Genetic Processes: Mendelian Genetics
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours) ⚠️ for some reason, the superscripts sometimes appear as subscripts, pretend they're superscripts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Gregor Mendel
the father of genetics
Austrian Botanist Monk
Mendel conducted experiments on what and when?
conducted experiments regarding the traits of pea plants, before knowledge of DNA and chromosomes
Monohybrid Cross
a cross designed to study the inheritence of only a single trait
true-breeding
purebred, refers to offspring that always carry the same trait as the parent
Factors
old term used by Mendel, replaced by “allele”
Allele
a form of a gene, each cell has two per gene
Homozygous individual
carries two of the same alleles
Heterozygous individual
carries two different alleles
Genotype
genetic make-up of an individual
Phenotype
an individual’s physical appearance with respect to a specific characteristic
Punnett Square
diagram that shows all possible allele combinations from the parents, used to determine the probability of an offspring’s genotype
Mendel originally thought that crossing true-breeding purple pea flowers with true-breeding white flowers would produce ____ coloured flowers (a blend). He was _____, instead, ___% produced ______ coloured flowers.
lavender, wrong, 100, purple
#1 Principle of Dominance
there are dominant and recessive traits, in which alleles dominate over others
if two homozygous individuals are crossed, all the offspring will be identical for phenotype and genotype
In Mendel’s 2nd experiment, he allowed plants of the F1 generation to ________. The resulting F2 generation always had the ________ ratio of ______% purple _______% white. The _____ ratio was 25% ____, 25% ____, and 50%____.
self/auto-pollinate, phenotype, 75%, 25%, genotype PP, pp, Pp
#2 Principle of Segregation
organisms inherit two copies of genes, one from each parent
organisms donate only one copy of each gene to their gametes due the genes being separated in meiosis
Sex determination in humans (% chances)
50% chance male and 50% chance female
Sex determination in other animals
birds - mother’s chromosomes determine sex
turtles - temperature determines sex
ants - fertilized=female
clownfish - age determines/changes sex
certain lizards - sex is always female
How to determine the probability that a couple will have 𝑥 amount of boys/girls in a row?
½ to the power of 𝑥
Test Cross
a cross used to determine the genotype of an individual expressing a dominant trait
Why are test crosses necessary? How do they work?
by appearance alone, it’s impossible to know if the individual is showing a homozygous or heterozygous dominant trait
to do a test cross, the unknown genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive genotype
the offspring are then examined to determine the unknown genotype (what matches the phenotype of the offspring best)
In Mendel’s 3rd experiment, he wanted to know if inheritance of a characteristic influenced the inheritance of another characteristic. The characteristics he experimented with were seed colour (____&____) , and seed shape (_____&______)
Yellow (Y), Green (y), Round (R), Wrinkled (r)
#3 Law of Independent Assortment
if genes are located on separate chromosomes, they will be inherited independently of one another
during meisosis I, chromosomes align and separate independently of those from other tetrads (no mixing of characteristics)
this allows for formation of gametes which would otherwise be impossible/not present
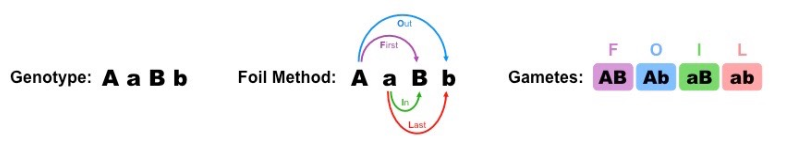
Dihybrid Cross
a type of cross involving two pairs of heterozygous alleles
how do you use a punnett square for dihybrid crosses
always use FOIL first to determine the gametes
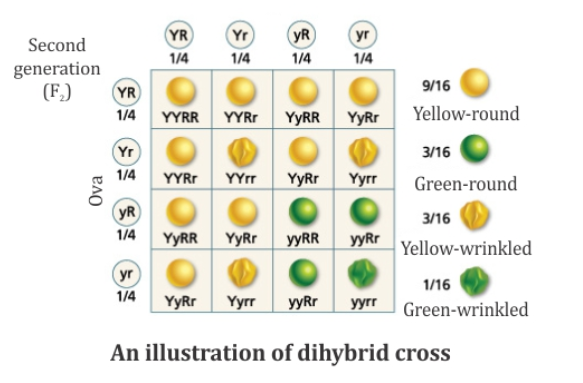
a dihybrid cross of the F1 generation produces how many different genotypes in the F2 generation?
