Ovaries, Oogenesis, and Folliculogenesis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is the difference between Menarche and Menopause?
Menarche
→ menarche is the when you start having menstrual cycles which occurs around 9-14 years old
Menopause
→ ovaries cease their reproductive and endocrine functions
→ occurs around 50 years of age
What are the functions of the ovaries?
The ovaries are involved in two primary functions:
1) Production of Gametes (Oogenesis)
→ developing gametes are oocytes
→ mature gametes are ova
2) Production of Steroids
→ Estrogen - responsible for growth and maturation of internal and external female sex organs
→ Progestogens - prepare the internal sex organs for pregnancy by promoting secretory changes in the endometrium
What is the structure of the ovaries?
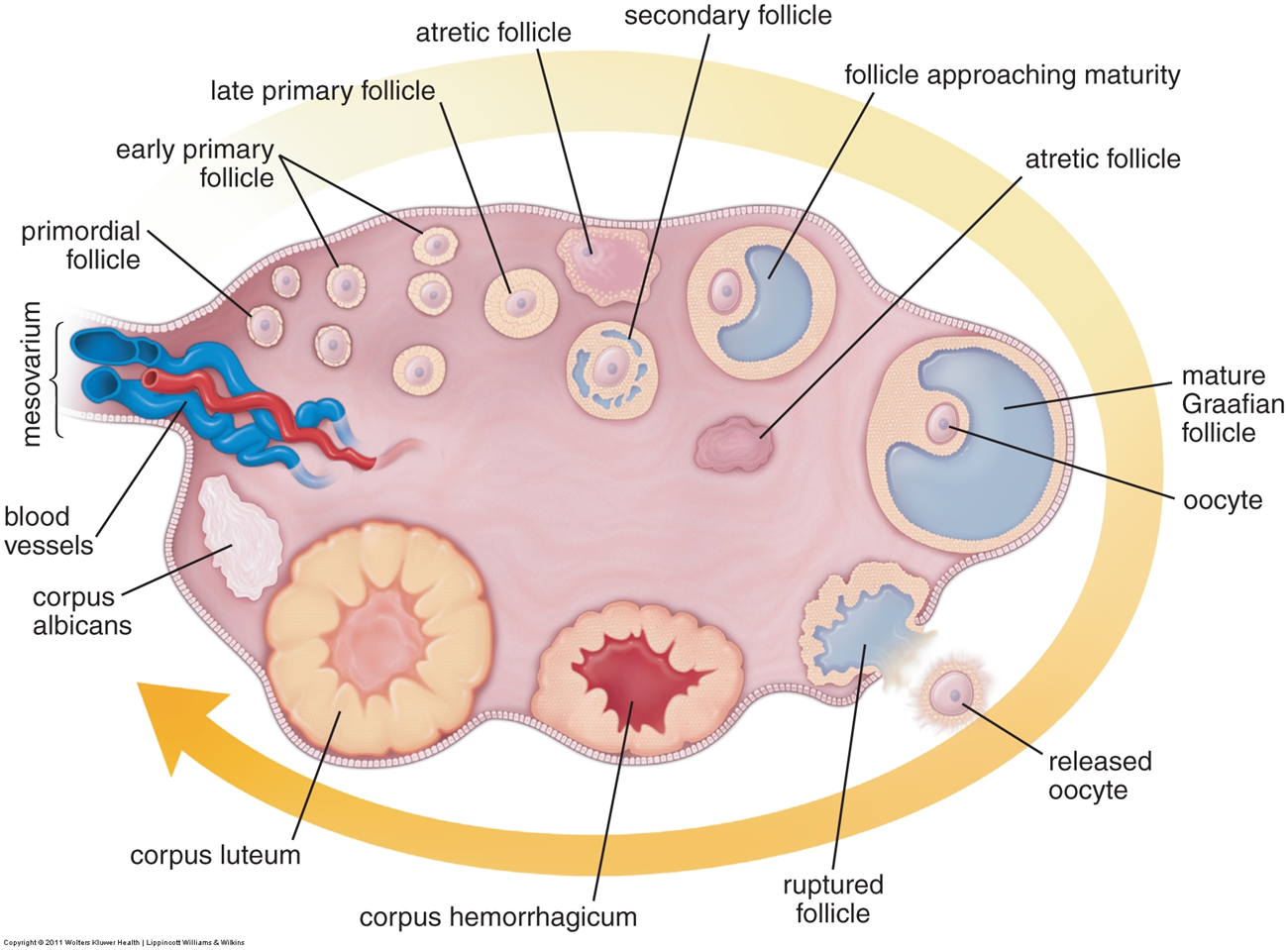
The ovaries are paired organs subdivided into a medulla and cortex
1) Medulla
→ loos connective tissue that is rich in blood supply and nerves
2) Cortex
→ the peripheral portion that contains the ovarian follicles
→ these ovarian follicles will develop in response to FSH which will eventually lead to release of oocyte
→ rupture follicles will form a temporary corpus luteum which secretes hormones for a brief period of time to promote pregnancy
What is Oogenesis?
