Bacteriology & Mycology Lecture 4: Staphylococcus Spp
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Facultative anaerobic
Staphyloccus spp. can grow with or without oxygen meaning they are ___________________
cocci
What shape are Staphylococcus spp ?
gram-positive
What shape is Staphylococcus spp?
grape-like
Staphylococcus sp arranges in ________________ clusters
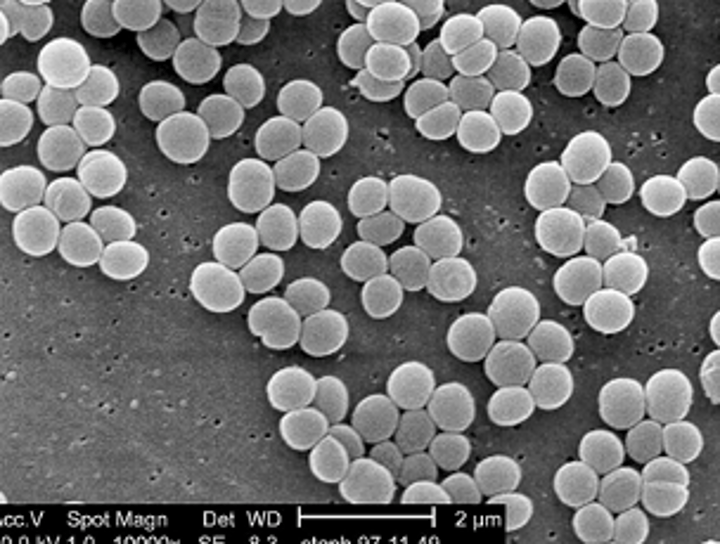
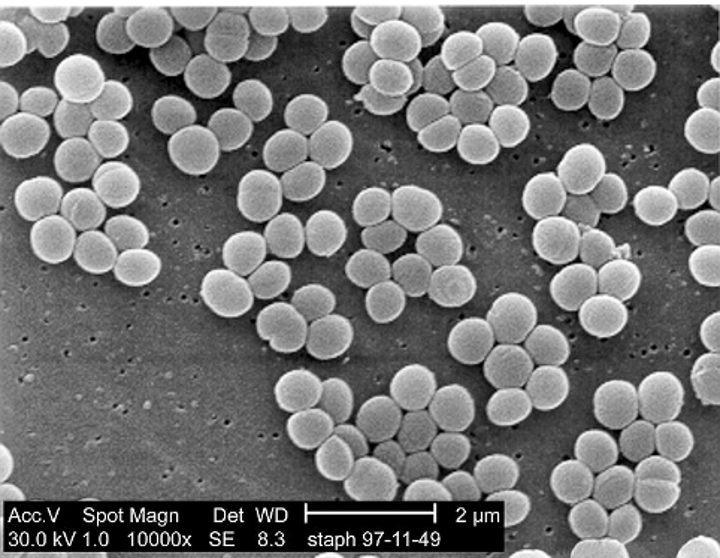
20
About how many species of Staphyloccocus spp are there?
host-specific
Species of Staphylococcus spp are mostly _________________
S. aureus, S. pseudintermedius, S. hyicus, S. epirdermidis
What four Staphylococcus species are common pathogens in humans and animals?
coagulase positive
S. aureus, S. pseudintermedius and S. hyicus are ___________________
S. epidermidis
What pathogenic species of Staphylococcus is coagulase negative?
S. aures
Staphylococcus spp. that is transient for humans and many domestic animals
S. pseudintermedius
What Staphyloccocus spp is transient and proven to cause disease in dogs?
S. hyicus
What Staphylococcus spp. is transient, usually on pigs and causes greasy pig disease?
