Microeconomics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
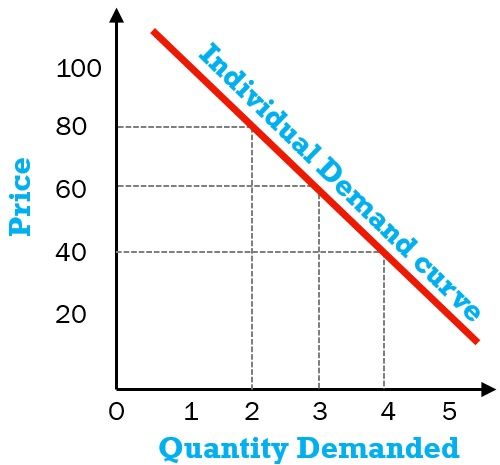
Individual Demand curve
graph plotting the quantity of an item that some plans to buy at each price
Interdependence principle
concept that individuals, businesses, and nations rely on one another to produce and consumer goods and services
Law of demand
tendency for quantity demanded to be higher when price is lower
Marginal principle
rule for making decisions by comparing extra benefit (marginal benefit) of one or more units of something against the extra cost (marginal cost) of the same unit
marginal benefit
the additional benefit arising from a unit increase in a particular activity.
marginal cost
the cost added by producing one additional unit of a product or service.
cost-benefit principle
action should only be taken if benefit ≥ cost
,
opportunity cost principle
tru cost of a decision is value of next best alternative
rational rule for buyers
buy more of an item if the marginal benefit is ≥ cost
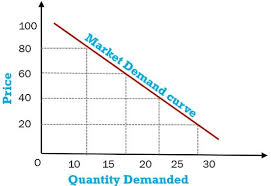
market demand curve
graph plotting the total quantity of an item demanded by the entire market, at each price
factors that shift demand curves
Income
Preferences
Expectations
Price of related goods
Congestion and network affects
Typer and number of buyers
Normal good
product for which demand increases when consumer income rises
Inferior good
good which income decrease in demand- something you stop buying when you earn more money EX instant noodles
Complementary good
goods that go together. demand for a good will increase if price of complementary good inceases
substitute good
goods that replace each other. demand for a good will increase if a price of a substitute good rises, and fall is substitute falls
Network effects
good becomes more useful because other people are using it
Congestion effect
good becomes less valuable because of other people using it
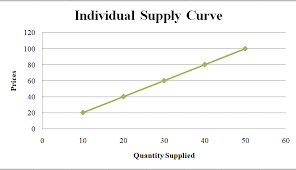
Individual supply curve
graph plotting the quantity of an item that a business plans to sell at each price
Law of supply
tendency for the quantity supplied to be higher when price is higher
Perfect competition
markets in which all firms in an industry sell an identical good
there are many buyers and sellers, each of who are small relative to the size of the market
Price takers
