Genetics Review 12U Bio
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Induced mutations
Result from the influence of an unrelated factor or agent, either natural or artificial
Spontaneous mutations
Happen naturally and randomly, arising from replication error and base modifications
Somatic mutations
occur in any cell except germ cells and are not heritable
Germ-like mutations
Occur in gametes and are inherited
Missense mutations
Change a codon resulting in altered amino acid
Nonsense mutation
changes a codon into a stop codon and results in premature termination of translation
Silent mutation
Alters a codon but does not result in a change in the amino acid at that position of the protein
Point mutations
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva - point mutation in a bone morphogenetic protein type I receptor
Frame shift mutation
Result from insertions or deletions of a base pair. Eg.
DNA replication errors
DNA polymerase occasionally insets incorrect nucleotides, generally due to base mispairing
- Lead to point mutations
Slippage
During replication can lead to small insertions or deletions
Transposons
Genes that can "jump" within chromosomes and insert themselves into various positions, potentially causing mutations
Induced mutations
Arise from DNA damage caused by chemicals and radiation
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
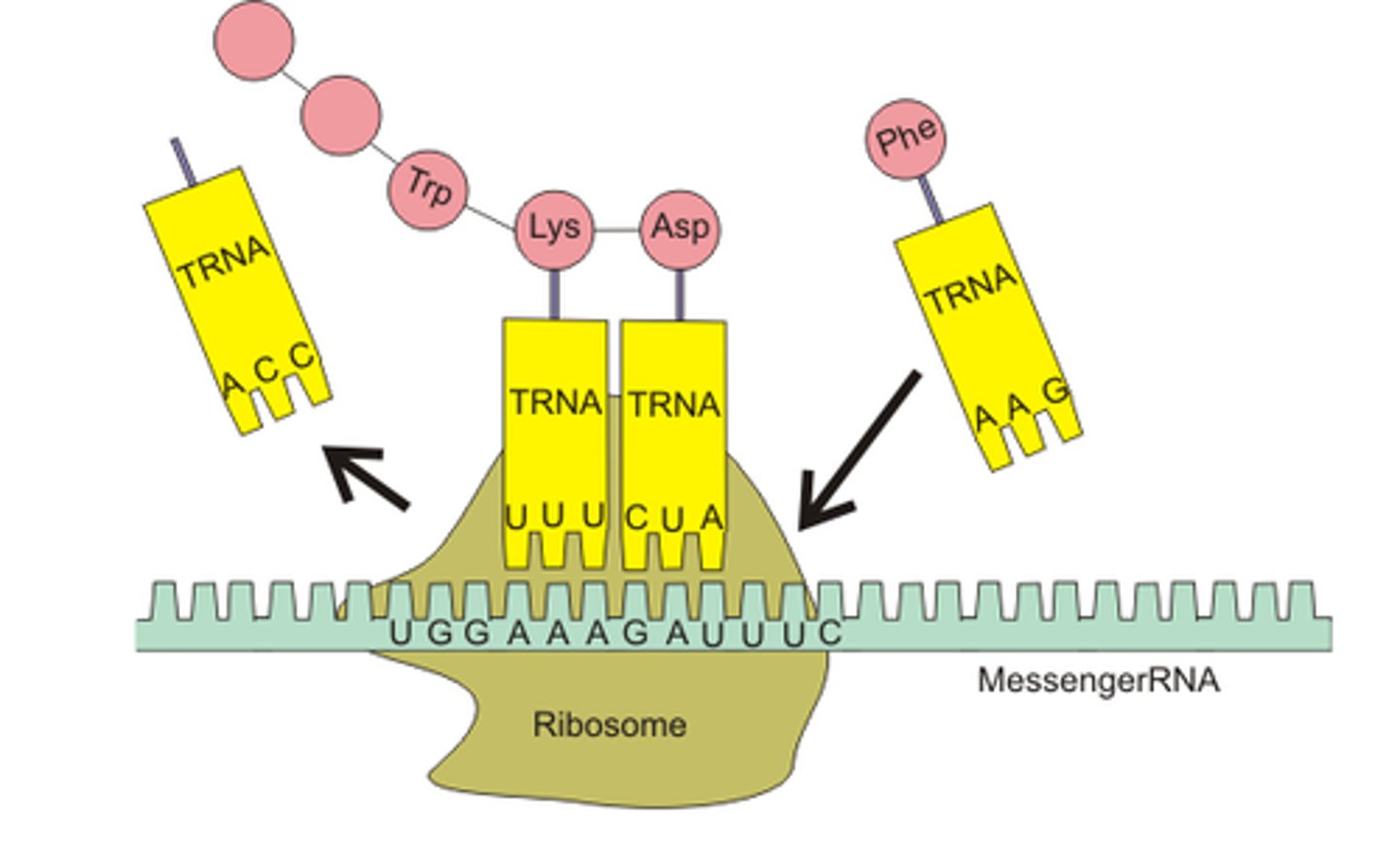
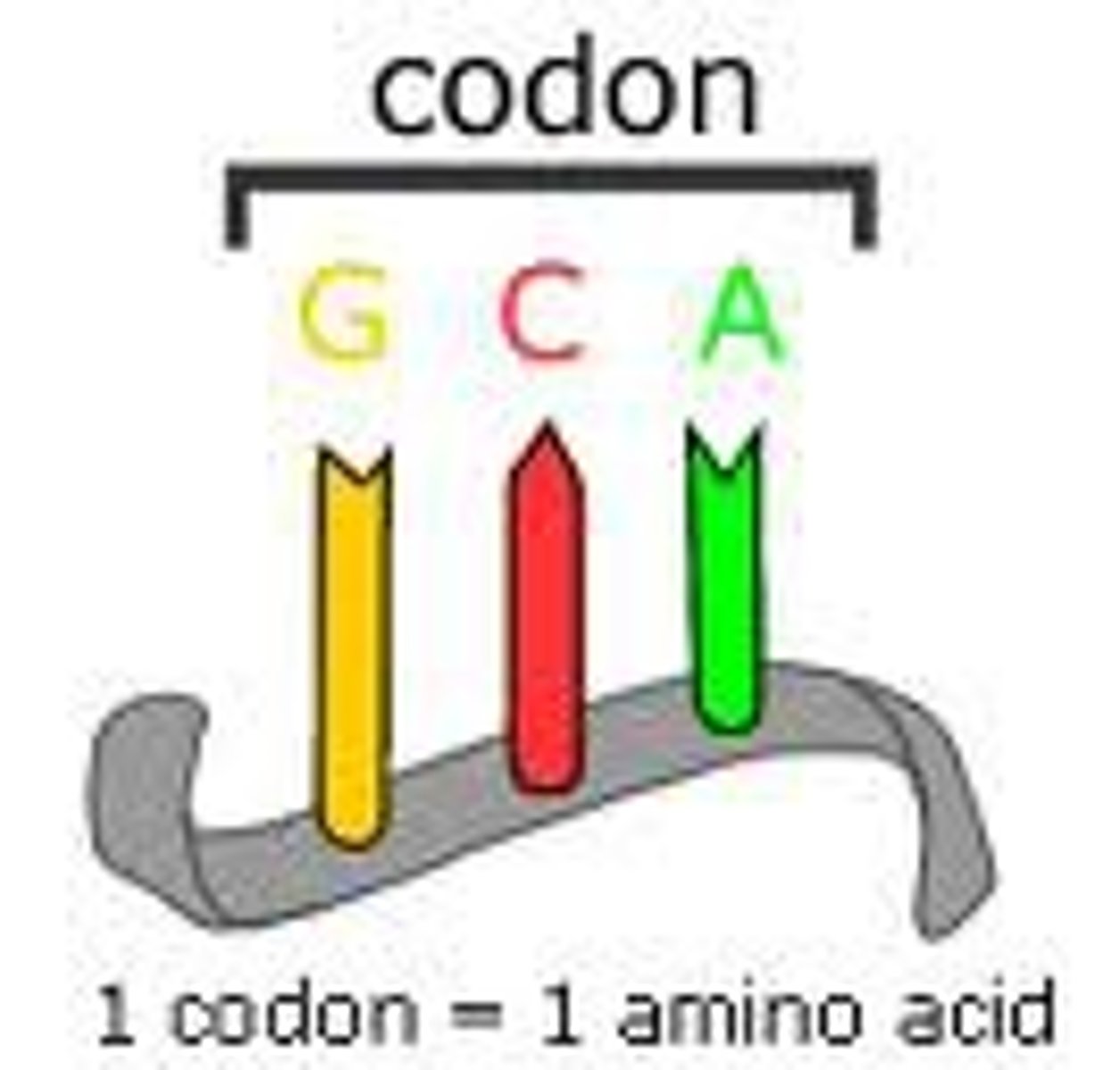
Codon
A three base sequence on the mRNA use to code for one amino acid
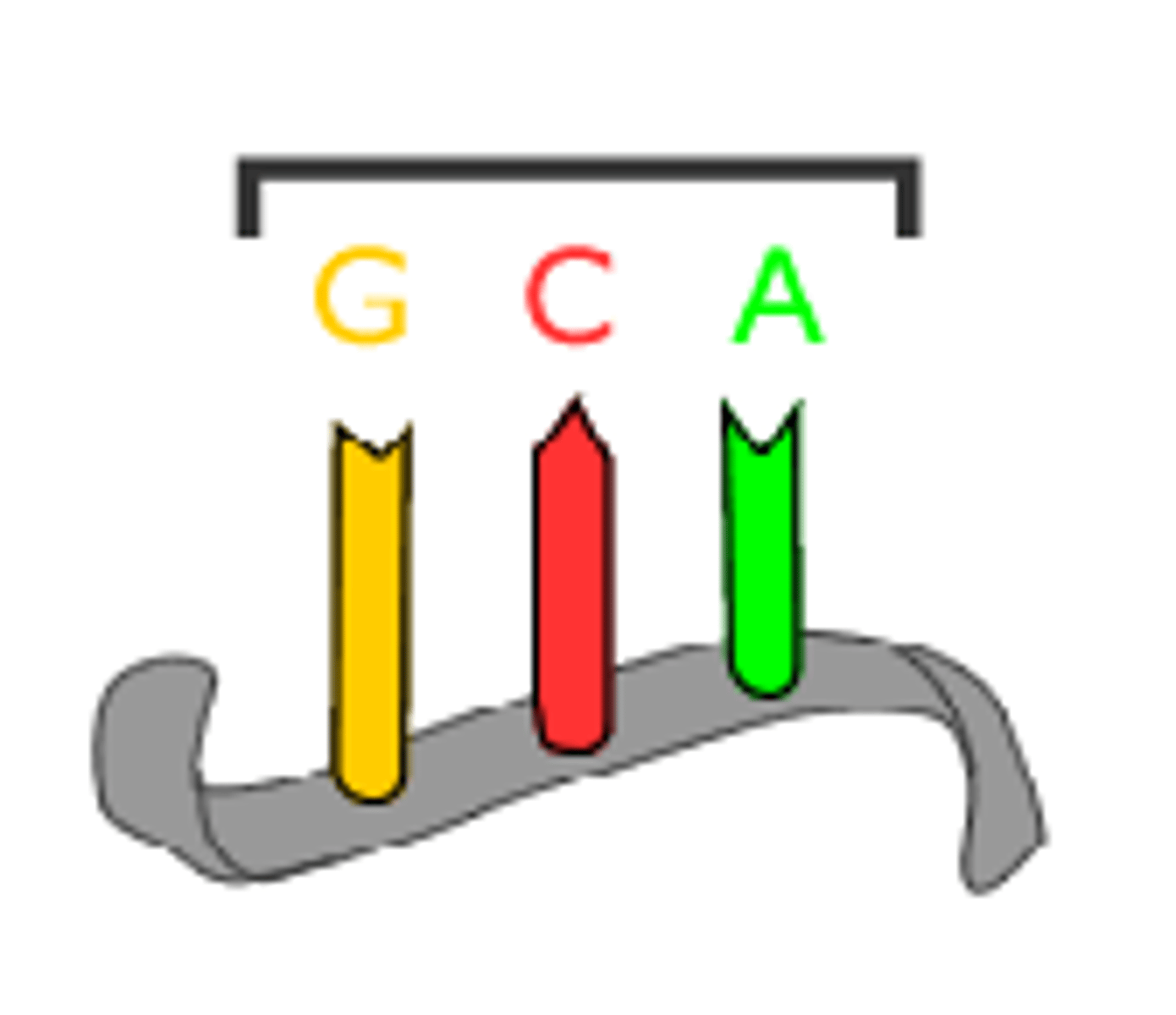
Anticodon
A three base sequence on the tRNA used to recognise and bind to the codon as each amino acid is added
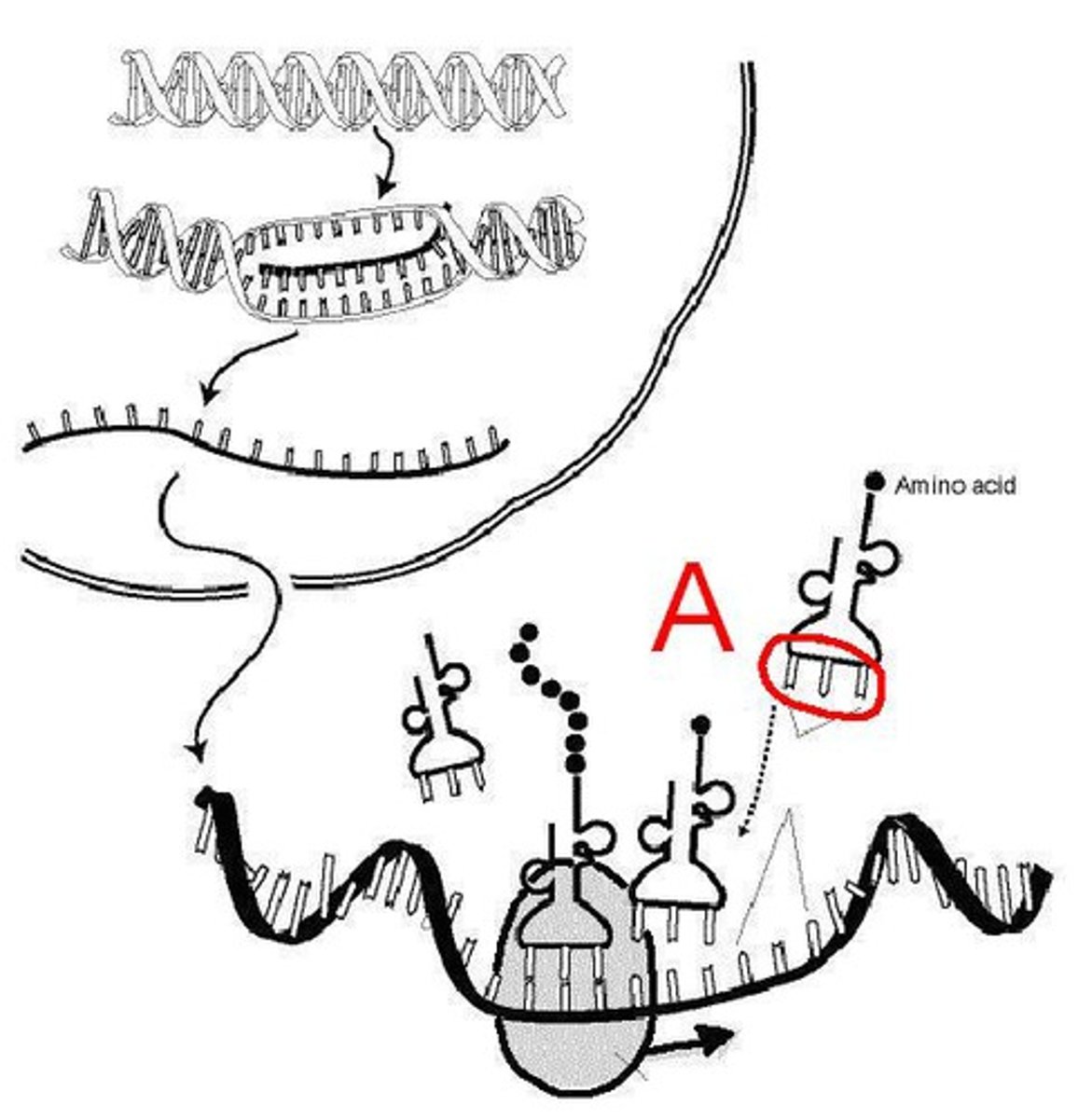
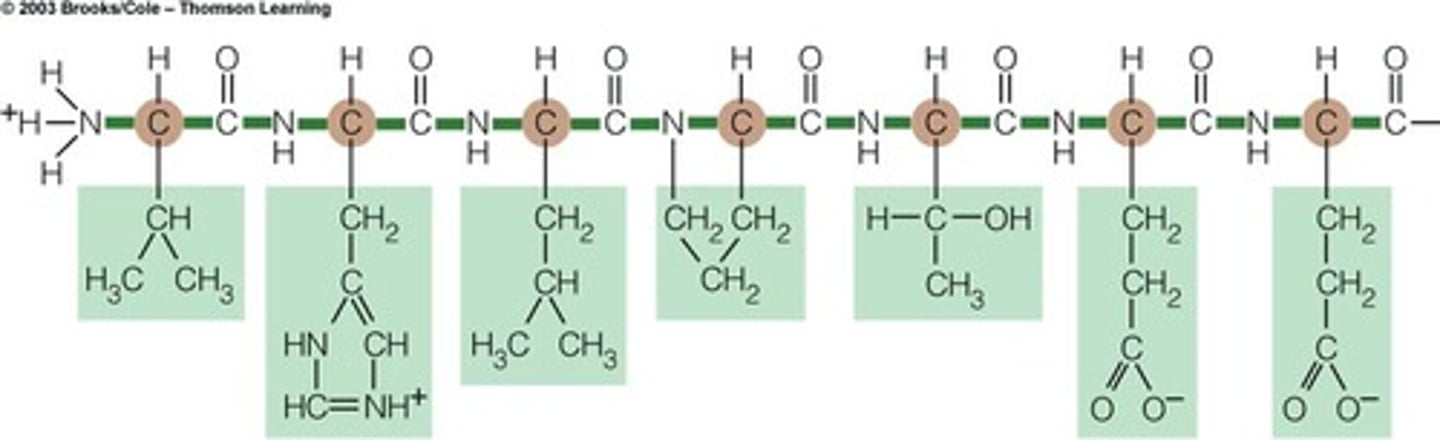
Polypeptide
A linked chain of amino acids created in the ribosome
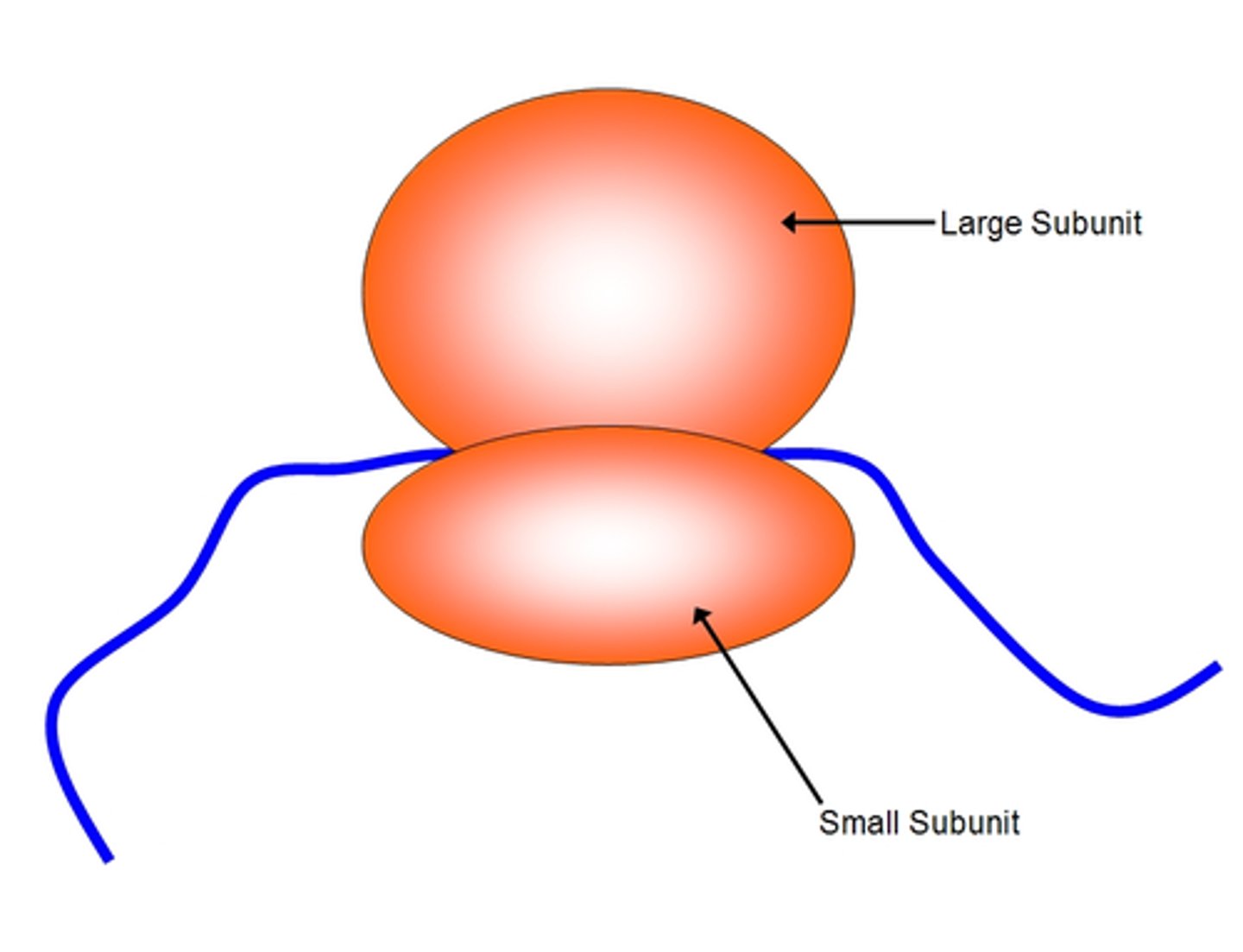