S. epidermidis
What Staphylococcus spp. is a resident on most animals, rarely a skin pathogen but may cause deeper infections?
long lived
Staphylococcus spp. are ________________ in the environment
heat and desiccation
What are Staphylococcus spp. resistant to in the environment?
ubiquitous
Staphylococcus spread easy and are _______________
recto-anal junction
Where can S. pseudintermedius be found on dogs?
low
How much resistance do most animals have against Staphylococcus spp. superficially colonizing?
injury, catheters, disruption of normal flora, concurrent infection, sub-optimal immune function
What are some predisposing factors that may allow Staphylococcus spp. to invade the body?
extracellular matrix
Once the epidermis is damaged, Staphylococcus spp. infect the dermis by binding to the host's ___________________
capsule and clot formation
How does Staphylococcus spp. resist phagocytosis?
true
Staphylococcus spp can survive inside phagocytic cells (true or false)
proteases
What digests host tissues, damages skin and helps Staphylococcus spp spread in a host?
leukocidin
What exotoxin kills leukocytes?
hemolysin
What exotoxin causes vasoconstriction and dermonecrosis?
coagulase
What exotoxin forms clots, which protect bacterium from phagocytosis?
leukocidin, hemolysin, coagulase
What exotoxins does Staphylococcus spp use?
species and strains
Clinical presentation and severity of Staphylococcus spp varies depending on what?
false
All strains of Staphylococcus spp produce all virulence factors possible (true or false)
progression and resolution
What do host factors play a factor in when considering virulence of Staphylococcus spp?
opsonization and phagocytosis
What host mechanisms have interplay with bacterial growth and clearance?
innate immunity
What type of immunity opsonizes Staphylococcus spp by complement and phagocytizes by neutrophils and macrophages?
humoral immunity
What type of immunity has a somewhat limited role in fighting Staphylococcus spp. - clears organisms by opsonizing with antibodies and clears toxins?
cell-mediated immunity
What type of immunity plays a role in killing intracellular staphylococcus spp by activated macrophages?
gram stains and cytology
What diagnosis methods on smears would be used to diagnose Staphylococcus spp?
surgical biopsy and histopathology
What can be done to diagnose the primary problem of a bacterial infection (Staphylococcus spp)?
primary
Staphylococcus is usually a ____________ invader
exotoxins
What does Staphylococcus produce to allow secondary invasions of other bacteria into host?
S. aureus
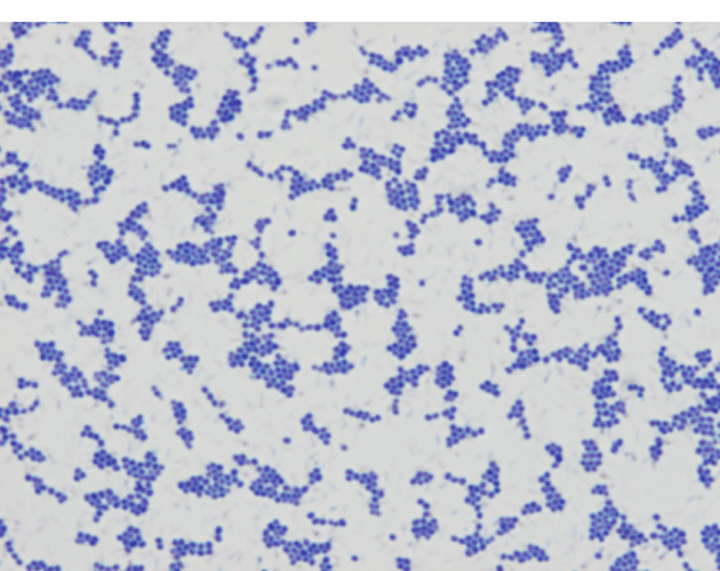
What Staphylococcus spp is pictured? (creamy color)
gram stain
What diagnostic technique was done to this bacteria? (s. aureus)
scanning electron micrograph
What diagnostic technique is pictured? (s. aureus)
antibiotics
What can be used to treat a bacterial skin infection of Staphylococcus spp?
address any underlying/predisposing issues
What is the first step in treating a bacterial skin infection?
Exudative Epidermitis (greasy pig disease)
What is pictured here?
