Pathology Final Exam - New Information Diagram | doestn include breast skin reproductive and eyes and ears
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Direct components of the endocrine system
Pituitary
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Adrenal
Indirect components of the endocrine system
Gonads
Pancreas
Intestine
Function of the endocrine system
Hormone production
Endocrine Effect
Indirect action
Hormones secreted into bloodstream
Paracrine Effect
Direct action
Hormones secreted into tissues
Hyperfunction
Overproducing hormones
Hypofunction
Underproducing hormones
Hyperplasia
Increased cellular growth -> gland enlargement
Neoplasia
Tumor formation - benign or malignant
Location of pituitary gland
Sella turcica at base of skull
Hormones produced by pituitary gland
Growth hormone
Prolactin
ACTH
Gonadotropins
TSH
Oxytocin
ADH
Growth Hormone
Bone and cartilage growth
Metabolism
Prolactin
Lactation
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Cortisol - stress response + metabolism
Androgens - sex hormones + metabolism
Gonadotropins
LH - sperm + ovulation
FSH - sperm + menstrual cycle
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Acts on thyroid gland
Oxytocin
Labor and childbirth
Lactation
Bonding hormone
Antiduiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Water + sodium levels
Kidney function
BP
Pituitary Hyperfunction
Due to neoplasia
Prolactinomas
Most common pituitary adenoma
Too much prolactin
Men: impotence
Women: amenorrhea + infertility
Somatotropic Adenomas
Too much growth hormone
Children: gigantism
Adult: acromegaly -> enlargement of internal organs and extremities
Corticotropic Adenomas
Too much ACTH
Panhypopituitarism
Lack of all pituitary hormones
Diabetes Insipidus
Lack of ADH
