Physical Chemistry
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Exothermic
Chemical reaction in which heat energy is given out (temperature rises)
Endothermic
Chemical reaction in which heat energy is taken in (temperature lowers)
Displacement reaction example
Mg displacing Copper from Copper (II) Sulfate
Copper (II) Sulfate measured and transferred into a polystyrene cup
Initial temp of the solution is measured
Mg added and the maximum temp is measured and recorded
The temp rise is then calculated
Q =
m x c x Δt
Molar enthalpy change (ΔH)
Amount of energy transferred (Q) in kJ / Number of Moles
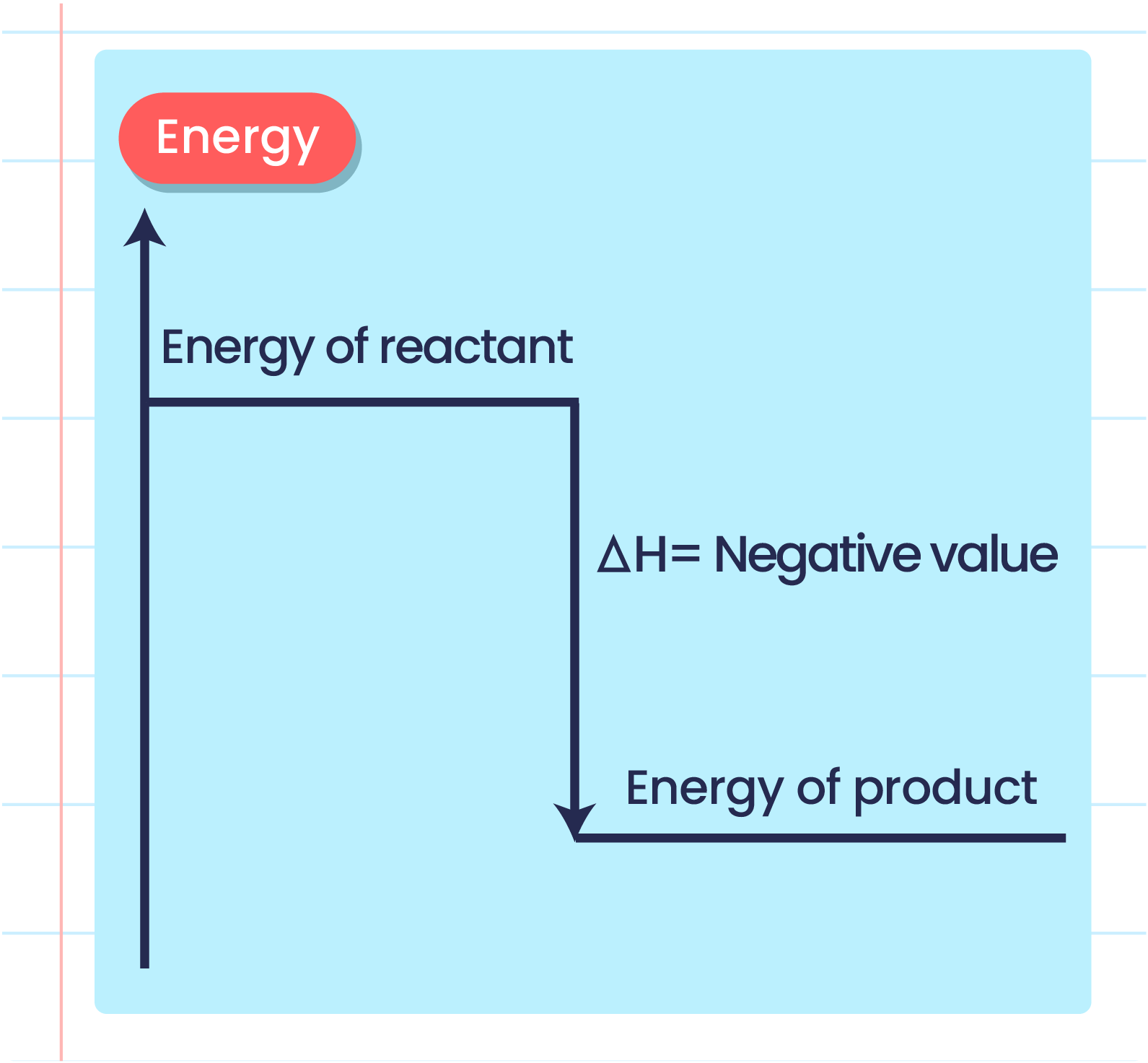
Exothermic energy level diagram
In an exothermic reaction reactants have more energy than the products
Energy is given out in the form of heat which warms the surroundings
ΔH is given as a negative sign because the reactants are losing energy

Endothermic energy level diagram
In an endothermic reaction, the reactants have less energy than the products.
Energy is taken in which cools the surroundings
ΔH is given as a positive sign because the reactants are gaining energy
Bond breaking is an ___________ process
Endothermic
Because breaking bonds requires energy
Bond making is an __________ process
Exothermic
Because energy is released when new bonds are made
Therefore when the energy needed to break the bonds is less than the energy released in making new bonds
The reaction is exothermic
Enthalpy change ΔH =
Energy needed to break all the bonds - Energy released to make all the new bonds
Rate of reaction =
Amount of reactant used or amount of product formed / time
Rate of reaction is measured by
How quickly reactantsa re used up or how quickly the products are formed.
