Induced potential and the generator effect: Magnetism and electromagnetism: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Induced potential difference
When an electrical conductor moves relative to a magnetic field or if there is a change in the magnetic field around a conductor, a potential difference is induced across the ends of the conductor
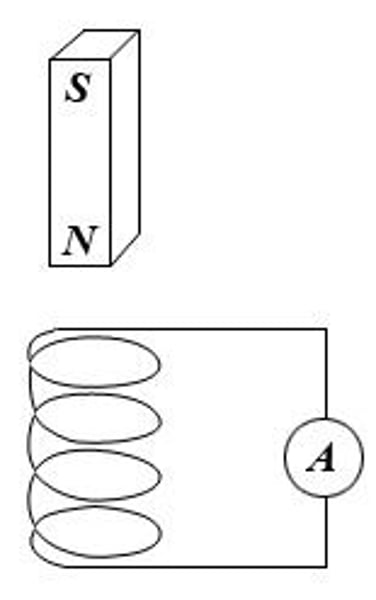
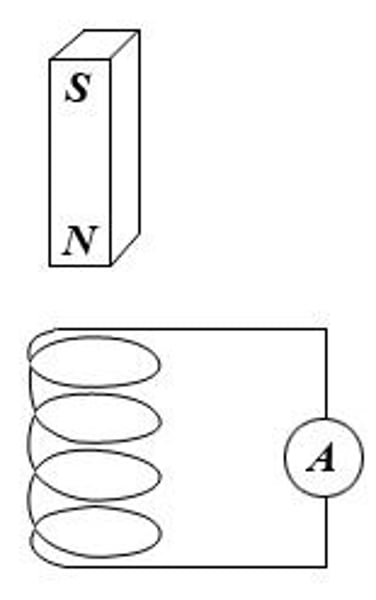
Induced current
If the conductor that has had a potential difference induced across its ends is part of a complete circuit, a current is induced in the conductor
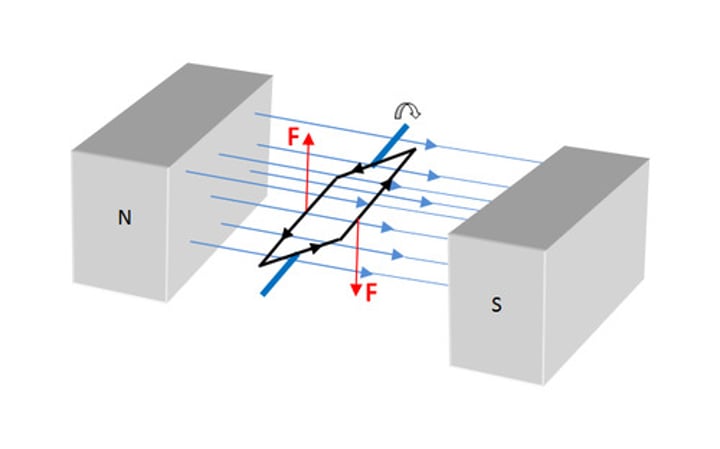
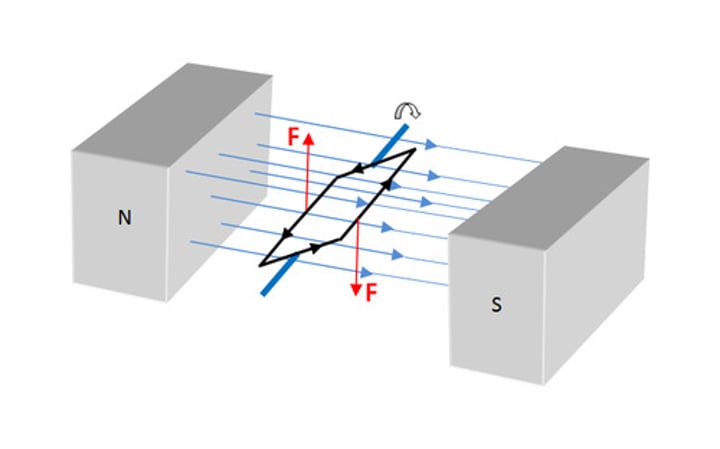
The generator effect
When the movement of a conductor relative to a magnetic field causes a potential difference and a current (if part of a complete circuit) to be induced in a conductor
