Biological molecules
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Define monomers.
the smaller units from which larger molecules are made
Define polymers.
molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together
Give 3 examples of monomers
Monosaccharides, amino acids and nucleotides
Define condensation reaction
A reaction that releases a molecule of water when it links molecules together
Define hydrolysis reaction
A chemical reaction in which water is used to break a chemical bond
What are carbohydrates?
Organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What are monosaccharides?
the monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made
Give examples of monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
What does a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides form?
A glycosidic bond
What are disaccharides formed by?
condensation of two monosaccharides
Give examples of disaccharides
sucrose, maltose, lactose
What is sucrose made of?
glucose and fructose
What is maltose made of?
glucose and glucose
What is lactose made of?
glucose and galactose
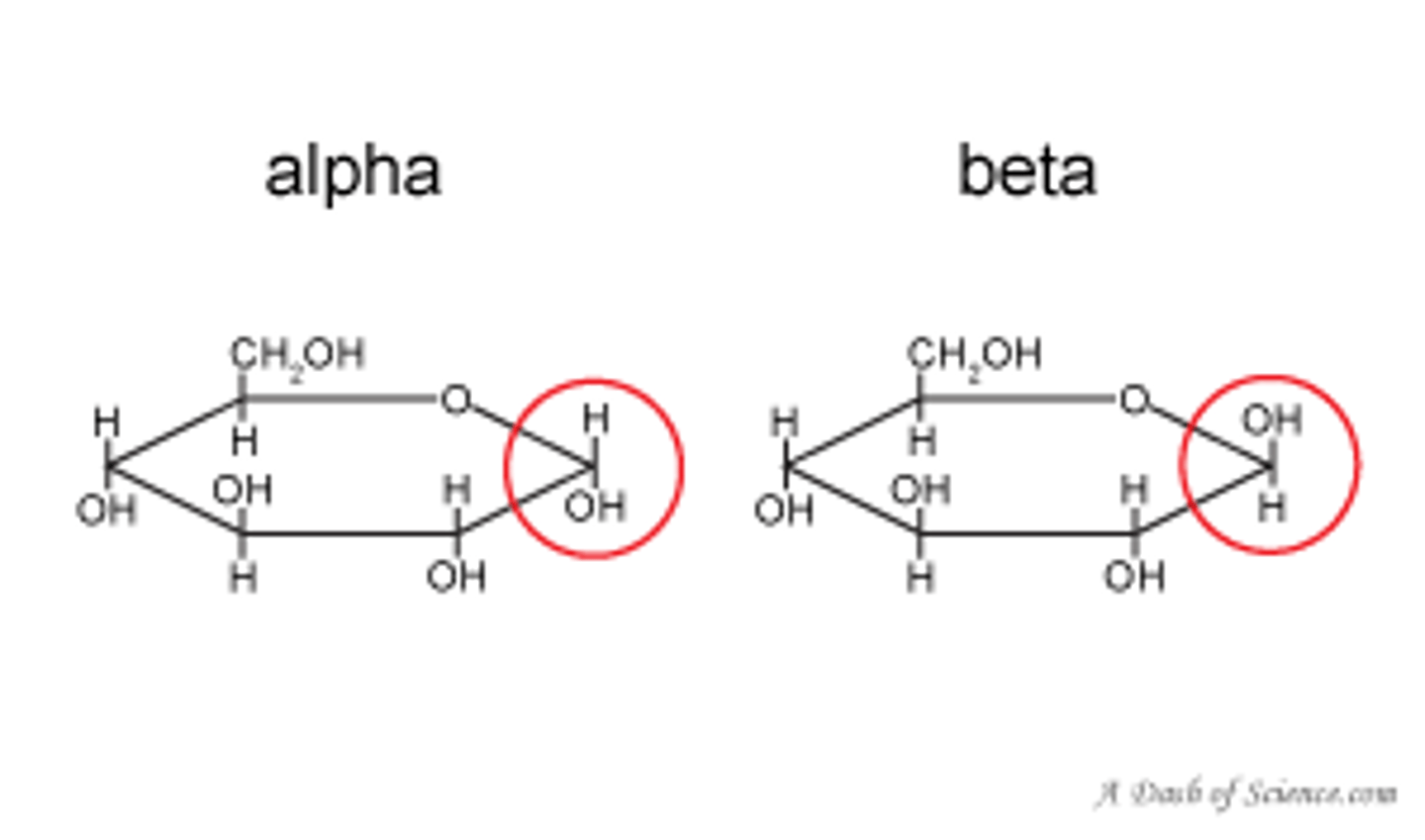
What are the two isomers of glucose?
alpha glucose and beta glucose
What are isomers?
compounds with the same formula but different arrangement of atoms
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose?
