Organelles
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What are the 2 types of cell that we need to know about?
Eukaryotic - you for your cells (animal and plants)
Prokaryotic - Bacterial cells
What are the structures in a eukaryotic cell which have membranes?
Plasma membrane
Golgi apparatus
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Mitochondria
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Lysosomes
Chloroplasts
Cilia
undulipodia
Vacuole
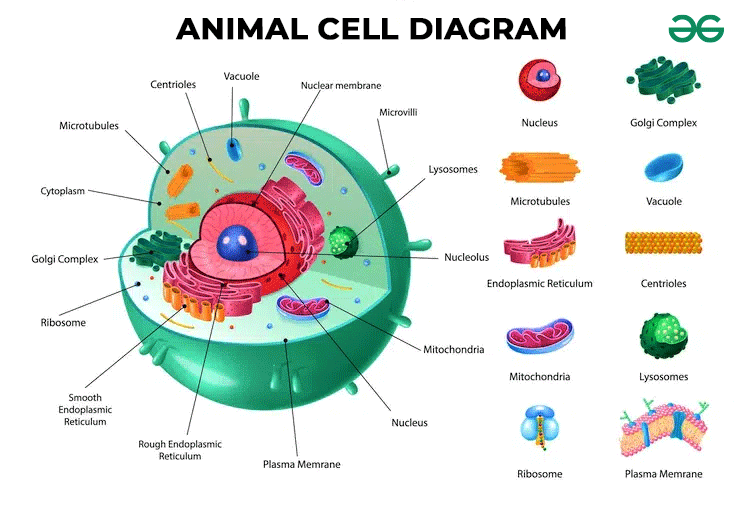
What structures make up the nucleus?
Nuclear envelope - double membrane
Nuclear pores
Nucleoplasm - Jelly like material
Chromosomes - Protein bound, linear DNA
Nucleolus - Small sphere inside of the nucleus
What is the function of the nuclear envolope?
Separates the contents of the nucleus from the rest of the cell
What is the function of the Nucleolus?
It is where rRNA is made
It is where ribosomes are made
What is the function of the Nuclear pores?
