BN Exam 3
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Attention
working memory (what you focus on). cognitive brain mechanism that enables one to process relevant inputs, thoughts, or actions while ignoring irrelevant or distracting ones
covert mechanism
operate without overt adjustments of sensory structures
voluntary “endogenous” attention
intentionally attending to something, selective attention
reflexive “exogenous” attention
something catches our attention (ex a sensory event)
covert attention
VF location where the gaze is separate from the location where one is paying attention
cocktail party effect
our ability to focus on 1 conversation in a loud confusing party atmosphere. Requires selective attention (tested with dichotic listening tasks
Generalized model of attention
deciding what to put our attention towards. Has two stages and a selector period. It involves receiving input from all your senses (stage 1), filtering out what is most important (selector) and then only acting on a small portion of that information (stage 2).
early selection theories
input is selected early on before full perceptual analysis, sensory input selected for stage 2 early.
late selection theories
sensory input is selected after lots of information processing/ encoding happens in stage 1, until then all information is processed equally
feature integration
requires attention and must be performed serially (like how you cant text and drive)
feature detection
preattentive perceptual process, can be parallel/ automatically done and is able to be learned over time (driving and reading street signs, reading is automatic)
feature pop out
tests with an obvious outlier (all slanted lines and one vertical is more automatically seen than a variety or horizontal and vertical but only one intersecting cross)
stroop effect
learned automaticity, abilities that used to take attention can become automatic with practice (reading is automatic, and can interfere with performance on other perceptual distinctions like naming colours of words)
dichotomous listening task
different sounds played in each ear and being instructed to listen to a specific ear (covert attention). Condition 1 attends to sound in one ear and ignores the other, condition 2 reverses and focuses on the opposite ear, this process is measured with ERPs
Auditory N1
sensory evoked wave manipulated by covert attention. the ERP that was larger in amp when stimuli was attended vs ignored
visual dichotomy task
fixate in the center and attend to stimuli in either RVF or LVF and ignore whatever is presented on the opposite field
Visual P1
sensory evoked wave manipulated by covert attention, V2 cortex, shows on ERP that larger amp happens when stimuli is attended vs ignored
reflexive attention
being automatically attracted towards a location/stimuli that follows a reflexive cue of 250msec
Basil ganglia
motor learning, developing new skills & capabilities, sequencing movements, preparing movements, memory guided movement, knowing stereotypical behavior in response to drives. It chooses the appropriate response for a given moment (most active/stimulated movement)
striatum
has ventral and dorsal areas. The dorsal area has the primary pathways that go to the SNC and LGP. The ventral part receives inhibition the pathways and sends signals back to the premotor cortex
Globus pallidus
2 sub portions, the indirect circuit aka LGP which inhibits the STN, and the direct circuit directly to the MGP which inhibits the ventrolateral thalamus
Subthalamic nucleus/ STN
inhibited by LGP. excites MGP (medial globus pallidus) and SNR (substantia nigra). Part of the indirect circuit.
Substantia nigra
2 portions: SNR (pars reticulata) and SNC (pars compacta). The SNR inhibits the thalamus, and the SNC sends efferent signals to the dorsal striatum.
disinhibition
two inhibiting things, stopping a stopper so an excitatory thing can fire
direct circuit
only two connections to go through, SP GABA to SNR or MGP are inhibiting thalamocortical neurons in the ventrolateral thalamus
indirect circuit
inhibiting the thalamus rather than excites it. Starts in LGP, then STN, which excites MGP and SNR to inhibit the ventrolateral thalamus
Ballistic dyskinesias
explosive and disruptive movements in extremities with little to no control over movements. Comes from STN lesions, indirect circuit does not shutdown possible movements.
huntington’s disease
loss of striatal neurons that use GABA and Enkephalins, inhibit projection is reduced. Reduced function of indirect circuit, which causes less inhibition of stimulating to the thalamus. This causes jerky, irregular movements of 1+ body parts due to inc cerebral cortex (+ some cognitive deficits)
Parkinson’s disease
loss of dopamine-producing neurons in substantia nigra causes a broken feedback loop that effects both circuits because there is no more exciting of circuits. Less activity in premotor cortex and therefore less movements. This results in trouble starting/stopping voluntary movement, tremors at rest, stooped posture, rigidity, and poor balance.
Tremors
can happen in different areas, inc thalamus activity from activation but no planned movements associated to them. This can be stopped with a brain surgery placing electrical stimulation (wire) that will stimulate the affected area of the brain and stop this movement as they develop.