Euthyroidism
Normally functioning thyroid
Location + cells that make up the thyroid gland
Neck
Follicular cells
C-Cells
Follicular Cells
Produce T3 + T4
Regulate metabolism
C-Cells
Produce Calcitonin
Regulate calcium levels
Thyroid Hyperfunction
Excessive thyroid hormones
Graves disease
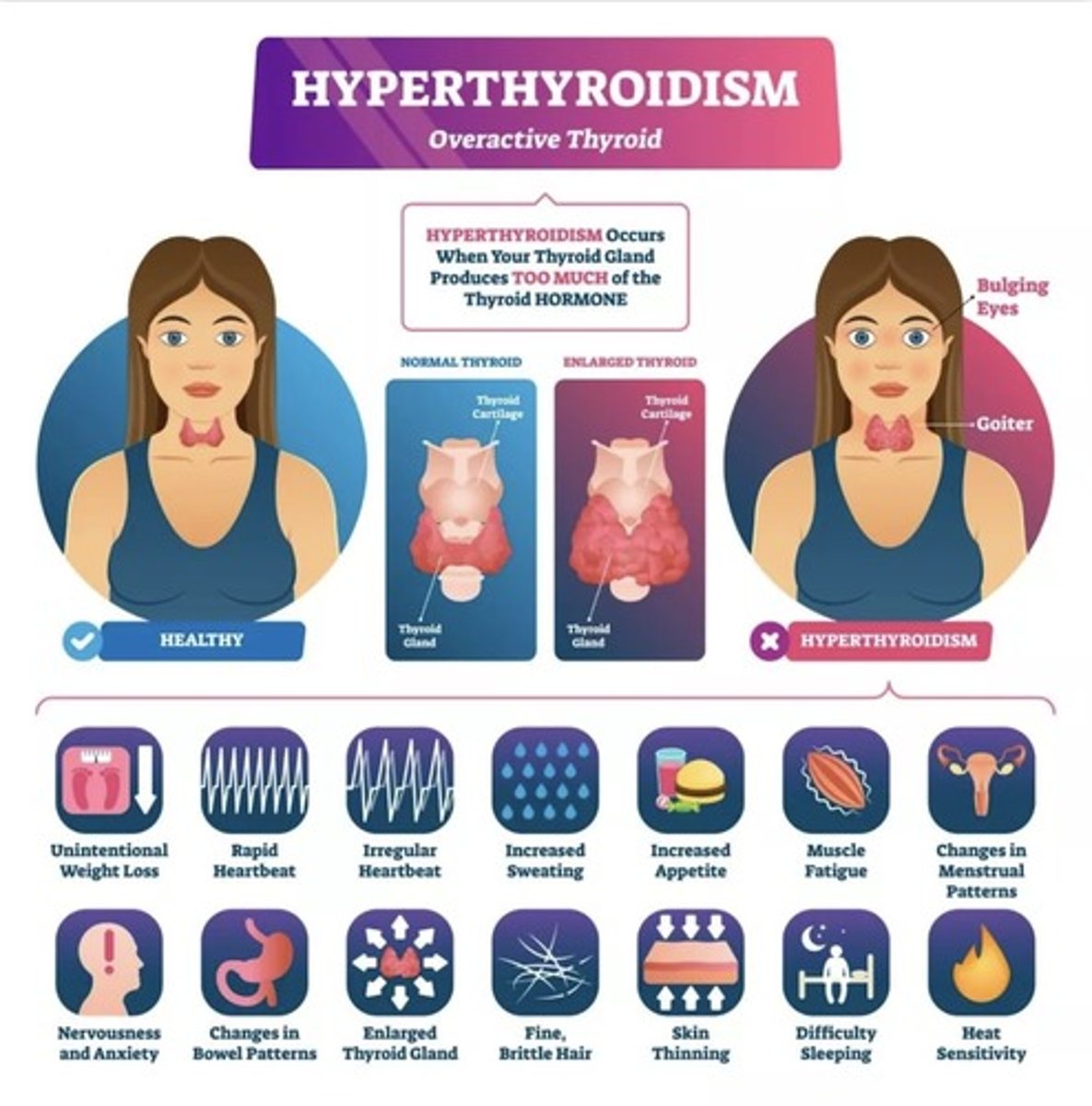
Thyroid Hypofunction
Lack of thyroid hormones
Hashimoto's disease, iodine deficiency
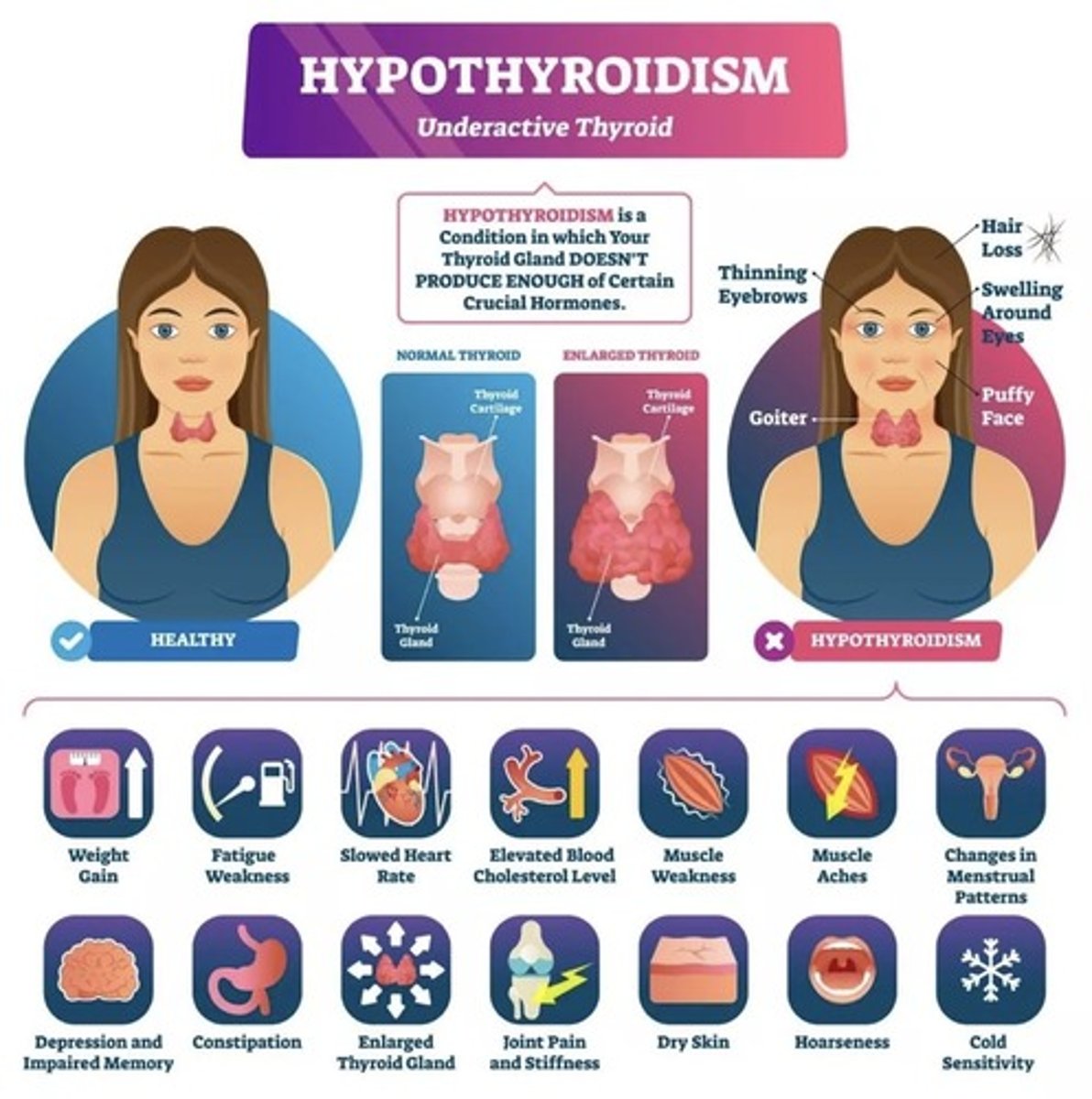
Thyroid Adenoma
Benign
May cause noticeable enlargement
Palpable mass
"Cold nodules" seen
Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma
Malignant
Affects follicular cells
Thyroid Follicular Carcinoma
Malignant
Affects follicular cells
Thyroid Anaplastic Carcinoma
Malignant
Affects follicular cells
Thyroid Medullary Carcinoma
Malignant
Affects C-Cells
Location of parathyroid glands
Behind thyroid
Usually 4 total
