Phenols
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are phenols?
Organic compounds. Containing OH functional group directly bonded to aromatic ring
What are the differences between alcohols and phenols?
Phenols are less soluble in water than other alcohols due to the presence of the non polar benzene ring
When dissolved in water, phenols partially dissociate to form phenoxide ion (O- attached to benzene ring)
More acidic than alcohols but less acidic than COOH - higher Ka than lcohols but lower Ka than COOH
What is the difference between reactions of ethanol, phenol and COOH? What does this tell us bout what type of acid they are?
ethanol does not react with Sodium hydroxide (a strong base) or sodium carbonate (a weak base)
Phenols reacts with strong bases e.g (NaOH)
COOH reacts with both strong and weak acid
Therefore phenols weak acid COOH strong acid
How can you distinguish between a phenol and a COOH?
React with sodium carbonate, carboxylic acid will react to produce CO2 and phenol won’t
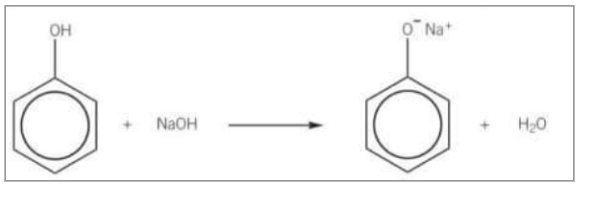
What does phenol produce when it reacts with sodium hydroxide?
Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide to form a salt (sodium phenoxide) and water in a neutralisation reaction
True or false phenols undergo electrophilic substitution? Expand (In relation to benzene)
True they are aromatic
They undergo electrophilic substitutions more readily than benzene and under milder conditions
Explain the bromination of phenol?
Phenol reacts with an aq solution of bromine (bromine water) to form white precipitate (2,4,6 tribromophenol) (plus HBr)
This reaction decolourises bromine water
Reaction is carried out at room temp and does not require a halogen carrier

Describe the nitration of phenol
Phenol reacts with dilute nitric acid at room temp to form a mixture of 2-nitro phenol and 4-nitro phenol (+water)

What is the difference between the reactions of phenol and the reactions of benzene?
Bromine and nitric acid react more readily with phenol than benzene - phenol nitrated with dilute nitric acid rather than concentrated nitric and sulphuric acid (like benzene)
Why is phenol more reactive than benzene?
caused by the lone pair of electrons from oxygen p-orbital f the -OH group being donated into the Pi system of phenol
Electron density of benzene ring in phenol increases + attracted electrophiles more strongly than benzene. = aromatic ring in phenol more susceptible to attack from electrophiles than benzene
For bromination, electron density in phenol ring is sufficient to polarise bromine molecules so no halogen carrier catalyst required
What groups are activators - go to the 2,4,6 directing groups? (ortha and para directing)
NH2
OH
OR
R
F/Cl/Br/I
What groups are deactivators - go to 3,5 directing groups? (meta directing)
NO2
CN
SO3H
CHO
COOH
NR3
True or false bromine reacts with phenylamine in the same way it reacts with phenol?
True

True or false bromine reacts readily with nitrobenzene - expand
False
Reacts slowly - requiring halogen carrier and high temp because benzene ring less susceptible to electrophilic substitution than benzene
NO2 group deactivates aromatic ring = reacts less readily with electrophiles + directs second substituent to position 3
True or false 2,4,6 are activating groups and 3,5 are deactivating groups
True hello my name is KHUSHIII haahahahha
Are the halogens activating groups?
no
they are 2,4,6 directing but not activating