Dentitions week 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Dentition
Term used to describe the natural teeth in the jawbones. A person has two dentitions during a lifetime.
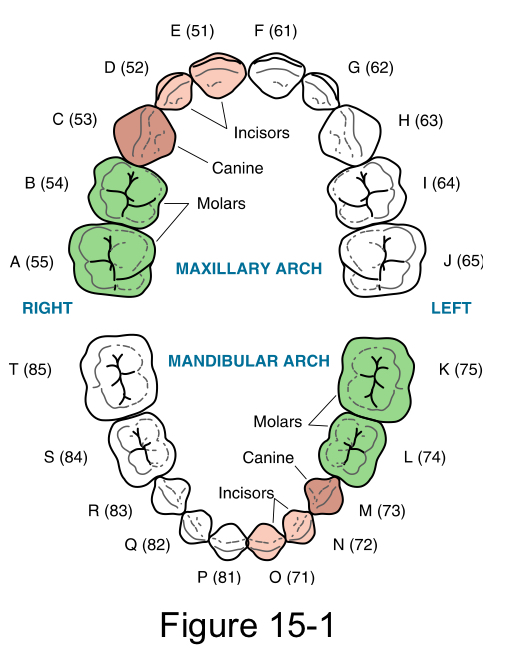
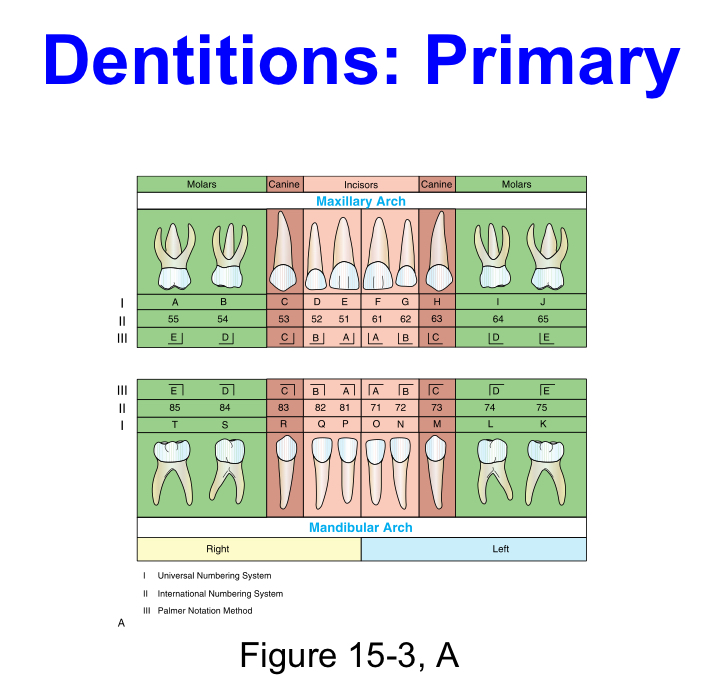
Primary dentition
Or deciduous dentition, or baby teeth.
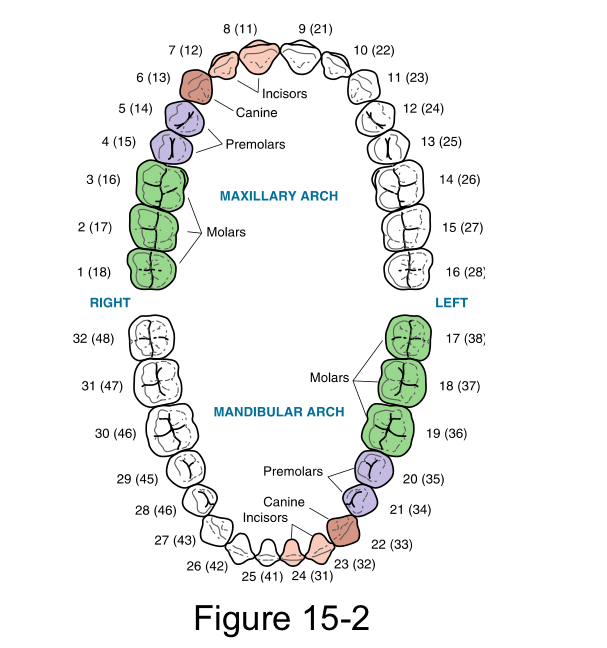
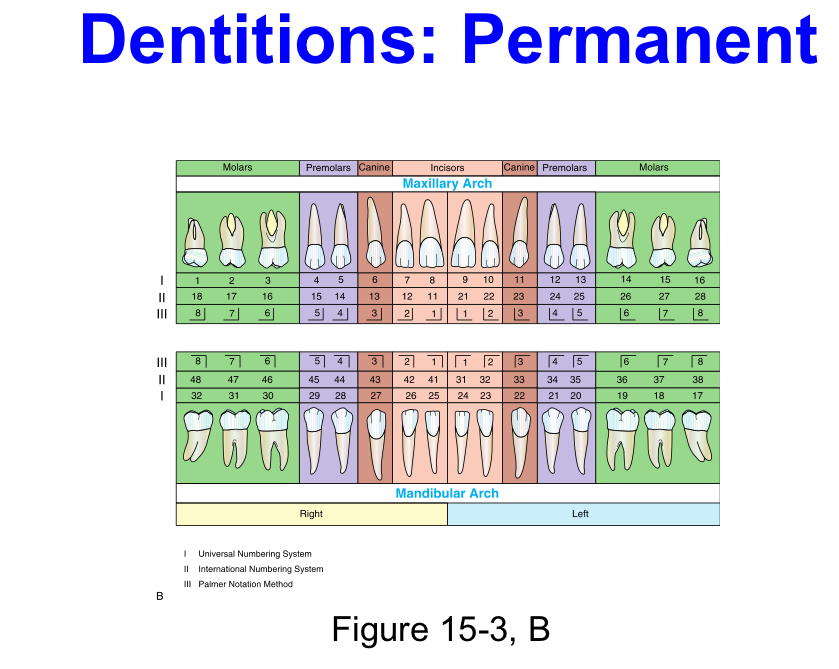
Permanent Dentition
Or secondary dentition, or adult teeth, or succedaneous dentition. (Except the molars which are non succedaneous)
Number of teeth in the primary dentition
20 teeth total. 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 molars
Number of teeth in permanent dentition
32 teeth total. 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars, 12 molars
Incisors mastication function
Function as instruments for biting and cutting the food.