They allow for substances to leave and enter the nucleus
Leave:
mRNA
Ribosomes
Enter:
Steroid hormones
What is the function of the nucleoplasm?
To hold genetic coding for each cell - Chromosomes
What are the 4 functions of the nucleus?
rRNA synthesis
Ribosome synthesis
Holding genetic material
The site for DNA replication
Controls the activities the cell
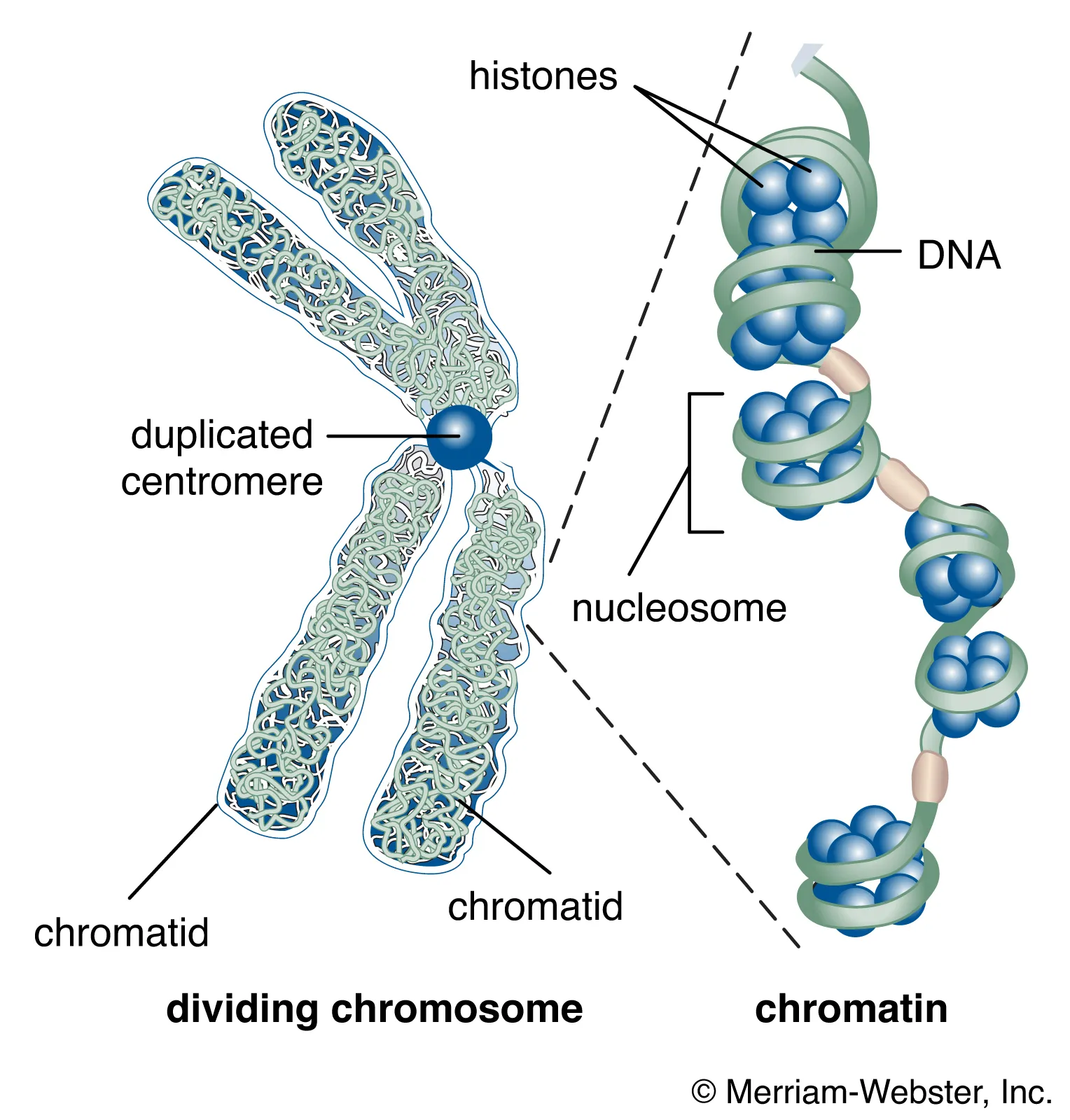
How is DNA packed so tightly?
Because they are in Chromatins which are wound around histone proteins
Describe the structure of the Rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER)?
A system of membranes, which contain fluid-filled cavities(cisternae) that are continuous with the nuclear membrane
It is coated in ribosomes
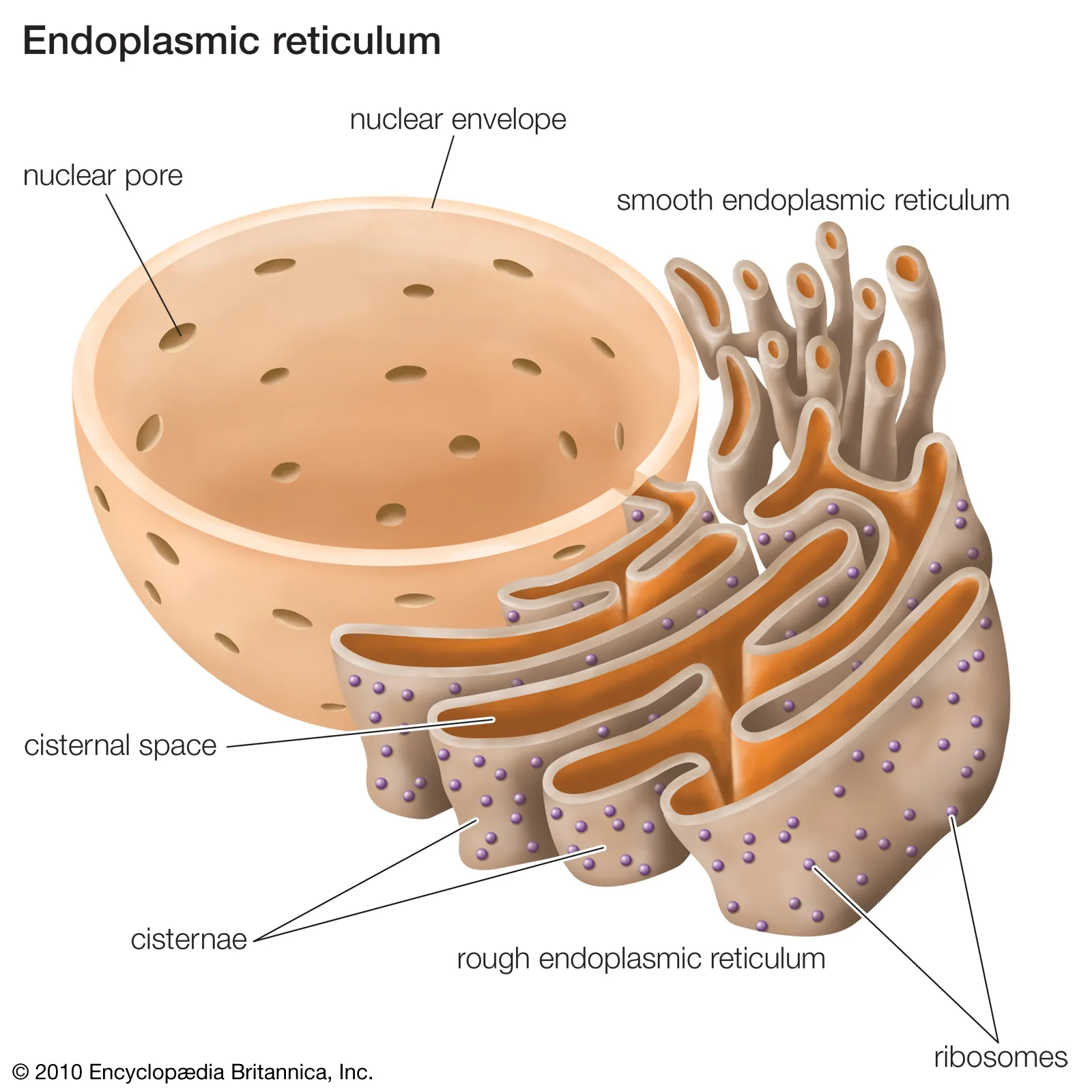
Describe and explain is the function of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
It is the intracellular transport system:
the cisternae form channels for transporting substances from one area of the cell to another
It provides a large surface area for ribosomes:
They assemble amino acids into proteins
These proteins actively pass through the membrane into the cisternae what are transported to the Golgi apparatus
What is the Smooth endoplasmic reticulum(SER)?
It is a system of membranes, containing fluid-filled cavities(cisternae) that are continuous with the nuclear membrane
There are no ribosomes on the surface
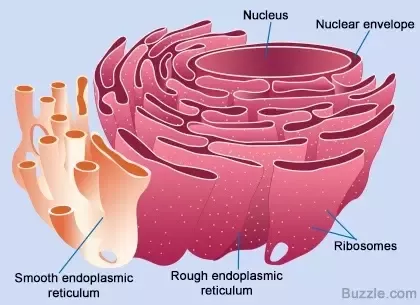
What are the functions of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum(SER)?
Contain enzymes that catalyse reactions involved with lipid metabolism:
Synthesis of cholesterol
Synthesis of lipids/phospholipids needed in the cell
Synthesis of Steroid hormones
It is involved with absorption, synthesis and transport of lipids(from the gut)
What is the structure of the Golgi apparatus?
It consists of a stack of membrane-bound flattened sacs.
