GMO's and biotechnology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is genetic modification?
The process of taking genes from one organism and inserting them into another organism
What is biotechnology?
A branch of science that uses living organisms to create useful products for humans
What is genetic engineering?
The science of altering an organism’s genes to improve it
What does GMO stand for?
Genetically Modified Organism
What is a GMO?
A living organism whose DNA has been altered using biotechnology in a way that wouldn't happen naturally
What is recombinant DNA?
DNA that contains genetic material from two different sources
What is the purpose of creating GMOs?
To transfer desirable traits like disease resistance or higher yield into other organisms
Which bacterium is commonly genetically modified to produce insulin?
E. coli
What is the role of insulin in the body?
It helps the body use sugar to produce energy
What disease requires insulin treatment?
Diabetes
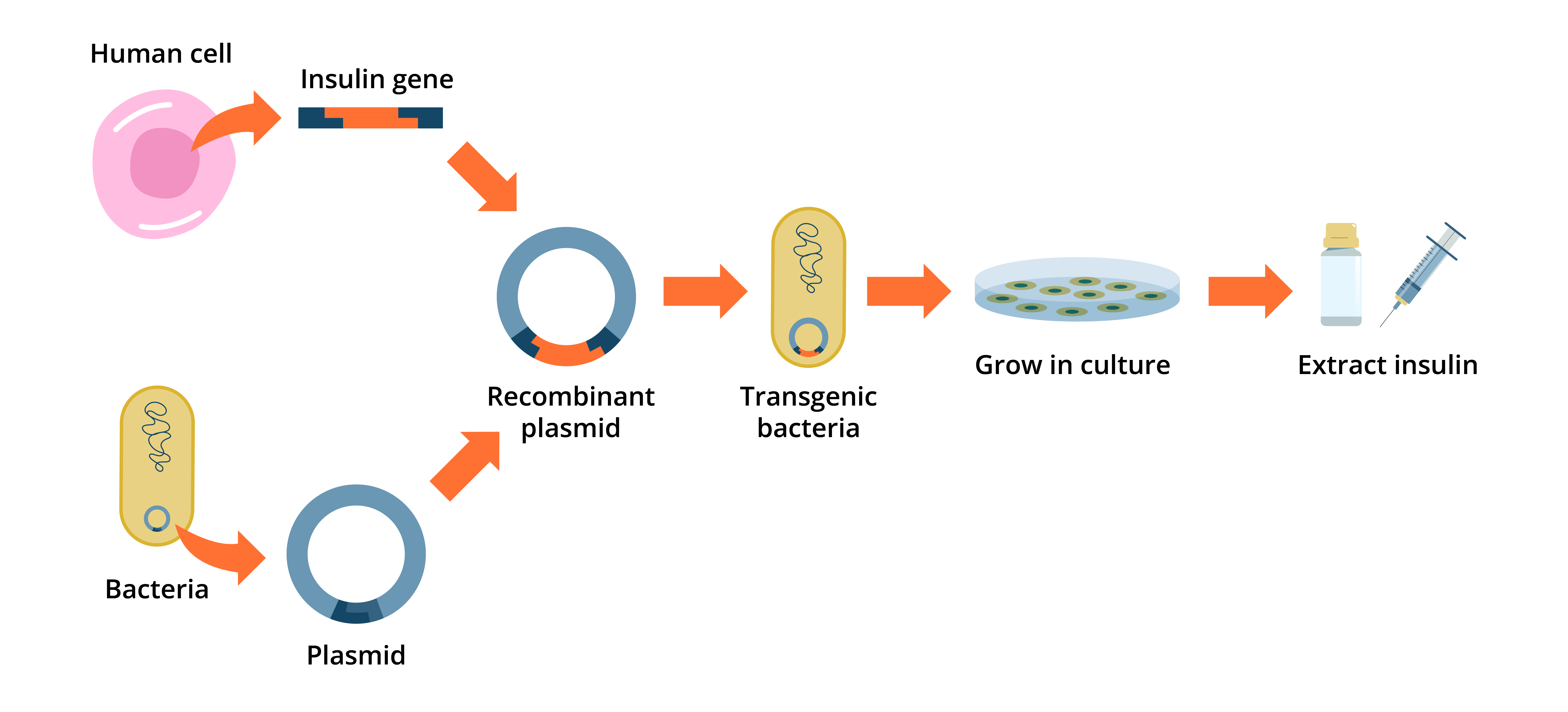
How is insulin produced using GM bacteria?
A human gene for insulin is inserted into bacterial DNA, and the bacteria produce insulin
What are some products made using genetically modified bacteria?
Growth hormones, hepatitis B vaccine proteins, insulin
How are genetically modified plants beneficial?
They can be more nutritious, drought-resistant, pest-resistant, and have higher yields
What are some traits genetically engineered into plants?
Disease resistance, herbicide resistance, improved nutritional value
How are genetically modified animals created?
By injecting a gene from one species into the fertilised egg of another
What is an example of a genetically modified animal?
