anatomy exam 4 workbook
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
what do mesanephros do?
deliver waste to mesonephric duct
What do metanephros turn into?
urteric bud and metanephric blastema
your kidney
what happens when there is retention of mesonephric duct
penis and associated
what happens when there is retention of the paramesonephric duct?
uterus and associated
what type of tissue makes up the kidney
dense connective, which keeps its shape and prevents infection
how does blood get to and from the kidney
renal artery branches from abdominal aorta and supplies blood to the kidney
which renal vein is longer?
left renal vein
what is the order of blood supply to the cortex of the kidney
renal artery
segmental artery
interlobar artery
arculate artery
cortical artery
really sweet interns always care
what is the mucosa of the ureter and bladder?
transitional epithelium
what is the purpose of the submucosa in the bladder?
helps maintain integrity of mucosa
how many layers of muscle is in the ureter?
2
how many layers of muscle is in the bladder?
3
what is the function of the adventitia in the ureter and bladder?
supports outside of ureter and bladder, helps with recoil
where does the urinary bladder sit?
behind the pubic bone
where does the prostate gland sit?
inferior to the bladder
how is the urethra formed?
extension of detrusor muscle
smooth muscle
autonomic control
explain the micturition reflex
stretch receptors in bladder trigger micturition reflex
impluses travel to detrusor muscle and internal anal sphincter
smooth muscle in internal sphincter relaxes
smooth muscle in detrusor contracts
person has to consciously relax external sphincter
where is the parotid gland located and what does it secrete
anterior to ear
serous secretions
where is the sublingual gland located and what does it release
below the tongue
mucus secretions
what is the first phase of swallowing
tongue raises against the palate to move food back into the pharynx
what is the second phase of swallowing
suprahyoid muscles contract to raise the larynx and lengthen the pharynx
hyoid moves anteriorly to increase pharynx diameter
what is the third phase of swallowing
infrahyoid muscles lower the larynx and lengthen the pharynx
hyoid returns posteriorly to decrease diameter of pharynx
what do duodenal glands release
alkaline bicarbonate to neutralize acid from stomach
what do goblet cells secrete
mucus to lubricate intestinal wall
what do enteroendocrine cells signal
gallbladder to release bile
what do parietal cells produce
HCl
where do digestive enzymes pool into
pancreatic duct
how does bile get to the common bile duct
bile leaves liver from hepatic ducts