someone who decides to charge the prevailing price and whose actions do not affect the prevailing price → follow market price
Variable costs
those costs-labor and raw materials- that vary with the quantity of output you produce
fixed costs
those costs that don”t vary when you change the quantity of output you produce
Rational rule for sellers in competitive markets
sell one more unit if the price is ≥ the marginal costs
marginal product
the increase in output that arises from an addition unit of input example : labor
Diminishing marginal product
an economic principle where adding more of one input (like labor) to a fixed input (like a factory) eventually leads to smaller increases in total output, eventually falling
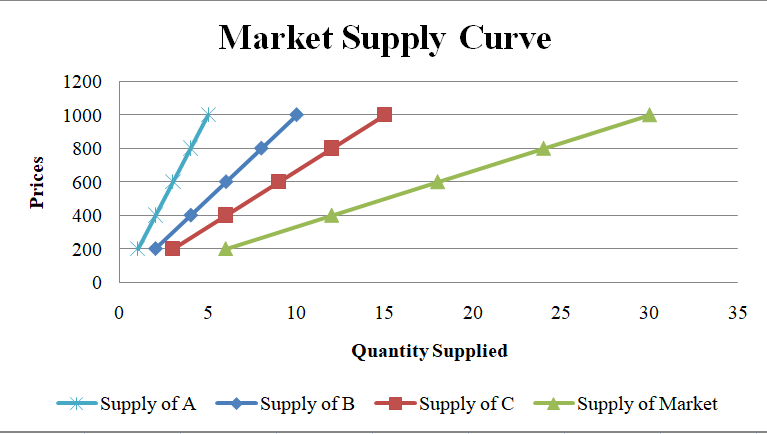
market supply curve
graph plotting the total quantity of an item supplied by the entire market at each price
substitute- in -production
alternative use of your resources. your supply of a good will decrease if the price of substitute- in -production increases ex: gas and diesel
complements- in- production
goods that are made together. your supply of a good will increase if complements- in- production rises
Price elasticity demand
measure of how responsive buyers are to price changes. measures the percent change in quantity demanded that follows from a 1% price change
Inelastic demand
buyers are not responsive to price. quantity demand rises very little
Elastic demand
buyers are responsive to the price. quantity demand increases a lot
price elasticity of supply
measure of how responsive sellers are to price changes. measure percent change in quantity supplied that follows a 1% in price change
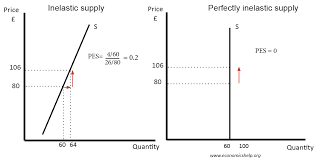
Perfectly inelastic supply
the quantity supplied of a good or service doesn't change, no matter the price, resulting in a vertical supply curve, where sellers are completely unresponsive to price changes
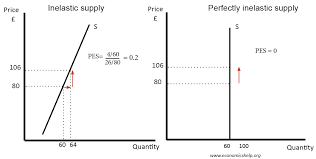
Inelastic supply
occurs when the quantity of a good or service supplied changes very little in response to price fluctuations
elastic supply
quantity supplied of a good or service is highly responsive to price changes
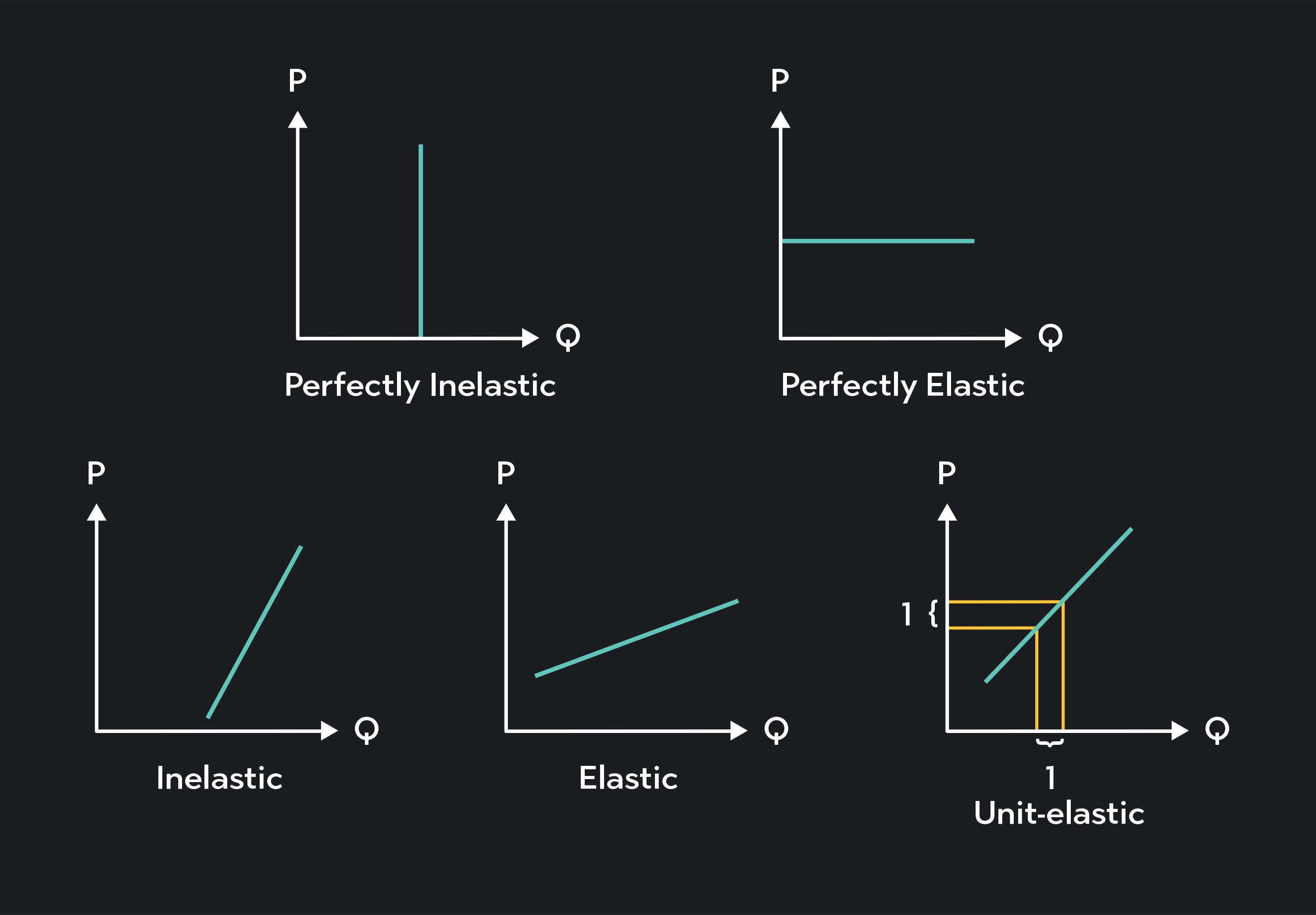
Perfectly elastic supply
an extreme case where the supply curve is a horizontal line, indicating that suppliers are willing to sell any quantity at the prevailing market price.