Hormones produced by parathyroid glands
Parathyroid hormone
Regulate calcium and phosphate levels
Primary Parathyroid Hyperfunction
Too much parathyroid hormone
Due to hyperplasia
Increased calcium levels
Decreased phosphate levels

Secondary Parathyroid Hyperfunction
Too much parathyroid hormone
Due to chronic renal failure
Decreased calcium levels
Decreased vitamin D levels
Parathyroid Hypofunction
Lack of parathyroid hormone
Due to agenesis or removal of glands
Decreased calcium levels
Location of Adrenal Glands
Retroperitoneal space
Above each kidney
Cortical hormones produced by adrenal glands
Aldosterone
Cortisol
Androgens
Medullary hormones produced by adrenal glands
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Aldosterone
Salt/water balance -> BP
Cortisol
Stress
Blood sugar
Metabolism
Androgens
Sex hormones -> especially testosterone
Epinephrine
Adrenaline
Norepinephrine
Fight/flight response
Sympathetic nervous system
Adrenomedullary Hyperfunction
Rare
Adrenocortical Hyperfunction
Common
Too many cortical hormones
Excess Cortisol
Cushing's syndrome
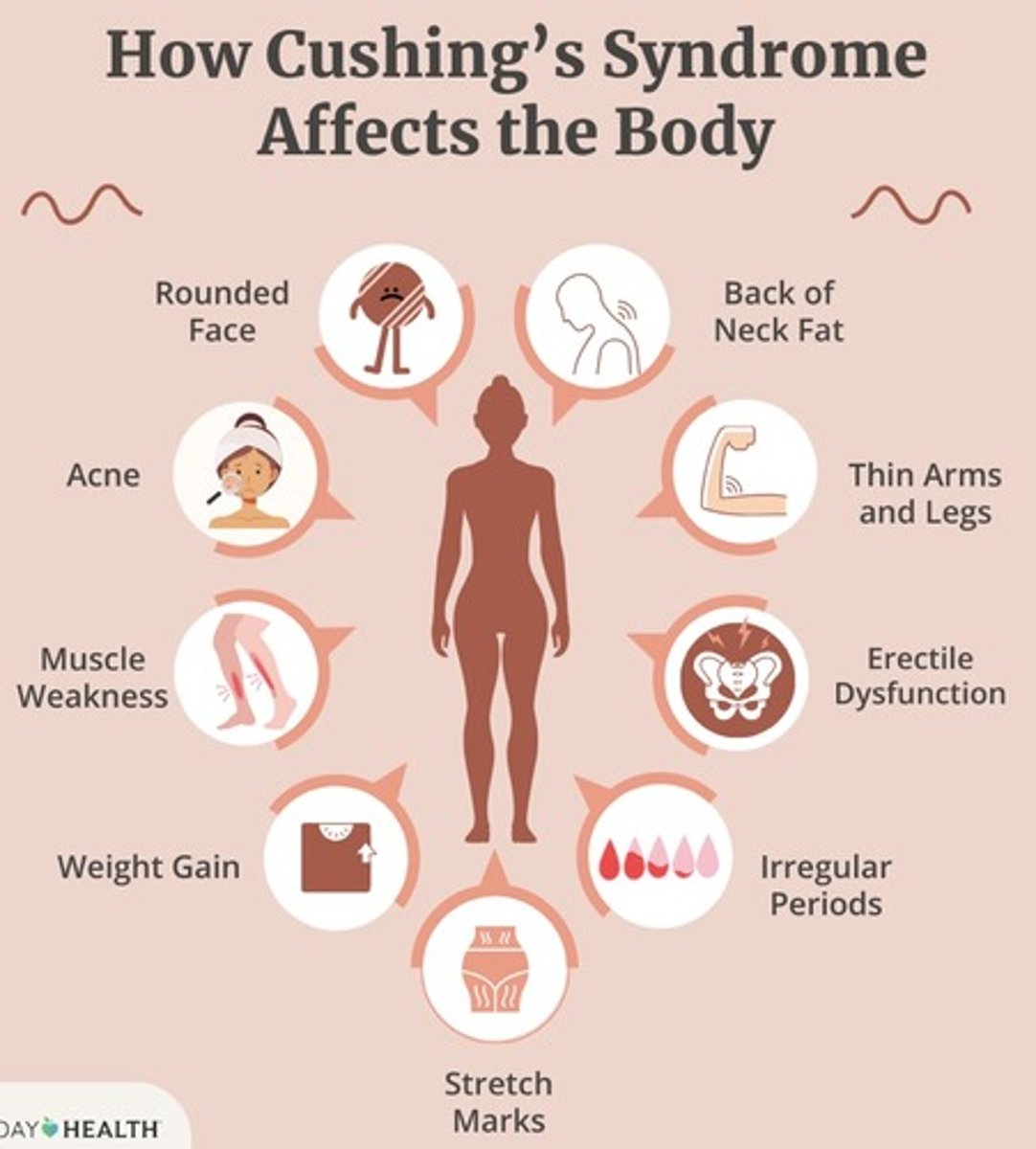
Excess Aldosterone
Conn's syndrome
Excess Androgens
Andrenogenital syndrome
Genitalia may not look typical
Women: fertility issues due to irregular menses or amenorrhea; hirsutism, deeper voice; virilization
Primary Adrenocortical Insufficiency
Addison's disease
Due damage of adrenal glands
Decreased cortisol and aldosterone
Secondary Adrenocortical Insufficiency
Lack of ACTH
Adrenal Adenomas
Benign
Cortical
Lead to hypersecretion of hormones
Adrenal Pheochromocytoma
Benign
Medullary
Lead to hypersecretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine
Adrenal Neuroblastoma
Malignant
Medullary
Seen in children