stored in gallbladder
travel through cystic duct
hepatic duct meets cystic duct
common bile duct
how does bile get to small intestine
common bile duct + pancreatic duct
hepatopancreatic ampulla
releases bile and digestive enzymes into duodenum
what are the muscles that form the pelvic floor diaphragm
levator ani
coccygeus
what type of erectile tissue form the body of the clitoris and cruras
corpora cavernosa
what does the dartos muscle do
regulates heat loss by wrinkling the scrotum, or relaxes and expands
what does the cremaster muscle do
elevates testes when cold
descends when warm
what is the space between the bladder and uterus
vesicouterine pouch
what is the space between the bladder and rectum
rectovesical pouch
what is the space between the uterus and rectum
rectouterine pounch
how does sperm get to the external urethral orifice
testes —> epididymis —> ductus deferens —> ejaculatoy duct —> urethra —> external urethral orifice
what does the bulbourethral gland secrete
mucus
what does the prostate gland secrete
prostate specific antigen
seminalplasmin
what does the seminal vesicle secrete
fructose
prostaglandins
bicarbonate
what three structures form the adnexa
fallopian tubes
ovarian ligament
round ligament
what are the three parts of broad ligament
mesometrium
mesovarium
mesoalpinx
what does the mesometrium cover
surronds the uterus
what does the mesovarium cover
the ovarian ligament and ovaries
what does the mesoalpinx cover
uterine tubes
what plexus provides autonomic innervation to the organs within the pelvis and control blood flow the erectile tissues
inferior hypoagstric plexus
what nerve carries sensory innervation from the external genitalia and somatic motor innervation to the muscles of the pelvic diaphragm
internal pudendal artery
where do ovarian arteries branch from
abdominal aorta
fertilization typically occurs in the __ of the uterine tube
ampulla
what hormone intiates the released of primordial follicles within the ovary
FSH
where is the adrenal gland located
superior to kidney
where is the thyroid gland located
inferior part of the neck
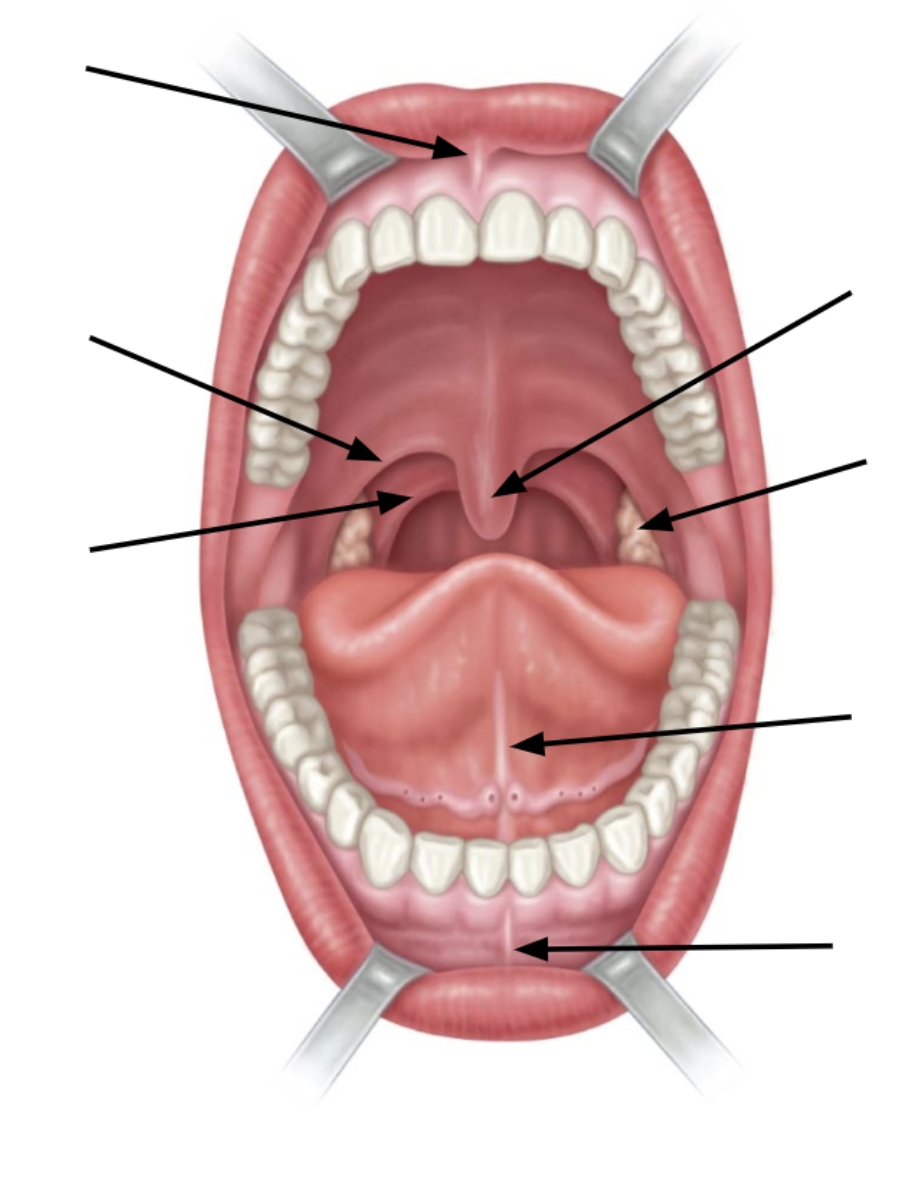
top arrow is
superior labial frenulum
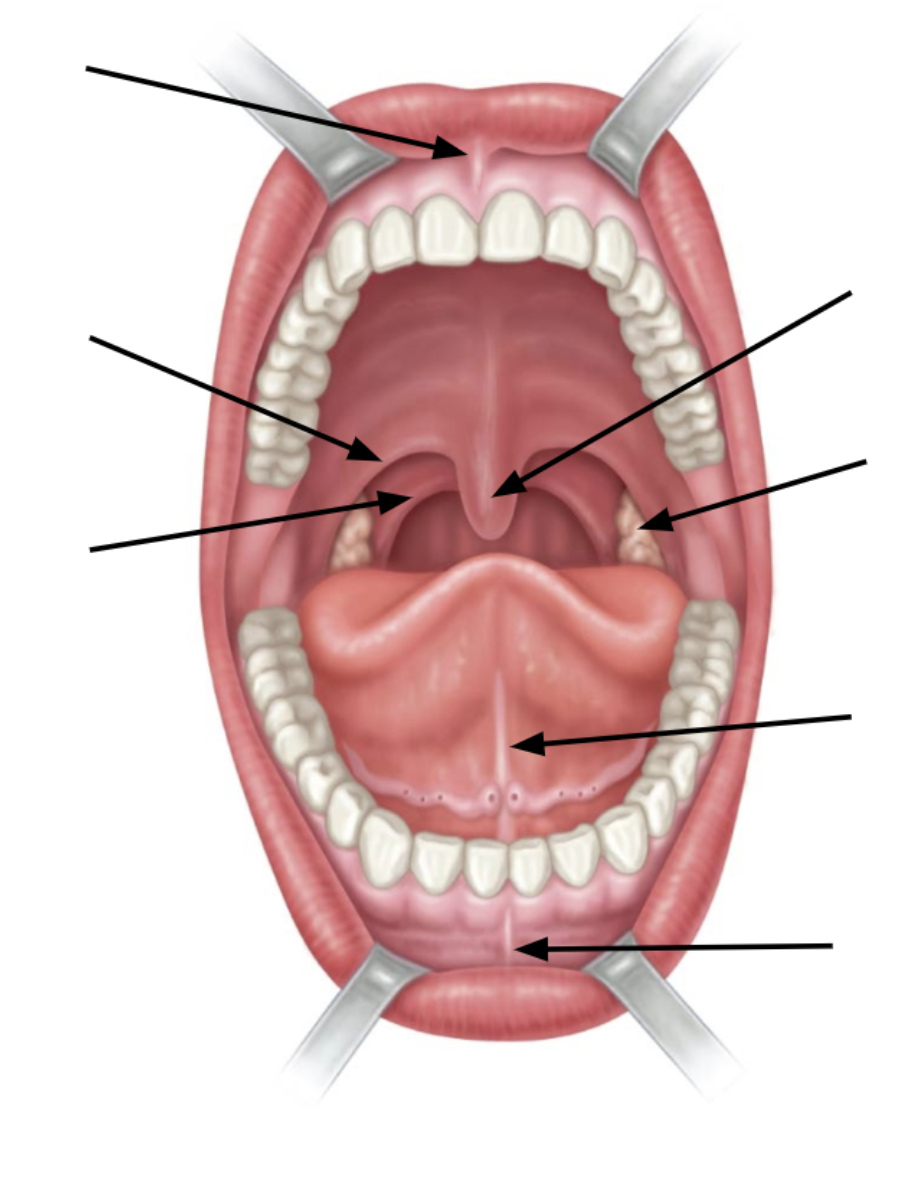
bottom arrow is
inferior labial frenulum
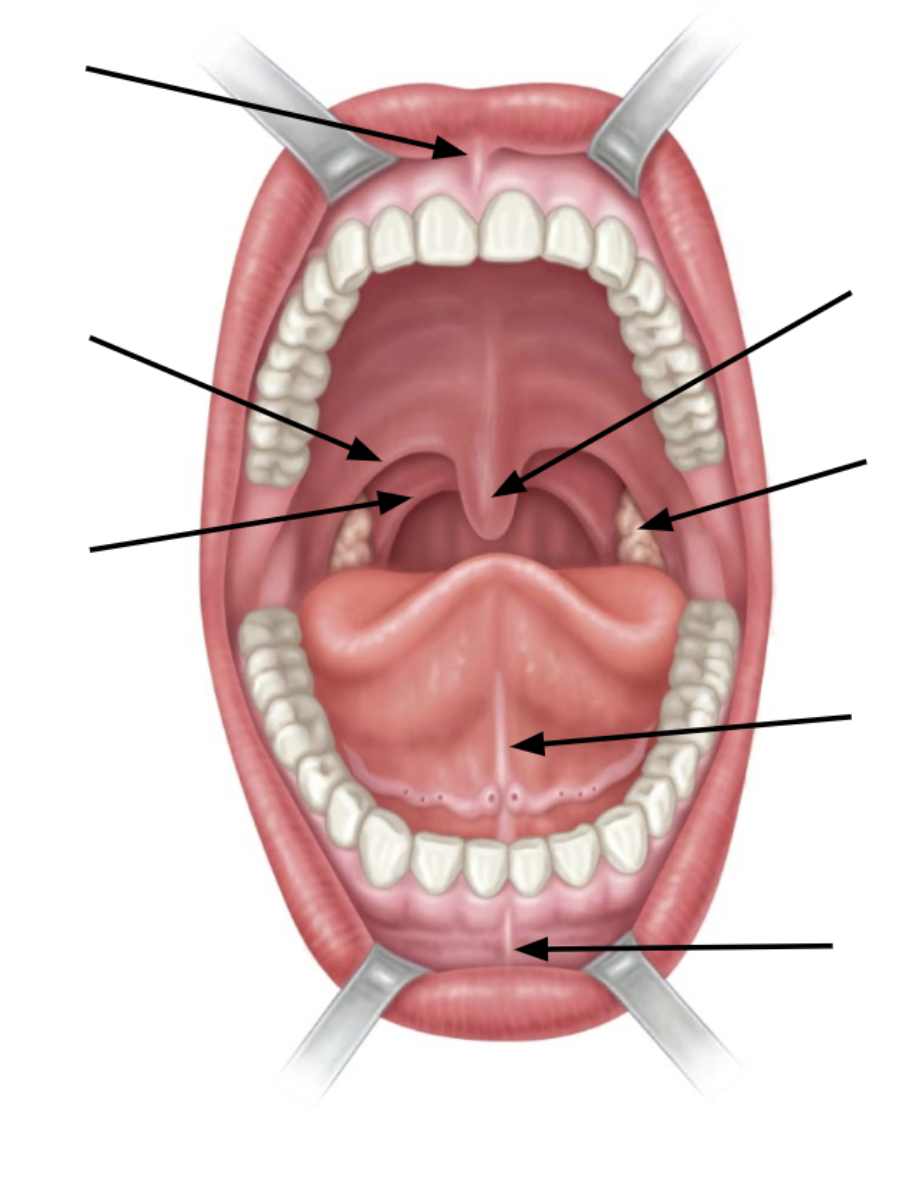
2nd arrow up from bottom is
lingual frenulum
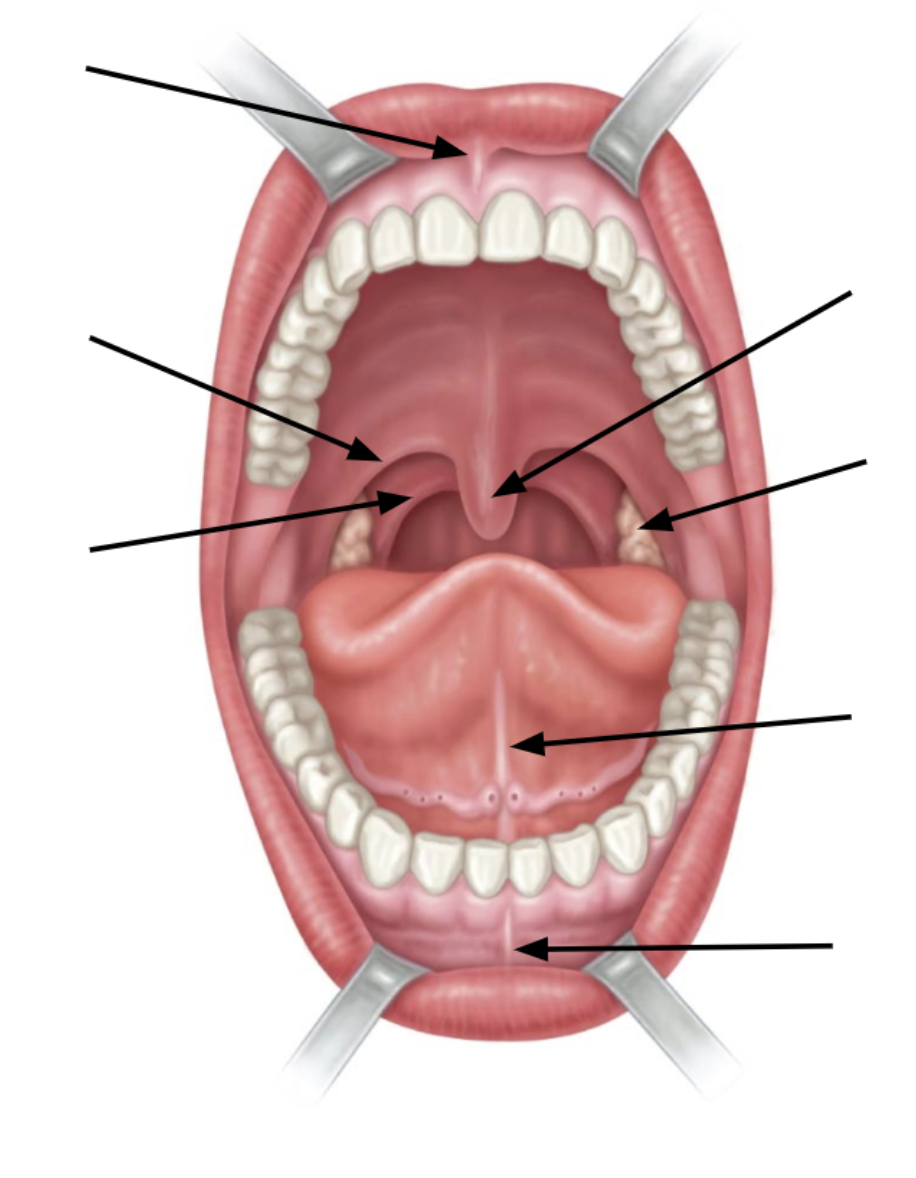
3rd arrow up from bottom is
palatine tonsil
where is the pituitary gland and what does it do
hypothalamus, anterior and posterior
where is the thyroid gland and what does it do
lower neck, anterior to trachea
releases the thyroid hormone
and increases basal metabolic rate/activity
how many parathyroid glands are there
4 on the posterior thyroid gland
where is parathyroid hormone released
when calcium levels are low
where are the adrenal (suprarenal) glands located
superior to the kidneys
cortex is outer
medulla is inner
what gland is responsible for your short-term stress response
adrenal medulla
what are chromaffin cells
modified post synaptic sympathetic neurons
what gland is responsible for your long-term stress response
adrenal cortex
what does aldosterone do
increases blood pressure by stimulating reabsorption of sodium and water
what does cortisol do
increase glucose levels in the blood and breaks down protein
where is the pancreas located
behind the stomach
what is the exocrine part of the pancreas
acinar cells secreting digestive enzymes into the duodenum
what does the endocrine part of the pancreas do
pancreatic islet cells, alpha (release glucagon) and beta cells (insulin, and signals liver)
what is homologus to the glans of clitoris
glans of penis
what is homologus to the body of clitoris
corpora cavernosa
what is homologus to the crus of clitoris
crus of penis
what is homologus to the bulb of vestibule
bulb of penis
what is homologus to the labia majora
scrotum
how long is menstrual cycle
1-5 days
when does ovulation occur
day 14
what happens after ovulation
luteal phase