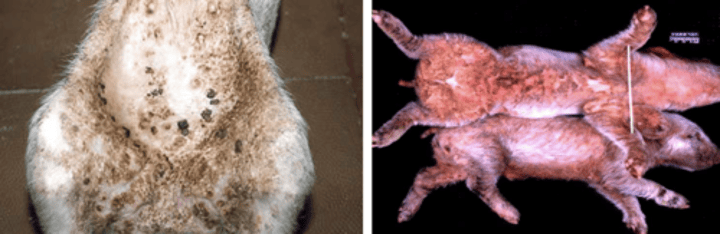
Staphylococcus hyicus
What bacteria causes exudative epidermitis (greasy pig disease)?
sucklers and weaned pigs up to 3 mo
Who is usually affected by exudative epidermitis?
highly
How contagious is exudative epidermitis?
excessive sebaceous secretion, exfoliation and exudation on skin surface
What is exudative epidermitis in pigs characterized by?
non-pruritic dermatitis
Pigs affected by exudative epidermitis causes pigs to be anorexic, depressed, and febrile as well as have extensive __________________ with greasy exudate
under 3mo
Piglets under ____________ may die from exudative epidermitis within 24-48 hours
vaginal mucosa
Where can S. hyicus be found on healthy sows?
bite wounds or small abrasions
How does S. hyicus most likely enter the skin of young pigs?
no
Is S. hyicus able to penetrate intact skin?
production of exofoliative toxins
What is virulence of S. hyicus linked to?
cell-cell adhesion of karatinocytes
What do exofoliative toxins produced by S. hyicus reduce in the superficial epidermis?
immunity, nutrition, skin damage
What are other factors that could predispose a piglet to exudative epidermitis?
gilt litters
What type of piglet litters are more likely to have exudative epidermitis outbreaks?
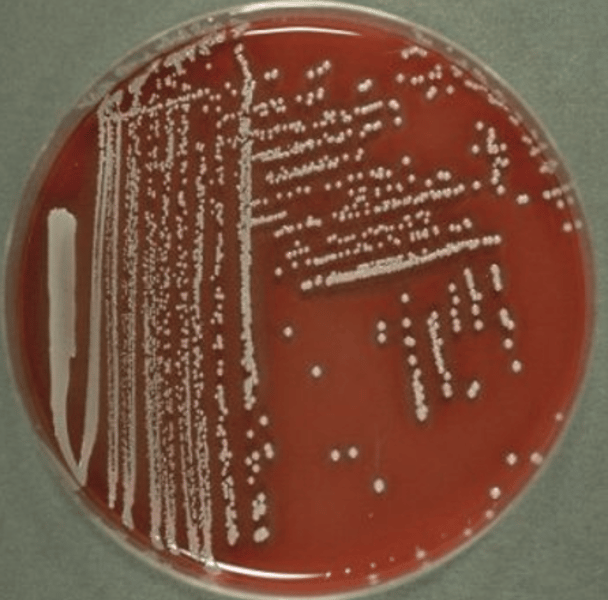
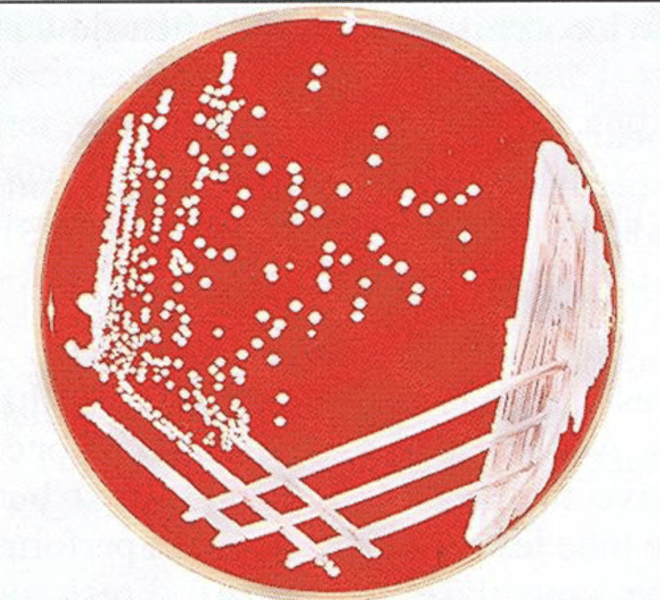
S. hyicus
What Staphylococcus spp is pictured here on sheep blood agar?
hydrated lime w/ phenol disinfectant
What should you brush over concrete surfaces with to manage exudative dermatitis?
tails and teeth
Removal procedures of ______________ should be reviewed to ensure they are not leading to damage and subsequent infection
skin of the udder
What is one resevoir for S. hyicus that should be sprayed daily 3 days before and after farrowing?
iodine-based skin antiseptic
What should sow udders be sprayed with to prevent exudative dermatitis?