Lab Practical Prep (Natural Selection & Microscopes and Prokaryote Diversity)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Full-sleeved, mid thigh lab coat, nitrile/latex gloves, safety goggles/glasses
Formula for number of allele in surviving population
Ex. Number of B alleles = [# of black mice (BB) x2] + [# of brown mice (Bb) x 1]
Black fur allele (mice)
BB
Brown fur allele (mice)
Bb
White fur allele (mice)
bb
Frequency of allele formula
Frequency of (desired allele) = number of (desired allele)/total alleles
phenotype
observable traits expressed by an organism
genotype
underlying genetic makeup consisting of both visible and non-expressed allele(s) of an organism
allele
gene variation that arise by mutation and exist the some relative location on homologous chromosomes, influencing traits.
evolution
the process of gradual change in population over time/change in allele frequency over time
natural selection
reproduction of individuals with favorable genetic traits that survive environment change because of those traits, leading to evolutionary change
adaptation
heritable traits that enhance an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
fitness
reproductive success of an individual relative to the rest of the population
Genetic variation
difference in DNA between individuals in the same species
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
Allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences
Hardy-Weinberg Equation
p²+2pq+q²=1
Ocular Lens
allows individual to observe specimen; has a magnification of 10x
rotating nosepiece
rotates to change objective lens
Arm
backbone of microscope where one carries the microscope
mechanical stage
holds slide
stage
where the specimen is placed
objective lens
has a certain magnification to observe the specimen
Four types of objective lenses
4x, 10x, 40x, 100x
Total magnification
10x multiplied by objective lens magnification equal this:
condenser
focuses light on specimen
Iris diaphragm
controls amount of light passing through the condensor
light source
provides light to specimen
coarse adjustment knob
makes large adjustments to focus specimen by raising stage
fine adjustment knob
makes small adjustments to focus specimen, used with 40x and 100x lenses