Ribosome
The location where translation takes place
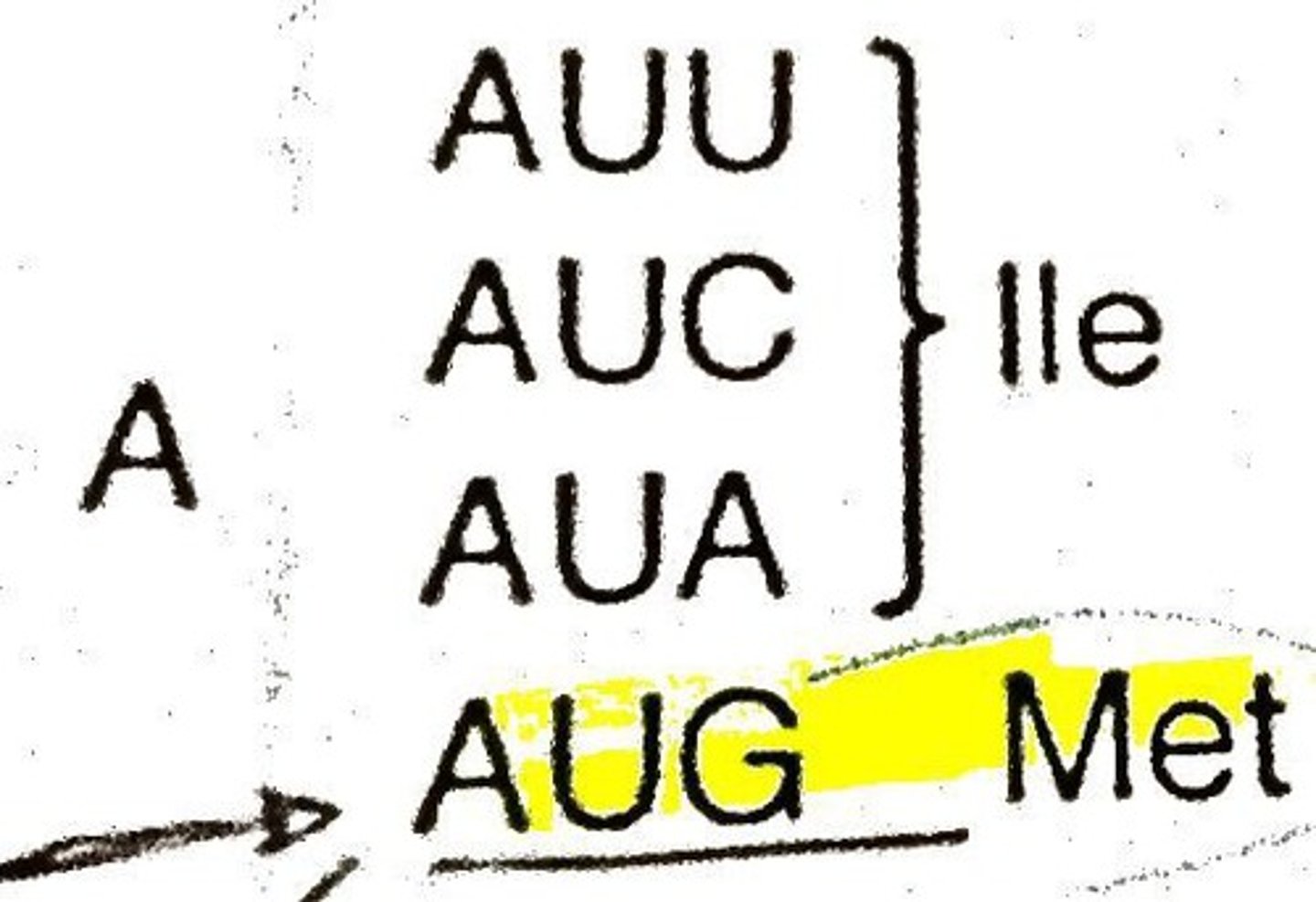
Start Codon
A first 3 base sequence that starts all genes; AUG
Stop Codon
A 3 bases sequence found at the end of each gene; UAA, UAG or UGA

Amino Acids
The units that make up a protein; each amino acid is coded for by one codon
Purine
has 2 rings (Adenine and Guanine)
Pyrimidine
has 1 ring (Thymine and Cytosine)
Difference between RNA and DNA
RNA us "U" instead of "T"
Transcription
The process by which the message from DNA is written down into RNA
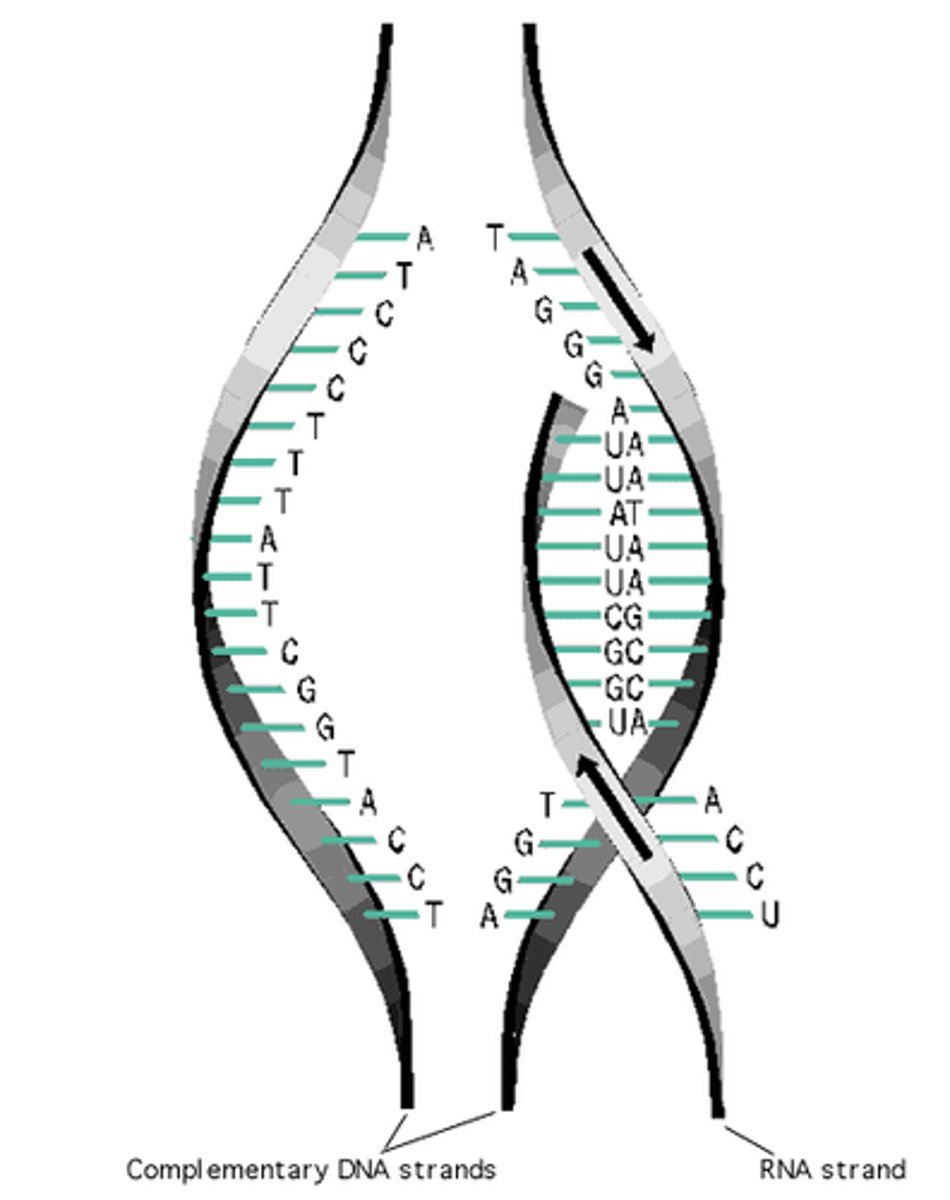
mRNA (messenger RNA)