The Canines mastication function
Function in piercing or tearing the food because of their tapered shape.
The premolars mastication function
Function to assist the molars in grinding the food during mastication, and also assist the canines in piercing or tearing the food with their cusps.
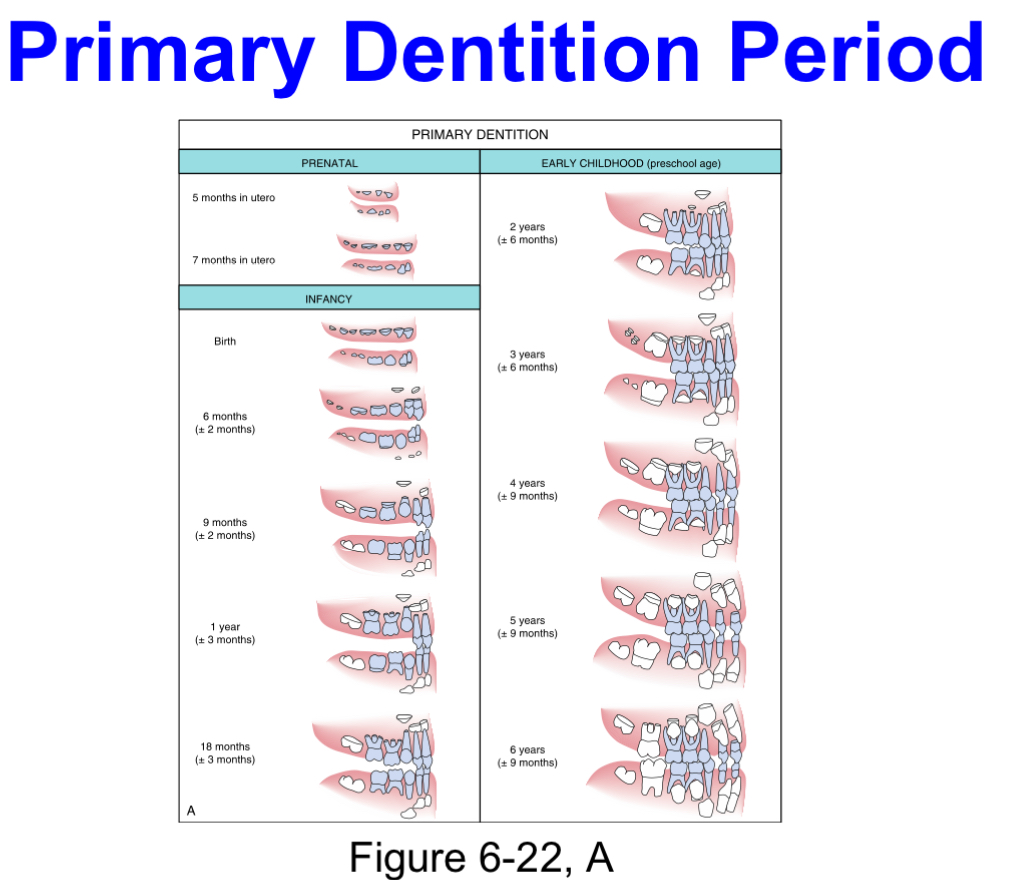
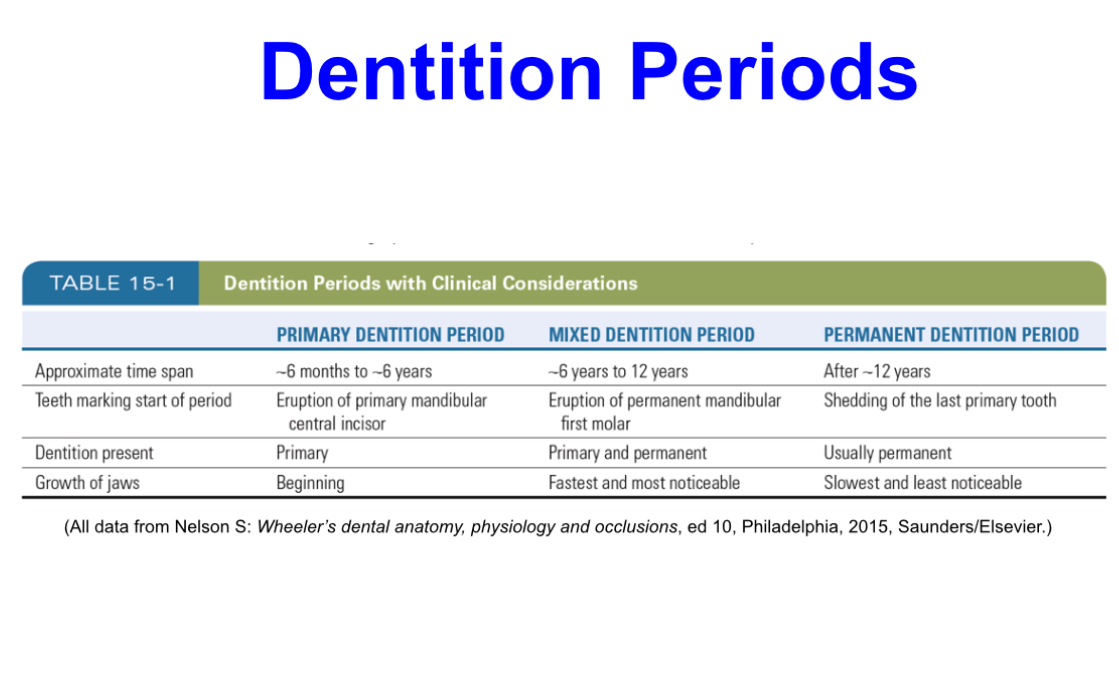
Primary dentition period
Approximate time span:6 months to 6 years
Begins:by the eruption of the primary mandibular central incisors
Ends:with the eruption of the first permanent tooth
Mixed dentition period
Approximate time span:6 years to 12 years
Begins:by the eruption of the permanent mandibular first molar
Ends:with the shedding of the last primary tooth