light intensity control knob
adjusts brightness of illumination
stage control knobs
moves the stage horizontally or back and forth vertically
base
bottom of the microscope
prokaryotes
in the domains bacteria and archaea; single-celled, no nucleus, no membrane bound organelles, much smaller than eukaryotes, single circular DNA, divide by binary fission, simple flagella, oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis, can be photoautrophic up to chemoheterotropic
coccus (spherical), spirillum (spiral), bacillus (rod)
three shapes of bacteria
colony
visible mass of microorganisms all originating from a single mother cell
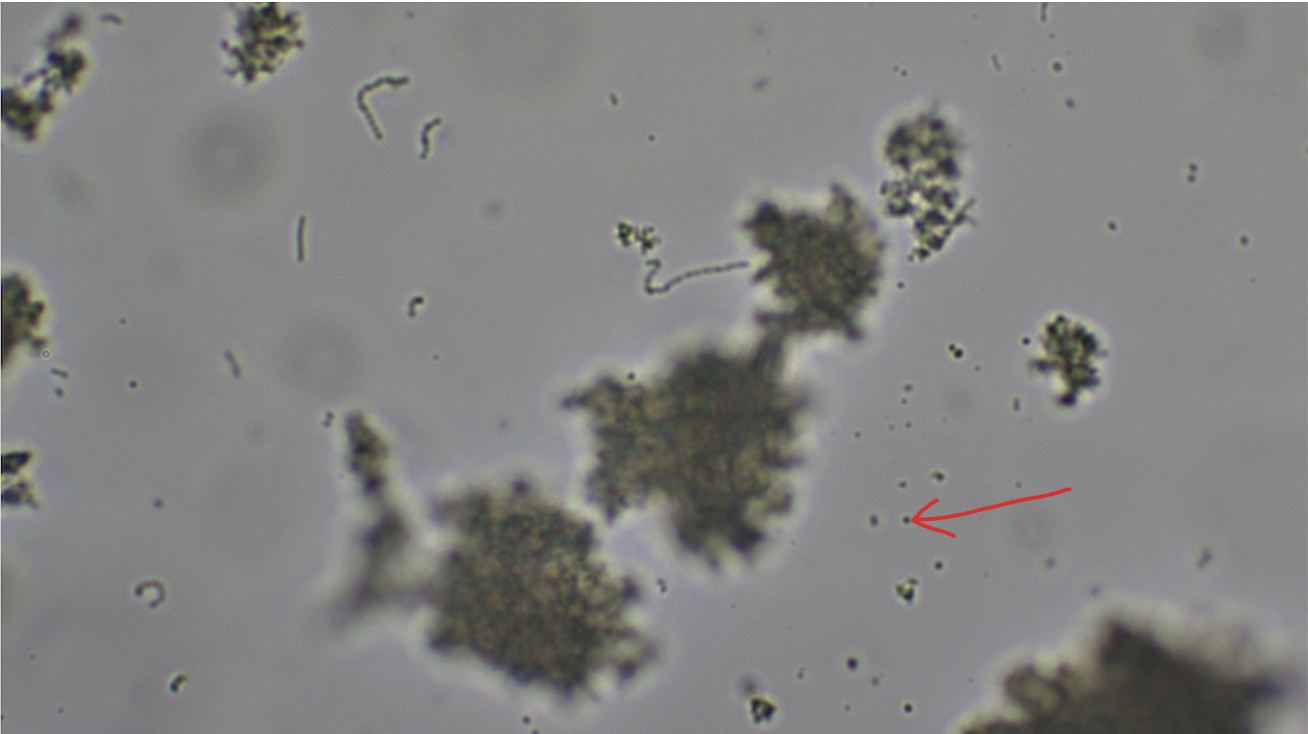
Lactobacillus