Components of nervous system
CNS & PNS
CNS
Brain
Spinal cord
PNS
Peripheral nerves
Autonomic ganglia
Functions of the nervous system
Regulation and of body functions through feedback loops
Regulation of musculoskeletal system
Gray Matter in the Brain
In cortex
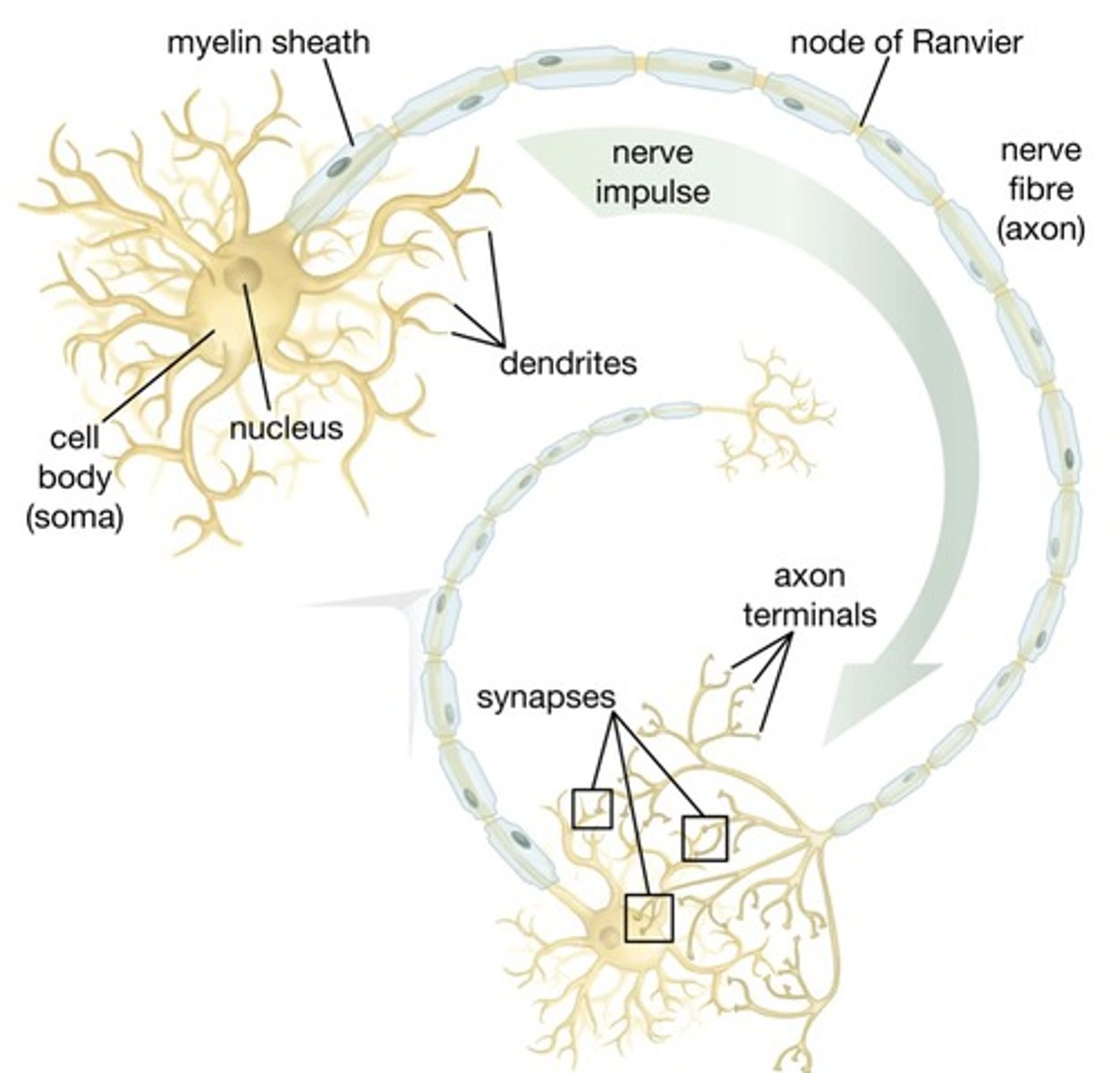
Contain neuron cell bodies and dendrites
Unmyelinated
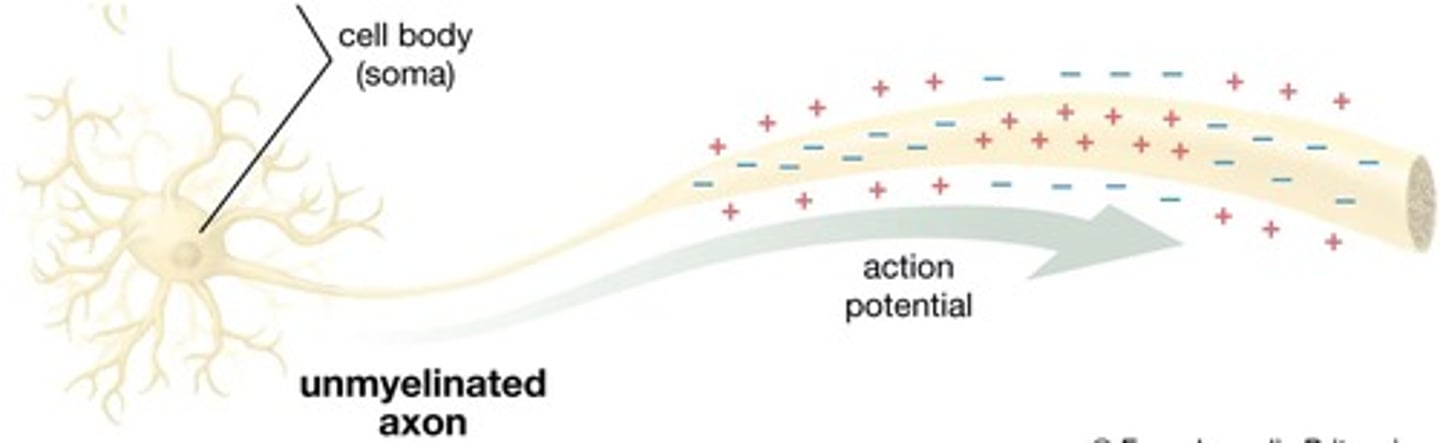
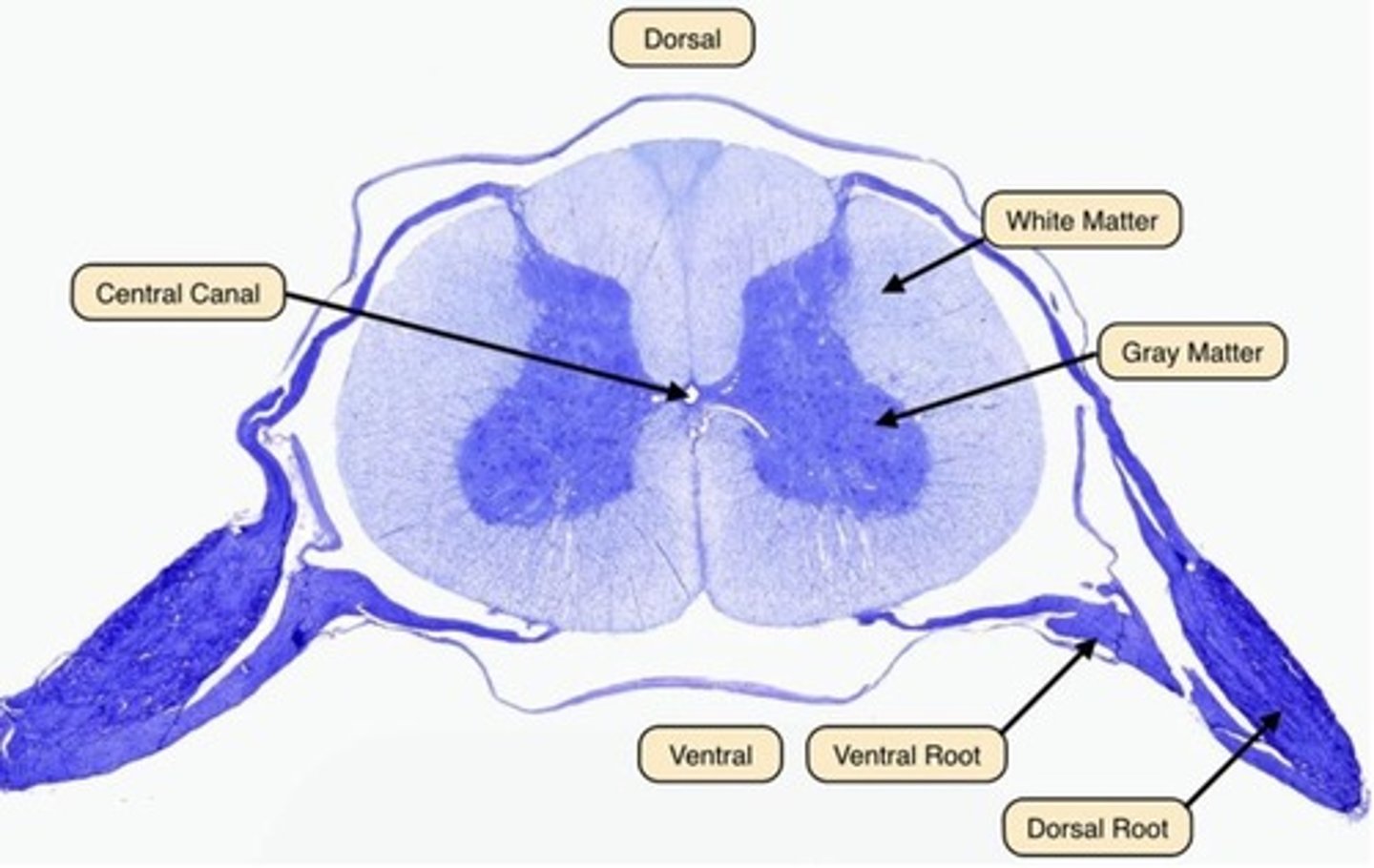
Gray Matter in Spinal Cord
Internal
Butterfly-shaped
White Matter in the Brain
Lies beneath cortex
Contains axons
Myelinated
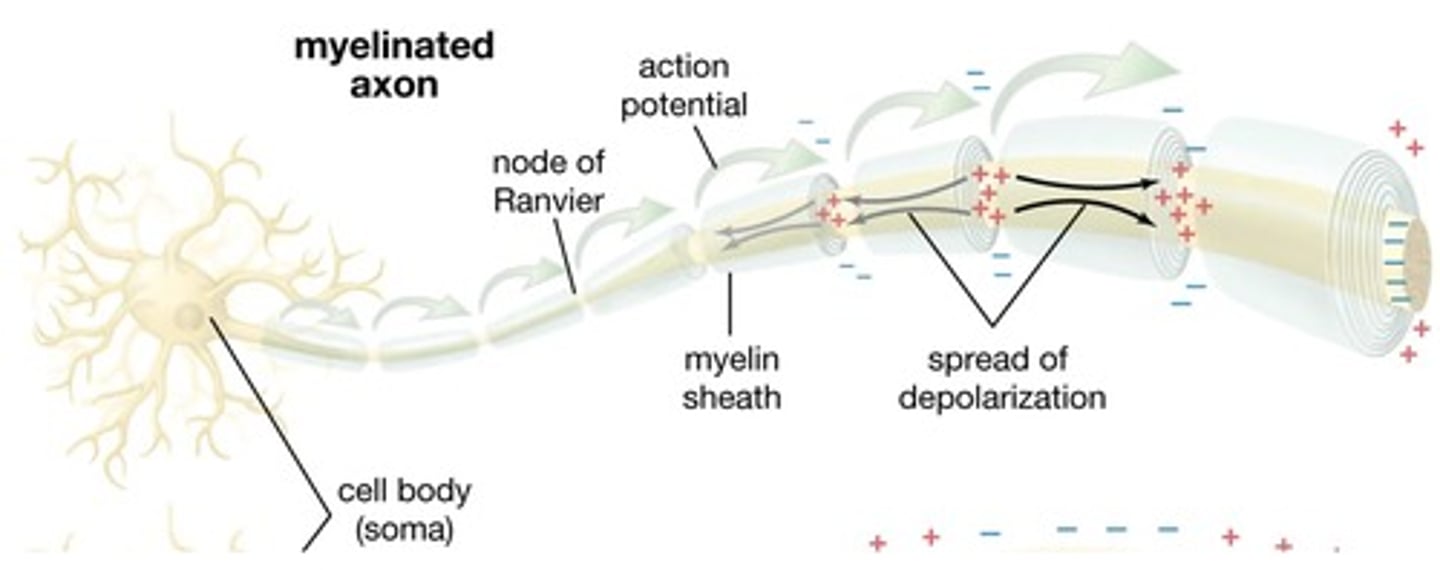
White Matter in Spinal Cord
Surrounds gray matter
Myelinated
Importance of myelin sheaths
Helps nerve signals move quickly
Cells that wrap around axons in CNS
Oligodendrocytes
Cells that wrap around axons in PNS
Schwann Cells
Frontal Lobe
Motor functions
Emotions
Intellect
Parietal Lobe
