Botany: Exam 3 Seedless Plants
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vascular and Non-Vascular
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
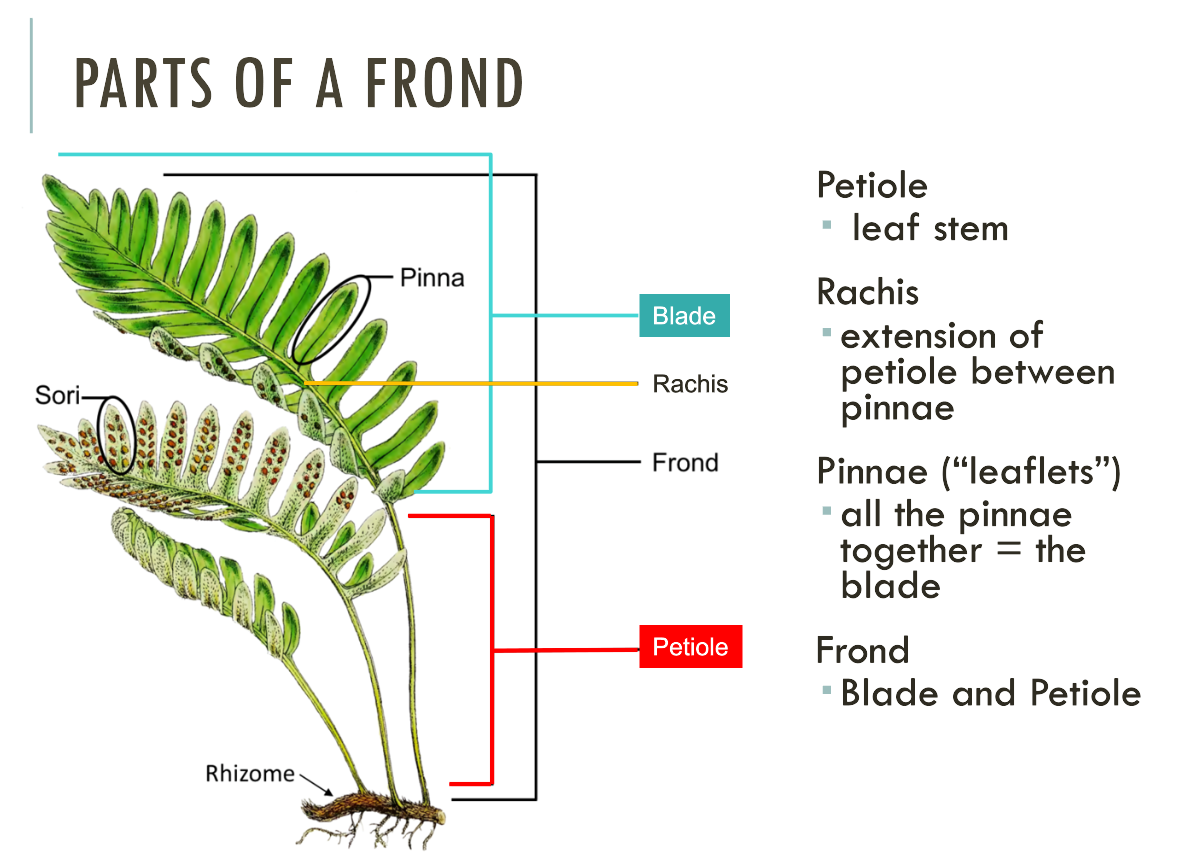
Fern Anatomy
Know: fronds, stipes/petiole, pinnae, sori, indusia
Leptosporangia vs Eusporangia
Leptosporangium:
Develops from 1 initial cell
Sporangial wall is 1 layer thick
Occurs in most ferns, not very common overall
Eusporangium: a true sporangium
Sporangium develops from 2+ initial cells
Sporangial wall (sterile jacket layer) is 2+ cell layers thick
Most vascular plants have this, most common type overall
Ferns have leptosporangium and everyone else has eusporangium.