Secretory vesicles bring materials to and from the Golgi apparatus
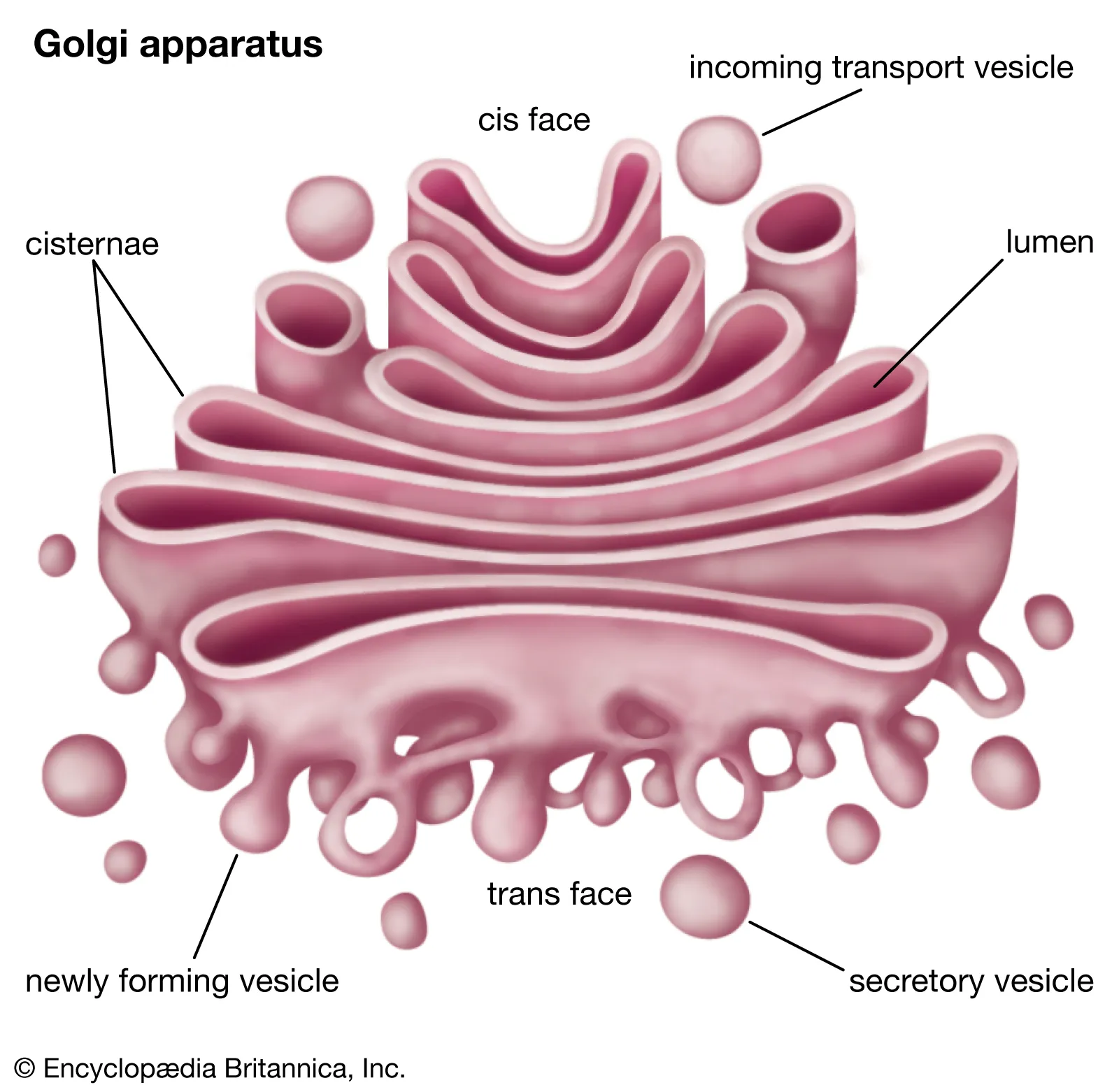
What are the functions of the Golgi apparatus?
Proteins are modified in the Golgi apparatus, for example by:
Adding sugar molecules to make glycoproteins
Adding lipid molecules to make lipoproteins
Being folded into their 3D Shape
The Golgi apparatus packages proteins into vesicles which are pinched off and then:
Stored in the cell or
Moved to the plasma membrane, wither to be incorporated into the plasma membrane, or exported outside of the cell
What is the structure of a mitochondrion?