Sheep that produce clotting factor IX in their milk
What is clotting factor IX used for?
Treating the blood clotting disorder haemophilia
What are some ethical benefits of genetic modification?
Treating genetic disorders, increasing crop yields, reducing environmental impact
What are some ethical concerns of genetic modification?
Possibility of designer babies, social inequality, environmental risks
Why is genetic modification controversial?
It raises questions about fairness, long-term safety, and natural balance
What is the first step in creating genetically modified insulin-producing bacteria?
Removing and cutting open a plastid from E. coli
Why is recombinant DNA important?
It allows genes from different organisms to be combined for beneficial traits
How does genetic engineering help in agriculture?
It creates crops that are stronger, more nutritious, and pest-resistant
What is one medical application of genetic engineering?
Producing insulin or clotting factors using genetically modified organisms
Why might genetically modified crops cause environmental concern?
They could affect wild plant populations or lead to resistant pests
What is the ethical issue with 'designer babies'?
It may create inequality and alter natural human diversity
Figure 1: Recombinant DNA.
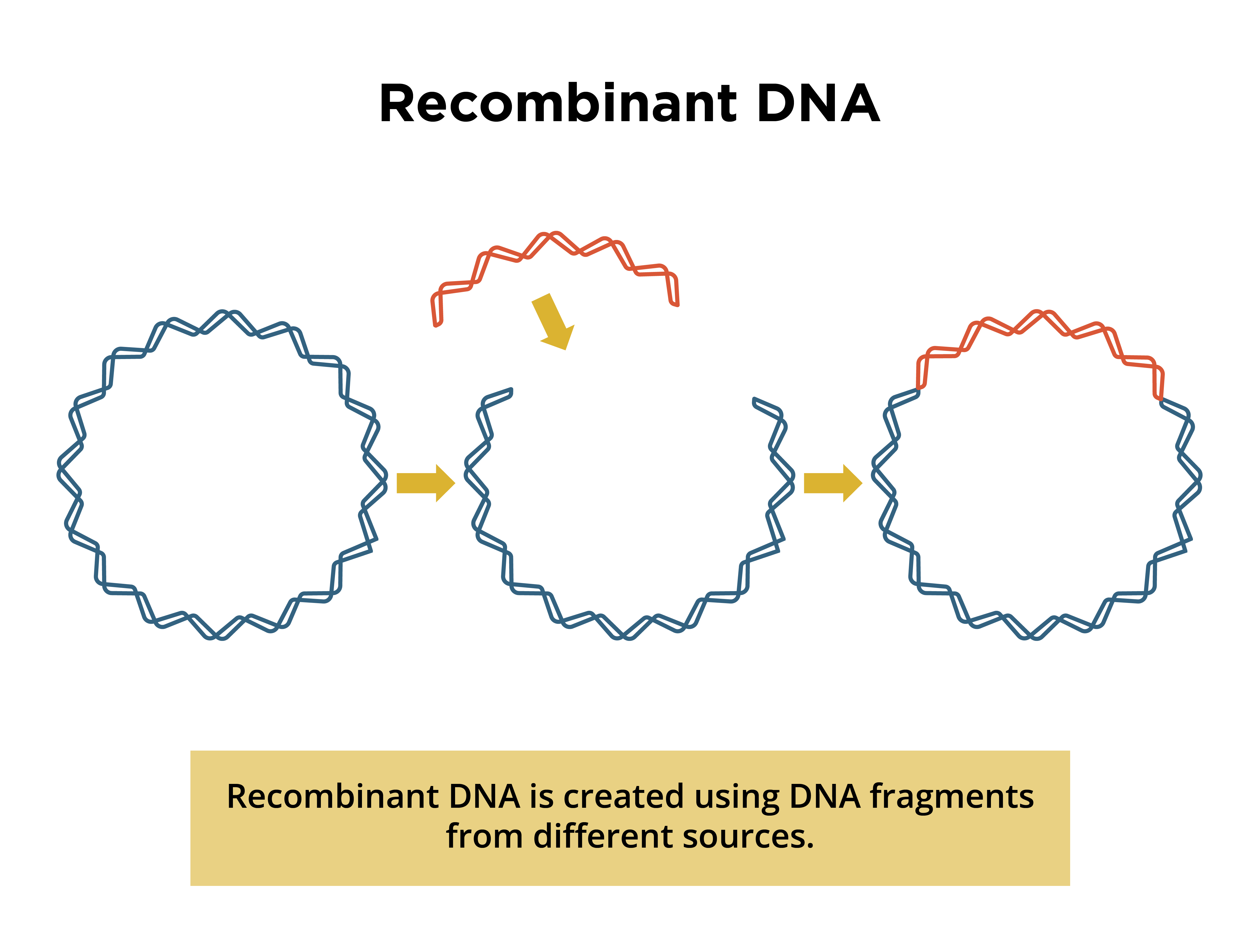
Figure 2: Genetically modified bacteria produce human insulin.