APES: THE NITROGEN CYCLE
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
atmosphere
what is the largest nitrogen reservoir on earth?
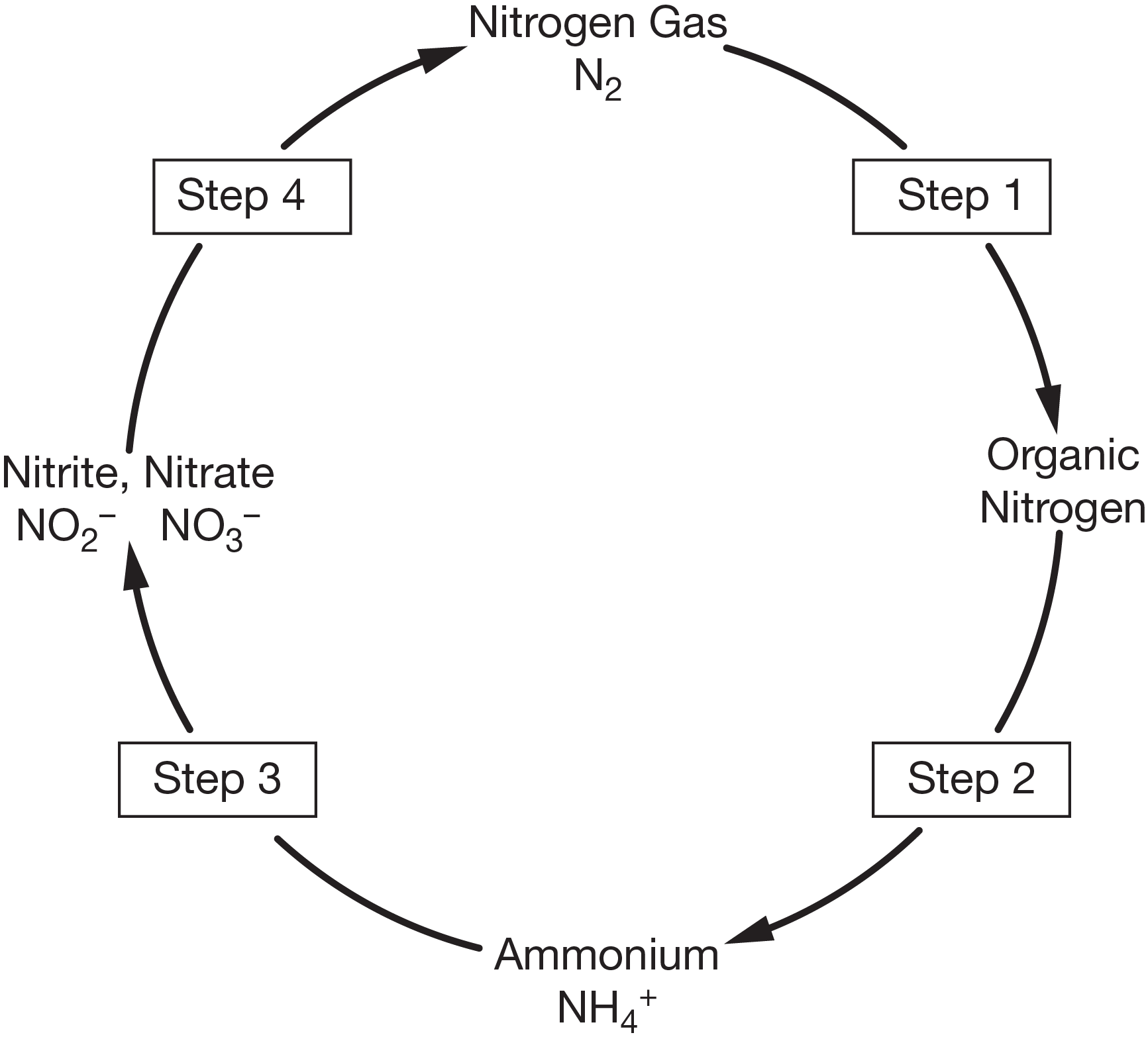
nitrogen fixation
During this step, atmospheric nitrogen gas is converted into a form that can be used by plants and animals. Two natural processes are responsible for this process. In the atmosphere, energy from lightning helps recombine the atoms in nitrogen gas and oxygen gas (\[\ce{O2}\]), forming nitrate (\[\ce{NO3-}\]). This nitrate falls to Earth's surface in precipitation. In the soil, nitrogen-converting bacteria use enzymes to combine nitrogen gas with hydrogen gas (\[\ce{H2}\]) to produce ammonia (\[\ce{NH3}\]). The bacteria can use this ammonia as a nutrient, or convert it into ammonium ions (\[\ce{NH4+}\]). Fixed nitrogen can be taken up by plants and incorporated into biological molecules in the plants’ tissues. This allows nitrogen to move up the food chain as plants are eaten by animals, who are themselves eaten.
