TV4101 - Bovine - Nervous 1
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms

What has happened here?
What else can happen with this affliction?
Issue with CNVII (Facial nerve)
• drooping of the ear
• ptosis of the upper eyelid
• drooping of the upper lip
• pulling of the nose towards unaffected side

What has happened here?
What else can happen with this affliction?
Issues with CNVIII (vestibulocochlear nerve) i.e. vestibular dz
- ataxia/staggering
- head tilt (usually directed towards side of lesion, tilt is milder in peripheral lesions than in central i.e. brainstem lesion)
- nystagmus

What has happened here?
CX?
Deficit of the vagus nerve (CN X) → paralysis of pharynx & larynx
In cattle with pharyngeal paralysis → usually food and water
are present at the nostrils and in the mouth

What has happened here?
CX?
Deficits of hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) → problems with prehension, mastication & swallowing
Tongue will be weak or paralysed
Menace Response
How to perform?
What is a normal response?
What does it test?
Thrusting a finger rapidly towards the eye (but without touching the eye or its surroundings)
Immediate closure of the eyelids
Optic nerve (→ as part of the incoming pathway) & facial
nerve (→ the outgoing pathway, responsible for the blinking)
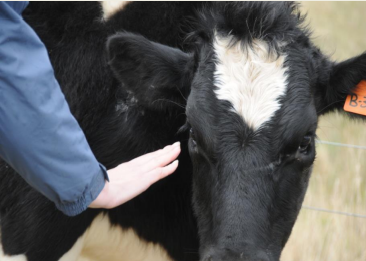
Palpebral Reflex
How to perform?
What does it test?
Touching of the peri-ocular skin with a finger (but without the animal being able to see the approach of the finger)
Afferent (sensory) pathway for the palpebral reflex is the trigeminal nerve (CN V); efferent (motor) pathway is the facial nerve (CN VII) → innervates the muscles that close the eyelids
What is the best test for examining vision in ruminants?
How to test?
Obstacle test
Animal to be tested is placed in an unfamiliar environment
which contains obstacles → an assessment is made of the
animal's ability to negotiate the obstacles