Their hydroxyl groups are reversed
What are polysaccharides formed by?
Condensation of many glucose units
What are glycogen and starch formed by?
condensation of alpha glucose
What is cellulose formed by?
condensation of beta glucose
What is glycogen?
the main energy storage molecule in animals
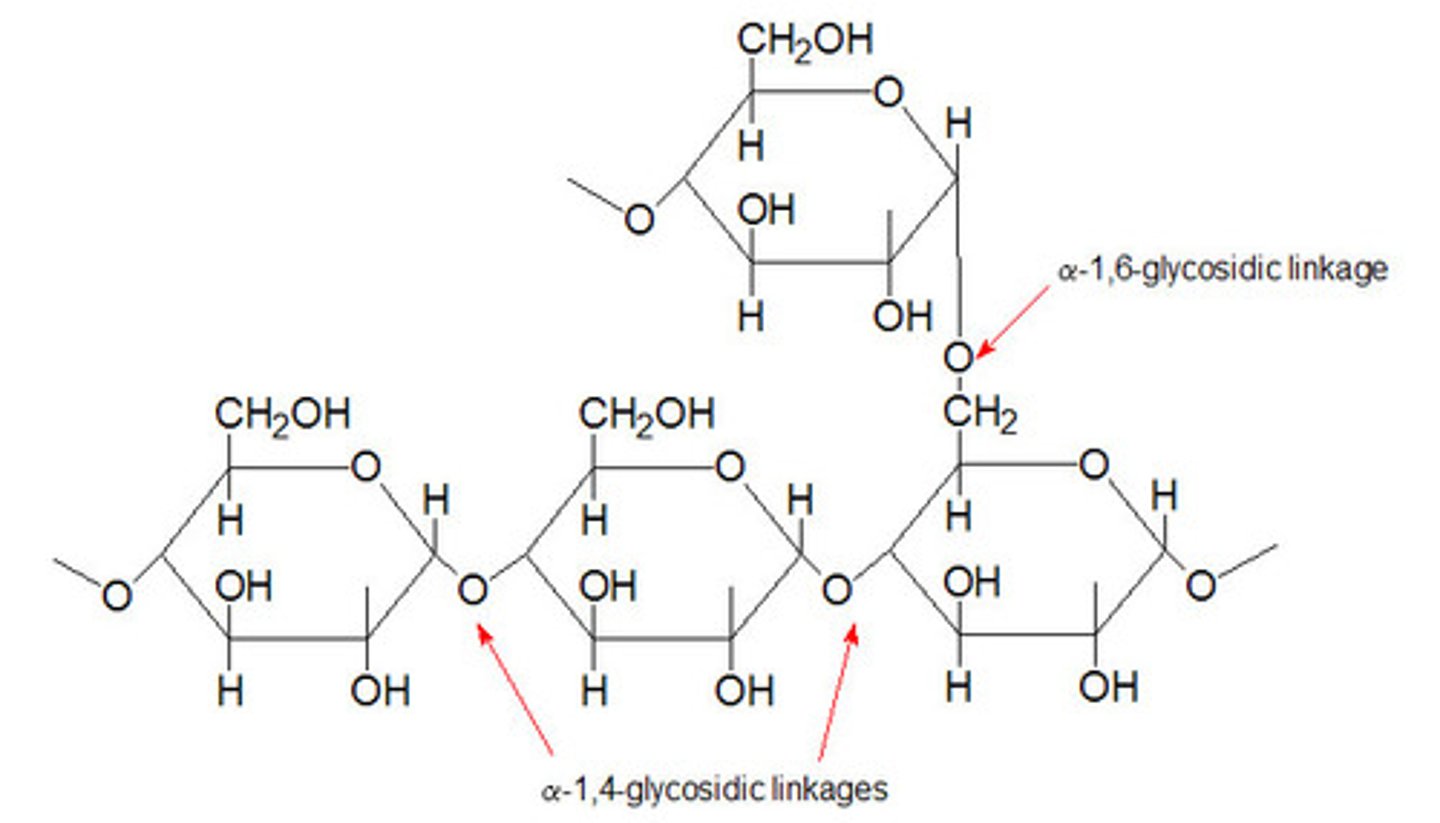
How is glycogen structured?