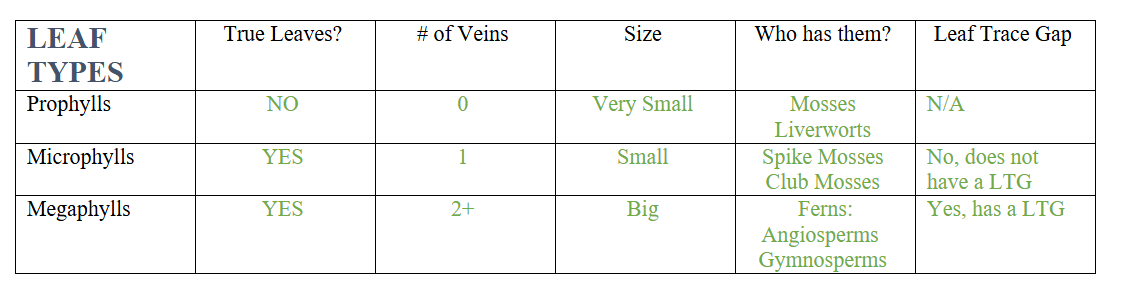
Leaf Types/Evolution
prophylls, microphylls, megaphylls
Lycopodium (clubmosses)
Structures
Stem: Creeping or erect, dichotomously branched.
Leaves (microphylls): Small, simple, with a single vein; arranged spirally or in whorls.
Roots: Adventitious, arising from the stem.
Sporangia: Located at the base of specialized leaves (sporophylls).
Strobilus
Cone-like reproductive structure
Vascular, Seedless Plants: Spore Dispersal Mechanism
The spore dispersal mechanism in vascular seedless plants involves the release of lightweight spores that are easily dispersed by wind.
Phyla matching: Monilophyta and Lycopodiophyta
