reading 10 (plp 148)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
morphological features of zygomycetes
zygospore
most species are hyphal
asexual spores are typically formed in a sporangia
morphological features of glomeromycotina
least variation in ecology across the phylum (except for microsporidia)
arbuscule mycorrhiza
mycelia are characteristically nonseptate
septa do form, but onlyl to delimit spores or to seal of old hyphae
spores typically form at the apex of hyphae
develop thick walls to survive harsh environmental conditions
germinate, infect into roots and set up new mycorrhizal association
large spores usually develop very thick walls
contain lipids, cytoplasm, and numerous nuclei
aggregated into groups called sporocarps
sexual reproduction in zygomycetes
progametangia come into contact
gametangia form as the tips of the progametangia are separated by formation of septa
the gametangia then fuse together at the point of contact, accomplishing plasmogamy
karyogamy follows quickly afterward to form a diploid zygote
thick cell wall forms around the mature zygospore to protect the zygote from the elements
meiosis occurs just before germination, with only 1 haploid nucleus surviving to develop a haploid thallus

asexual reproduction in zygomycetes
zygospores germinate (?) into a sporangiophore which contains a sporangium
sporangium produce spores (1n)
hyphae of different mating types interact and lead to gametangia production
as gametangia are being produced, plasmogamy occurs, and karyogamy right after
resulting in multinucleate zygospore that undergoes meiosis to produce 1 haploid nucleus

rhizoids
in Rhizopus
anchor the fungus to its substrate, and serve in nutrient uptake
zygospore
unicellular sexual spore that characterizes zygomycetes
sexual reproduction in the zygomycetes results in the formation of a multi-nucleate zygospore and thick-walled, resistant, or resting spore
sporangiophore
a specialized stalk or hypha that bears one or more structures called sporangia, which contain spores used for asexual reproduction
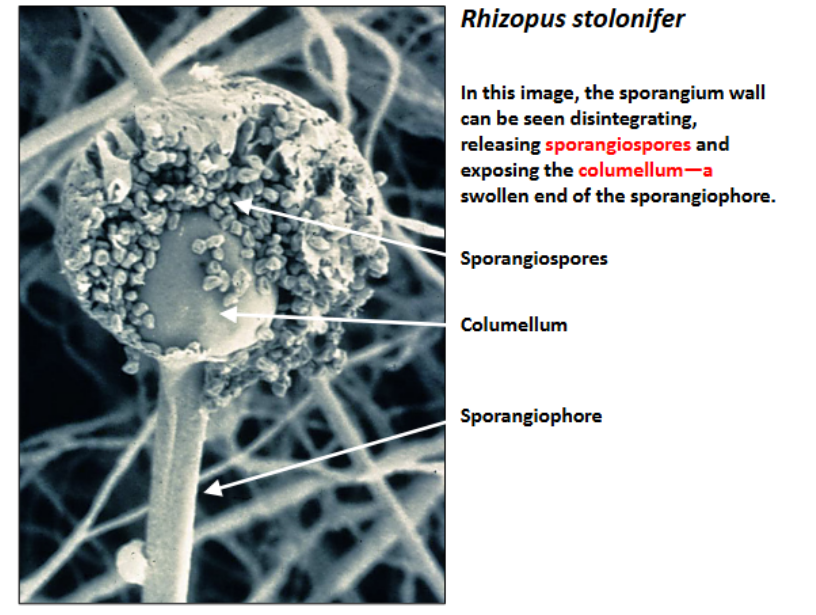
columellum
a sterile, column-like structure that protrudes into the sporangium to provide support and aid in the release of spores
arbuscule
tree-like structures are points of nutrient exchange between fungus and plant within plant root cells
found within individual plant cells between the cell wall and the cell membrane
vesicle
subsporangial vesicle
swollen area in the sporangiophore just below the sporangium
detects light at its base, causes sporangiophore to grow toward the light
at maturity, sporangiophores are all pointed toward the light
turgor pressure builds up until wall ruptures, sporangium is “squirted” up to a meter
Glomeromycota
form vesicles in roots
hyphal swellings in the root cortex that contain lipids and cytoplasm
storage organs
sporocarp
glomeromycota
some species, spores are aggregate into groups called sporocarps
may be encased in an outer layer (peridium)
ecological features of zygomycetes
majority are saprobes, growing on damaged fruit and also on mammal dung
Rhizopus and Pilobolus
grow as hyphae, or as yeasts where oxygen is scarce and carbon dioxide is abundant
septa in hyphae are rare, most septa that are formed separate hyphae from reproductive structures
mitotic spores are formed in sporangia in process similar to zoospore formation within chytrid sporangia , but w/o flagella and WITH cell walls
Rhizopus
forms stolons rapidly to colonize a substrate, cobwebby appearance of cultures is due to the presence of the stolons
rhizoids anchor the fungus to its substrate,
Pilobolus
dung-fungus
spores attach to grass and eaten by cows
pass through cows gut, which breaks down the resistant spore wall, grows on organic matter,
as patties decompose, fungus is exposed to light, which stimulates formation of the next generation of spores
entomophthora
zygomycetes
insect host
sporangia are actually conidia, forming via blastic process similar to Ascomycota and diff than what is typically seen in zygomycetes
spores actively discharged
shot away from dead insect
ecological features of glomeromycotina
biotrophic symbionts
least variation in ecology across the phylum (with possible exception of the microsporidia)
all but 1 species are obligately symbiotic with plant roots
arbuscular mycorrhiza with plants