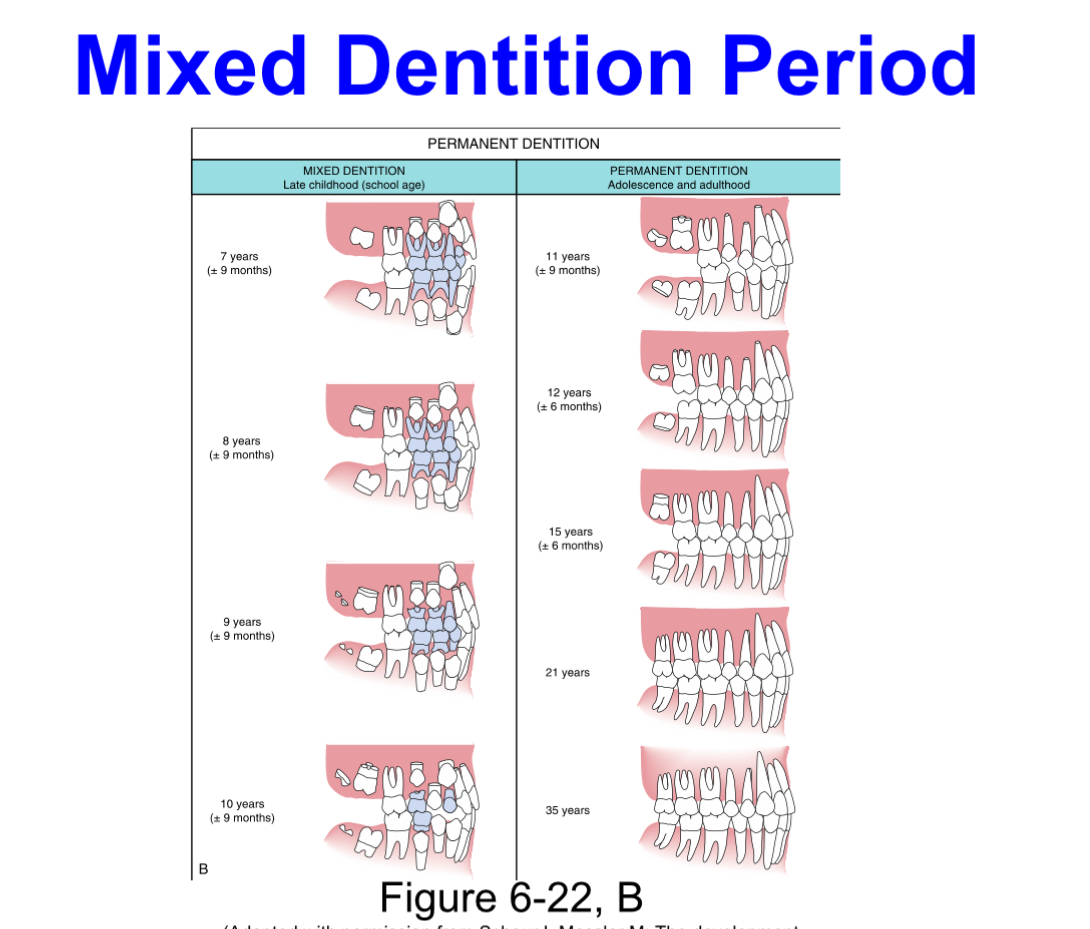
Permanent dentition period
Approximate time span:after 12 years
Begins:by the shedding of the primary maxillary canine
Dental Anatomy
the area of dental sciences that deals with the form or morphology of teeth
Alveolus (plural: alveoli)
the tooth socket
Alveolar process or dental arch
the tooth bearing portion of each jawbone
Maxilla
the upper jawbone, holds the maxillary teeth
Mandible
the lower jawbone, holds the mandibular teeth
Occlusion
the way in which the teeth of the mandibular arch come into contact with those of the maxillary arch. Also is used to describe the anatomical alignment of the teeth and their relationship to the rest of the masticatory system.