The form of RNA which is created as a blueprint from DNA; carries instructions for making a protein
Uracil (U)
The base found only in RNA (replaces thymine in DNA)
Nucleus
The location where transcription takes place
RNA editing
A process that takes place before the mRNA is sent to the ribosome; some RNA bases are removed in order to create a final draft of the mRNA
Introns
The sections of RNA removed from the final draft of mRNA that remain in the nucleus
Exons
The sections of RNA that make up the final draft of mRNA which is sent out of the nucleus to the ribosome
RNA polymerase
The main enzyme that transcribes DNA into mRNA
One
Number of strands RNA is made of
5' to 3'
The direction mRNA is synthesized
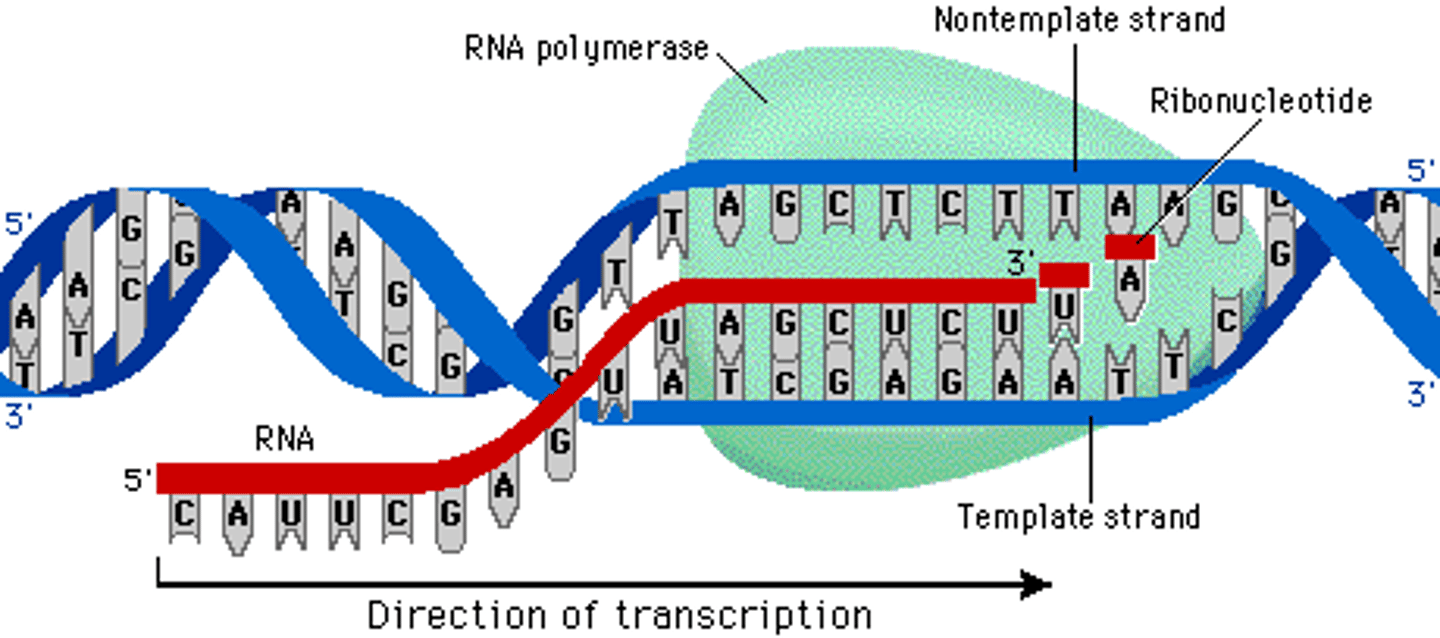
DNA 3' ATG CGT TAG 5' transcribes to
5' UAC GCA AUC 3'
rho protein
RNA binding protein responsible for terminating transcription
5' cap
a methylated guanine nucleotide added to the 5' end of eukaryotic mRNA
Poly-A tail
Prevents mRNA from being degraded in cytoplasm
100-250 A's at 3' end
spliceosome
complex of enzymes that serves to splice out the introns of a pre-mRNA transcript
SNRP
Small nuclear ribonuclear peptide
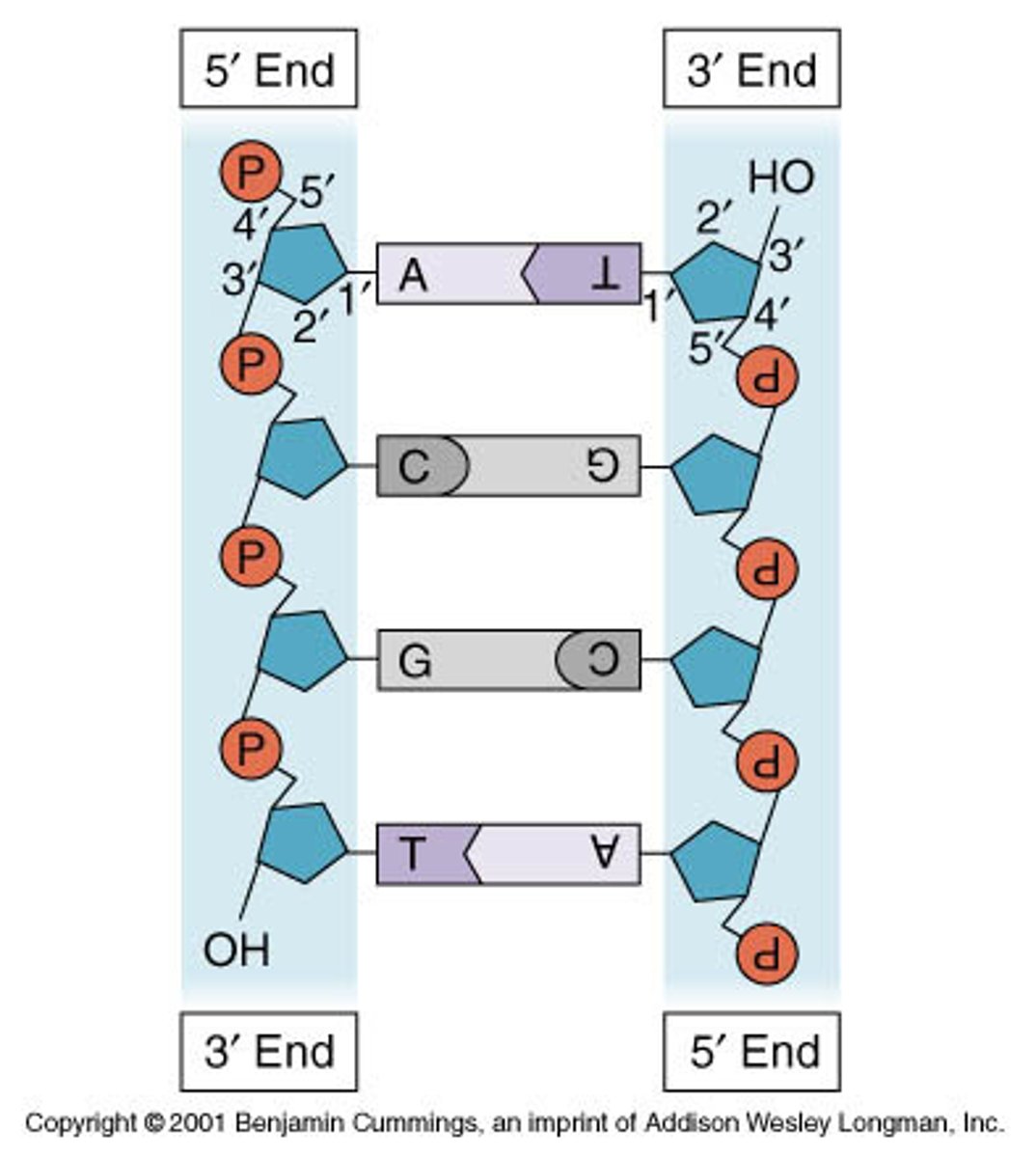
Shape of DNA
a double helix.