many alpha-glucose monomers joined by 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds to form highly branched chains
Give some properties of glycogen
- Compact
- Insoluble
- Highly branched - Releases energy quickly
What is starch used for?
energy storage in plants
What polysaccharides make up starch?
amylose and amylopectin
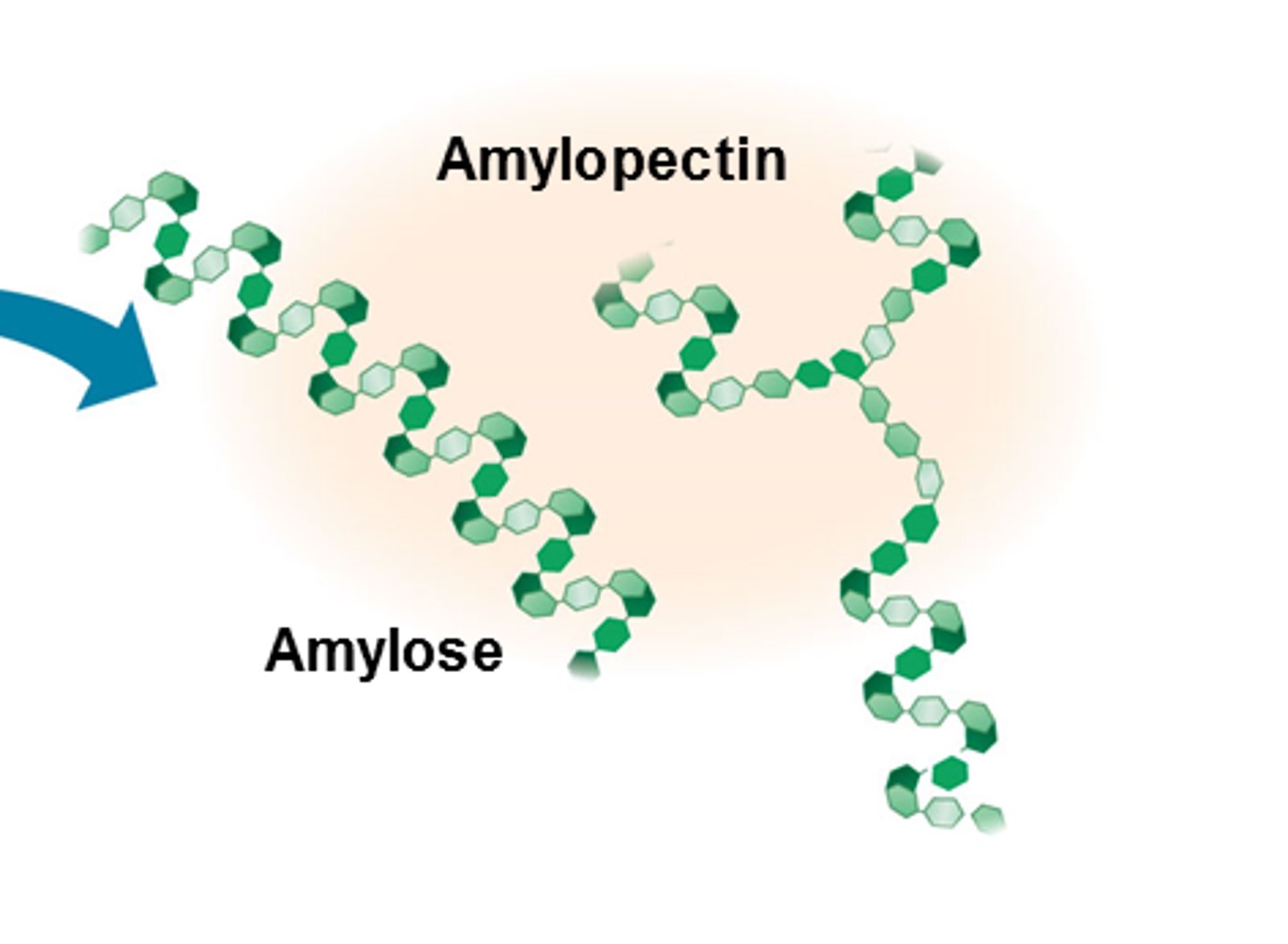
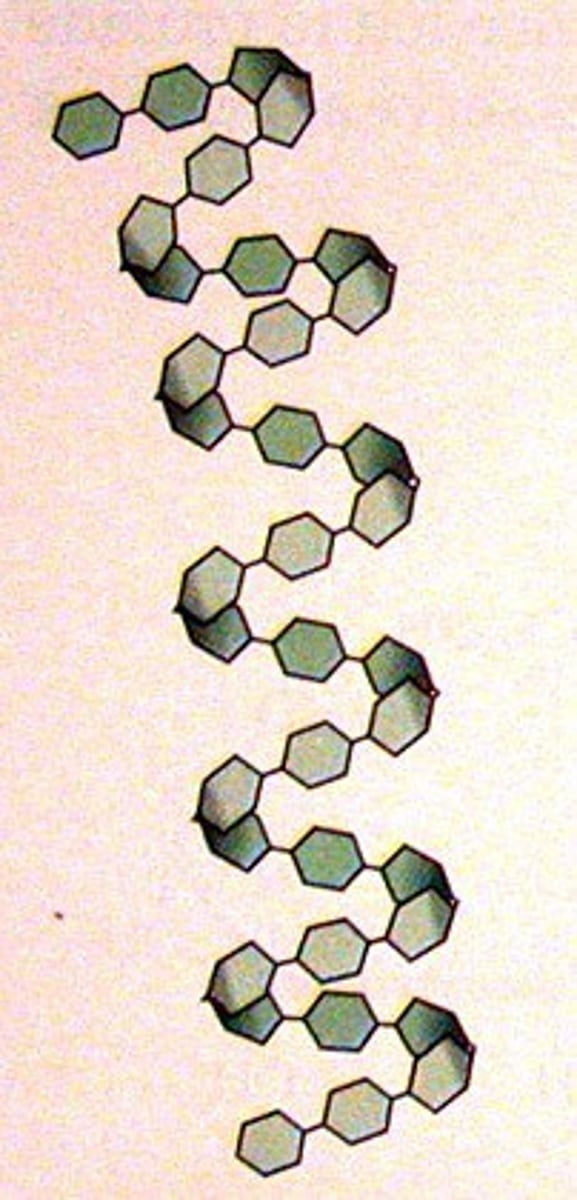
What is amylose?
unbranched chain of glucose molecules joined by 1, 4 glycosidic bonds
What is amylopectin?
A long, branched chain of alpha glucose molecules joined by 1, 4 and 1, 6 glycosidic bonds