The phyla Monilophyta and Lycopodiophyta are both seedless vascular plants, but they belong to different phyla. Monilophyta includes ferns and horsetails, while Lycopodiophyta includes club mosses. These phyla are characterized by their seedless nature and lack of true roots, leaves, and vascular tissue. They have a life cycle that alternates between haploid and diploid stages, with the diploid sporophyte being the dominant phase.
Non-vascular, seedless plants (Bryophytes):
Is the gametophyte or sporophyte the dominant generation?
The gametophyte in the dominant/conspicuous generation.
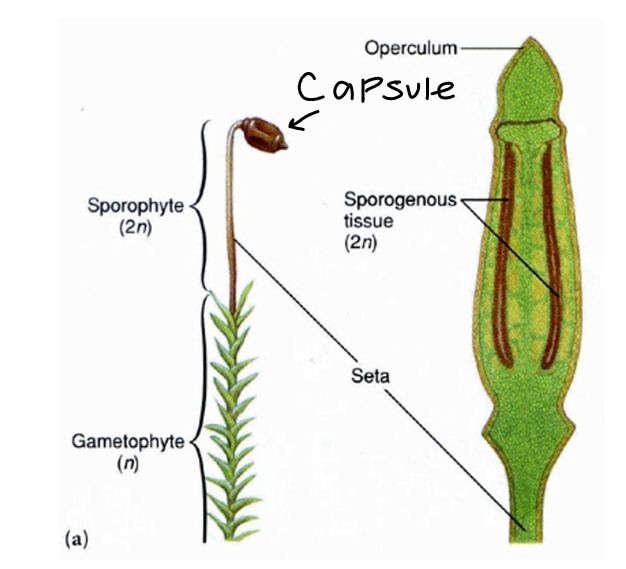
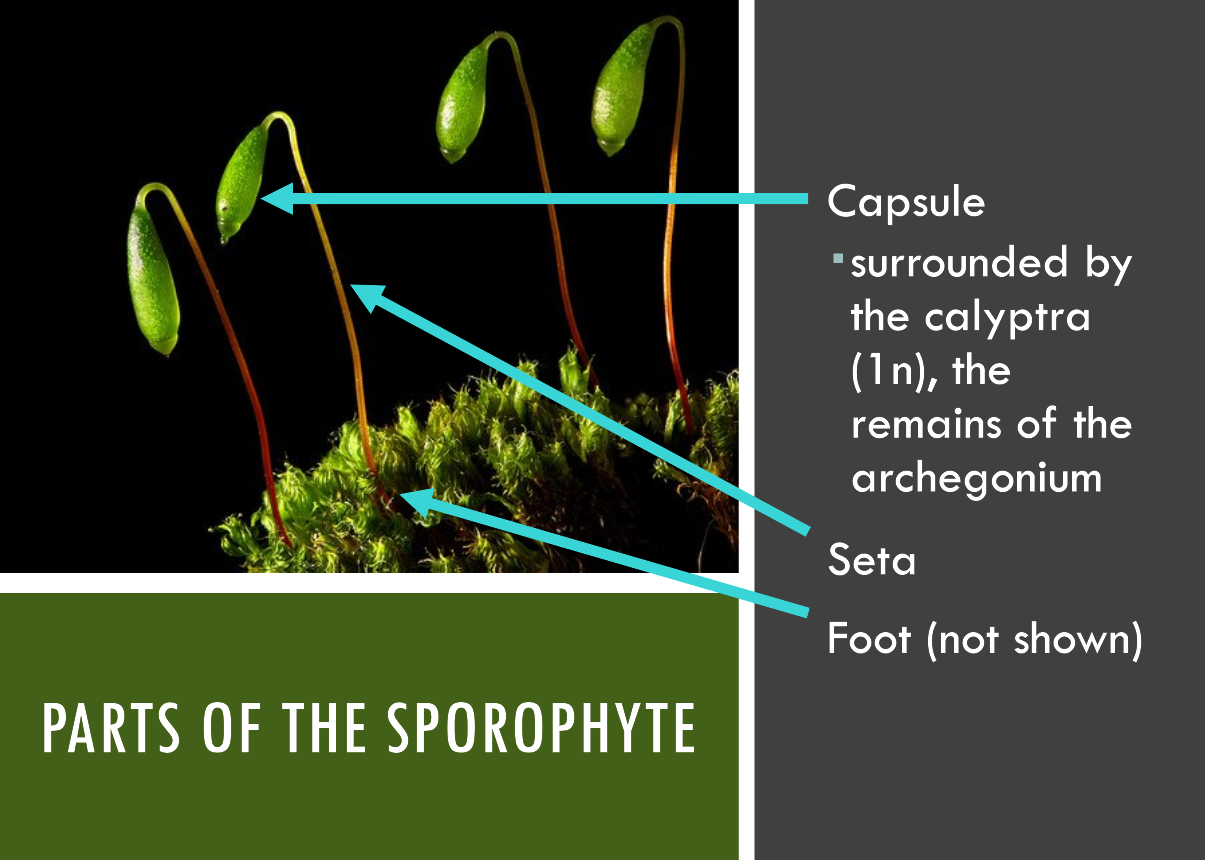
Bryophyte Sporangia Structures
know:
seta
capsule
operculum
peristome teeth
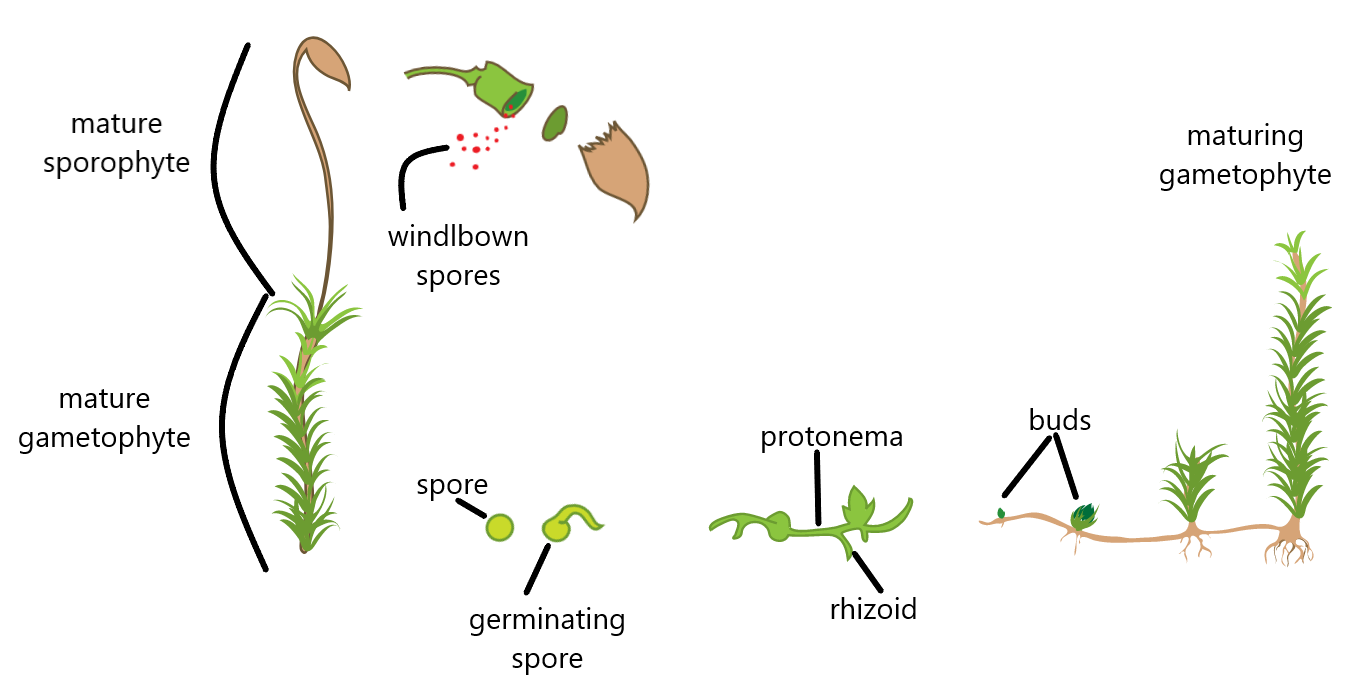