Rod-shaped bacteria, nonmotile, chemoheterotroph, found in yogurt, helps partially digest proteins and milk solids
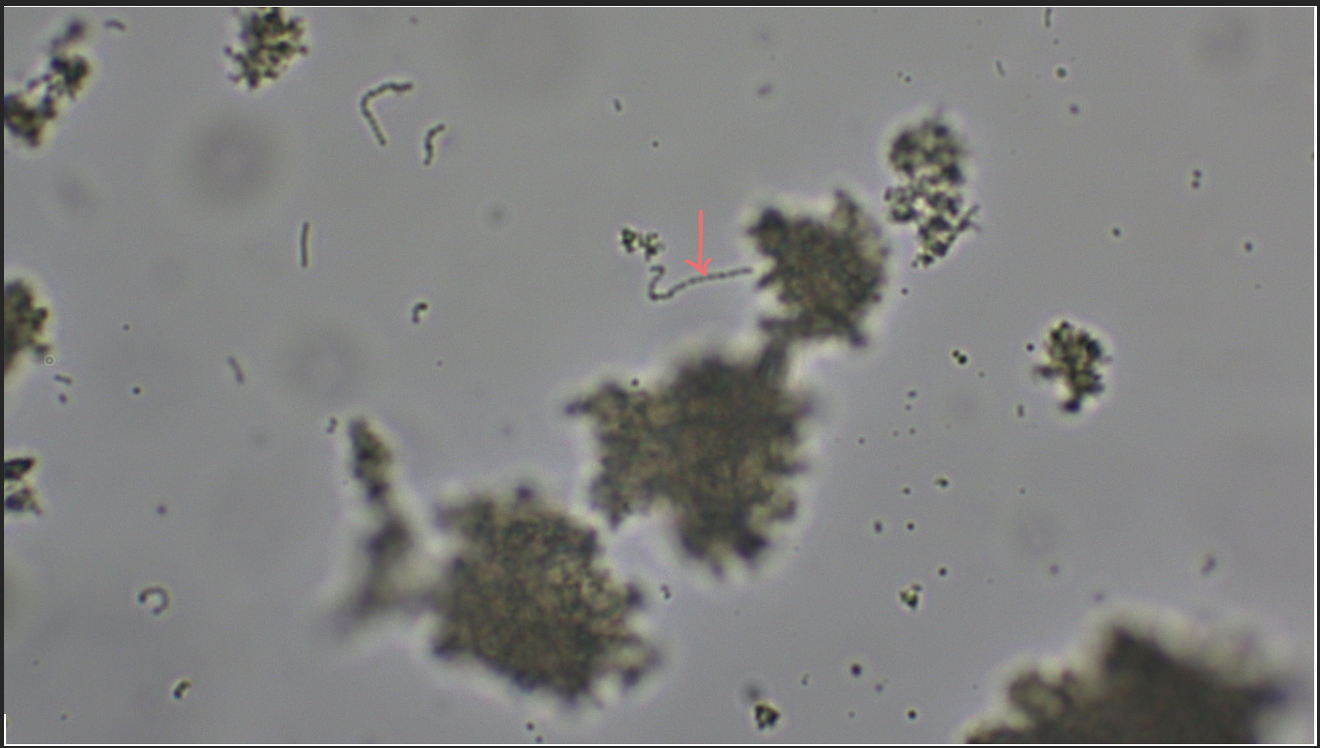
Streptococcus
round-shaped bacteria, nonmotile, chemoheterotroph, found in yogurt, helps partially digest proteins and milk solids, also includes some notorious pathogens
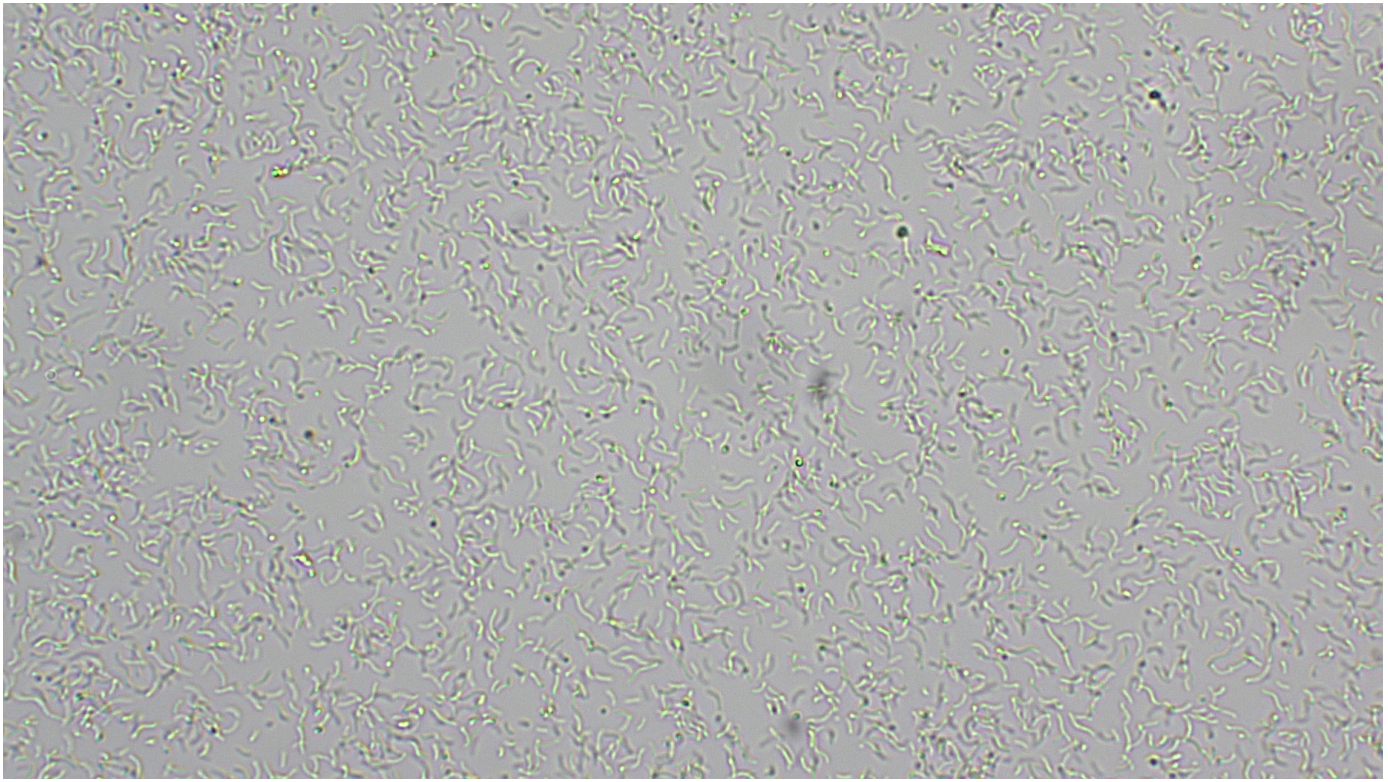
Rhodospirillum rubum
purple, non-sulfur bacteria, bacteriochlorophyll captures light energy, photosynthesize without producing oxygen. Colorless in high oxygen levels and purple-red when oxygen levels are low.
Doman: Bacteria
Shape: spirillum
Movement: Motile-flagellum
Metabolic features: photoautotroph (can also perform fermentation)
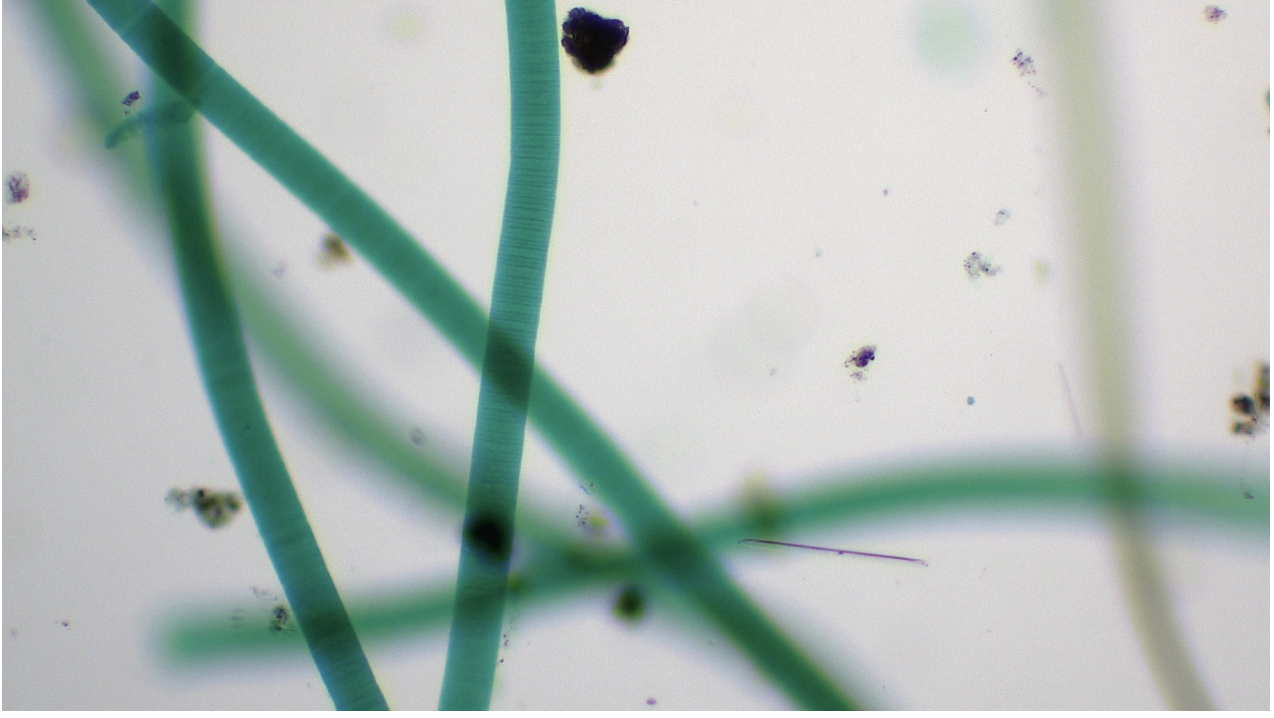
Oscillatoria