Ammonification
containing biological molecules may stay in organisms’ tissues, or be broken down and released as waste. As dead organisms and waste decompose, ammonia and ammonium ions are returned to the environment through this process. This process is carried out by certain bacteria and fungi.
nitrification
During this process, groups of nitrifying bacteria convert the products of ammonification into nitrites (\[\ce{NO2-}\]), and then nitrates.
denitrifcation
During this process, denitrifying bacteria convert nitrites and nitrates back into nitrogen gas, returning nitrogen to the atmosphere.
nitrogen fixation
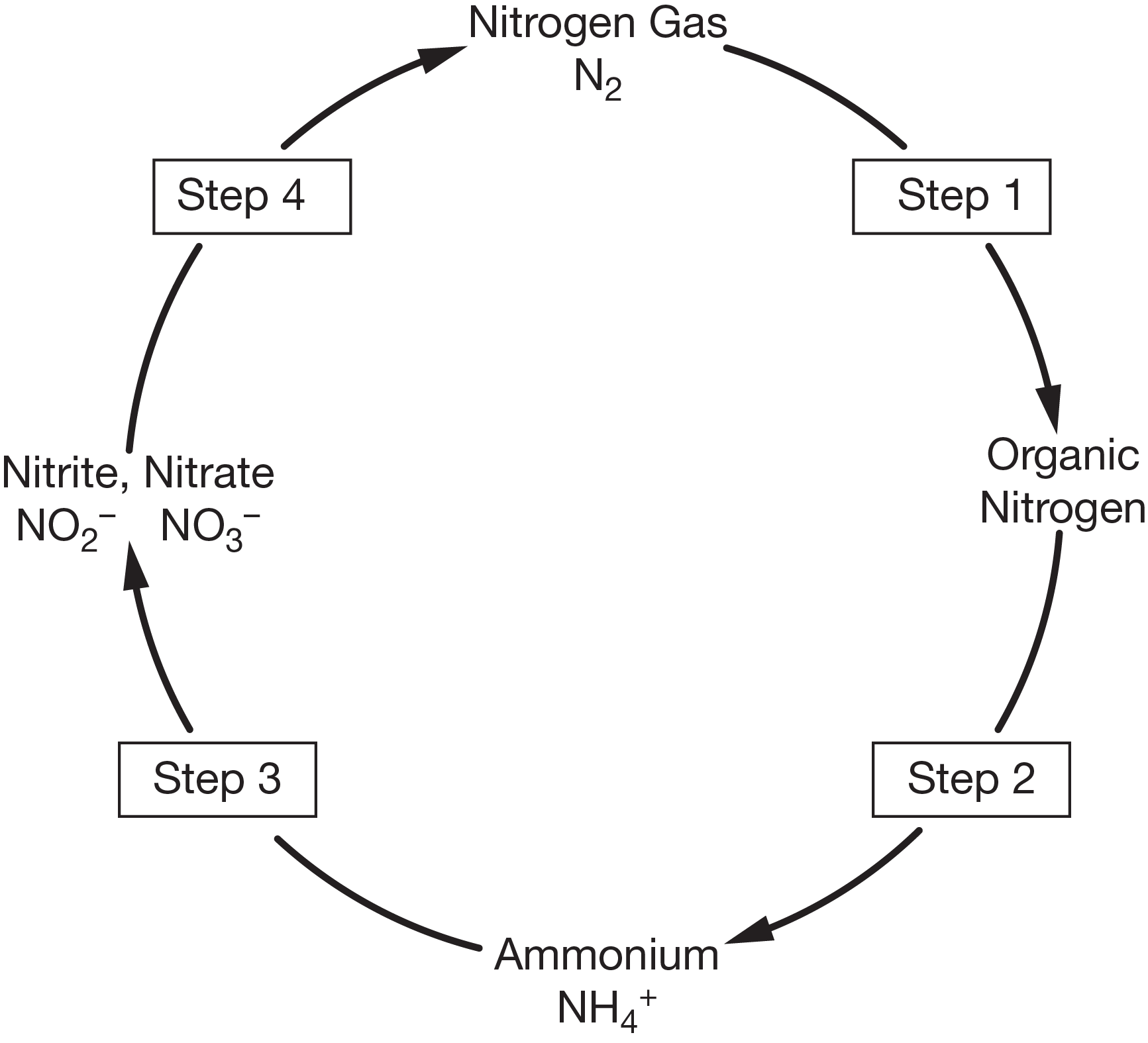
What is step 1?