Investigating the reaction between marble chips and HCl
As the marble chips react with the acid, CO2 is given off.
The purpose of the cotton wool is to allow CO2 to escape, but to stop any acid from spraying out
The mass of CO2 lost is measured at intervals.
Investigating the effects of change in surface area of solid between marble chips and HCl
This time the chips are larger (have a smaller surface area)
Since the surface area is smaller, the rate of reaction is less
Same amount of CO2 produced
Investigating the effects of changes in concentration of solutions between marble chips and HCl
This time the there is half the concentration of acid
The marble chips however must be in excess
The reaction with half the concentration of acid happens slower and produces half the amount of CO2
Investigating the effects of changes in temperature on the rate of a reaction
Same quantities of everything but at a higher temperature
Higher rate of reaction
Investigating the effects of the use of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction
Rate of reaction increases because an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy is provided by the catalyst
Increasing the surface area of a solid (particle collision theory)
More particles exposed
Higher frequency of collisions
Increased rate of reaction
Increasing the concentration of a solution or pressure of a gas (particle collision theory)
More particles in the same space
Higher frequency of collisions
Increased rate of reaction
Increasing the temperature
Particles have more KE
Higher frequency of collisions
Higher proportion of those collisions are successful because the collision energy is greater or equal to the Activation Energy
Increased rate of reaction
Catalyst definition
A catalyst is substance that increases the rate of a reaction, but is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction
How does a catalyst work?
Catalyst is not used up in a reaction
Speeds up a reaction by providing an alternative pathway with lower activation energy
Activation energy
The minimum amount of energy required for the reaction to be successful
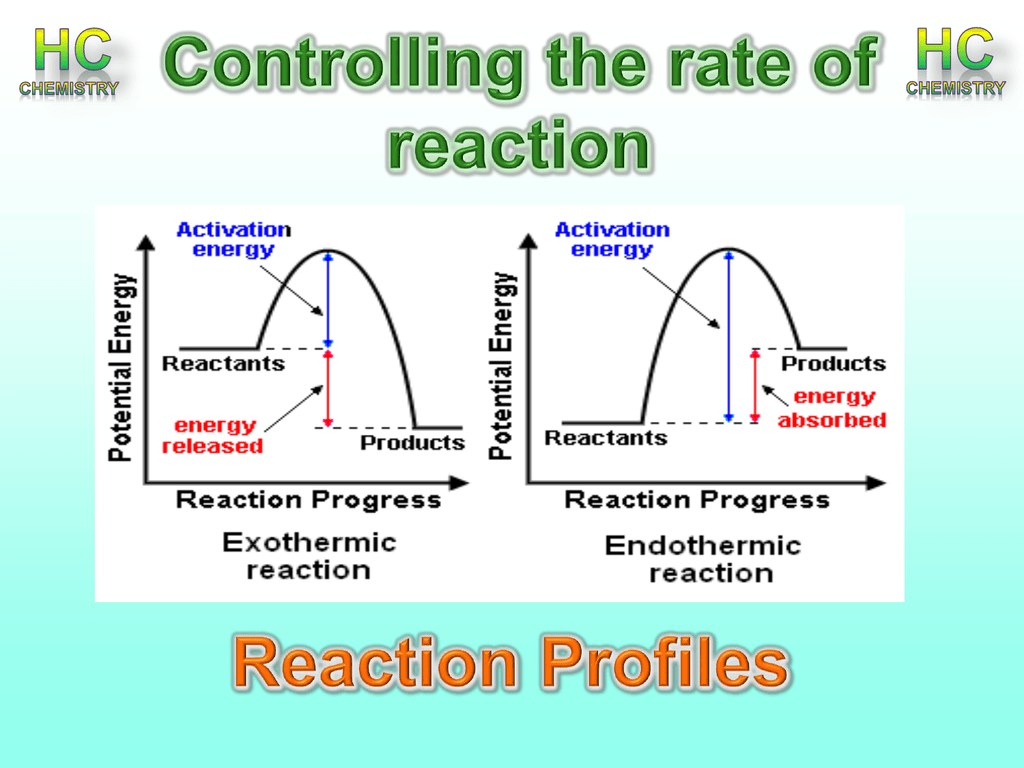
Reaction profile diagram
the larger the chips the….
smaller the surface area
practical question: surface area is bigger (smaller marble chips)
faster rate of reaction
same amount of CO2 produced
practical question: solution concentration is half, marble chips are in excess
slower rate of reaction
half the amount of CO2 produced
practical question: catalytic decomposition result if substance is not a catalyst (liver is a very good catalyst)
no bubbles of oxygen produced
⇌
reversible reaction symbol
hydrated copper sulfate colour
blue
anhydrous copper sulfate colour
white
A reversible reaction can only reach dynamic equilibrium
In a sealed container
Characteristics of a reaction at dynamic equilibrium
forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate
concentrations of reactants and products remain constant
Why does a catalyst not affect the position of equilibrium in a reversible reaction
A catalyst speeds up both the forward and the backward reactions.
Dynamic equilibrium is reached quicker, therefore the addition of a catalyst does not affect the position of equilibrium.
Equilibrium shift when the temperature is increased
Moves in the endothermic reaction
Equilibrium shift when pressure is increased
To the side with fewer molecules