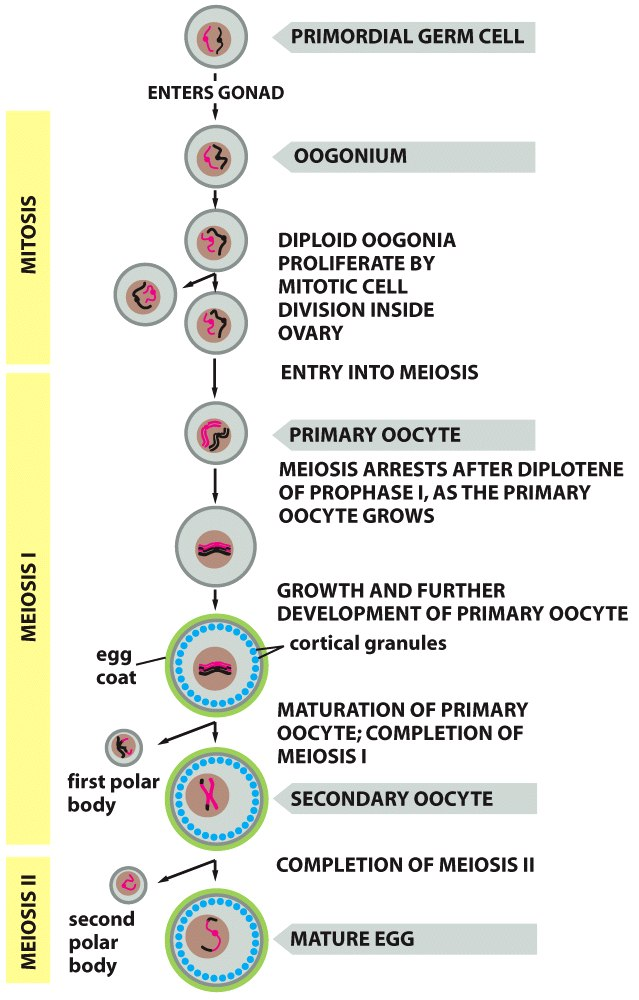
Oogenesis is the process of developing a mature egg cell
1) Oogonium will enter into multiple rounds of mitosis before being converted into primary oocytes
→ these primary oocytes are then arrested in meiosis 1 at prophase I
2) The primary oocyte will then resume meiosis I during puberty where 12 follicles develop with only one dominant follicle entering to fully complete meiosis to become the ovum
→ undergoes unequal cytokinesis where one large secondary oocyte is made and one smaller polar body is made
→ the remaining follicles used for development become atretic or undergo apoptosis
3) The secondary oocyte will then undergo meiosis two
→ unequal cytokinesis occurs again which forms a mature egg and a second polar body
What are the five stages of follicle cell development?