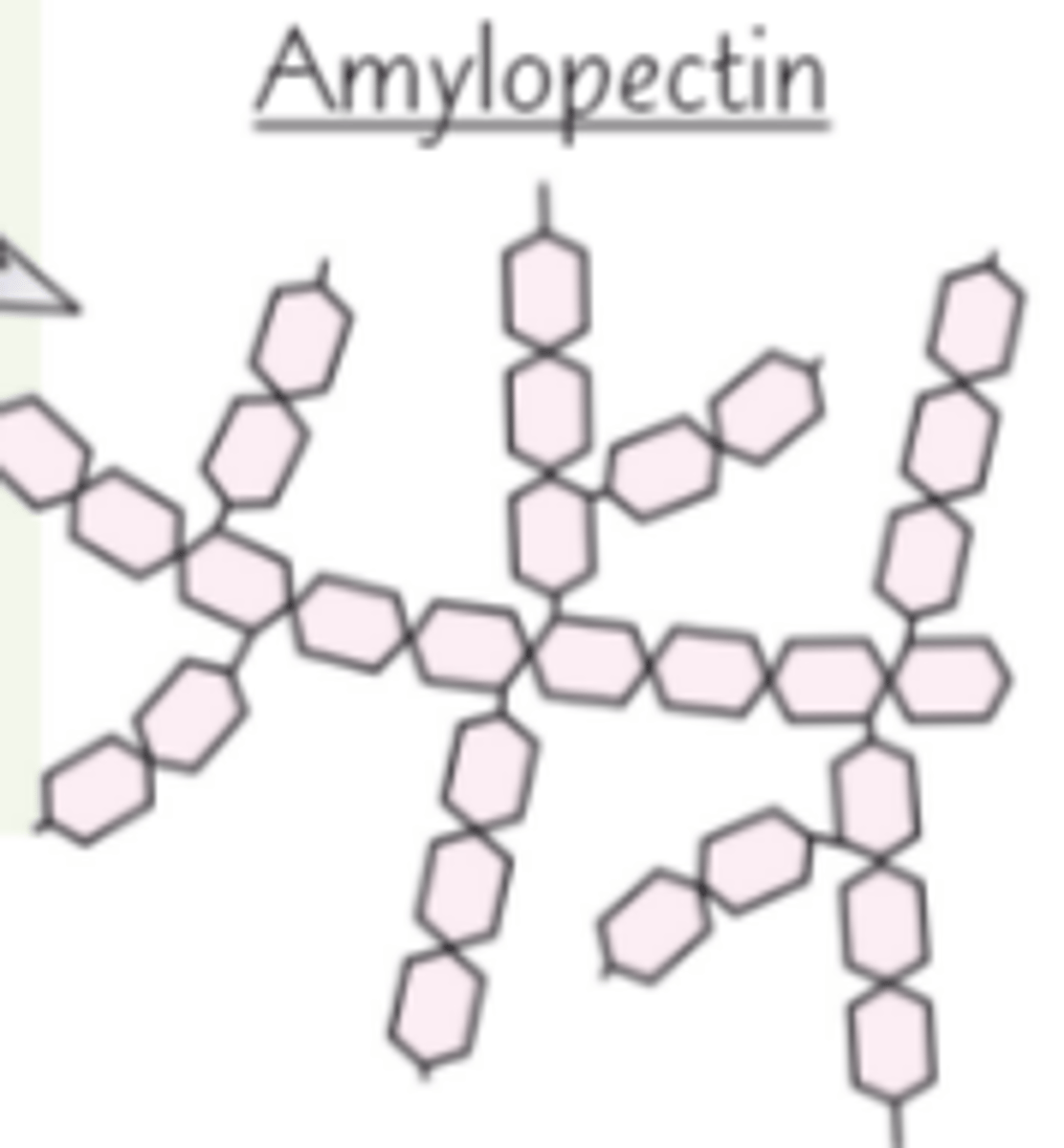
What are some properties of starch?
- Insoluble in water (no osmotic effect)
- Large molecule - Can't diffuse out of the cell
- Branched - Compact
What is cellulose?
polysaccharide of beta glucose
What is the function of cellulose?
structural component of plant cell walls
What is the structure of cellulose?
long, unbranched chains of β glucose linked by hydrogen bonds to form microfibrils. Every other beta glucose molecule is inverted to form 1,4 glycosidic bonds.
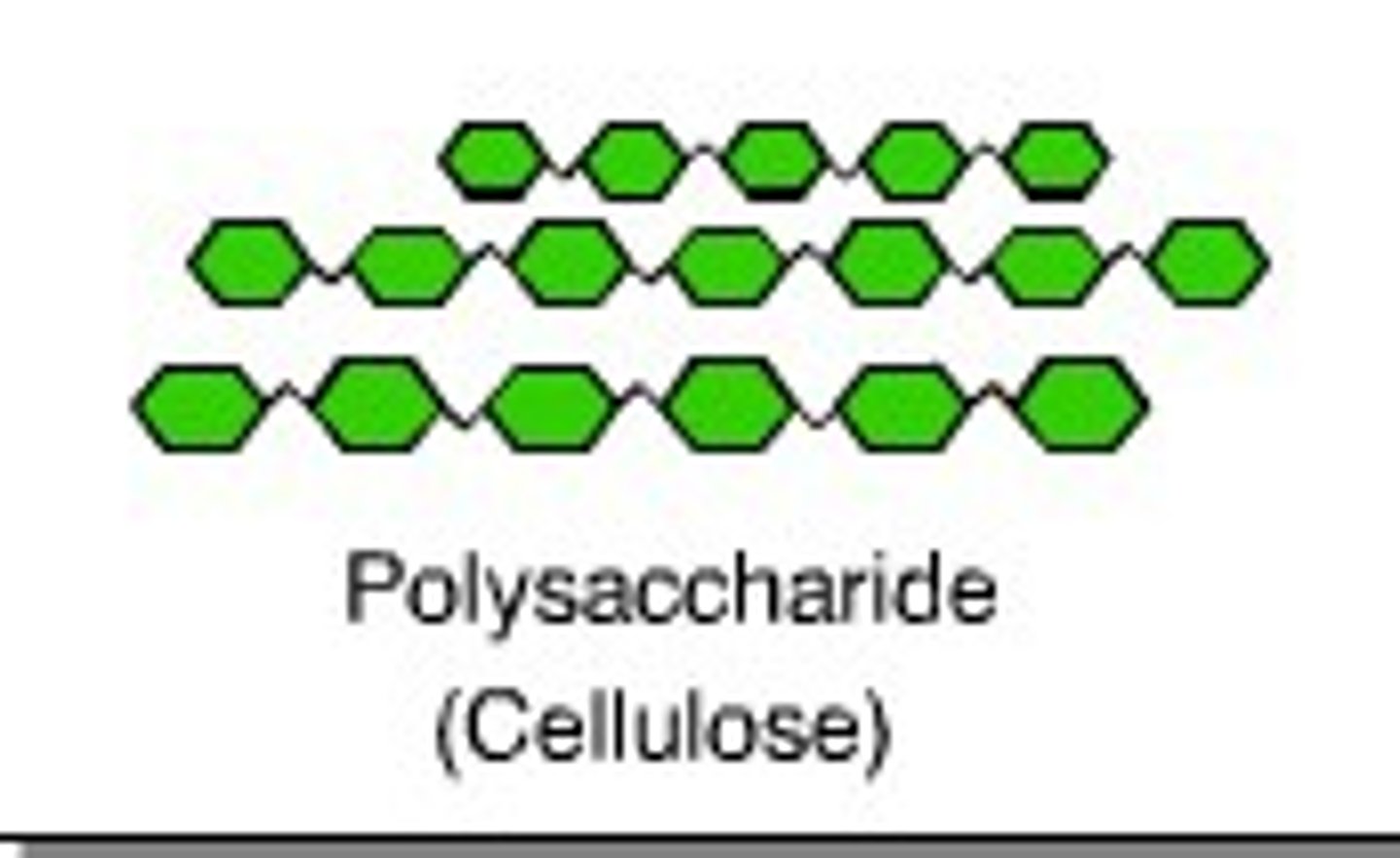
What are microfibrils?
strong fibres made of many cellulose chains held together by hydrogen bonds
How does cellulose prevent the cell from bursting?
exerts inward pressure that stops the influx of water, keeping cells turgid and rigid
How do you test for starch?
Add a drop of dilute iodine solution to the subject. If starch is present it will turn a 'blue-black' colour.
What is a reducing sugar?
A sugar that can donate electrons to another chemical
Give examples of reducing sugars
All monosaccharides and some disaccharides — maltose and lactose
Describe the test for reducing sugars
Add benedicts and heat in water bath for 5 minutes.
if sample contains reducing sugars = turn brick red
Give examples of non reducing sugars
Some disaccharides e.g. sucrose and all polysaccharides
Describe the test for non reducing sugars
1. Do Benedict's test with negative result
2. Heat in water bath with dilute HCl (to hydrolyse into reducing sugars)
3. Neutralise with sodium hydrogencarbonate
4. Re-test using Benedict's reagent
5. Positive result = colour change
What are the two types of lipids?
triglycerides and phospholipids
What are triglycerides composed of?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
How are triglycerides formed?