They may be spherical, rod shaped or branched and are 2-5 micrometres long
They are surrounded by 2 membranes with a fluid-filled space between them called the intermembrane space:
The inner membrane
The outer membrane
The inner membrane is highly folded into cristae
The inner per of the mitochondrion is a fluid-filled matrix
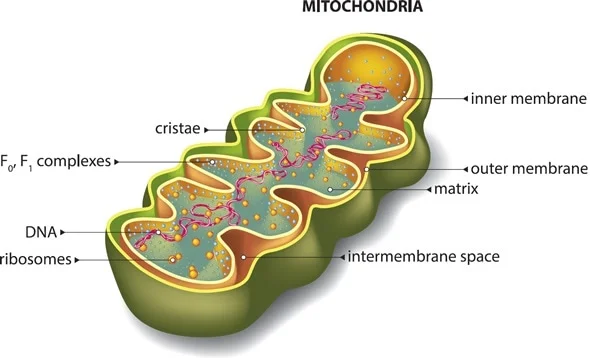
What are the functions of mitochondria?
The site of ATP production during aerobic respiration
Self-replicating, so more can be made if the cell’s energy needs increase
Abundant in cells where a lot of metabolic activity take place:
Liver cells
Synapses between neurons where neurotransmitter is synthesised and released
Muscle cells
What is the structure of lysosomes and what do they contain?
They are small bags, which are formed from the Golgi apparatus
Each lysosome is surrounded by a single membrane
They contain powerful hydrolytic(digestive)enzymes
They are abundant in phagocytic cells such as:
Macrophages
Neutrophils
What are the functions of lysosomes?
Lysosomes keep the powerful hydrolytic enzymes separate from the rest of the cell
Phagocytic cells can ingest or digest invading pathogens
Recycling - Lysosomes can engulf old cell organelles and foreign matter, digest the and return the digested components to the cell for reuse
What is the structure of chloroplasts and what is it made of?
Large organelles: 4-10 micrometres long
They are surrounded by a double membrane or envelope
It is made of an:
Inner membrane which is continuous with thylakoids, which contain chlorophyll
Each stake or pie of thylakoids is called a granum
There is a fluid-matrix called stroma
They also contain intergranal lamellae
In-between the inner and outer membrane there is a intermembrane compartment
What does the stroma contain?
loops of DNA, starch, ribosomes and lipids(enzymes)
What is the function of chloroplasts?
The site of photosynthesis
What is the structure of Vacuoles?
It is surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast, and contains fluid
What are vacuoles in plants called?
Permanent vacuoles
What is the function of the vacoule?
Holds water and solutes
It makes the cell turgid:
When the vacuole is full it pushes against the cell wall
What is the structure of cilia?
They are small hair like protrusions from the cell are surrounded by the cell surface membrane
They contain microtubes which are in a 9+2 arrangement
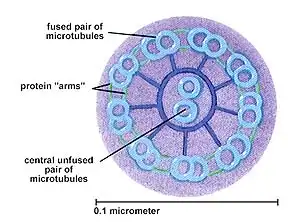
What is the function of cilia?
The epithelial cell which lines the air way each have many hundreds of cilia which beat and move mucus
Nearly all cell types in the body has 1 cilium that acts as an antenna. It contains receptors and allows the cell to detect singles about its immediate environment
What is the structure of undulipodia?
It is a tail protruding from the cell and is surrounded by the cell surface membrane
They contain microtubules in a 9 + 2 formation
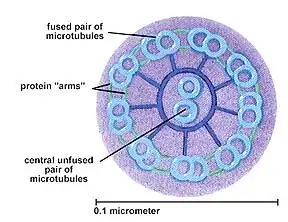
What are both cilia and undulipodia formed from?
Centrioles
What is the structure of ribosomes, what are they made of and where are they located?