ammonification
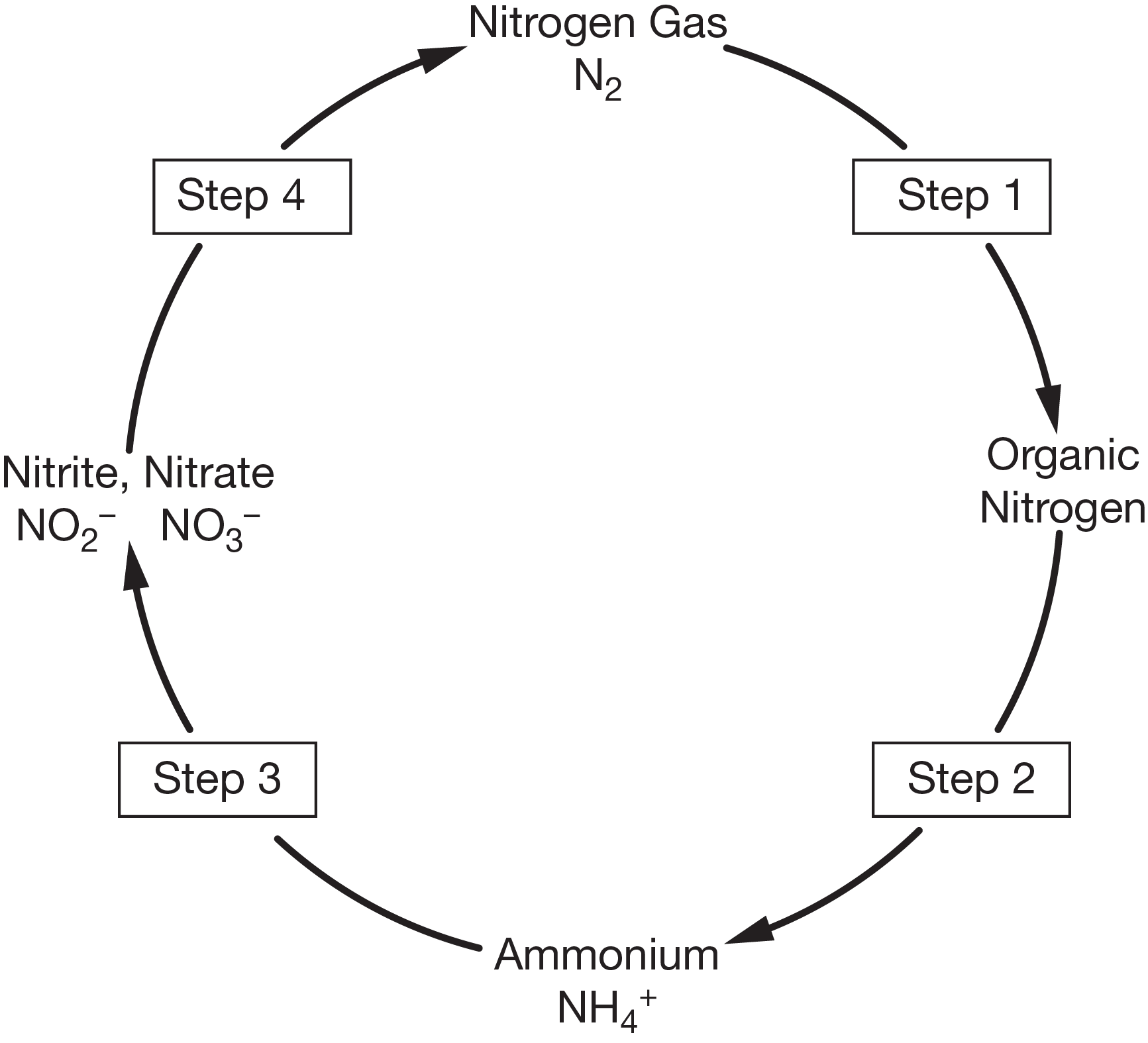
What is step 2?
