Chemistry Rates and Enthalpy (AO3 main)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Exothermic reaction
A chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of heat, resulting in an increase in the temperature of the surroundings.
Endothermic reaction
A chemical reaction that absorbs energy in the form of heat, leading to a decrease in the temperature of the surroundings.
Enthalpy change
The overall change in energy in a reaction (ΔH)
Units for enthalpy
kJ/mol
ΔH when exothermic
negative, as energy is released into the surrounds
ΔH when endothermic
positive, as energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
Activation energy in a reaction profile
From reactants to the peak
ΔH in a reaction profile
From the reactants to the products
Reaction profiles
Diagram that show the relative energies of the reactants and products in a reaction, and how the energy changes over the course of the reaction.
Activation energy
Minimum amount of energy reactants need to collide with each other and react. This is the energy needed to break the bonds in the reactants and start the reaction. (energy supplied via heating)
What type of reactions are combustion reactions, neutralization reactions
Exothermic
What type of reaction is thermal decomposition
endothermic
Write down the equation for the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate.
CaCO3 (+HEAT) → CO2 + CaO
Calorimetry
Allows to measure the amount of energy transferred in a chemical reaction.
Biggest issue with calorimetry
Energy is lost to the surroundings
How to prevent energy from being lost into the surroundings in neutralization calorimetry?
Use insulation and use a lid to reduce energy lost by evaporation.
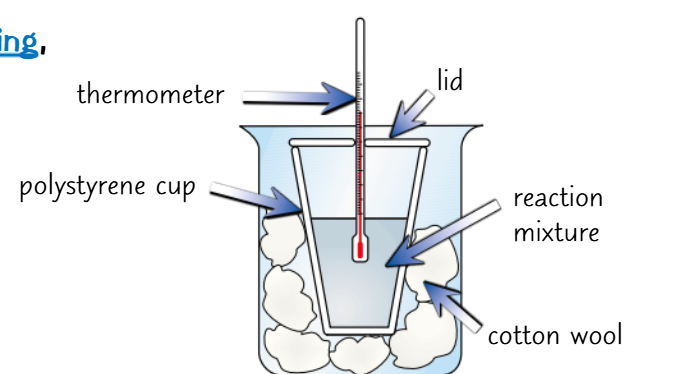
How do you test the effect of acid concentration on the energy released in a neutralisation reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide?
1) Put 25cm3 of 0.25mol/dm3 of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide into separate beakers.
2) Place the beakers in a water bath set to 25 degrees Celsius until they are both at the same temperature.
3) Add the HCl followed by the NaOH to a polystyrene cup with a lid.
4) Take the temperature of the mixture every 30 seconds and record the highest temperature.
5) Repeat steps 1-4 using different concentrations of hydrochloric acid.
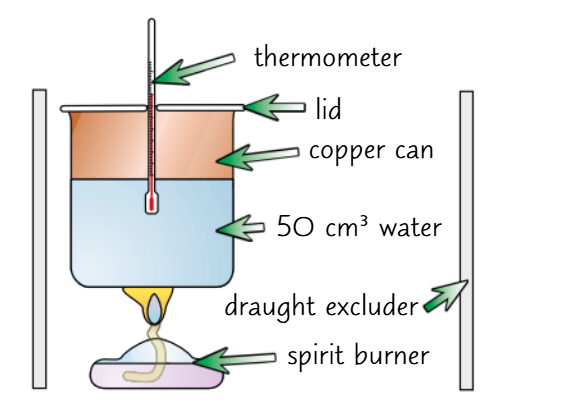
How to measure enthalpy change in a combustion reaction?
1) Put 50g of water of water in a copper can and record its temperature.
2) Weight the spirit burner with the fuel and a lid.
3) Put the spirit burner underneath the can, and light the wick. Heat the water, stirring constantly, until the temperature reaches about 50°C.
4) Put the flame out using the burner lid, and measure the final temperature.
5) Calculate the enthalpy change using the mass of water, temperature change, and the energy released by the fuel.
How to increase the accuracy of combustion calorimetry?
Use insulation, use a screen to prevent wind, stir the water constantly
Why is copper used in combustion calorimetry?
Copper conducts heat well
Enthalpy change for endothermic reactions.
The energy used to break bonds are greater than the energy released forming them.
Enthalpy change for exothermic reactions.
The energy released forming bonds is greater than the energy used to break them.
Enthalpy change formula
total energy absorbed to break bonds - total energy released forming bonds
rate of reaction
How fast the reactants of a reaction are changed into products
2 things the rate of reaction depend on
1) collision frequency of reacting particles; the more collisions there are the faster the reaction is
2) the energy transferred during a collision (particles must have enough energy for the collision to be successful)
List the factors affecting the rate of reaction
temperature, concentration/pressure, SA:V ratio, catalyst
How does temperature affect the rate of reaction?
When temperature is increased, particles move faster, therefore collide more frequently. Particles also gain more energy at higher temperatures, therefore there will be more successful collisions. Therefore, the rate of reaction increases.
How does concentration/pressure affect rate of reaction?
A more concetrated solution or more pressured gas would contain more particles of the reactant in the same volume, therefore collisions are more likely, increasing the reaction rate.
How does SA:V ratio affect rate of reaction?
A substance with a greater SA:V ratio would have a higher rate of reaction, as more of the solid will be exposed compared to its overall volume. Therefore, the particles around it will have more area to work on, increasing the frequency of collisions.
Catalyst
A catalyst is a substance which increases the rate of reaction without being chemically changed or used up in the reaction.
How does catalyst affect rate of reaction?
A catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur, by providing an alternative reaction pathway. As a result, more particles have the minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur when particles collide.
Formula for rate of reaction
rate of reaction = amount of reactant used or amount of product formed / time
3 ways to measure reaction rates
precipitation, change in mass, volume of gas given off
How to measure reaction rates for precipitation?
Place a beaker containing the reactant solutions onto a piece of paper with a mark on it. Once the mark dissapears, due to the precipitate is being formed, the reaction has ended. The faster the mark dissapears, the fast the reaction.
How to measure reaction rates using change in mass?
The rate of reaction for a reaction that produces a gas can be measured using a mass balance. As the gas is released, the lost mass is measured on the balance at regular time intervals. Once the mass stops changing, the reaction has ended.
How can gas released during this experiment be dangerous, how to counterract it.
Gas may be harmful, thus can be done in a fume cupboard.
Why is cotton wool used in this reaction?
To let gas escape but prevent substances from splashing out.
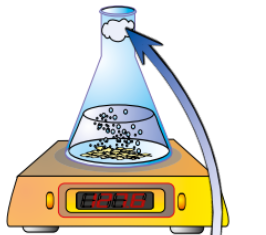
How to use the volume of gas given off to measure measure reaction rates?
A gas syringe can be used to measure the volume of gas given off. The more gas given off during a set time interval, the faster the reaction. The reaction is finished when no more gas is produced.
How may the size of the syringe of the experiment be dangerous?
If the reaction is too vigourous it may blow the plunger out of the end of the syringe.
How to test if a solid in a reaction is a catalyst?
Filter the solution and weigh it. If the mass is unchanged then it is a catalyst.