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Cyanobacteria
Shape: filament/bacillus
Movement: oscillating/whip-like motion
Metabolic: Autotrophic
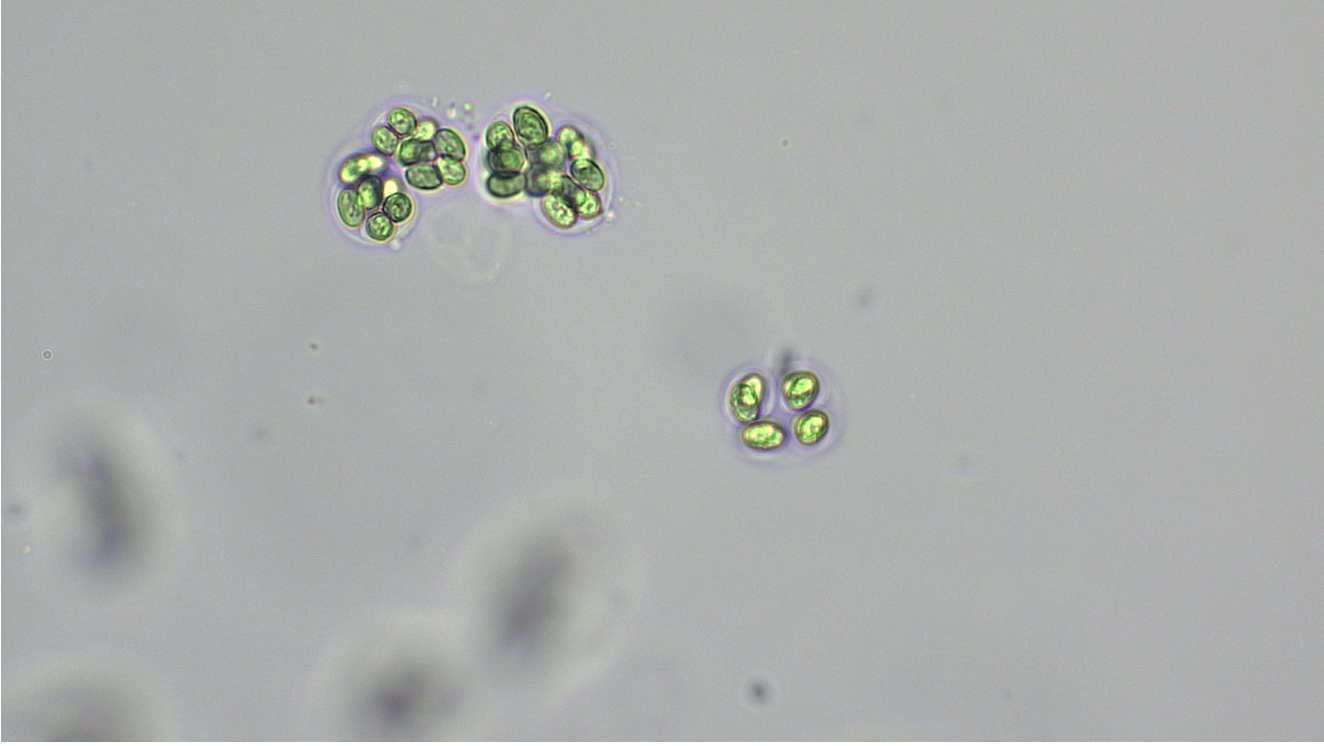
Gloeocapsa
cells held together by secreted gelatinous mixture
Domain: Bacteria
Phylum: Cyanobacteria
Shape: Coccus
Movement: non-motile
Metabolic: Autotrophic
Form colonies
Anabaena
Contains heterocysts
Domain: Bacteria
Shape: Coccus but forms filaments
Movement: non-motile
Metabolic features: autotrophic
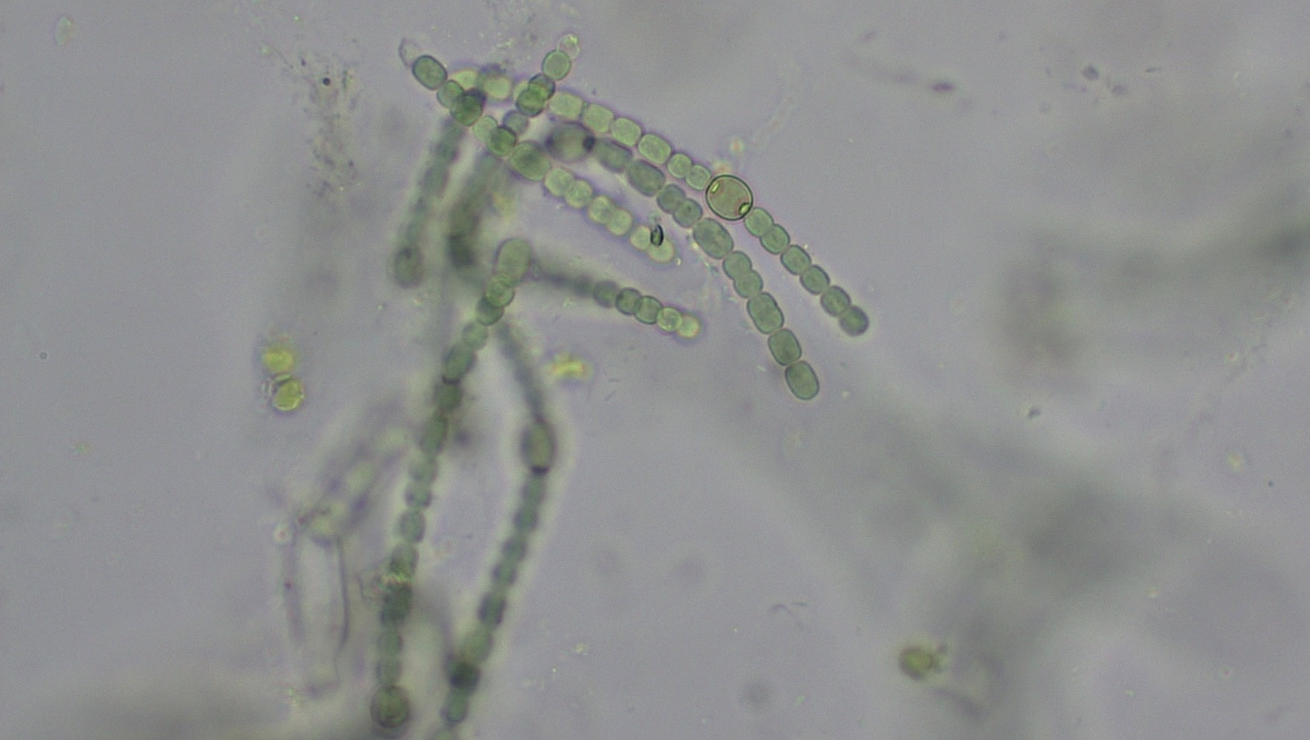
Heterocysts
Enlarged cells that have thickened cell walls and fix nitrogen
Extremophile
an organism that can survive and thrive in extreme environmental conditions
Halobacterium salinarum