condensation of glycerol and 3 fatty acids forming ester bonds and 3 water molecules
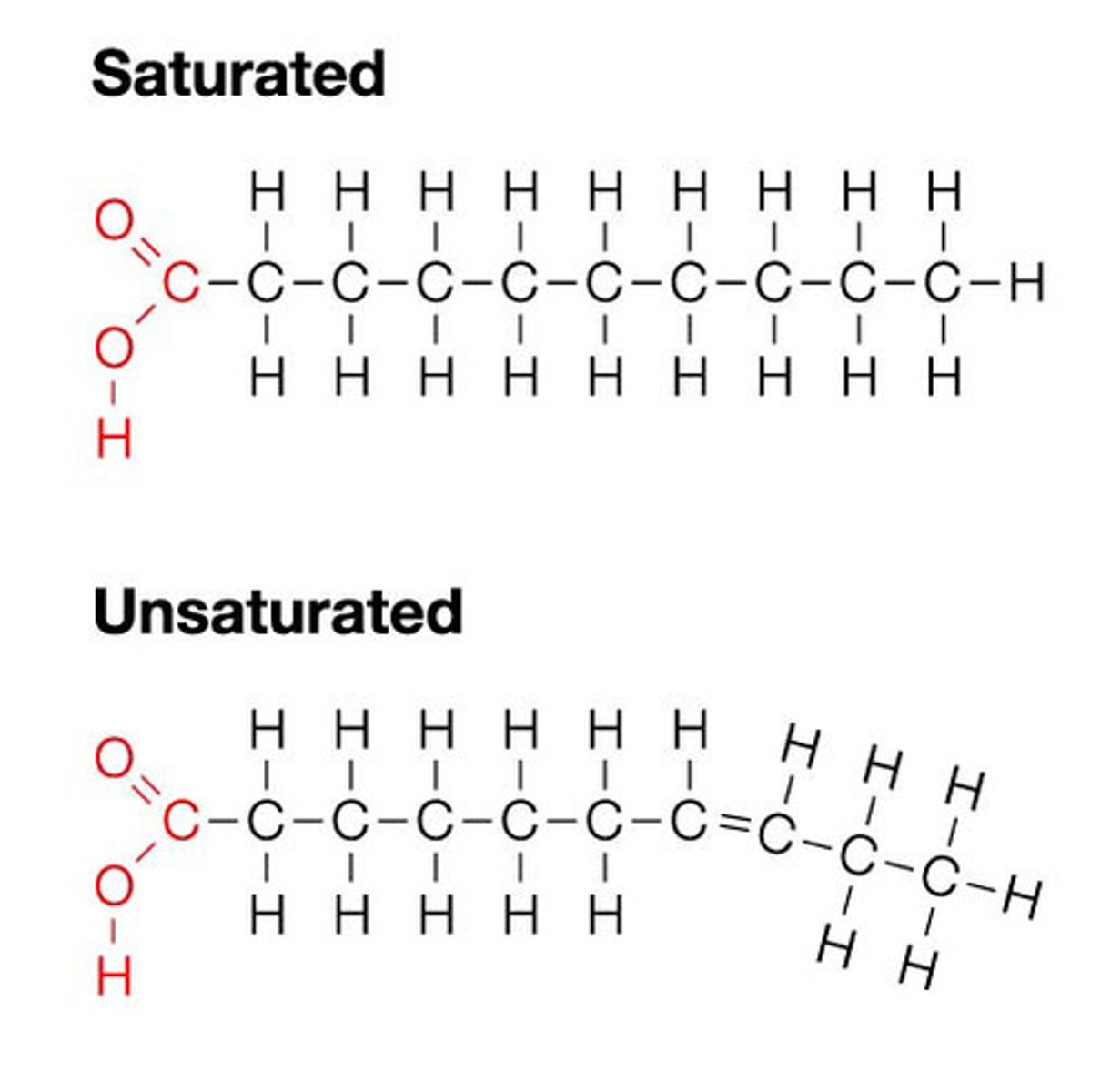
What are the 2 types of fatty acids?
Unsaturated and saturated
Describe the difference between unsaturated and saturated fatty acids
Unsaturated fatty acids have at least one double bond between carbon atoms while saturated fatty acids don't have any
What are the properties of triglycerides?
-the long hydrocarbon chains contain lots of energy
-insoluble in water so no osmotic effect (fatty acid tails are hydrophobic)
-low mass to energy ratio making them good storage molecules
What are phospholipids composed of?
glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and a phosphate group
What are phospholipids made of?
hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
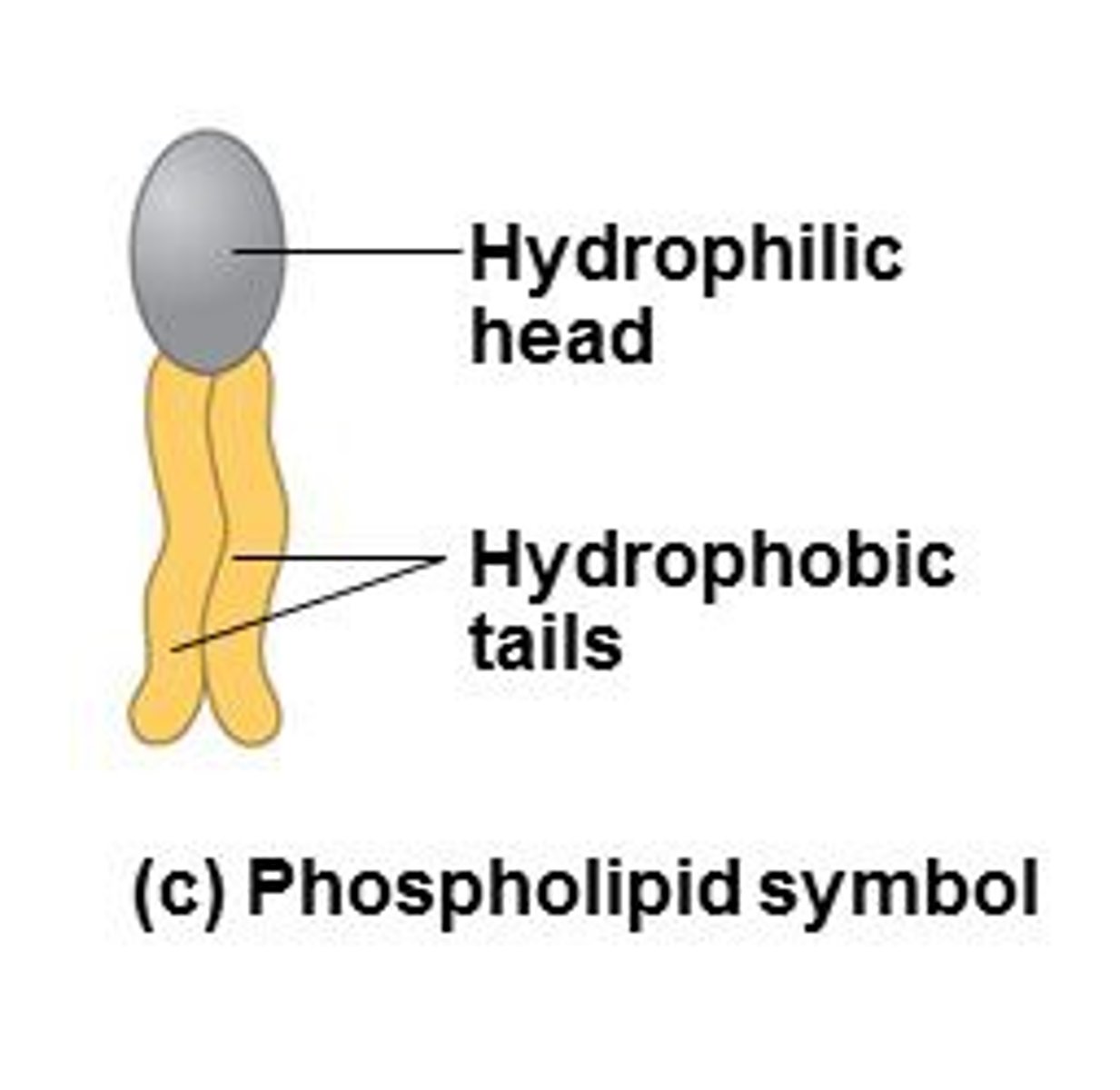
What does the hydrophilic head contain?
glycerol and phosphate
What does the hydrophobic tail contain?
fatty acids
What do phospholipids make up?
Hydrophobic bilayer of cell membranes
What can carbohydrates combine with phospholipids in the cell surface membrane to create?
Glycolipids - Important in cell recognition
Are phospholipids polar and how does this relate to it's function?
Yes - so can form a bilayer
Are triglycerides polar and how does this relate to it's function?
No - makes them hydrophobic - useful for storage
List 4 roles of lipids
- Source of energy
- Waterproofing (insoluble)
- Provides insulation
- Protects organs
Describe how to test for lipids in a sample
1. Dissolve solid samples in ethanol.
2. Add an equal volume of water and shake.
3. Positive result: milky white emulsion forms
The scientist used quantitative Benedict's tests to produce a calibration curve of colorimeter reading against concentration of maltose.
Describe how the scientist would have produced the calibration curve and used it to obtain the results in the graph.
- Make maltose solutions of different concentrations (and carry out Benedict's test on each);
- Use colorimeter to measure colorimeter value of each solution and plot calibration curve
- Find concentration of sample from calibration curve
What test did the scientist use to produce a calibration curve for maltose concentration?
Quantitative Benedict's tests
What is the first step the scientist took to produce the calibration curve?
Make maltose solutions of different concentrations and carry out Benedict's test on each.
How did the scientist measure the colorimeter value of each solution?
Using a colorimeter.
What did the scientist do after measuring the colorimeter values?
Plot the calibration curve.
How does the scientist find the concentration of a sample?
By using the calibration curve.