Bryophyte Protonema
The protonema is a thread-like chain of cells that forms the earliest stage of development of the gametophyte in the life cycle of mosses
Bryophyte Gemmae
Gemmae are asexual reproductive structures in bryophytes, allowing for vegetative reproduction and the establishment of new individuals and rapid population increase.

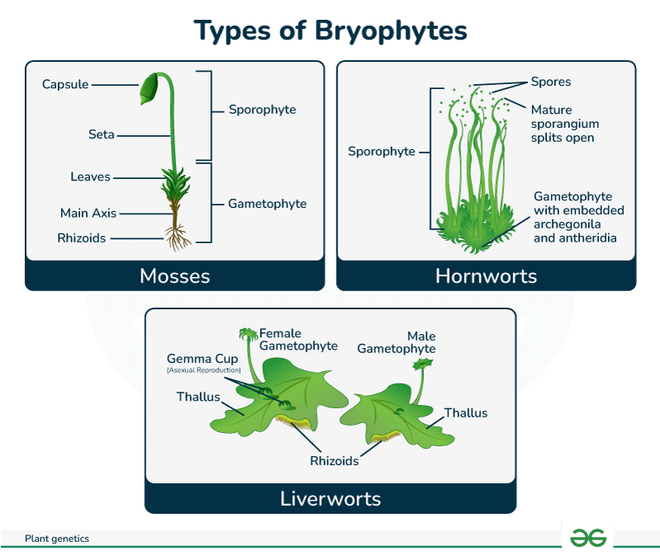
Types of Bryophytes
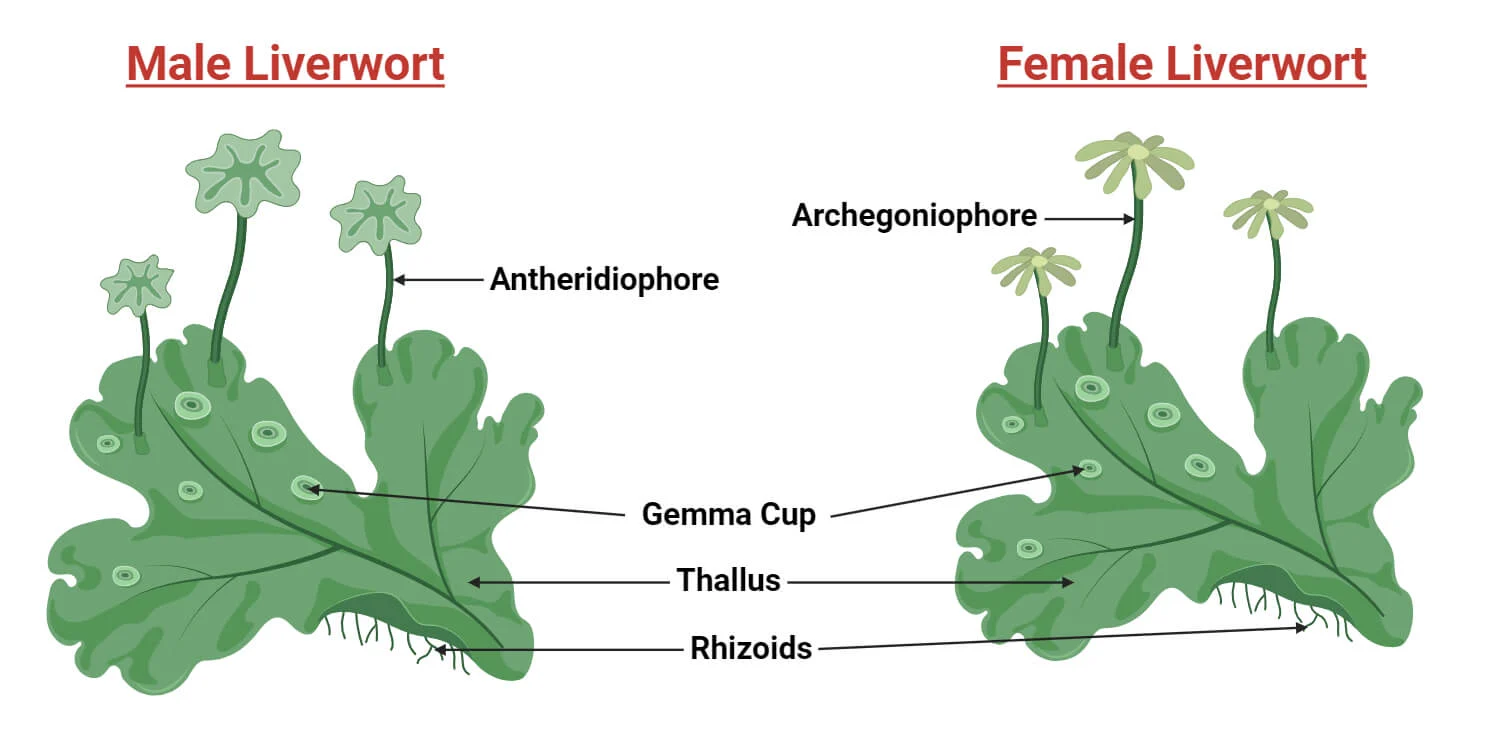
Liverworts Reproductive Structures
Antheridiophore: Syngamy occurs by water droplets splashing the cup, causing the sperm to splash onto the archegonia
Archegoniophore: When the sperm is splashed over, the syngamy occurs under the archegonia’s ray (“palm tree leaf”)