Aerobic heterotrophs when oxygen is present, but phototrophs most of the time due to lack of oxygen. Use bacteriorhodopsin to generate ATP. Halophile
Domain: Archaea
Shape: Bacillus
Movement: Motile-flagellum
Metabolic features: heterotrophic in oxygen rich environments, phototrophic in low oxygen environments
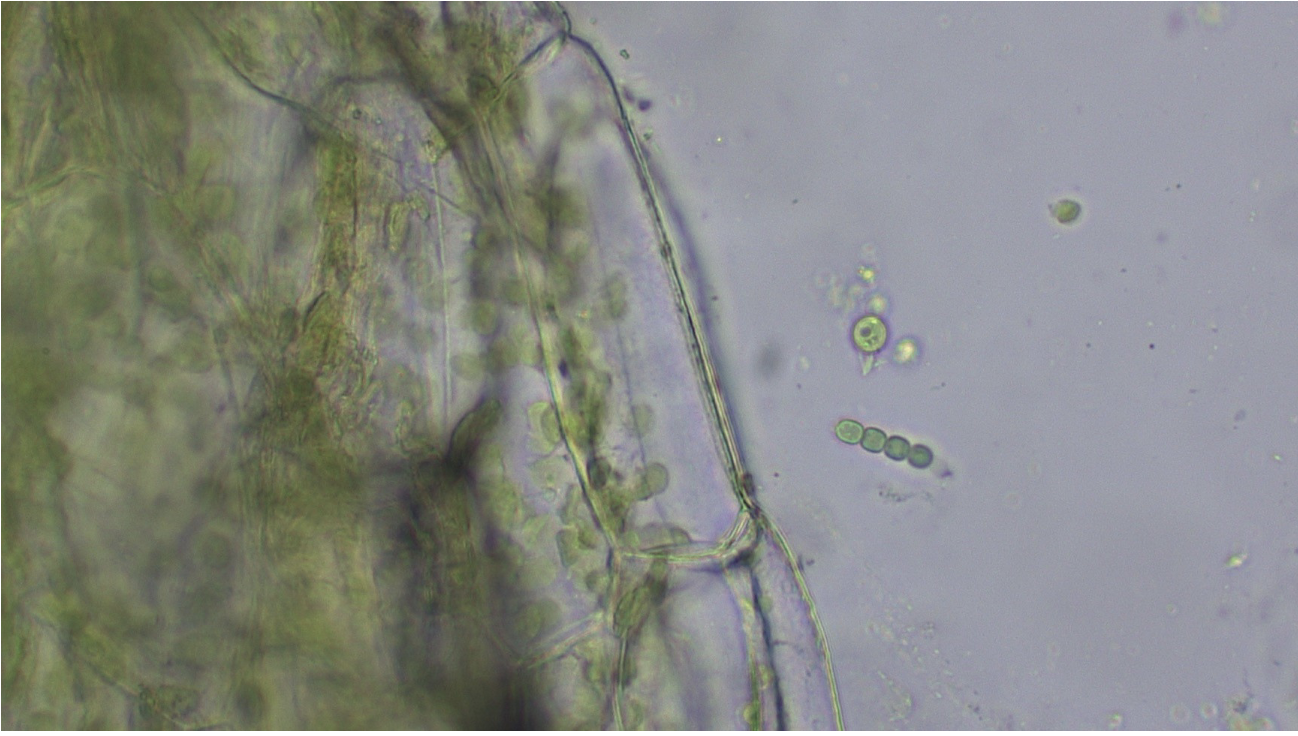
Azolla and Anabaena
symbiotic mutualistic relationship
One is a plant, photosynthetic other is a bacteria also photosynthetic
(Plant) provides an enclosed environment for (bacteria) within its leaves. In return, (bacteria) sequesters nitrogen directly from the atmosphere which then becomes available for (plants)'s growth, freeing it from the soil that is needed by most other land plants for their nitrogen fertilization.