Introduction to Syntax and Semantics: Language Structure and Meaning
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Syntax
Traditionally considered a component of grammar; deals with the linguistic theories underlying the structure of phrases and sentences - describes hidden rules.
Semantics
The study of meaning in language.
Deep structure
The underlying linguistic representation of a phrase or sentence.
Surface structure
The observable presentation of the phrase or sentence.
Structural ambiguity
When a sentence can have multiple meanings due to its structure.
Noun phrase (NP)
A phrase that must have a noun (or noun phrase, serving as subject) and can include articles, adjectives, and pronouns.
Verb phrase (VP)
A phrase that includes a verb and can include objects and modifiers.
Prepositional phrase (PP)
A phrase that begins with a preposition and includes a noun phrase.
Syntactic analysis
The process of analyzing the structure of sentences.
Sentence definition
A grammatical construction that must contain a subject and a verb.
Semantic anomalies
Syntactically well-formed sentences that violate semantic rules.
Referential meaning
The 'dictionary' meaning of a word.
Associative/Emotive meaning
Personal or qualitative associations that individuals have with a word.
Types of meaning
Different categories of meaning that words can convey.
Semantic features
Characteristics that help define the meaning of a word.
Prototypes
Typical examples of a category that help define its meaning.
Semantic relationships
Connections between words based on their meanings.
Thematic roles
The functions that participants play in the context of a sentence.
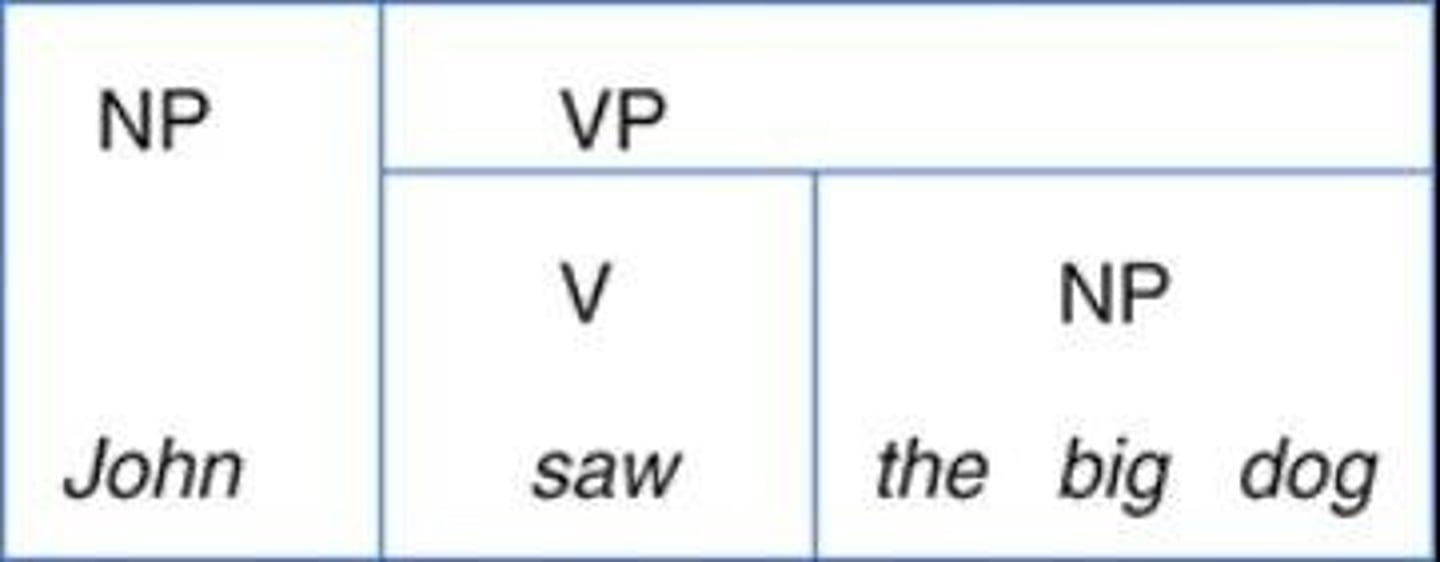
Syntactic trees
Diagrams that represent the structure of sentences and show the relationships between words.
Grammar
Defines the rules of a language.
Ambiguity in sentences
When a sentence can be interpreted in more than one way.
Example of structural ambiguity
The girl hit the boy with the book.
Example of semantic anomaly
*The ball read the newspaper.
Semantic feature (component) analysis
Analysis of features that define categories.
Agent
Entity that performs the action/verb.
Theme/Patient
Entity that is affected by the action or is being described.
Instrument
Used by an entity to perform an action.
Experiencer
Entity that has a feeling, perception, or state.
Location
Where an entity is.
Source
Where an entity moves from.
Goal
Where an entity moves to.
Synonymy
Words with completely or closely overlapping meanings.
Antonymy
Words with opposite or nearly opposite meanings.
Hyponymy
The meaning of one word (more restricted meaning) is included in the meaning of another word (broader meaning).
Homophones
Words that sound the same but are spelled differently.
Homonyms
Words that sound the same and are spelled the same but have completely different meanings.
Polysemy
Words that sound the same and are spelled the same and have different but related meanings.
Metonymy
A closely related word that is used in place of the word that actually matches the intended meaning.
Collocations
Words that are commonly used together.
Acronyms
Abbreviations formed from the initial letters of a series of words.
Puns
Play on words that exploits multiple meanings.