Calyptra (Bryophytes)
Leftover remains of the parent archegonia; the epidermal tissue of the old archegonia because they are only used once
Elaters (Bryophytes)
Elaters are elongated, tubular cells that are typically found alongside spores within the spore capsules of liverworts. They have spiral thickenings that allow them to respond to changes in humidity. When conditions are dry, elaters coil and uncoil, propelling the spores into the air to enhance their chances of landing in suitable environments for germination. This mechanism is vital for the reproductive success of these non-vascular plants.
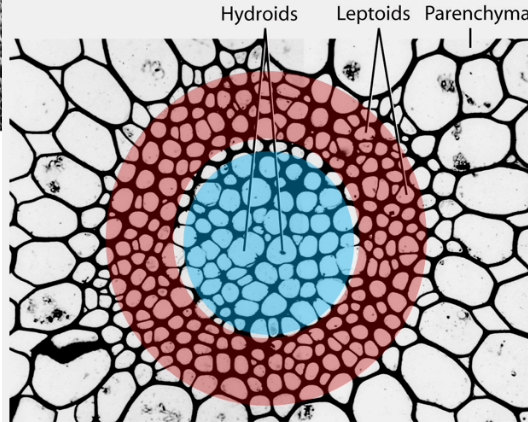
Hydroids (Bryophytes)
transport water and minerals (like xylem)