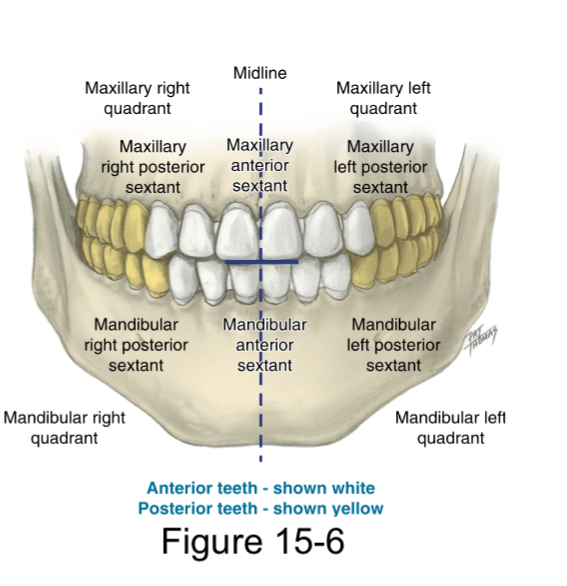
Midline
imaginary vertical plane that divides the arch into two equal halves.
The entire oral cavity has four quadrants
right maxillary left maxillary
_________________________________________
right mandibular left mandibular
