GraphQL Distributed Systems
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What problem does GraphQL address compared to REST?
Over-fetching, under-fetching, and complex client-side orchestration across multiple endpoints.
When should query-driven APIs be preferred?
When clients need flexible data shapes and aggregation across multiple resources.
How does a GraphQL response relate to its request?
The response shape mirrors the query exactly.
What is introspection in GraphQL?
The ability to query the schema itself to discover types, fields, and capabilities.
What is a selection set in GraphQL?
The set of fields a client explicitly requests for a type.
Why are selection sets important?
They ensure clients receive exactly the data they need—no more, no less.
How does GraphQL handle relationships between entities?
By allowing natural traversal across related fields in a single query.
What are arguments in GraphQL?
Typed inputs used to filter or parameterize fields.
Why use variables in GraphQL queries?
To make queries reusable and separate query structure from values.
Why should pagination be applied early in GraphQL queries?
To bound execution cost and prevent unbounded result sets.
What is a fragment in GraphQL?
A reusable selection of fields that can be included in multiple queries.
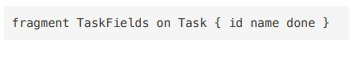
Why are fragments useful?
They reduce duplication and keep response shapes consistent.
What are directives in GraphQL?
Annotations like @include and @skip that conditionally include fields.

What are aliases used for in GraphQL?
To rename fields in the response without changing the schema.
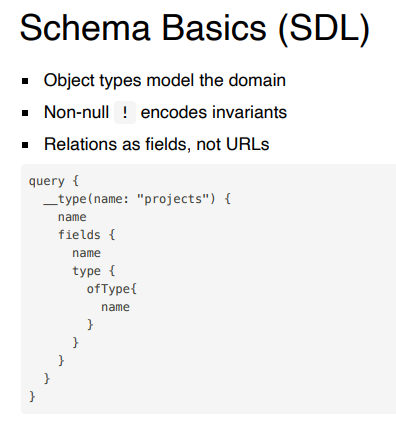
What is the GraphQL schema?
A strongly typed contract that defines types, fields, and relationships.
What does the non-null operator (!) mean?
The field must always return a value and can never be null.
How are relationships modeled in GraphQL schemas?
As fields on object types, not as URLs.
SDL Meaning
Schema Definition Language
What are GraphQL mutations used for?
To change server-side state.
How do GraphQL mutations differ from REST writes?
The client controls exactly which fields are returned after the mutation.

Why are mutations useful for optimistic UI updates?
Because the response shape can immediately update the client state.
What are GraphQL subscriptions?
Long-lived operations for real-time data streams, usually over WebSockets.

When should subscriptions be used?
For live updates such as dashboards or activity feeds.
What must be considered when using subscriptions?
Filtering early, applying backpressure, and limiting resource usage.
How does GraphQL structure responses?
A top-level data object, optionally combined with an errors array.
What does partial success mean in GraphQL?
Some fields resolve successfully while others return errors.
Why is partial data important in distributed systems?
Because failures are common and should not break the entire response.
What pagination strategies exist in GraphQL?
Offset/limit and cursor-based pagination.
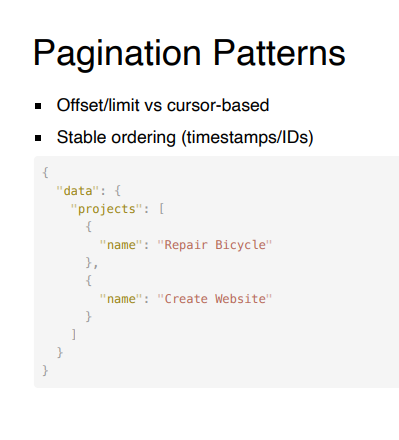
Why is cursor-based pagination preferred?
It provides stable ordering and avoids inconsistencies when data changes.
What is the N+1 problem in GraphQL?
Executing one query for a list and one additional query per item.
How can the N+1 problem be mitigated?
By batching requests and caching per request (e.g., DataLoader).
Why is field-level tracing important?
To identify slow resolvers and performance bottlenecks.
What are persisted queries?
Pre-registered queries identified by stable hashes.

Why use persisted queries?
They improve caching, reduce payload size, and limit attack surface.
Where can caching be applied in GraphQL?
On the client, at the edge, and inside resolvers.
How is authentication typically handled in GraphQL?
Via headers or tokens injected into the request context.
Why enforce depth and complexity limits?
To protect against expensive or abusive queries.
What is the principle of least privilege in GraphQL?
Each field should only expose the minimum required data.
What are the core types in the Task Manager example?
Project and Task.
What operations are demonstrated in the running case?
Queries, mutations, and subscriptions.
Why is the running case useful?
It shows end-to-end GraphQL usage in a realistic scenario.
What should be logged in GraphQL systems?
Operation name or hash, duration, errors, and resolver metrics.
How should GraphQL schemas evolve safely?
Through additive changes, deprecations, and clear sunset policies.
Why is the schema considered a long-term contract?
Because clients depend on it directly.
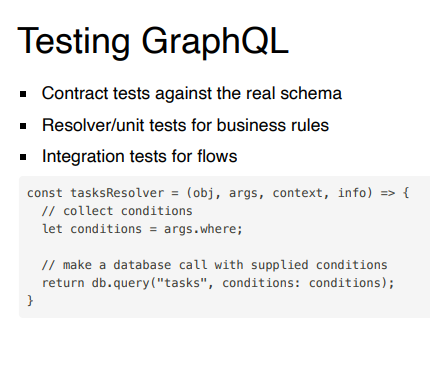
What types of tests are used in GraphQL applications?
Contract tests, Resolver/ unit tests, Integration tests