nitrification
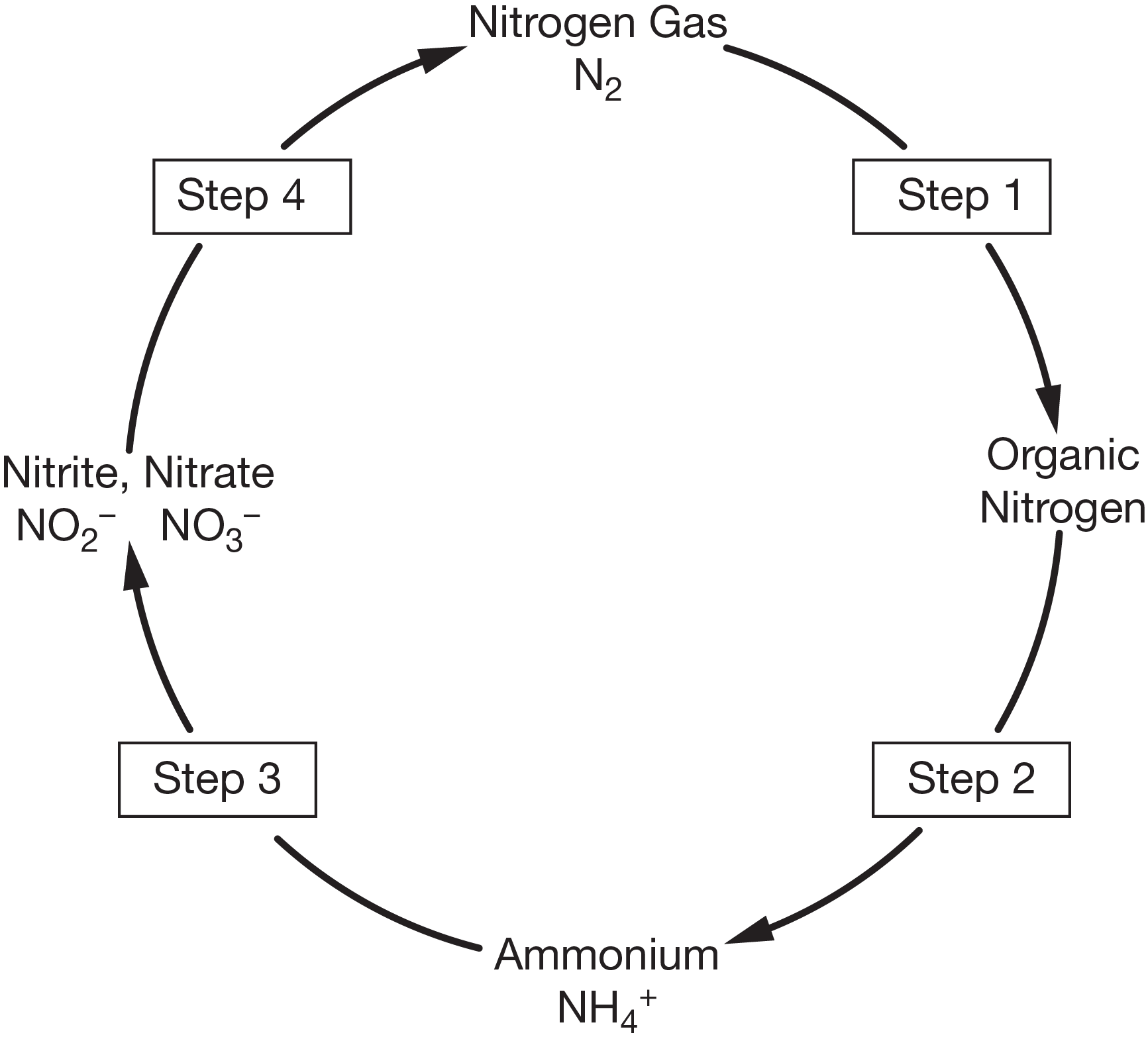
What is step 3?
denitification
What is step 4?