The correct sequence of words when describing a tooth is based on a D-A-Q-T System
D for dentition
A for arch
Q for quadrant
T for tooth type
Example: permanent maxillary right canine
Anterior teeth
the teeth which are closer to the midline (incisors and canines)
Posterior teeth
the teeth which are farther from the midline (premolars if present and molars)
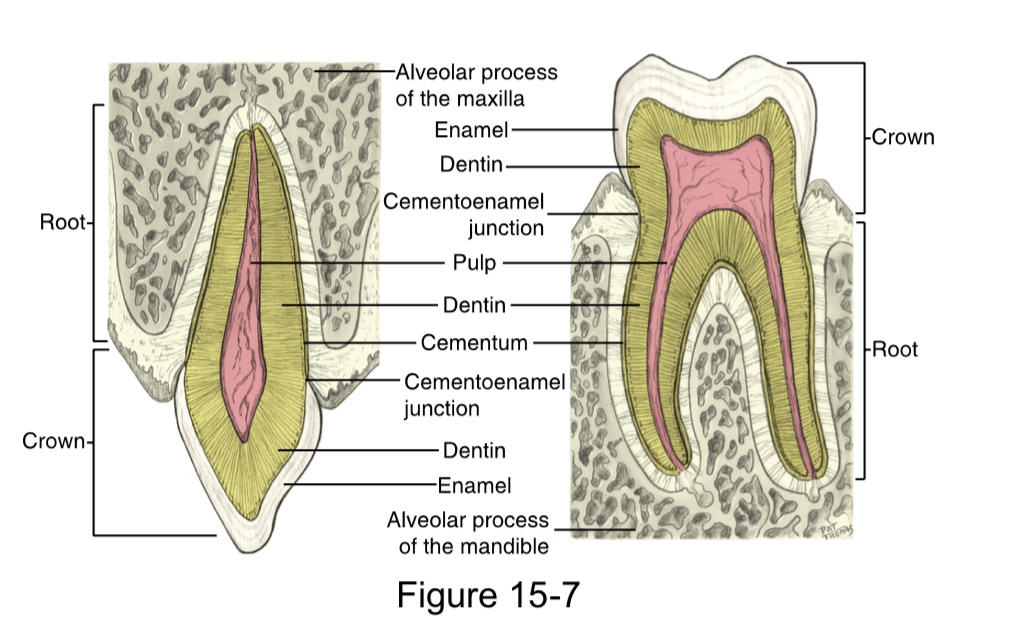
Crown
Dentin covered by enamel
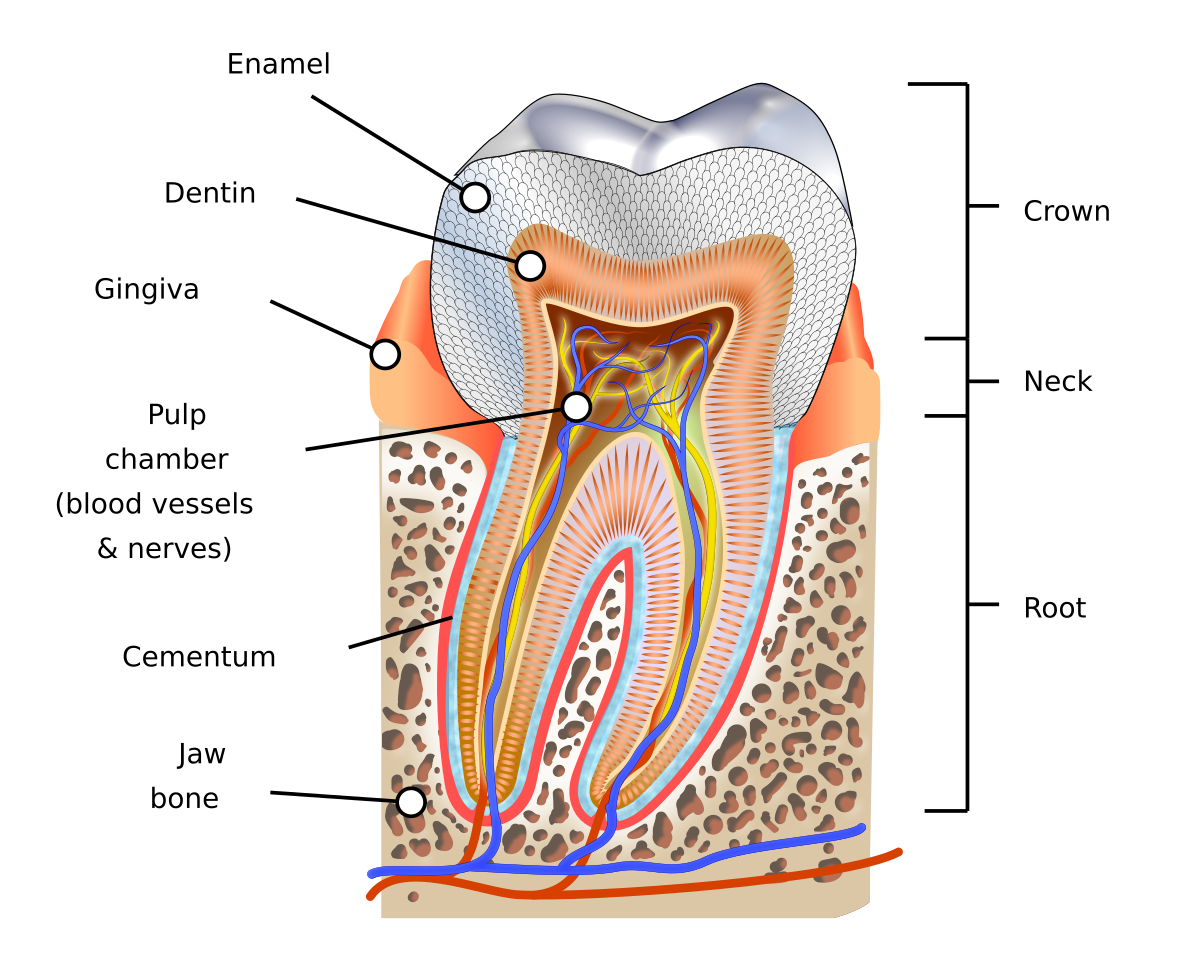
Root(s)
has dentin covered by cementum
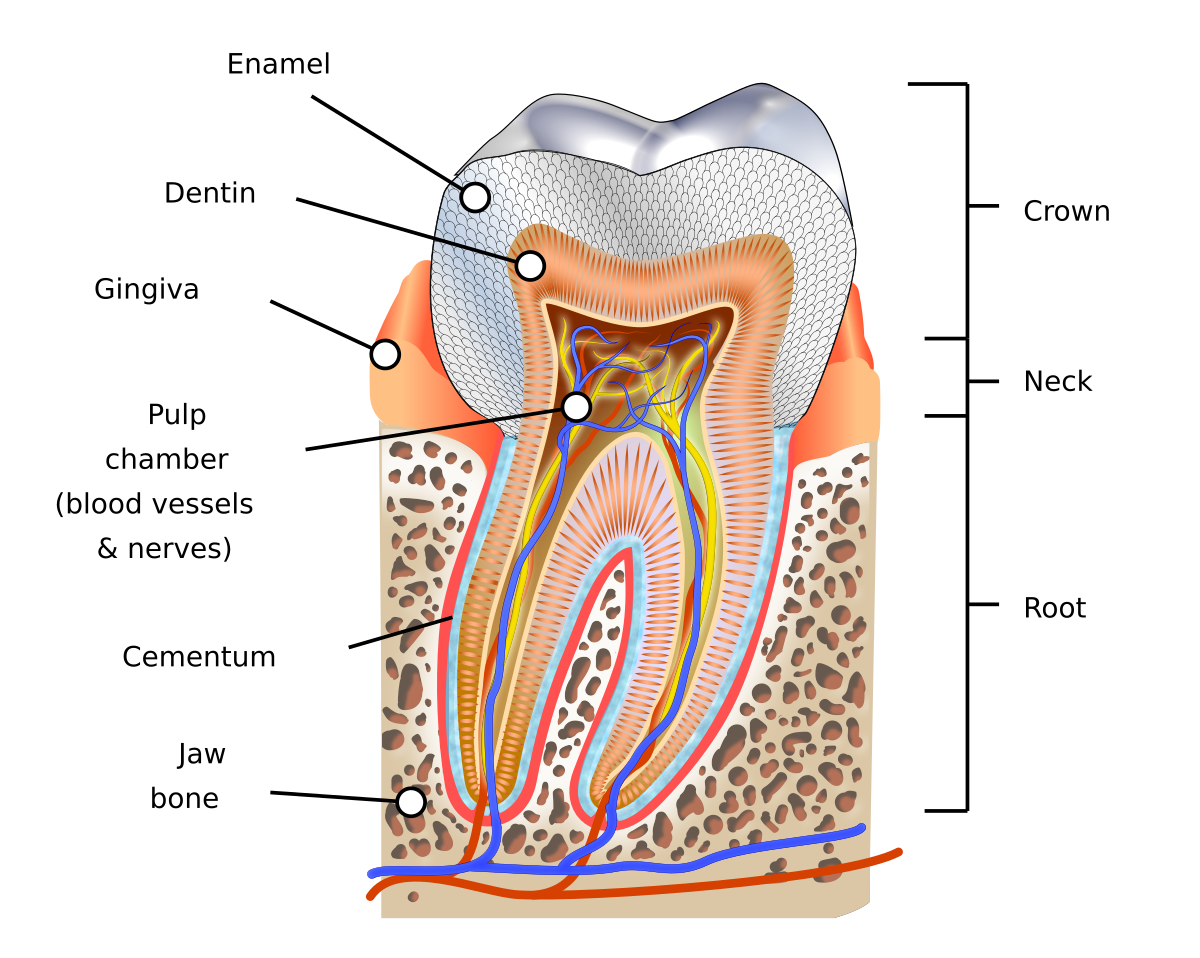
Pulp cavity