Structure:
Small spherical organelles, about 20 nanometres in diameter
Formation:
Made of ribosomal DNA
Made in the nucleolus, as 2 separate subunits, which combine after passing through the nuclear envelope
Location
some remain in the cytoplasm and some attach to the RER
What are the 2 sub-units of ribosomes?
70s and 80s
What are the functions of ribosomes?
They are for protein synthesis
What s the structure of centrioles?
Consist of 2 bundles of microtubules at right angle to each other.
The microtubules are made of tubulin proteinn subunits and are arranged in a cylinder
The micro tubules are arranged in microtubule triplets
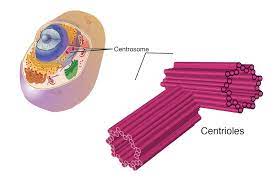
What are the functions of centrioles?
In cell division:
Before cell division, The spindle, which are made of threads of tubulin, forms from the centrioles
Chromosomes attach to the middle part of the spindle and then motor proteins walk along the tubulin threads which pull the chromosomes to opposite ends of the cell
Formation of cilia and undulipodia
Before the cilia form, the centrioles multiply and line up beneath the cell surface membrane
Microtubules then sprout outwards from each centriole forming a cilium or an undulipodium
Are centrioles present in plants?
No
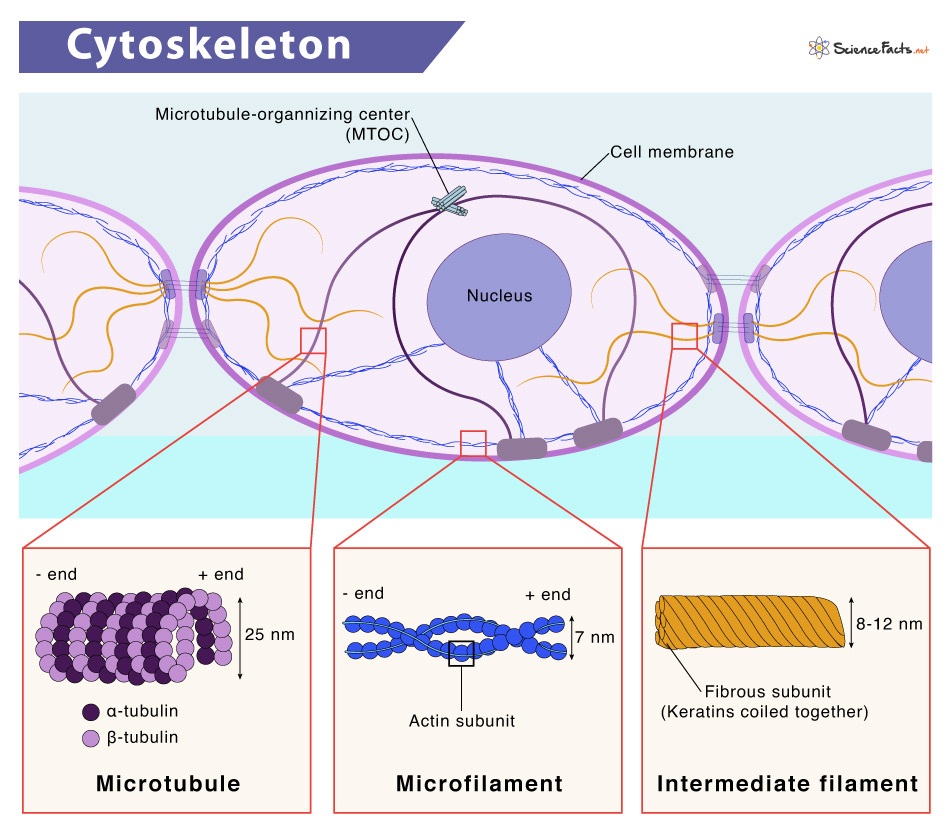
What is the cytoskeleton?
A network of protein structures within the cytoplasm
What are the 3 types of protein structures of cytoskeleton and what is their structure?
