
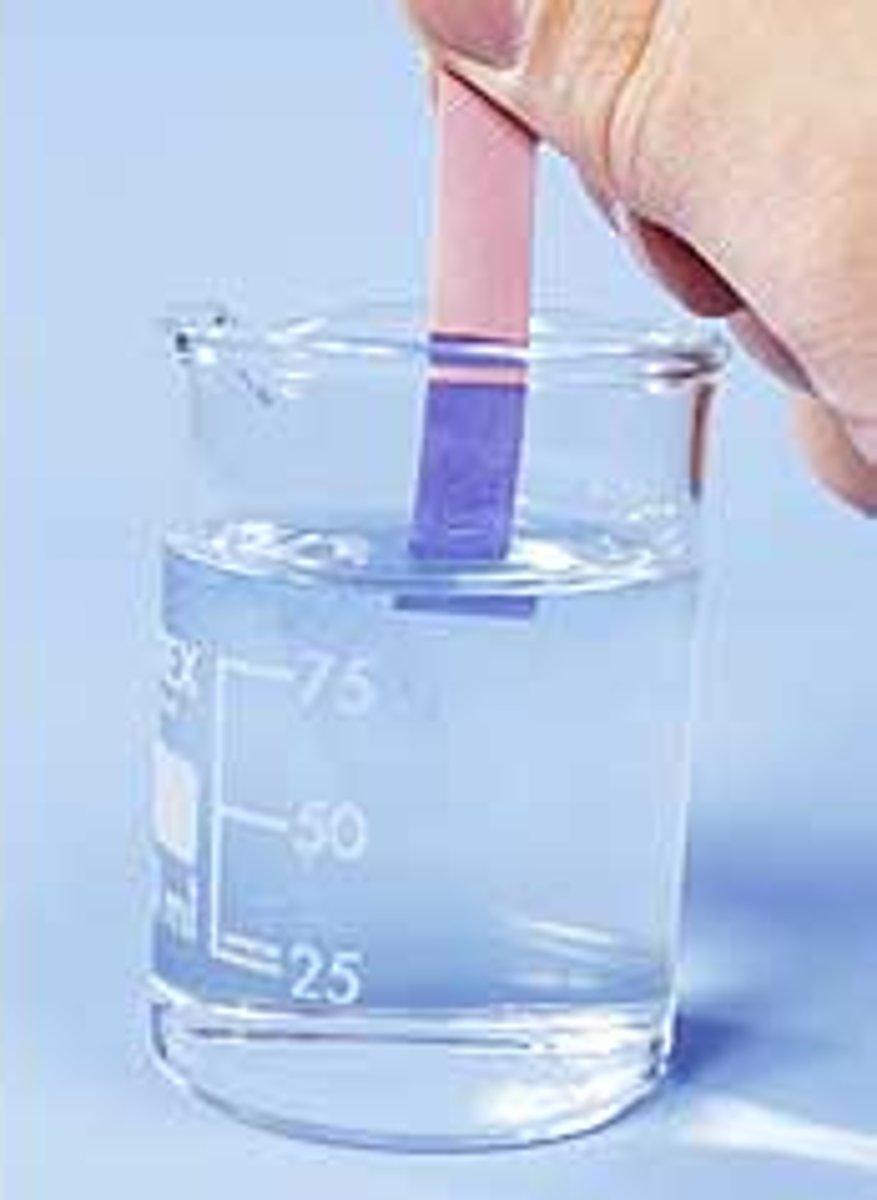

pH paper
a piece of paper that has one or more chemical indicators on it and that changes colors depending on the amount of H+ ions in a solution
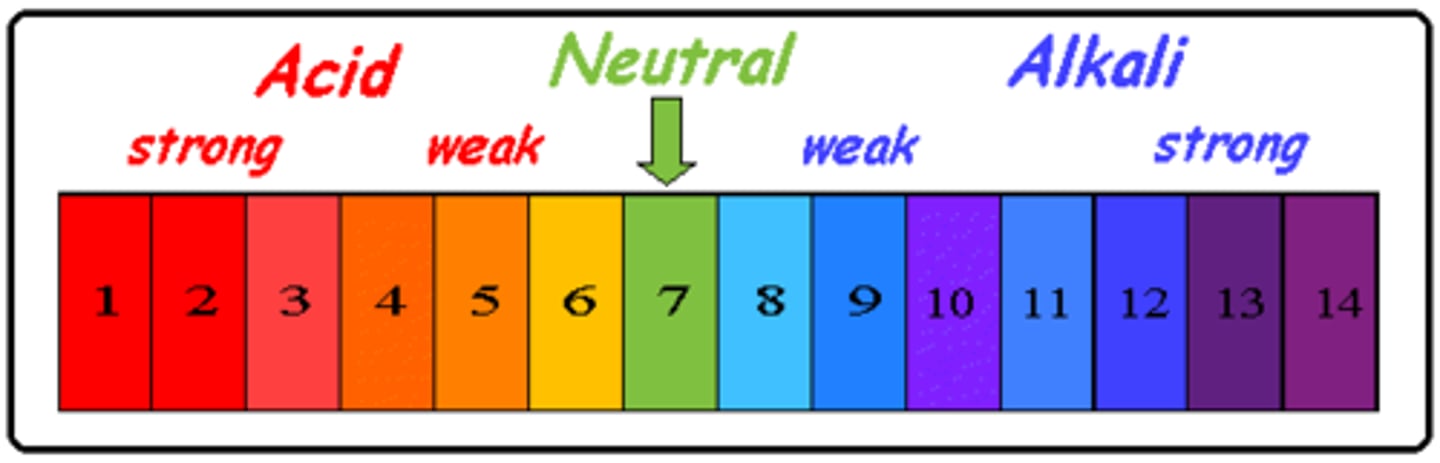
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14

acid precipitation
Conversion of sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides to acids that return to Earth as rain, snow, or fog
liming
the process of adding calcium carbonate to the environment; increases nutrient content of soil
acid-base neutralization
The combining of an acid and a base to produce salt and water
catalytic converter
a device that encourages complete oxidation during combustion
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
oxidation
a chemical reaction in which oxygen combines with other elements to form new substances; loss of electrons
scrubber
a device that uses a sorbent to reduce oxide emissions
acute toxicity
the ability of a chemical to cause harm to an organism with only one exposure; hydrogen cyanide is an example
chronic toxicity
the ability of a chemical to cause harm to an organism only after the chemical accumulates to a specific level after many exposures over time; asbestos is an example
LD50
lethal dose (of a toxin) for 50% of the test population
pollutant
any material, or form of energy, that will cause harm to a living organism
pollution
an alteration of the environment producing a condition harmful to living things
toxicity
the ability of a chemical to cause harm to an organism
biological indicators
species that can be used to monitor the health of an environment or ecosystem.
point source
a specific location where pollution originates
non-point source
a source of pollution in which pollutants are diffuse and originate from no specific location
non-persistent waste
wastes that can be broken down into simple nonpolluting compounds by naturally occurring chemical reactions or bacterial action
persistent waste
wastes that accumulate in the environment and break down very slowly, if at all
NIMBY
Not In My Backyard attitude. People don't want things like landfills to be put where they live.
CFCs
Chlorinated Fluorocarbons are chemicals that break down the ozone layer
Ozone
A form of oxygen that has three oxygen atoms in each molecule instead of the usual two; ozone layer absorbs most of the ultraviolet radiation reaching the earth from the sun.
surface water pollution
raw sewage and excess fertilizer flow into lakes and streams
ground water pollution
Anything dumped/sprayed on the surface or buried in the ground has the potential to pollute ground water
biodegradable
capable of being readily decomposed into harmless substances by microorganisms
bioremediation
The use of living organisms to detoxify and restore polluted and degraded ecosystems
hazardous waste
Any material that can be harmful to human health or the environment if it is not properly disposed of
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
bioreactor
an apparatus in which a biological reaction or process is carried out, especially on an industrial scale.