English Language Arts and Reading
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
semantics
a. the study of meaning.
b. the study of linguistic development by classifying and examining changes in meaning and form.
syntax
the study of the rules for the formation of grammatical sentences in a language.
pragmatics
the study of the aspects of meaning and language use that are dependent on the speaker, the addressee and other features of the context of utterance
morpheme
in a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning; may be a word or a part of a word (such as a prefix)
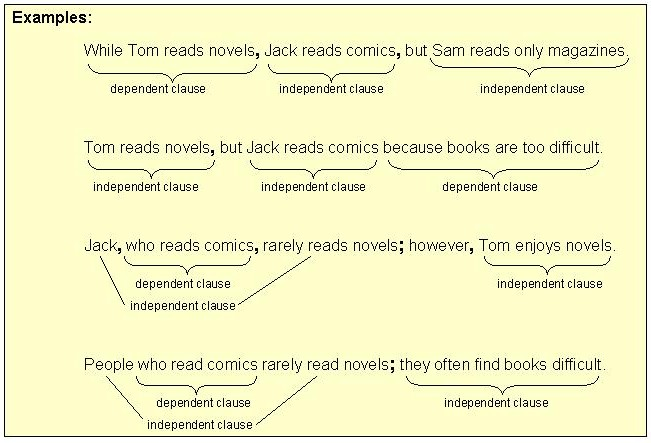
simple sentence
one independent clause
compound sentence
2 independent clauses joined by:
A. a coordinating conjunction (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so),
B. a conjunctive adverb (e.g. however, therefore), or
C. a semicolon alone.

complex sentence
1 dependent clause joined to 1 independent clause
Punctuation patterns (to match A, B, C and D above):
A. Dependent clause, independent clause
B. Independent clause dependent clause
C. Independent, nonessential dependent clause, clause.
D. Independent essential dependent clause clause.

compound-complex sentence
2 independent clauses joined to 1 or more dependent clause
scaffolding
an instructional technique where the teacher models the desired learning strategy or task, then gradually shifts responsibility to the students.
Semantic Mapping
relationship between concept and knowledge
phonology
(phonological awareness)
the ability to hear and work with the spoken language
phonemic awareness
The ability to hear and manipulate sounds in words
(Phonemic awareness is not phonics.
Phonemic awareness is auditory and does not involve words in print )
Examples:
Blending: What word am I trying to say?
Mmmm / ooooo / p.
Segmentation (first sound isolation): What is the first sound in mop?
Segmentation (last sound isolation): What is the last sound in mop?
Segmentation (complete): What are all the sounds you hear in mop?
Emergent literacy
"the reading and writing behaviors that precede and develop into conventional literacy," notes Sulzby (1989). Sulzby and Teale (1996, p. 728) state, "Emergent literacy is concerned with the earliest phases of literacy development, the period between birth and the time when children read and write conventionally. The term emergent literacy signals a belief that, in a literate society, young children--even 1- and 2-year-olds--are in the process of becoming literate."
conventional literacy
ability to read and write in ways that most people in our literate society recognize as 'really' reading and writing. For example, they use a variety of reading strategies, know hundreds of sight words, read texts written in a variety of structures, are aware of audience, monitor their own performances as writers and readers, and spell conventionally." (p. 30)
word identification skills
-decoding
-blending
-structural analysis
-sight word vocabulary
factors affecting students' eading comprehension
oral language development, word analysis skills, prior knowledge, language background, previous reading experiences, fluency, vocabulary development, ability to monitor understanding, characteristics of specific texts
metacognitive skills
learners' automatic awareness of their own knowledge and their ability to understand, control, and manipulate their own cognitive processes.
Example:
self-evaluation and self-monitoring
strategies to facilitate comprehension of text before, during, and after
previewing, making predictions, questioning, self-monitoring, rereading, mapping, using reading journals and discussing texts
After what grade do early literacy interventions seem to not have the same impact?
third
Why do some children sometimes need more thorough early literacy screenings?
all of these
The importance of the 'Read Aloud/Think Aloud' strategy is:
It teaches students how to read fluently and think critically about the text as they read
What type of thinking is required to form a sound point of view?
analysis and synthesis
what is synthesis?
putting together information and drawing a conclusion
Which of the following BEST summarizes the approach to teaching vocabulary recommended by researchers?
Immerse students in words.
what is the Star Model?
an explicit vocabulary instruction method for teaching new words to students.
It is a four-step process that involves selecting key words from a text, teaching their meaning and use, activating students' understanding through activities, and revisiting the words to ensure long-term retention
steps in STAR model
select, teach, activate, revisit
What does the KWL strategy ask students to do?
to write what they know, what they wonder, and what they learned
what measure can determine a student's initial fluency before doing repeated readings?
accurate words read per minute
organization patterns of writing
Description
Sequence (chronological/priority order)
Cause & effect
Compare & contrast
Problem & solution
stages of spelling development
Pre-communicative Stage (ages 3 – 5)
In this stage, kids are learning that print contains meaning, but have not mastered letter sounds, or phonemic awareness.

Semi-phonetic Stage (ages 4 – 6)
In this stage, kids are beginning to grasp that letters represent sounds, which is the basics of phonics. However, their understanding of letter sounds is still developing.

Phonetic Stage (ages 5 – 7)
In this stage, kids are able to write letters to correctly represent the letter sounds, or phonemes, that they hear.

Transitional Stage (ages 6 – 8)
In this stage, kids begin to shift from phonetic spelling to more conventional spelling patterns.

Conventional Stage (ages 8+)
In this stage, kids have a strong understanding of standard spelling rules and patterns.
when do children begin to develop phonological awareness?
Between their second and third birthday
In what age range can children isolate and identify beginning and ending sounds?
5-6
What is a phonological skill that four-year-old children can do?
Hear and count phonemes
In what age range can we anticipate children being able to substitute and delete
phonemes?
6-7
Stage ____ of punctuation development involves being able to correctly use simple end-
sentence punctuation.
one
what develops first?
learning the alphabet
reading comprehension
decoding
learning morphemes
listening comprehension
listening comprehension
alphabetic principle definition
the understanding that letters and letter patterns represent the sounds of spoken language
which is critical for understanding the development of reading skills in young children?
the difference between phonemic awareness and the alphabetic principle
which skill is considered more advanced along the phonological awareness continuum?
segmenting multisyllabic words into their constituent syllables
homographs
words spelled the same but with different meanings and origins, and occasionally different pronunciations
ex: rose (flower vs verb); second (time vs rank)