Anatomy Midterm Review
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Which of the following increases base metabolic rate in the body
Glucagon
Thyroid Hormone
Secretin
Parathyroid Hormone
Thyroid Hormone
What type of information synapses in the nucleus gracilis?
proprioception from the legs
motor information to the trunk
pain from the arms
temperature of the hands
proprioception from the legs
Which one of the following would have the slowest conduction speed
myelinated large diameter
unmyelinated small diameter
myelinated small dynamiter
unmyelinated large diameter
unmyelinated small diameter
At which location do upper motor neurons synapse with lower motor neurons?
anterior horn of the spinal cord
thalamus
dorsal root ganglion
sympathetic chain
anterior horn of the spinal cord
The corticobulbar tract bilaterally innervate cranial nerves to head and neck in most cases, Which of the following is an exception to this rule
CNII
CN V
CN XII
CN X
CN XII
What endocrine gland receives its blood supply from suprarenal arteries?
ovary
adrenal
testicle
thymus
adrenal
Which of the following is NOT a direct target if anterior pituitary hormone?
mammary glands
thyroid gland
kidneys
adrenal cortex
kidneys
Which of the following is a space or fluid in which you would NOT expect to find a hormone?
duct
blood plasma
capillaries
interstitial fluid
duct
Which neurotransmitter is present at the somatic neuromuscular junction?
Adrenaline
glutamate
NE
ACh
ACh
On/near/within with structure would you look to find basilar artery?
in the transverse foramen of vertebrae
between the left and right frontal lobes
surface of the pons
next to pituitary gland
surface of the pons
Your stroke patient is having difficulty seeing. Which of the following is most likely to be occluded?
lateral cerebral
posterior cerebral
anterior cerebral
middle cerebral
posterior cerebral
Which of the following is true regarding grey matter in the PNS?
it is sometimes called a “tract”
it is composed of axons
it is found at the neuromuscular junction
it exits in ganglia
it exits in ganglia
Which of the following hormones would be expected to increase if you were studying all day for a test and skipped breakfast and lunch?
insulin
growth hormone
glucagon
calcitonin
glucagon
Which of the following is part of the CNS?
sensory receptors in the skin
frontal lobe
cranial nerve II
sympathetic ganglion
frontal lobe
Blood travelling to the circle of willis may travel through all of the following arteries EXCEPT for
brachiocephalic trunk
vertebral artery
basilar artery
external carotid artery
external carotid artery
Which of the following is a physiological function of a hormone released by the posterior pituitary?
egg and sperm maturation
increase in thyroid level
water retention
decrease in calcium levels
water retention
The _____ is the main link between the nervous system and the endocrine system, due to its control over secretory activities of the ___ gland
thalamus, thyroid
thalamus, pituitary
hypothalamus, pituitary
hypothalamus, thyroid
hypothalamus, pituitary
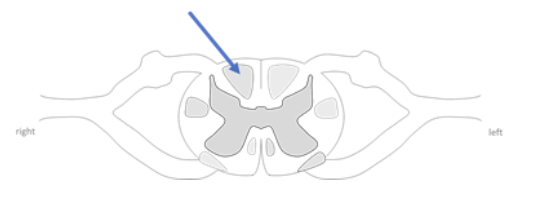
A lesion to the tract in the imagine would result in an impairment of which of the following
motor to trunk
motor to trunk + limbs
sensation of temperature
proprioception form the trunk + limbs
proprioception form the trunk + limbs
What types of information is contained by the ventral rami of the spinal nerve?
sensory + motor
motor, sensory and autonomic
just motor
autonomic
motor, sensory and autonomic
Where do upper motor neurones destined to innervate the limbs originate?
inferolateral portion of post central gyrus
inferolateral portion of pre central gyrus
superomedial portion of pre central gyrus
superomedial portion of post central gyrus
superomedial portion of pre central gyrus
Hypothalamic hormones travel via the primary plexus, the hypophyseal portal veins, and the secondary plexus, where they diffuse into the ____
thalamus
post pituitary
ant pituitary
neurohypophysis
anterior pituitary
Which hormone inhibits the secretion of FSH?
inhibin
progesterone
relaxin
luteinizing hormone
inhibin
Which of the following nerves would Not help with eating?