Sensory
Temporal Lobe
Hearing
Smell
Occipital Lobe
Sight
Basal Ganglia
Muscle contraction
Thalamus
Sensory processing
Consciousness
Hypothalamus
Regulates temp, HR, hunger
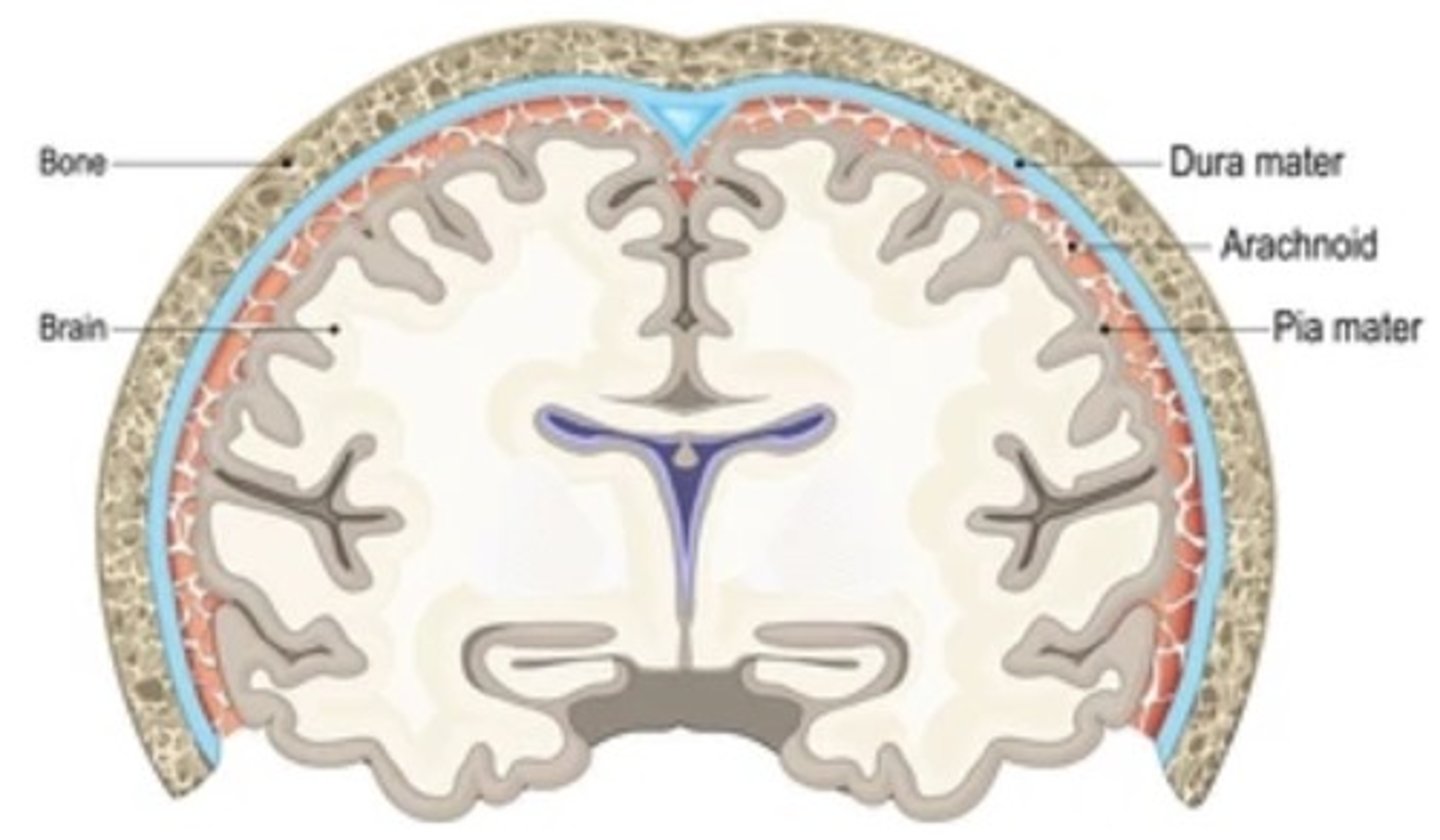
Meninges of the Skull (outer to inner)
Dura
Arachnoid
Pia
Importance of CSF
Provides cushion and transports nutrients
Components of a neuron
Support cells of CNS
Glial cells
Glial Cell Types
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Micegolia
Ependymal cells
Dysraphic Diseases
Incomplete fusion of neural tube
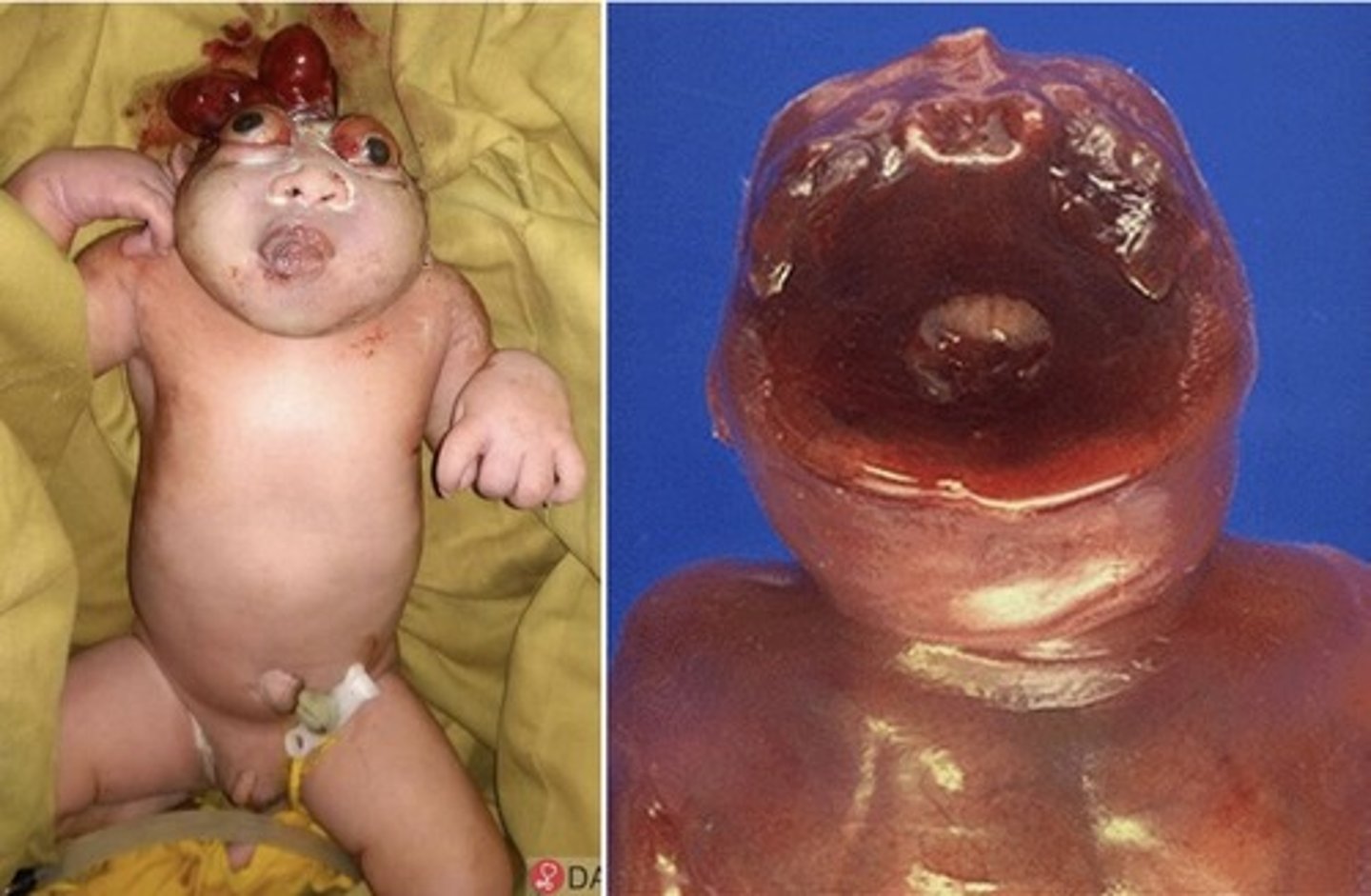
Ancephaly
Lack of calvaria
Destruction of brain tissue
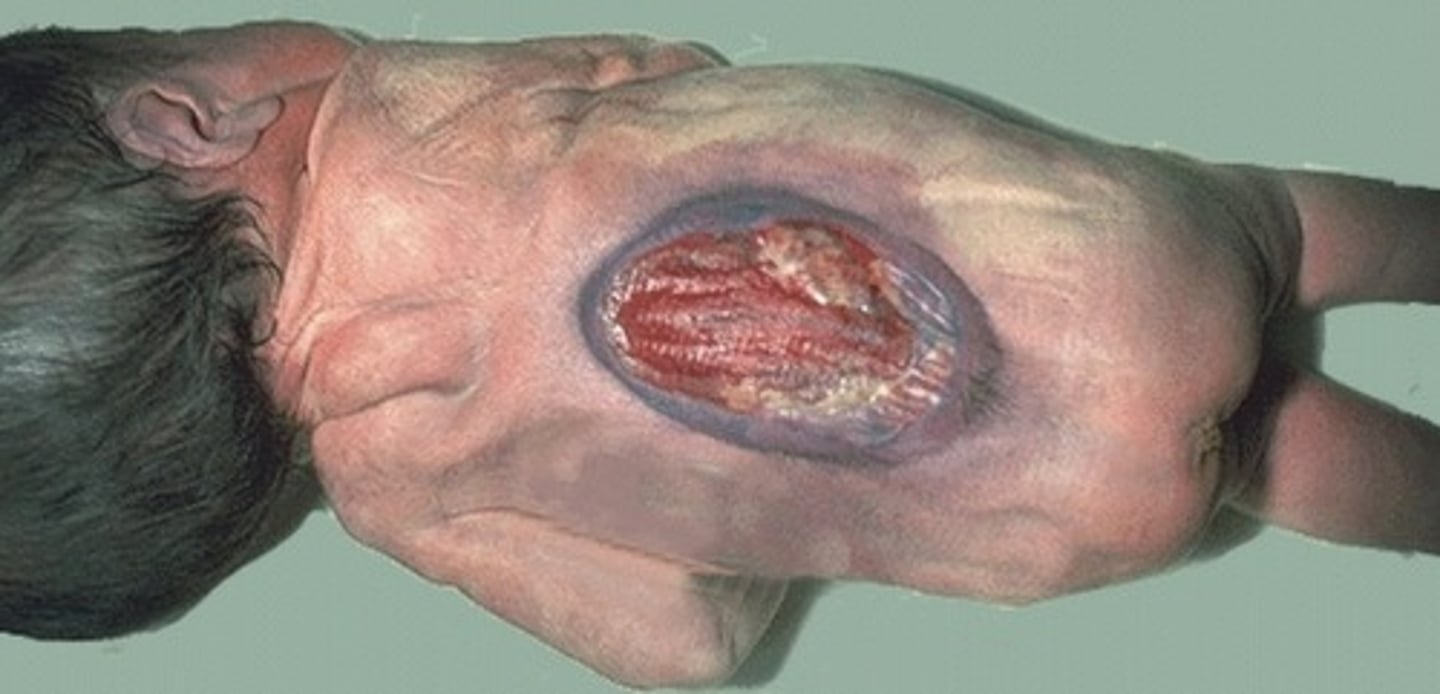
Meningocele
Herniation of meninges
Myelomeningocele
Herniation of meninges and spinal cord
Spina Bifida
No vertebral arches
Exposed meninges or spinal cord
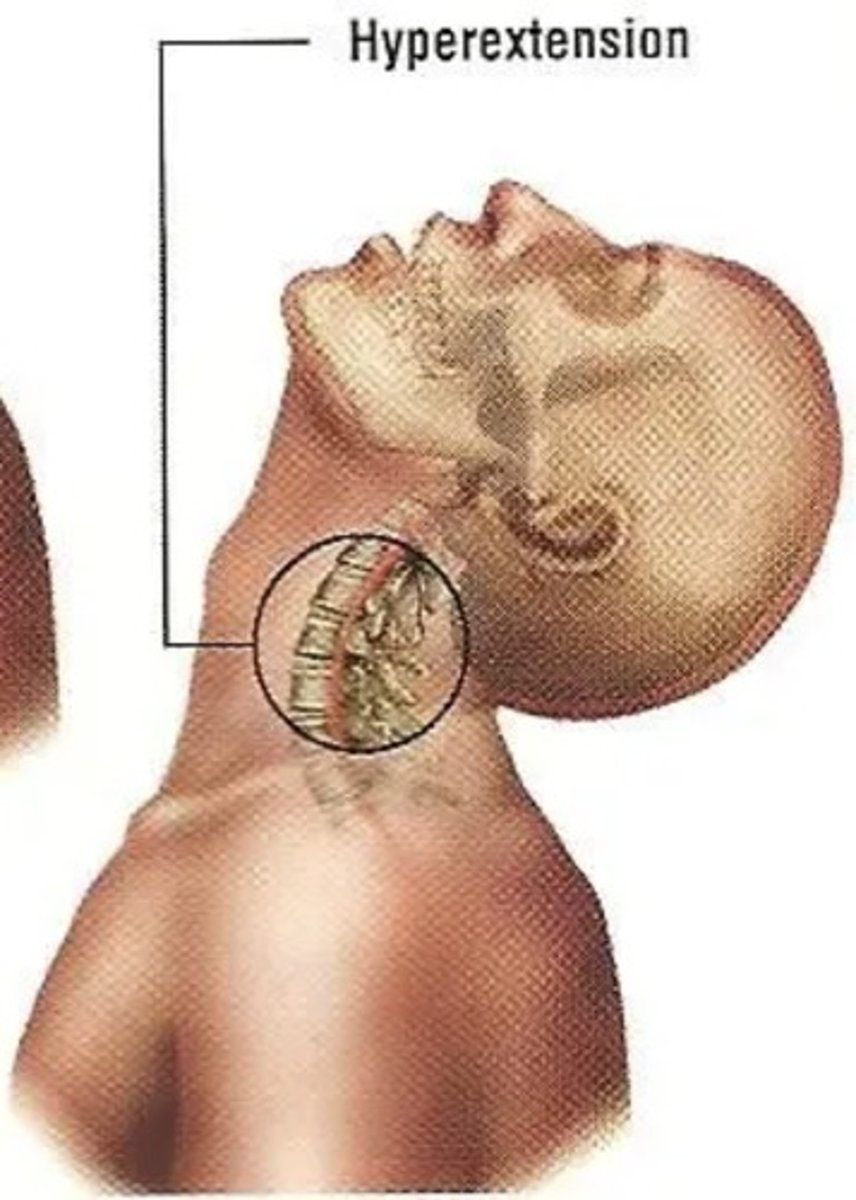
