Molecular Interactions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Boyle’s Law
Constant temperature volume of a fixed amount of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure
P = 1/v
Charles Law
Volume of a fixed amount of gas, at a constant pressure, is proportional to absolute temperature
v = T
Avogadro’s Law
Equal volumes of gases at constant temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules
v = n
Combined Gas Law
Pv = T
Pv/T = constant
Ideal Gas Law
Pv = nRT
Dalton’s Law
Total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas
Partial pressure
Ptotal = Pa + Pb + Pc + …..
Pa
= naRT/V
Partial pressure of a component
Px
Mole fraction
Xa = na/(na + nb + nc + ….)
How do gas molecules move?
In a random (but straight) line
When do molecules interact?
When they collide
Polarizability
An electric field induces a dipole
More electronegative
lower polarisability
Bigger atoms/molecules
higher polarisability
Interactions between ions
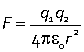
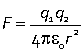
Coulomb potential
potential energy associated with the electrostatic interaction between charged particles
Interaction between an ion and a dipole
u = μ1q2/4πε0r²
Dipole-Dipole interaction (Keesom)
𝑉 = − 2𝜇1²𝜇2²/3(4𝜋ε0)𝑟^6𝑘𝑇
Dipole induced dipole interaction (Debye)
A polar molecule has an electric field which can induce a dipole in a neighbouring polarizable molecule - these dipoles attract
𝑉 = − 𝜇1²𝛼2′/4𝜋ε0𝑟6
Induced dipole - induced dipole interaction (London/dispersion)
Non polar molecules attract
Fluctuations in the instantaneous electron density creates a dipole. This dipole can then induce a dipole in a neighbouring molecule
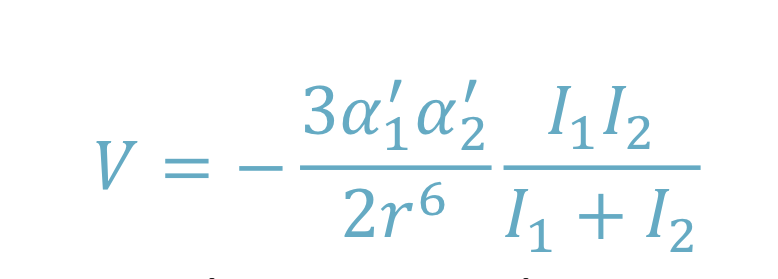
Van der Waals interactions
Sum of all the dipole interactions
V = C/r6
Magnitude of C depends on the molecule and which interaction it has
No dipoles
varying polarisability
equal polarizability
varying dipole strength
When can a molecule leave a liquid
When kinetic energy > strength of attraction
What is boiling point dependent on?
Strength of attraction
Evaporation can occur
below the boiling point
Enthalpy of Vaporisation
Stronger the attractions, the more energy is needed to convert from liquid to gas at the boiling point
ΔHvap/Tbp
ΔSvap
Troutons rule with Hydrogen bonding
Above the line = more structure in liquid
Below the line = more structure in gas
Vapour pressure
Pressure exerted by gas in co-existance with liquid
Surface tension
Molecules at the surface have fewer neighbours so the system tries to minimise the surface area
Attractive interactions between atoms
Van der Waals
Repulsive interactions between atoms
Nuclear + electronic