Magnetic field generated by the induced current
An induced current generates a magnetic field that opposes the original change, either the movement of the conductor or the change in magnetic field
How to reverse the direction of the induced potential difference/current
Reverse direction of movement of the magnet or the coil
Factors affecting the size of the induced potential difference/current
Speed of movement, magnetic field strength is increased, number of turns on the coil
Generator
A device that uses the generator effect to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy
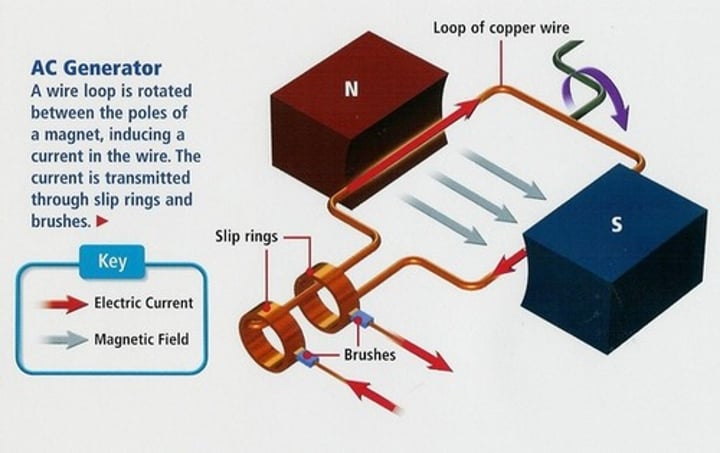
Alternator
An electrical generator which produces alternating current (an ac generator)