has a pulp chamber with pulp horn(s), and pulp canal(s) with apex (apices) and apical foramen (foramina)
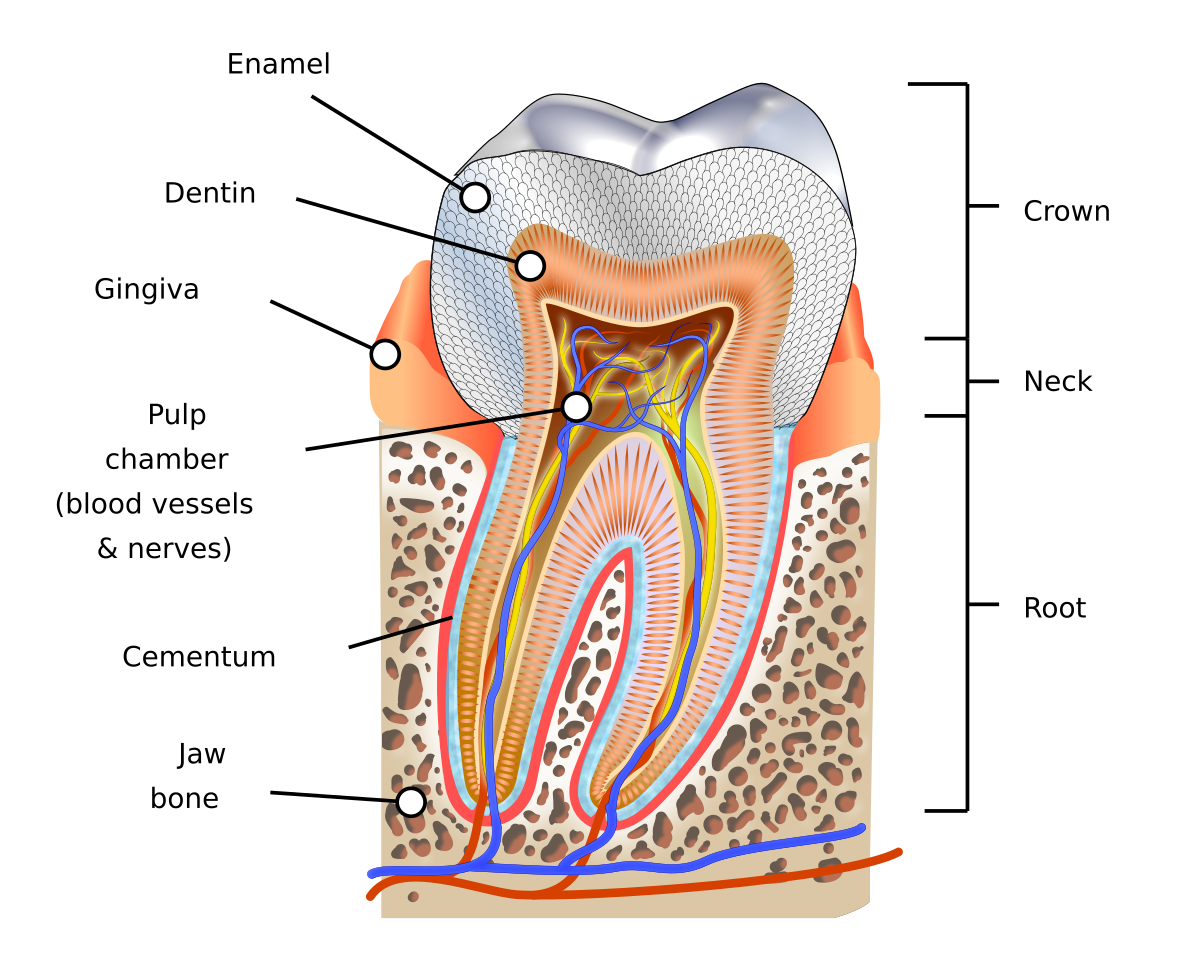
Cementoenamel junction (CEJ)
an external line at the cervix of the tooth where the enamel meets the cementum
The anatomical crown
is the portion of the tooth that is covered by the enamel
