TDL3 - Heat Capacity
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
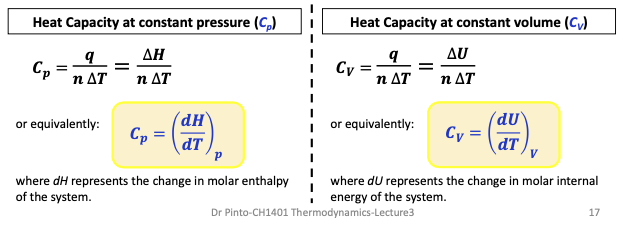
Heat cap def + formula
amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 K. It is extensive (depends on amount of substance)
Mathematically:
C = q/ΔT jK-1
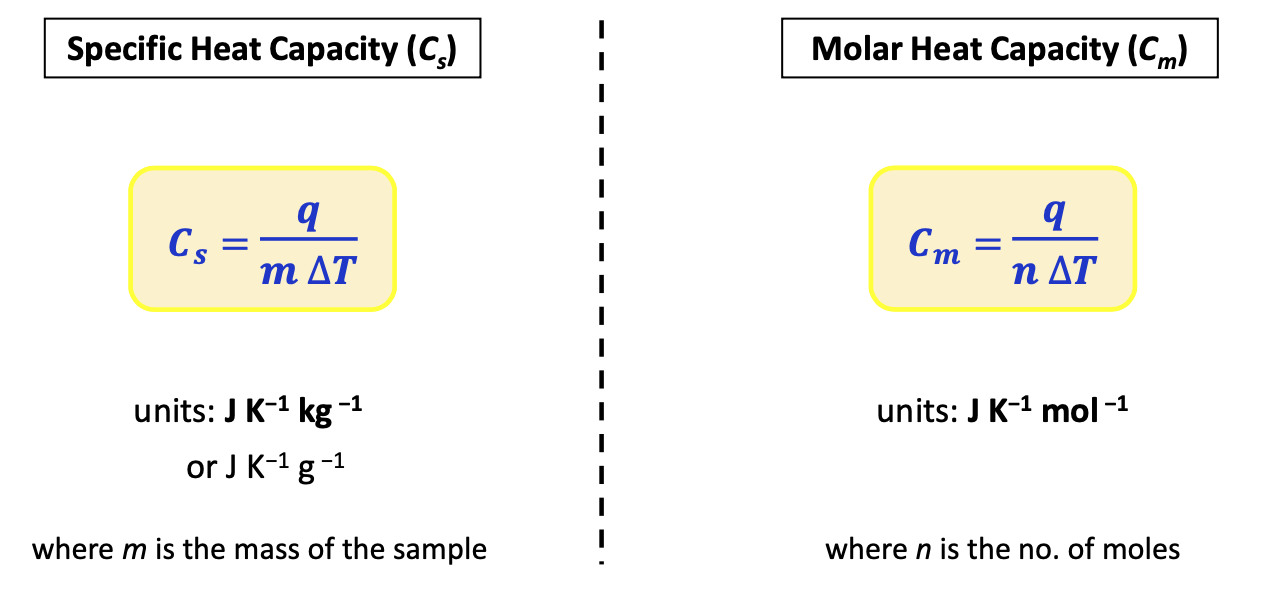
Specific heat cap vs molar heat cap (img)
Internal energy def
Sum of all the Ek and Ep contributions to the energy of all the atoms, ions, and molecules in the system. In essence, U is the total energy stored within a system.
U includes all microscopic forms of energy (translational, rotational, vibrational motion of molecules), as well as the electronic and nuclear energies. U is an extensive property (depends on amount of subs.)
How is ∆𝑼 measured
The transfer of energy as heat during a physical or chemical process can be via a calorimeter.
If this is done at process is performed at constant volume (ΔV = 0), then the system cant do expansion work. Hence:
w = 0,
so ΔU = q + w
W--> ΔU = q
When a SYS does work, what happens to gas and to w and q (picture piston picture)
SYS doing work = expansion
The piston moves up as the gas pushes it.
Gas uses its internal energy to expand.
So energy leaves the system as work.
Heat flows from the gas to the surroundings. (because the gas is doing work on surr. To expand)
w<0 (system loses energy)
q<0(system loses energy)
When WD ON sys what happens to gas and to w and q (picture piston picture)
Work done on the system = Compression
The piston moves down, forcing the gas to compress.
The surroundings are doing work on the gas. Energy enters the system as work.
w>0(system gains energy)
q>0(system gains energy)
Sign convention for 1st TD law
ΔU = q + w
If WD on the system, the WD gets transferred to sys as heat so +ve
If work is done by the sys on the surr, E is lost by the sys to do the work so -ve
memorise pls
In adiabatic (normal) processes
no heat is exchanged; all WD affects the internal energy → T changes.
In isothermal processes
T is constant, so internal energy cannot change; heat flows out exactly to balance WD.
A state function is a property that
depends only on the current state of the system, not on how the system got there.
Ex: U, Temp, Pressure, Vol, Enthalpy (H).
it depends only on the present pressure, vol, temp, and composition of the system. It does not matter whether the system got to this state by a fast process, a slow process, expansion, compression, heating, or cooling.
So ΔU by Ufinal - Uinitial
what happens to first TD law when an ideal gas changes vol isothermally
U depends only T
In an isothermal process T is constant so ΔT = 0, so ΔU = 0
Thus q=w
If the gas expands, W > 0, so heat must enter (Q > 0) to keep T constant.
If the gas is compressed, W < 0, so heat is released (Q < 0).
enthalpy
ΔH tells us how much heat the system absorbs or releases under normal laboratory conditions. Enthalpy is a state fucntion.
qp=ΔH
Aside from qp=ΔH, how can we define enthalpy
H = U +pV
ΔH = ΔU + pΔV
enthalpy and heat for endo and exo rxn
For an endothermic reaction.
q > 0
ΔH >0
This is an increase in enthalpy because energy enters sys as heat
For an exothermic reaction
q < 0
ΔH < 0
This is a decrease in enthalpy because energy leaves sys as heat
Heat cap at constant pressure / constant vol (img)