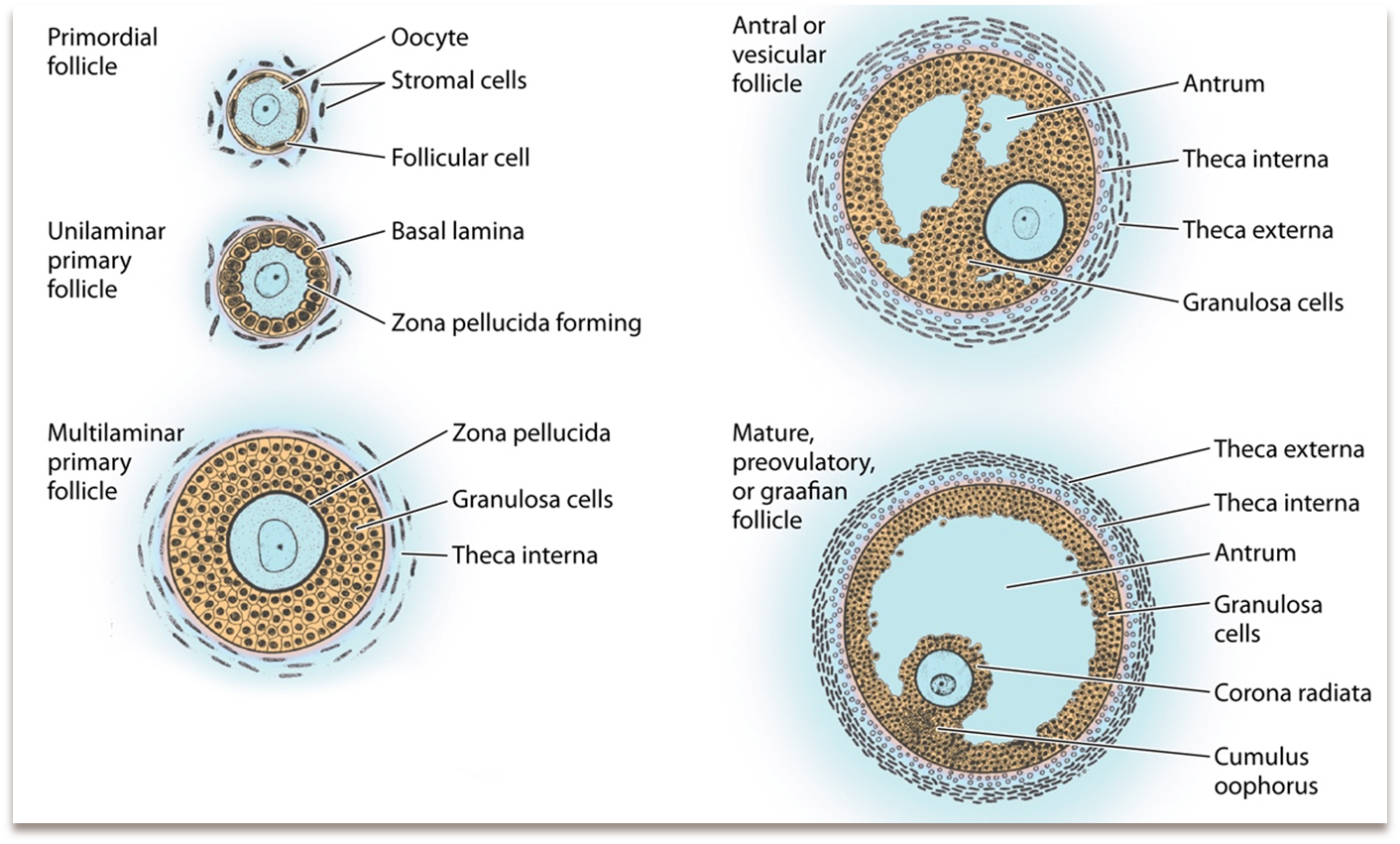
Each oocyte is surrounded by layers of epithelial cells which are subdivided into five stages, which develop over 90 days
1) Primordial Follicle (non-active)
→ most common, making up the most of the ovary
→ is made of single layer of follicular (squamous) cells and contains a primary oocyte
2) Early Primary Follicle (Unilaminar)
→ follicle cells grow and become large and cuboidal
→ the zona pellucida forms, which is a thick glycoprotein coat around the oocyte
3) Late Primary Follicle (Multilaminar)
→ the zona pellucida proliferates more which are made of glycoproteins ZP1, ZP2, and ZP3
→ the zona pellucida will have binding sites for sperm
4) Secondary (Antral) Follicle
→ begin to make a liquor folliculi, which is fluid that fills the antrum
→ liquor folliculi has oocyte maturation inhibitor which helps prevent premature maturation of the egg
→ the corona radiata or a layer of granulosa cells forms around the oocyte
→ the cumulus oophorus develops, which is a clump of granulosa cells around the oocyte that supports oocyte development
→ formation of the theca interna which makes androgens in response to LH
→ formation of the theca externa which is connective tissue and smooth muscle
5) Mature Graafian Follicle
→ large follicle that will burst through the ovary and undergo ovulation
What are hormonal levels correlated with ovarian and menstrual cycles?

Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone are the main hormones driving the process of follicle development and ovulation respectively
1) Estrogen will peak prior to ovulation due to release from Graafian follicles
→ Estrogen release from Graafian follicles leads to a rise in blood estrogen and and causes an LH surge
2) FSH will be consistently high during the entire development of the follicle before, dipping and then surging alongside LH before ovulation
→ LH surge caused by increase in estrogen release will cause increased blood flow to the follicle and increase the permeability of the theca externa allowing for local edema
→ LH will cause the release of meiosis-inducing factor which causes the primary oocyte to complete first meiotic division into a secondary oocyte
→ the secondary oocyte will immediately enter into prophase II and line up for metaphase and arrest again
3) Progesterone will peak after ovulation
What occurs at ovulation?