CN IX
CN VII
CN V
CN XI
CN XI
Which of the following best describes the term “dural sinus”
the adherence of dura and arachnoid mater
the space where CSF is produced
a separation between the periosteal and meningeal dural layers
a double layer of meningeal dura
a separation between the periosteal and meningeal dural layers
Symptoms of Graves disease include
decrease sweating, metabolism, regular HR
increase sweating, decreased metabolism, irregular HR
decrease in sweating, increase in metabolism, regular HR
increase in sweating, increase in metabolism irregular HR
increase in sweating, increase in metabolism irregular HR
Which of the following nerves innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye?
CN IV
CN VI
CN II
CN III
CN VI
A basilar skull fracture which injures the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone will directly affect release of which hormone?
somatostatin
calcitonin
ADH
aldosterone
ADH
Which structure separates the frontal and temporal lobe?
longitudinal fissure
lateral fissure
Pareto-occiptial sulcus
central sulcus
lateral fissure
Milk production in the mammary glands is initiated by
relaxin
inhibit
ADH
prolactin
prolactin
Where do fibres of the sympathetic nervous system exit the spinal cord?
brainstem region
cervicothoracic region
thoracolumbar region
lumbosacral region
thoracolumbar region
Two lobes of the thyopid are joined but a mass of tissue called?
infundibulum
parathyroid
follicle
isthmus
isthmus
Which of the following is an adrenal gland hormone that is essential for life?
NE
Aldosterone
Epinephrine
Insulin
aldosterone
Which of the following is not a cell found in your CNS?
astrocytes
Schwann
oligodendrogolia
Schwann
What is the primary function of the parathyroid gland?
to regulate calcium levels
to maintain homeostais
receive hormonal signals from the hypothalamus
to send hormonal signals to other endocrine glands
to regulate calcium levels
Which is not a cell type of the pancreatic islets?
beta
F cells
acinar
delta
acinar
Which endocrine gland arises from ectoderm?
adrenal medulla
pancreas
thymus
thyroid
adrenal medulla
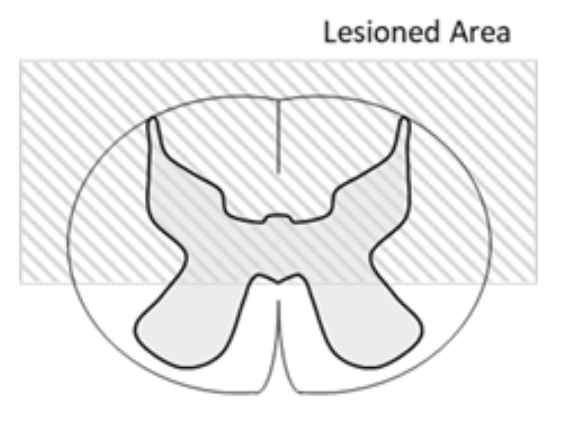
A 30 year old male experienced a spinal cord lesion at the level of L1. The posterior half of the spinal cord has been damaged (image), though the anterior portion remains intact. Which of the following symptoms would u expect to see?
bilateral loss of motor. to anterior trunk
loss of proprioception in legs
bilateral loss of motor to arms
loss of temperature sensation in feet
loss of proprioception in legs
Which endocrine gland mimics the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system?
hypothalamus
adrenal cortex
adrenal medulla
parathyroid
adrenal medulla
Which pathway would you expect the following neuron to belong to? 2 neuron pathway synapsing at a ganglion located in the PNS and sensitivity to both ACh and NE
somatic sensory
parasympathetic
sympathetic
somatic motor
sympathetic
What is the function of the hypophyseal portal veins?