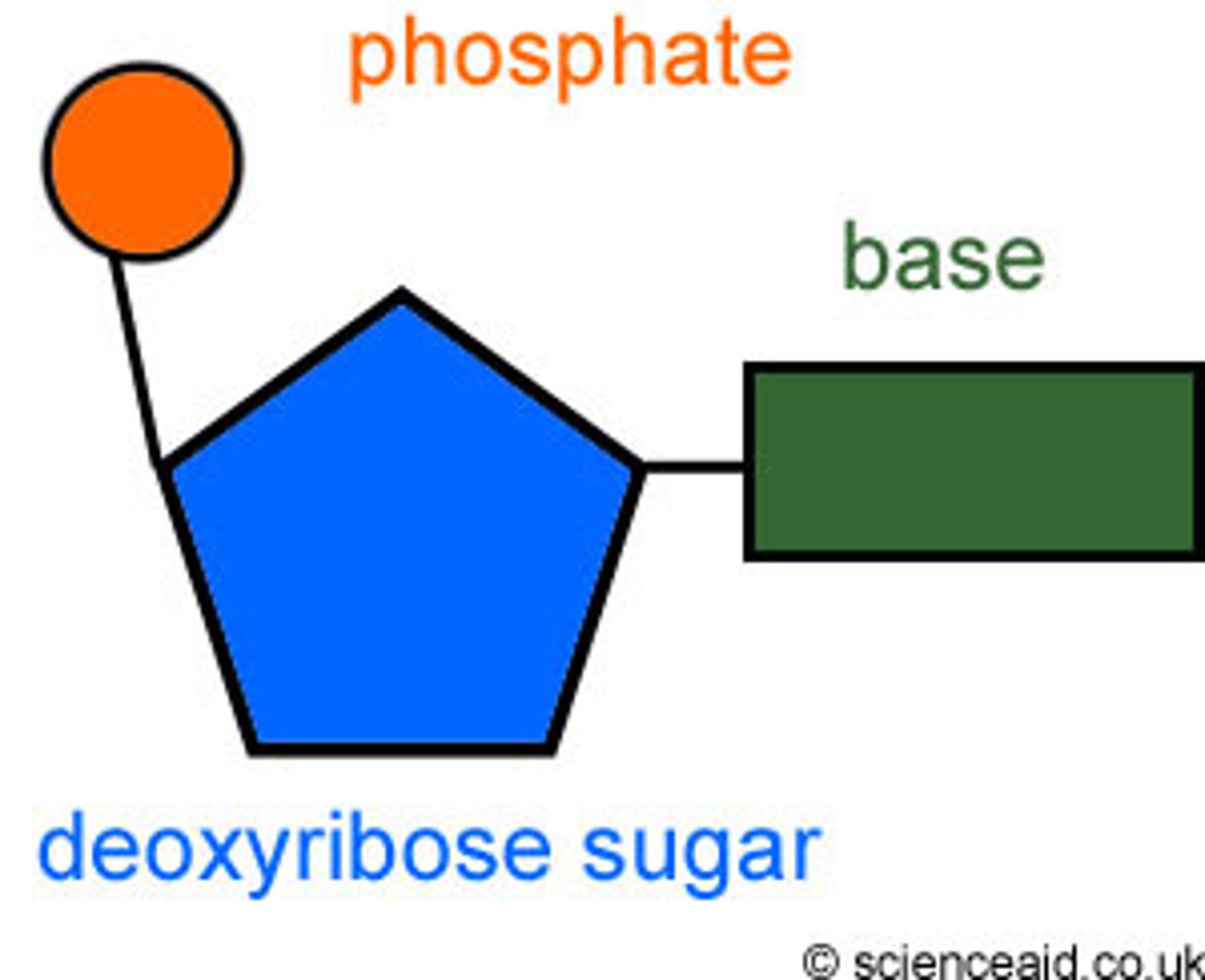
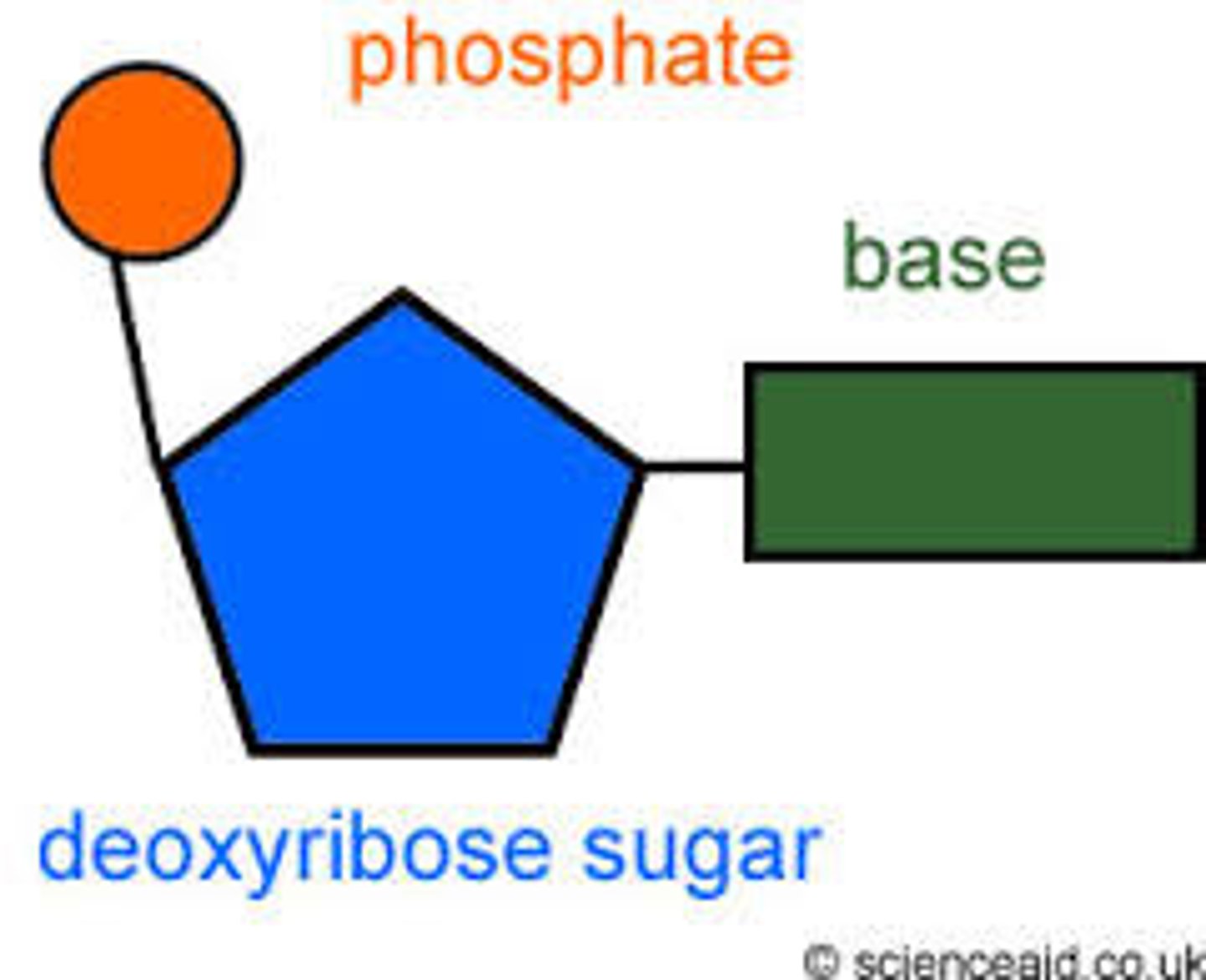
Nucleotide
sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
Nitrogenous base
A nitrogen containing molecule that is a part of nucleotides
Complementary Base to Adenine
Thymine
Complementary Base to Cytosine
Guanine
Backbone of DNA is made of
Deoxyribose sugar and phosphate
Rungs of ladder are made of
Nitrogen bases
Nucleotide
Diagram
The complimentary DNA strand of the following is:
ATT TAA ACC GAG
TAA ATT TGG CTC
The complimentary DNA strand of the following is:
GGG CCC AAA TTT
CCC GGG TTT AAA
Nucleotide
DNA
Contains ATCG, A Deoxiribose Sugar, and is double stranded
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a trait
T
The Base Pair A matches with
C
The Base Pair G matches with
DNA Back Bone
Made from Phosphate and Deoxiribose
origin of replication
a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated
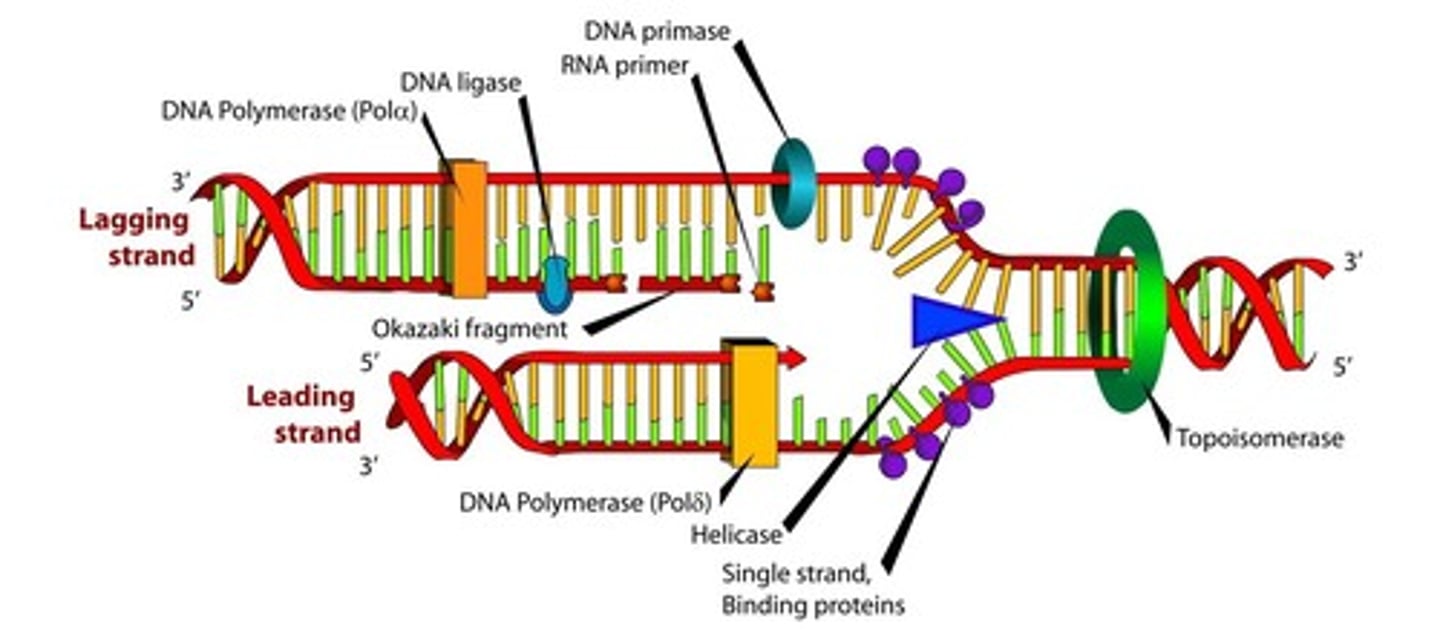
replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing.
replication bubble
an unwound and open region of a DNA helix where DNA replication occurs
helicase
separate double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied; unzips dna
gyrase (topoisomorase)
relieves strain while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by helicase. This causes negative supercoiling of the DNA
single-stranded binding protein