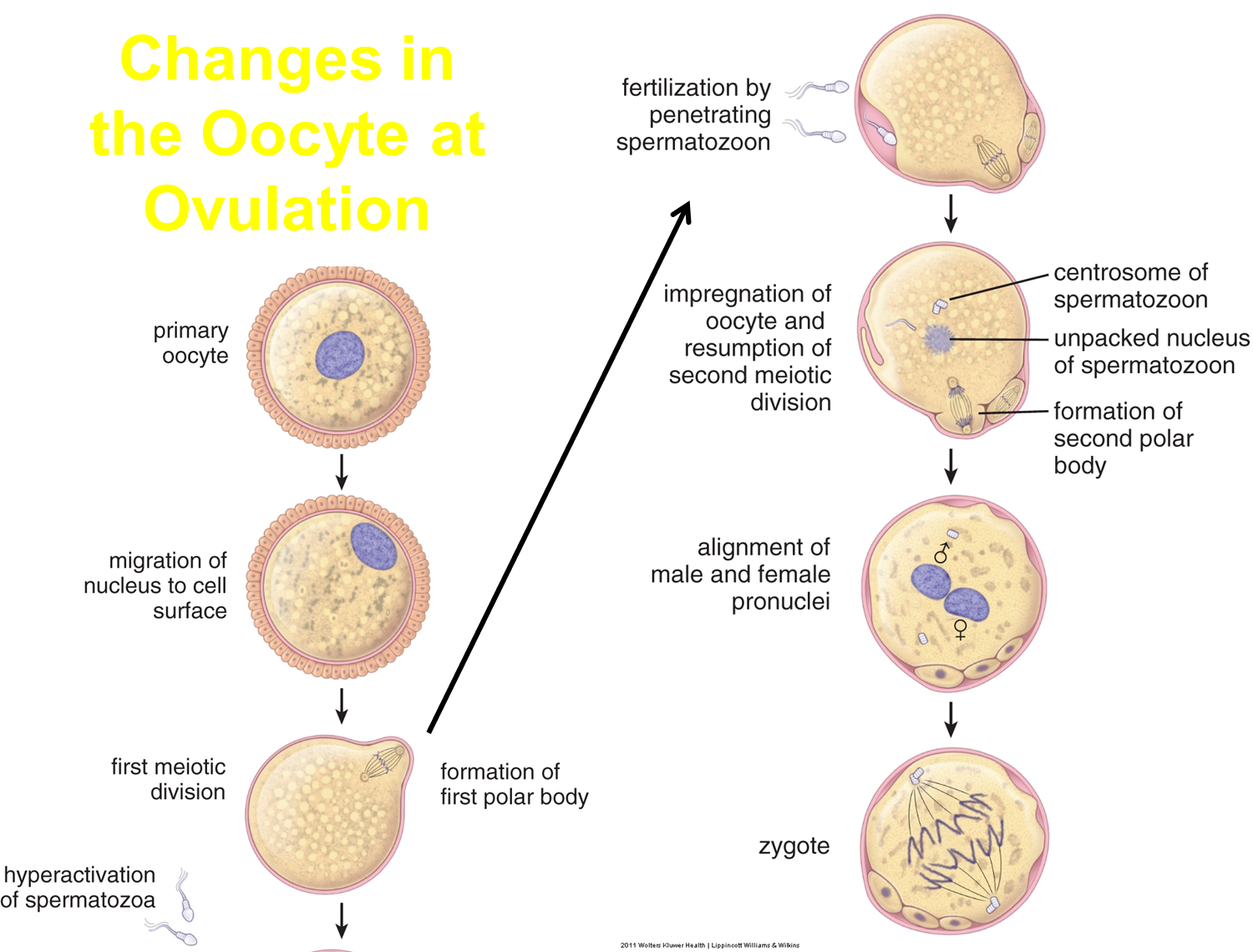
In response to luteinizing hormone, granuloa cells of the Graafian follicle will produce glycoproteins and fluid that causes the antrum to swell
2) swelling of the antrum pushes the Graafian follicle to burst outward through the cortex leading to rupture and release
→ the Graafian follicle will collapse and be converted into the corpus luteum by luteinizing hormone
1) the secondary oocyte will enter the duct, and will only complete second meiotic division to become ovum following fertilization
What is the corpus luteum?