supply blood to the primary plexus capillaries in the base of the hypothalamus
carry hypothalamic hormones to the anterior pituitary
receiver anterior pituitary hormones as they are secreted
receive posterior pituitary hormones via the plexus of the infundibular process
carry hypothalamic hormones to the anterior pituitary
A surplus of insulin resulting in the down regulation of insulin receptors is found in
Type 1 diabetes
kidney disease
Type 2 diabetes
diabetes mellitus
Type 2 diabetes
Flexibility of the pubic symphysis is increased during pregnancy by
estrogen
inhibin
relaxin
progesterone
relaxin
Which of the following hormones has the ovaries and testes as its target tissue?
inhibit
relaxin
progesterone
FSH
FSH
Which of the following pairs are INCORRECTLY matched
glucagon secreted by alpha cells
insulin secreted by beta cells
somatostatin screwed by delta cells
pancreatic polypeptide, secreted by C cells
pancreatic polypeptide, secreted by C cells
In which cerebella lobe would you find the primary somatosensory cortex?
occipital
parietal
frontal
temporal
parietal
Which of the following is true regarding the DCML spinal tract?
2 neuron pathway
provides ipsilateral innervation
carries motor information
fibres decussate at the medulla
fibres decussate at the medulla
Which spinal tract carries information about temperature?
anterior spinothalamic
lateral spinothalamic
anterior corticospinal
lateral corticpsinal
lateral spinothalamic
In which structure do fibres of the anterior corticospinal tract decussate?
medulla
thalamus
spinal cord
they don’t decussate
spinal cord
In which lobe does the DCML originate?
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
parietal
Your patient is unable to taste anything on the anterior 2/3 on their tongue. Which nerve is most likely damaged?
hypoglossal
glossopharyngeal
trigeminal
facial
facial
Which nerve is also known as cranial nerve X?
vestibulocochlear
vagus
accessory
abducens
vagus
Which of the following nerves carries only motor information
olfactory
trigeminal
hypoglossal
facial
hypoglossal
Which structure creates CSF?
arachnoid granulations
choroid plexus
dural sinuses
cerebral aqueduct
choroid plexus
Your patient has a blockage in his left anterior cerebral artery. Which of the following is most likely to be impaired?
motor within left arm
sensation within right leg
sight in left eye
hearing in right ear
sensation within right leg
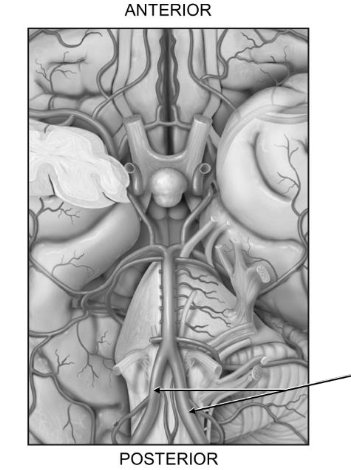
Which vessel is labeled in this diagram of the circle of willis?
vertebral
Which of the following cell types is responsible for myelinating axons in the PNS?
oligodendrocyte
Schwann cells
ependymal
astrocytes
Schwann cells
At what spinal level will you find conus medullaris?
T4- 5
T11-12
L1-2
L4-5
L1-2
Which of the following features would help you distinguish between a somatic vs autonomic motor neuron?
myelinated axon
presence of acetylcholine
synapse with a muscle cell
origin at a peripheral ganglion
origin at a peripheral ganglion
Which neurotransmitter is present at autonomic ganglia?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Epinephrine (E)
Norepinephrine (NE)
Dopamine (D)
Acetylcholine (ACh)Wh
Which of the following structures can be found in grey matter within the spinal cord?
longitudinal motor tracts
myelin
sensory bodies
glial cells
glial cells
Your patient just received spinal anesthesia prior to surgery. Which structure was the last to be pierced by the anesthetist before they administered the drug?
pia mater
epidural fat
subcutaneous fat
ligamentum flavum
epidural fat