prevent ssDNA from re-forming a double helix; speeds up replication
primase
functions by synthesizing short RNA sequences that are complementary to a single-stranded piece of DNA; primer for dna polymerase
primer
a short strand of RNA that serves as a starting point for DNA synthesis
deoxynucleoside triphosphate
individual nucleotides with three phosphate groups
5 to 3 direction
direction new DNA is formed. The 5' carbon has a phosphate group attached to it and the 3' carbon a hydroxyl (-OH) group
dna polymerase III
enzyme that builds new DNA strand
dna polymerase I
removes the RNA primer and fills in the nucleotides which are necessary for the formation of the DNA in the direction- 5' to 3'. It also helps in proof reading to see if there is any mistake done while replication and while matching base pairs
okazaki fragments
short, newly synthesized DNA fragments that are formed on the lagging template strand during DNA replication.
ligase
seals repairs in the DNA, it seals recombination fragments, and it connects Okazaki fragments
Helicase
unwinds DNA
Ligase
Joins Okasaki fragments
Primase
creates RNA primer
DNA Polymerase
creates new DNA strands
leading strand
DNA created towards the replication fork
Lagging strand
DNA created away from the replication fork
Okasaki fragment
Short segment of DNA on lagging strand
RNA primer
Binding site for DNA polymerase