Computer Science - OCR GCSE - 1.2.2 Secondary Storage
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is meant by secondary storage?
A non-volatile storage that generally holds much more data than main memory as permanent storage and is relatively inexpensive per MB. It is outside the CPU and is under its control.
Explain why is Secondary Storage necessary:
To store data - Long term/Permanent
Larger capacity
Some forms of secondary storage are portable
How many bits in a Byte?
8
How many bytes in a Kilobyte?
1000 (1024)
How many bytes in a Megabyte?
1,000,000
How many Megabytes in a Gigabytes:
1000
How many Megabytes in a Gigabyte?
1,000,000
State the names of three types of storage devices:
Solid State Drives
Optical Devices
Magnetic Devices
Describe what is meant by a magnetic storage device:
A storage device which uses magnetic states (north/south polarization) to store data in binary form
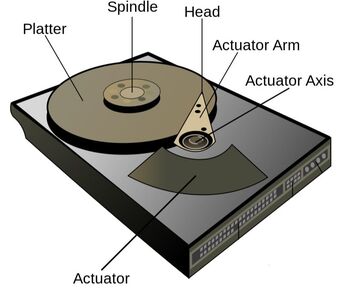
Describe how this works:
The platter spins at 7200RPM
A read-write head moves over a surface of a rotating disk (platter)
The magnetic surface of the disk is magnetised - using north/south polarisation
The data is saved to the disk using tracks and sectors
What is a hard disk?
A Hard Disk drive is a type of secondary storage with moving parts.
It can have access speeds of up to 10,000 revolutions per minute and can transfer data at a rate of 50–120 megabytes per second using latest interface technology.
It can be affected by heat and magnetic fields and is therefore normally kept inside a sealed enclosure.
Describe how optical media is read from and written to:
A laser is used to scan the surface of the disk. A laser creates pits and lands on the surface of the disk.
Pits reflect less light than lands therefore allowing data in the binary form to be stored.
Describe how solid state media stores data:
Data stored in electrical signals in microchips
Solid state media can also be known as?
Flash memory
Characteristics of Solid State Memory/ Flash Memory:
Has no moving parts
Has a high access speed, but not as fast as RAM
Less likely to fail than optical media
A way to make additional storage available to a computer
Describe the meaning of each of the criteria used to determine the suitability of storage media:
Capacity - Amount of Bytes it can contain
Speed - The data transfer speed between the device and RAM (measured in bps) or the access time (how fast the CPU can locate the file on the storage medium - measured in milliseconds)
Portability - How easy it is to use the storage medium to transfer data from one computer to another, or one location to another
Durability - How easily it gets damaged -can also be described as how ‘robust’ the storage medium is in response to the physical environment (e.g. movement, extreme temperatures, underwater etc.)
Reliability - How long it will last with repeated use
Cost - The price per byte
Rank the best for these criteria:
Capacity | Speed | Portability | Durability | Reliability | Cost |
Magnetic | Solid State | Solid State | Solid State | Solid State | Optical |
Why does internal solid state media have a faster access speed than an internal hard disk?
They have no moving parts as they store data electronically
Why do external portable magnetic and solid state media have a much slower access speed than their internal counterparts?
Since they are not directly connected to the device, they take longer to access data externally as they need to connect to the device.