9
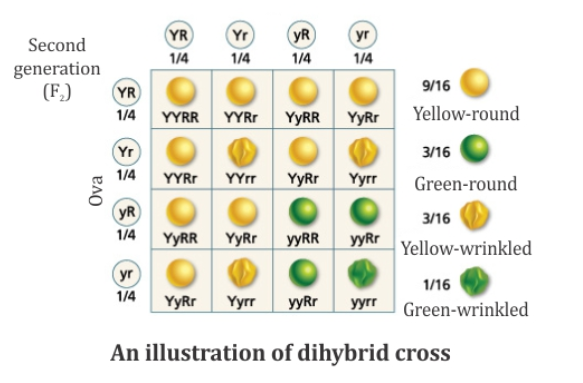
what is the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation?
9:3:3:1
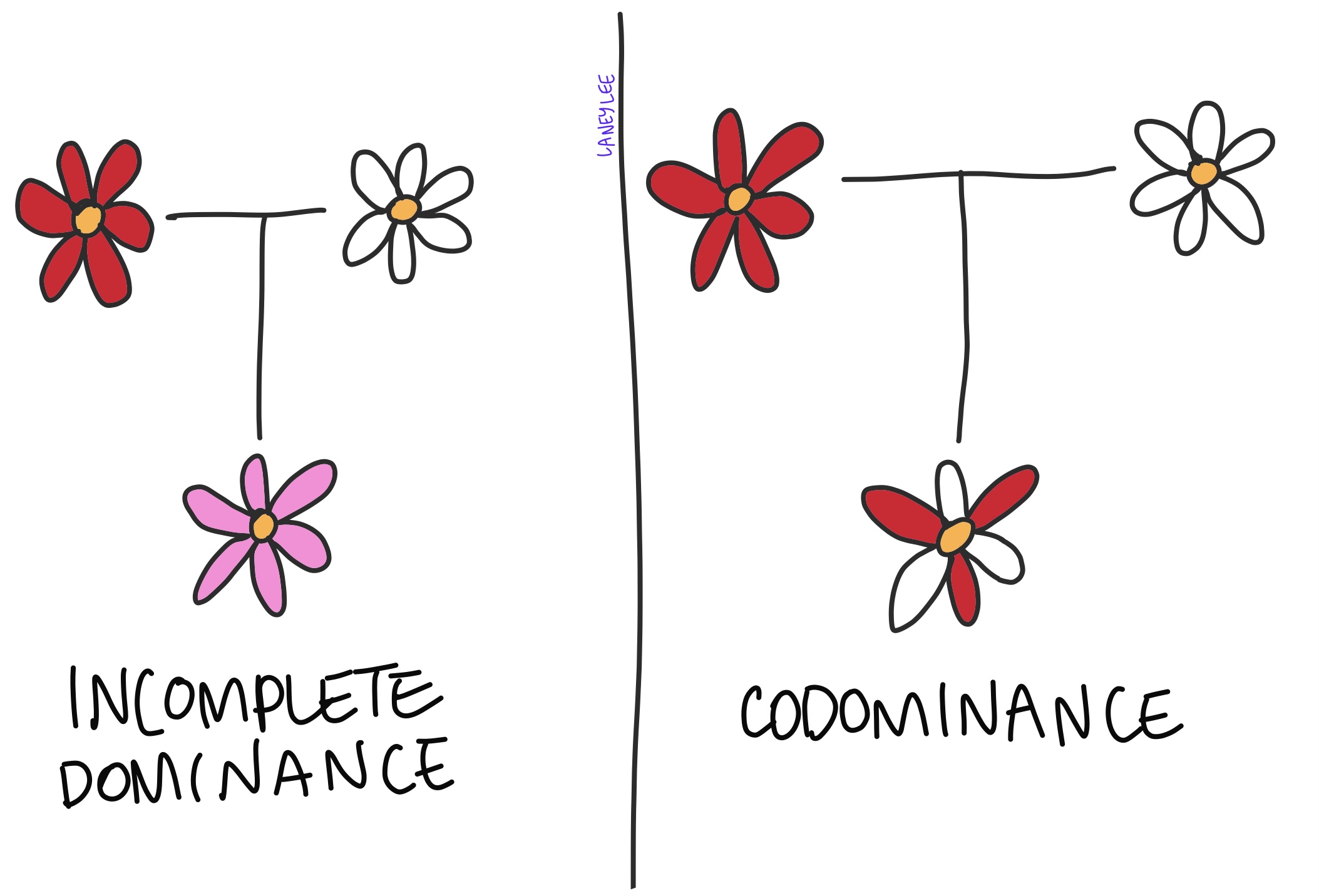
Incomplete Dominance
a situation where allele will determine the phenotype regardless of the presence of another allele
⇨ blend of two homozygous phenotypes
examples of organisms and characteristics that use the pattern of incomplete dominance
roses, curly hair, skin colour, fur colour of certain animals (ex: horses)
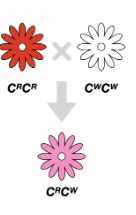
in the red and white flower example, how are incomplete dominance allele written?
colour indicated by superscript: CR and CW
if a red and white snapdragon flower (incomplete dominance) are crossed, what is the resulting F1 generation’s genotype and phenotype?
100% CRCW , meaning 100% pink flowers
Lethal Alleles
alleles that cause death at the embryonic stage
if two creeper (Cc) chickens mate, what are their phenotypes?
25% lethal, 25% normal, 50% creeper
if a creeper and a normal chicken mate, what are their phenotypes? Do lethal alleles cause death in any embryo? why?
50% normal, 50% creeper