Microfilaments:
Rod-like microfilaments which is a polymer of the monomer actin
About 7nm is diameter
Intermediate filaments:
About 10 nm is diameter
Microtubules
Straight and cylindrical, made of protein subunits called tubulin
About 18-30 nm in diameter
What is present on the cytoskeletons
Enzymes called Cytoskeletal motor proteins
What is the energy source of cytoskeletal motor proteins and how is it formed?
ATP
Formed by hydrolysing ATP after binding onto its active site
What are the 3 cytoskeletal motor proteins?
Myosin
Kinesin
Dynein
What is the function of cytoskeleton microfilaments?
They give support and mechanical strength
They keep the cell’s shape stable an
Allow cell movement
What are the functions of cytoskeletal microtubules?
Provide shape and support to cell
Help substances and organelles to move through the cytoplasm within the cell
They form a track which motor proteins can walk along and drag organelles from one part of the cell to the other
They form spindle before cell division
They form cilia and undulipodia
What is the function of cytoskeletal intermediate filaments ?
They anchor the nucleus within the cytoplasm
They extend between cells in some tissue, which enables cell-cell signalling
What is the structure of the cell wall?
In plants it is on the outside of the plasma membrane
It is made from bundles of cellulose fibres which are perpendicular to each other
What is the function of cell walls?
It provides strength and prevents cells from bursting(plants-when turgid)
Maintains cell’s shape
Contribute to the strength and support of the whole plant
Are permeable and allow solutions to pass through
What organisms have a cell wall?
Fungi
Bacteria cells
Plant cells
What is the cell wall in fungi made of?
Chitin
What Structures are present in plant cells but not in most animal cells?
Vacuole
Cell wall
Chloroplasts
Describe how a protein is made and secreted
DNA is transcribed into mRNA
mRNA leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore
The mRNA goes to rough endoplasmic reticulum and binds to a ribosome
The mRNA is translated by the ribosome and forms a protein
The protein is the packaged into a vesicle and is pinched off the RER
The cytoskeletal motor proteins move the vesicle towards the Golgi apparatus and fuses the Golgi apparatus
The protein is now in the Golgi apparatus where it is being modified
After modification a secretory vesicle is formed by the Golgi apparatus and is pinched off
The vesicle is moved towards the plasma membrane by motor proteins on the cytoskeleton and fuses to the plasma membrane - exocytosis
The plasma membrane opens to release the protein
What are the similarities between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells?
Both have a plasma membrane
Both have Cytoplasm
Both have Ribosomes for assembling amino acids into proteins
Both have DNA and RNA
What is the difference between Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus - DNA is free in the cytoplasm while eukaryotic cells do
Prokaryotic vells have no membrane bound organelles while eukaryotic have many membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic cells have cell wall made of peptidoglycan while eukaryotic cell walls are made from cellulose or chitin
Prokaryotic cells have DNA is plasmids while eukaryotic cells have linear DNA
Why do prokaryotic cells have DNA in plasmids?
Because the DNA is “naked” and so therefore it is not wound around histone proteins
What structures are present in prokaryotic cells which are not in eukaryotic cells?
Flagellum - tails which allow bacteria to move
Pili - Hairs which enable bacteria to adhere ti host cells or to each other. Also allow the passage of plasmid DNA from one cell to another
Small loops of DNA called plasmids and main large ones too - Nucleoid
A protective waxy capsule surrounding the cell
What is the endosymbiont theory?
The theory that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes
How does the endosymbiont theory work?
1.5 - 2 billion years ago much larger prokaryotic cells engulfed smaller prokaryotic cells - some which can undergo aerobic respiration to produce ATP - mitochondria. and some which can under to photosynthesis to produce glucose - Chloroplasts
However, instead of these cells being destroyed, increase their membrane remained intact in the cell and they survived together
This prokaryotes have no evolved into eukaryotes
What is the evidence that this theory is true?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA which is also in plasmids which are found in prokaryotic cells
They also contained ribosomes which are also found in prokaryotic cells
When the organelles undergo division they also divide by binary fission which is the same as prokaryotic cells