Cerebellum
needed for motor execution, has more cells than whole nervous system. It receives info from somatosensory, vestibular, visual, and auditory areas. Issues with this appear as failing a sobriety test
vestibulocerebellum
the input/output from brainstem vestibular nuclei. Coordinates eye movements (hand-eye-coordination) and your ability to focus your eyes.
vestibular ocular reflex
your ability to keep eyes on something the rest of your body is movement
nystagmus
problem with the vestibulocerebellum. inability to fixate on an object, eyes drift away from what is being looked at and they will have to constantly refocus. Also comes with dec reflexes, posture, more nausea, and inability to respond to what they see.
spinocerebellum
handles precision of movements, ascending sensory inputs through the spinal cord. Controls descending motor outputs. Involves regulating the performance/ execution of movements
Hypermetria
damage to the spinocerebellum. issues with smooth motor movements, problems walking, may have a bow legged stance. cannot control execution of movements, goes into oscillation (cannot stop, or takes a long time very thoughtfully)
neocerebellum
control of voluntary movements (dance, sport, ect). Involves the planning of movements.
hypermetria of voluntary movements
problem with neocerebellum. clumsy, issues with sequencing gestures, problems with coordinating multiple body parts. Prolonged initiation of movements.
What is considered cognitive control
Applying mental effort, complex aspects of cognition with is in the frontal lobes. INC: executive function/ inhibitory control initiating/ceasing action , making predictions (planning schedule), working memory, switching tasks, goal-directed behavior.
preservation
previously learned/ planned action even if that system incorrect. Doing the same thing that you have always done. (this can happen with anything)
Wisconsin card sorting task
4 category options to sort cards, and a rule for sorting is chosen, and then changed at random. Normal people can adapt to new rules and figure out that they changed, people with damage to lateral prefrontal cortex persist the initial sorting rule even if the rule does not work.
Environmental dependence syndrome
behavioral actions triggered by a social or psychical situation or environment. Person feels compelled or obligated by the environment to carry out tasks that they routinely did throughout their life (very strong ingrained behaviors, often career related)
Cognitive estimation prediction problems
Comes from damage to lateral prefrontal cortex (i think..) When patients cannot use information to make judgements. They cannot understand perspectives, they’ll have a lack of understanding on price estimations, measuring estimates of unusual things, relative frequency of occurrence, or theory of mind
Novelty
event, situations, or action that has low probability of occurring given particular context. Flexibility is esesntial for novelty and new reactions that alter/ add old situations
P3a (Novelty P300)
higher responses to stronger stimuli, responds to oddball tasks. The more out of place a stimuli seems, the higher the signal/ response. Amplitude is correlated with volume of gray matter
Novelty deficits
caused by prefrontal deficits, alcohol, marijuana. Aging dec gray matter in frontal lobes.
goal directed behavior
everything we intentionally do. Relies on forming a plan of action and following steps towards the plan. The plan can be thought of as a hierarchy, and organizing this depends on your prefrontal lobe
prefrontal lesions and goal behaviors
problems filtering unnecessary behavior (keeping eye on the prize), having appropriate subgoal(s), trouble identifying a goal
switch cost
amount of time required to switch from 1 task to another. (automatic tasks are less time than tasks that take conscious)
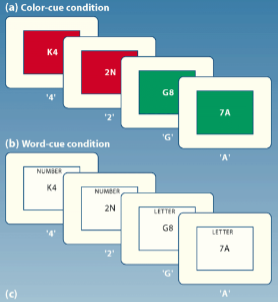
switch tasks
Measures differences in reaction time for switch trials vs no-switch trials. It looks at how we switch between things the involve different processing styles (like associating a colour with a rule vs the rule being written down)
Norman Shallice 1986 model of exec control
thought action is competitive and linked to schema control units. These receive input from multiple sources and actions can simultaneously activate multiple schema control units. These units need a control process to ensure the appropriate control unit is chosen
contention scheduling
passive type of control with direct competition of schema control units dictate which one is activated. Loudest voice wins/is activated
supervisory attentional system SAS
mechanism for favoring certain schema control units, favoritism may reflect situational demands or strong emphasis for specific goals. A psychological model of exec control
anterior cingulate cortex ACC
in charge of coordinating/ goal directing (this is the SAS). Present in anything motivational or prefrontal inc: painful/threatening situations, novel situations, difficult situations, error correction, and overcoming habitual responses.
error monitoring
an electrophysiological signal correlated with errors. ACC is found when this is present, and it is more apparent after making a mistake.
ERN event related negativity
negative going component of response locked ERP, reflects neuroelectric indices of action monitoring, peaks around 100ms after error. “oh shit” reaction (present in any error task and is bigger when the error is greater/higher stakes)
erikson flanker task
Task that measures ERN/ ACC. Has incompatible trials vs easy trials (where surrounding is dif than center vs the same, or rule is opposite center vs equal). harder when surrounding things are different than center, congruent vs incongruent trials. The ACC with having higher firing when first learning a rule (easy to incompat is higher firing than incompat to incompat)