because only one lethal allele is present, it cannot be homozygous therefore it doesn’t cause death
Multiple Alleles
existence of 3 or more alleles for the same characteristic (ex: blood type)
What are the 3 alleles possible for blood types?
IA (dominant), IB (dominant), ii (recessive)
What do the blood type alleles refer to?
the types of antigens (proteins) found in red blood cells.
⇨ type A has antigen A, type B has antigen B, type AB has both A and B antigens, and type O has no antigens
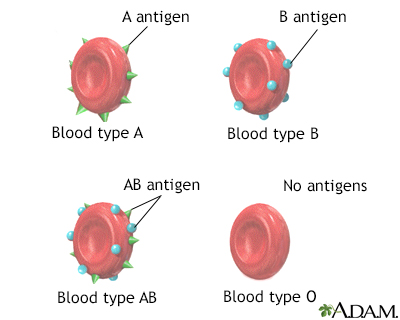
What is the universal donor blood type?
type O
What is the universal blood recipient?
type AB
What blood type is the most common in Canada? What type is the least common?
O is most common, AB is the least common
Co-dominance
phenomenon where the phenotypes of two different alleles are displayed simultaneously.
Incomplete Dominance vs Co-dominance
incomplete dominance results in a mix of traits, while codominance results in both traits being expressed separately
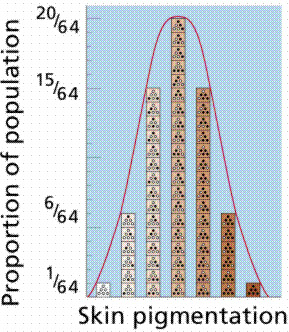
Polygenic Inheritence
Characteristics that are expressed by multiple genes
ex: eye colour, skin colour