Most common spinal cord injury
Whiplash
Hyperextension of the head
Head violently moves forward and quickly hyperextends backwards
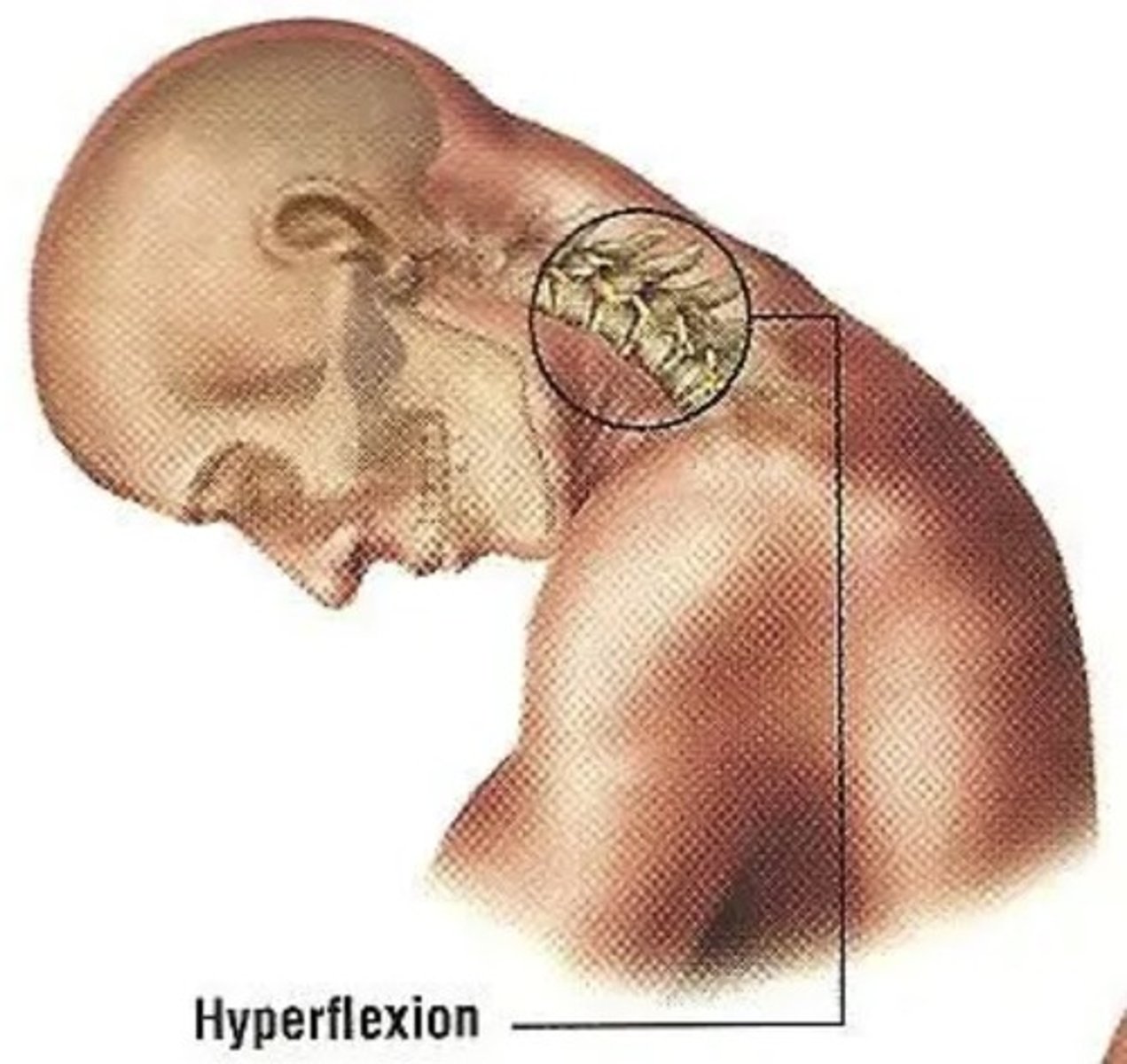
Hyperflexion of the head
Head violently moves backward and quickly hyperflexes forwards
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Brain bleed
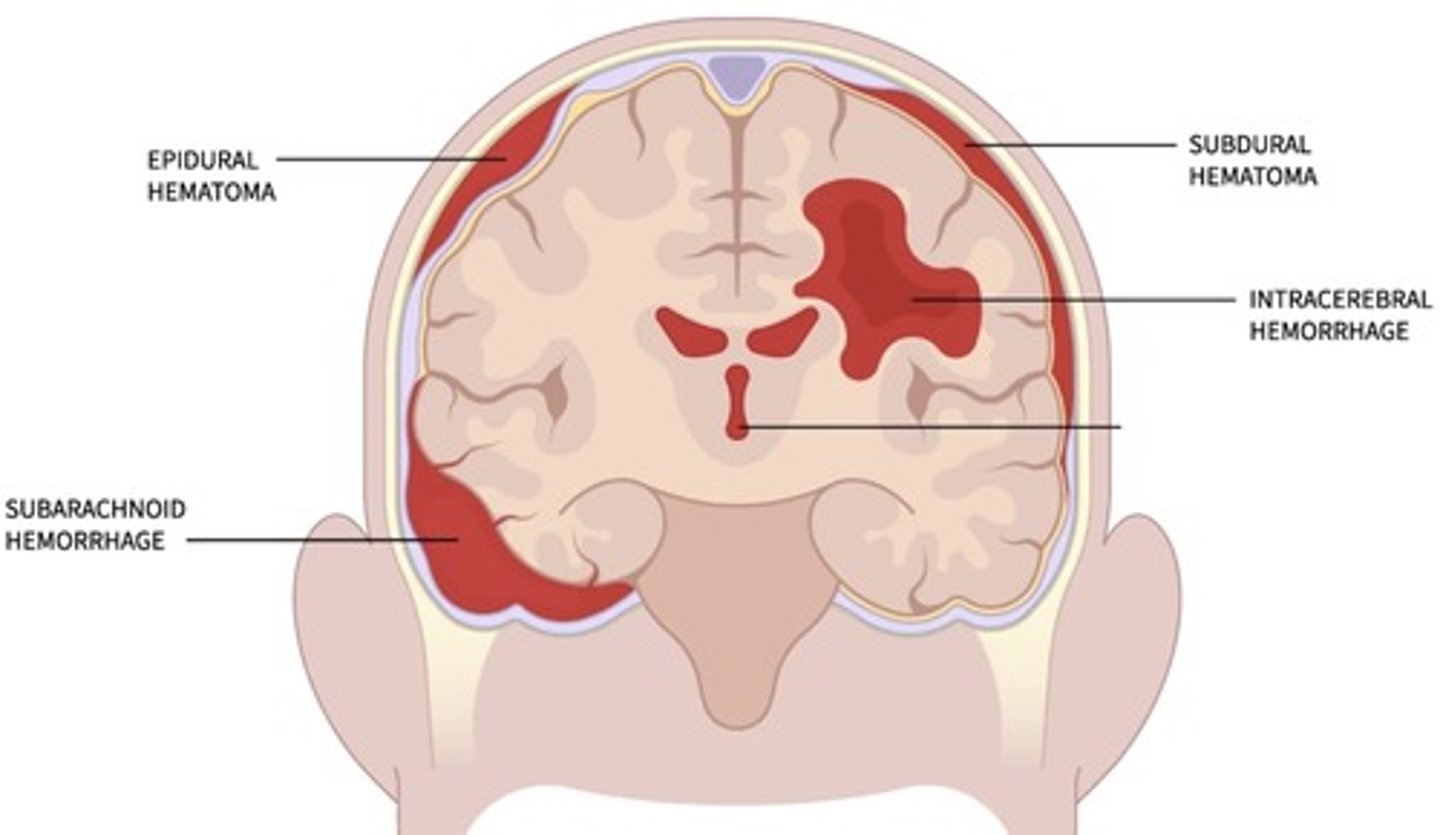
Concussion
Brain is shaken
Contusion
Bruising of the brain - causes bleeding and swelling
Hematoma
Localized brain bleed
Laceration
Bleeding from penetrating trauma
Epidural Hematoma
Bleeding between skill and dura
Subdural Hematoma
Bleeding between dura and arachnoid
Subarachnoid Hematoma
Bleeding between arachnid and Pia
Causes of Ischemic Stroke
Atherosclerosis
Embolism
Acute CVA
Chronic ischemia
Causes of Hemorrhagic Stroke
HTN -> ruptures vessels
Aneurysm or arteriovenous malformations
Meningitis
Inflammation of meninges