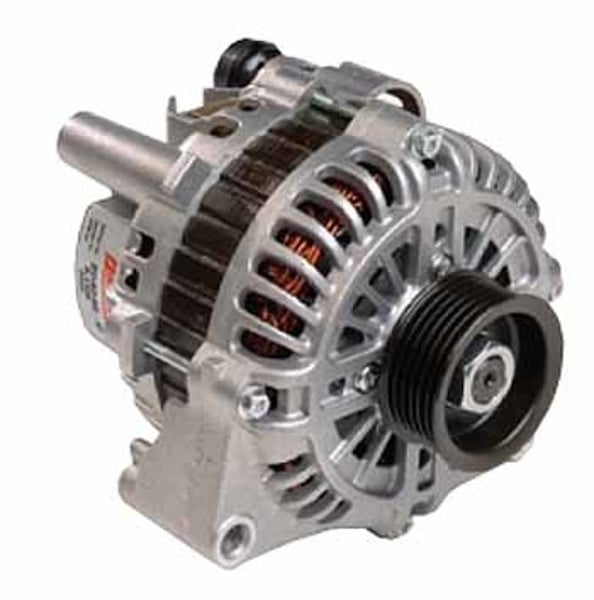

Structure of an alternator
Consists of a coil of wire rotating in a magnetic field and two slip rings
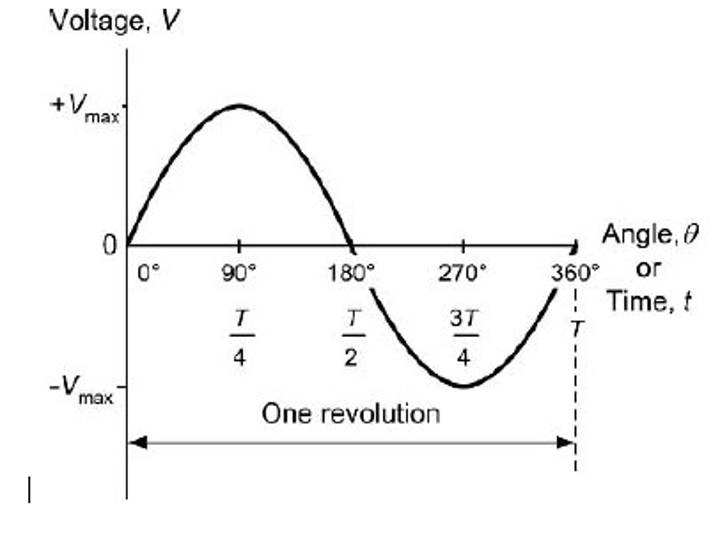
Sine curve
The potential difference produced by an ac generator follows the shape of the graph obtained for y = sin x
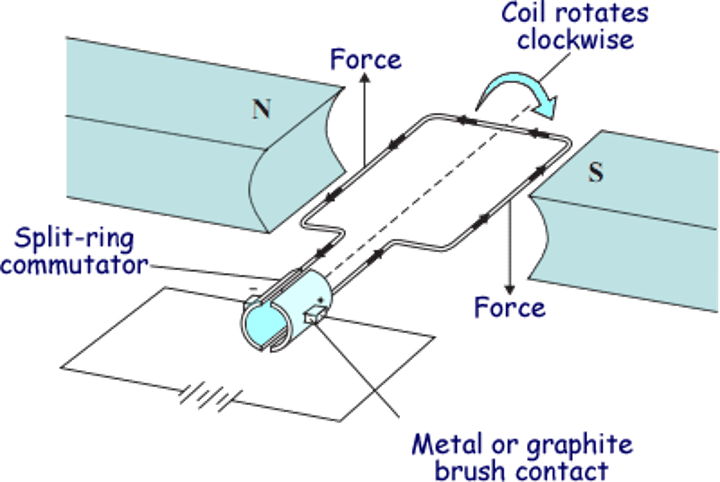
Dynamo
An electrical generator which produces direct current (a dc generator)
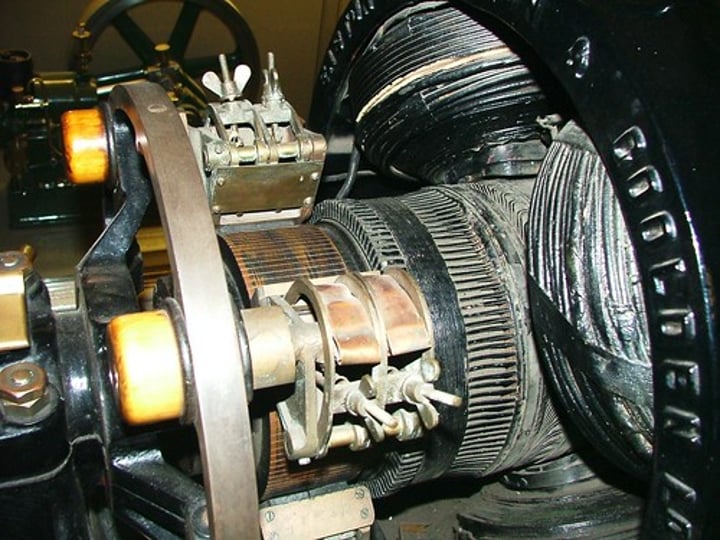

Structure of a dynamo
Consists of a coil of wire rotating in a magnetic field and a split ring commutator
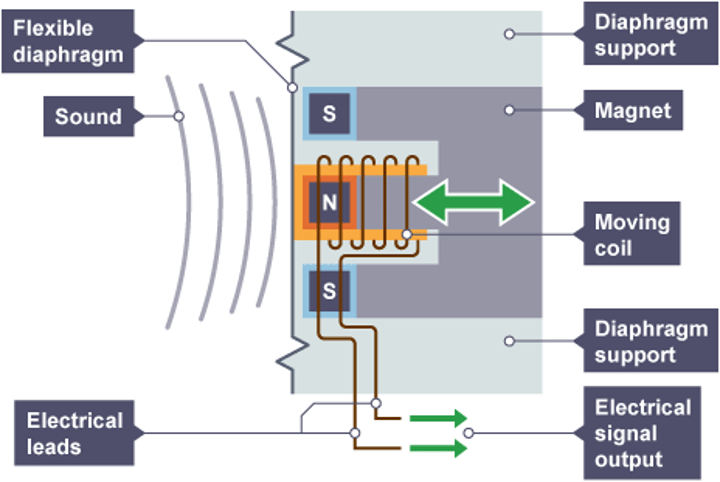
Moving-coil microphone
A microphone in which electrical signals are produced when pressure variations in sound waves vibrate a coil of wire inside a magnetic field