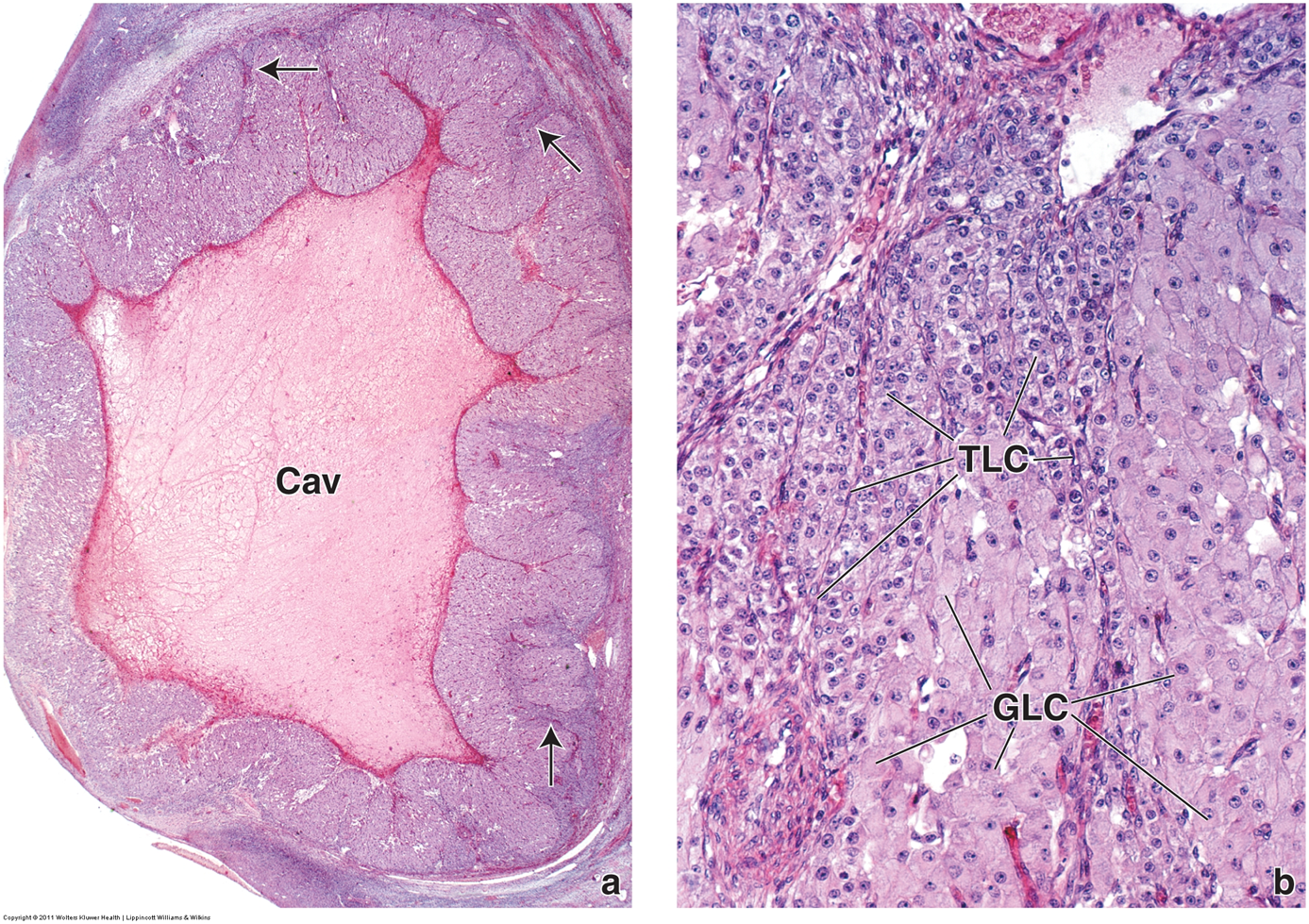
After the Graafian Follicle ruptures, in response to Luteinizing hormone will become the corpus luteum
1) The Granulosa cells become granulosa-lutein cells and will begin producing estrogen and progesterone
2) The Theca-interna will enlarge and become theca-lutein cells making progesterone
3) If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates
→ if pregnancy occurs, the placenta will produce hormones that helps to maintain the corpus luteum