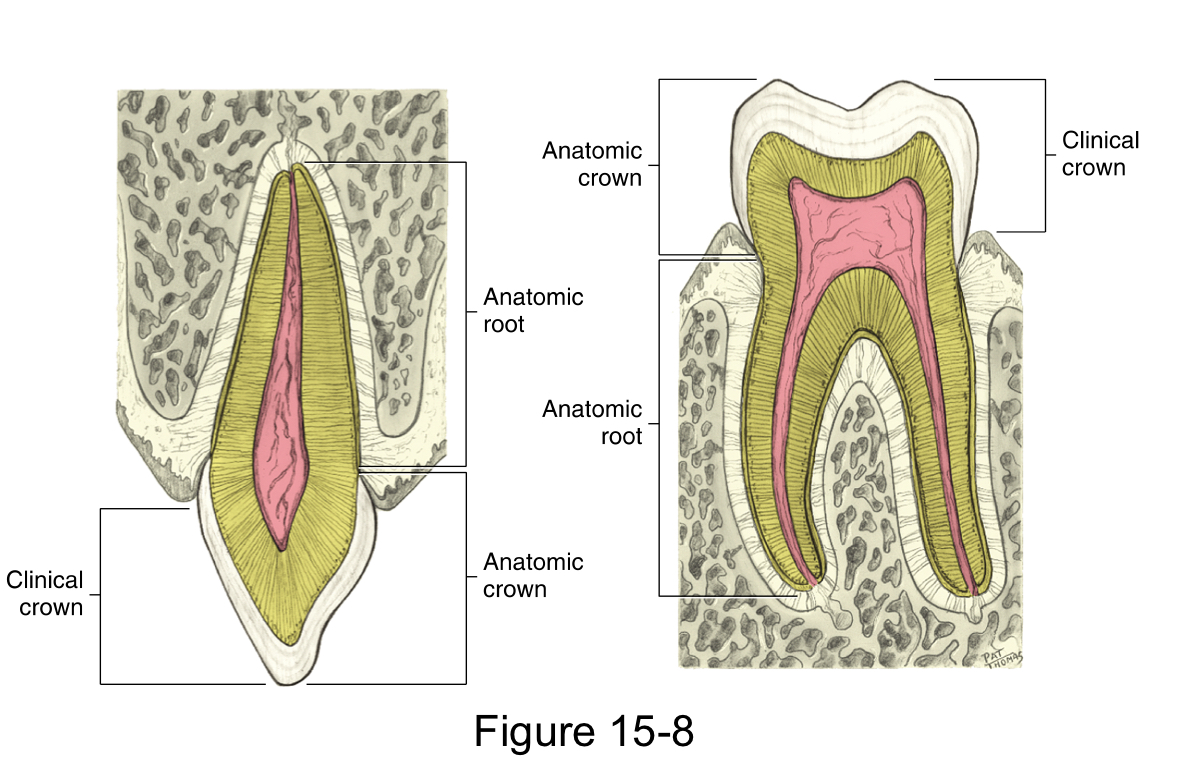
The clinical crown
is the portion of the tooth that is visible in the oral cavity
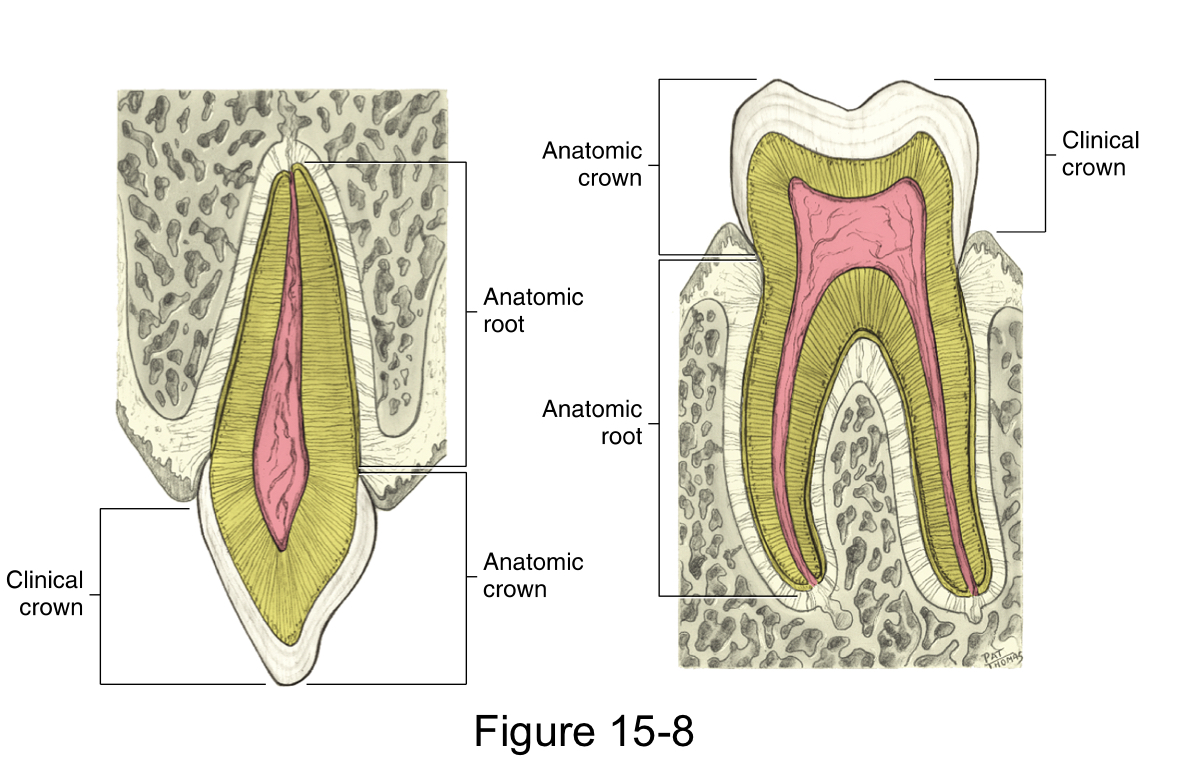
The anatomical root
is the portion of the tooth that is covered by the cementum
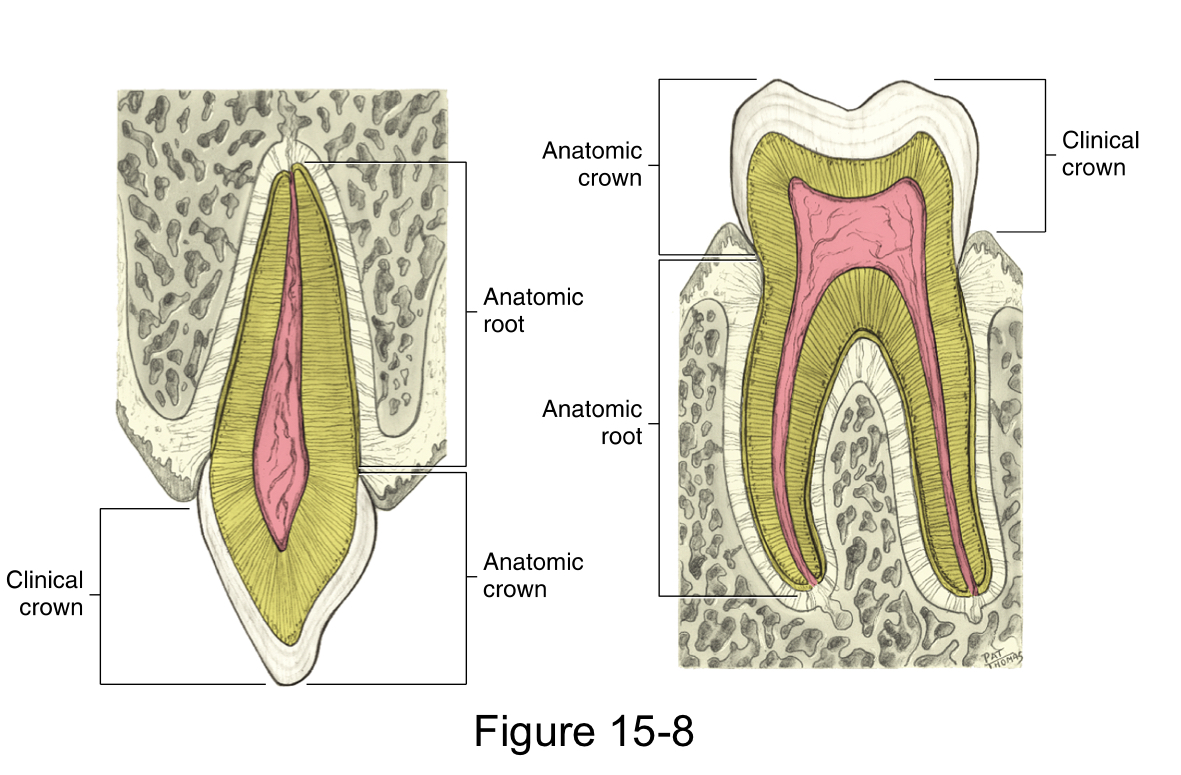
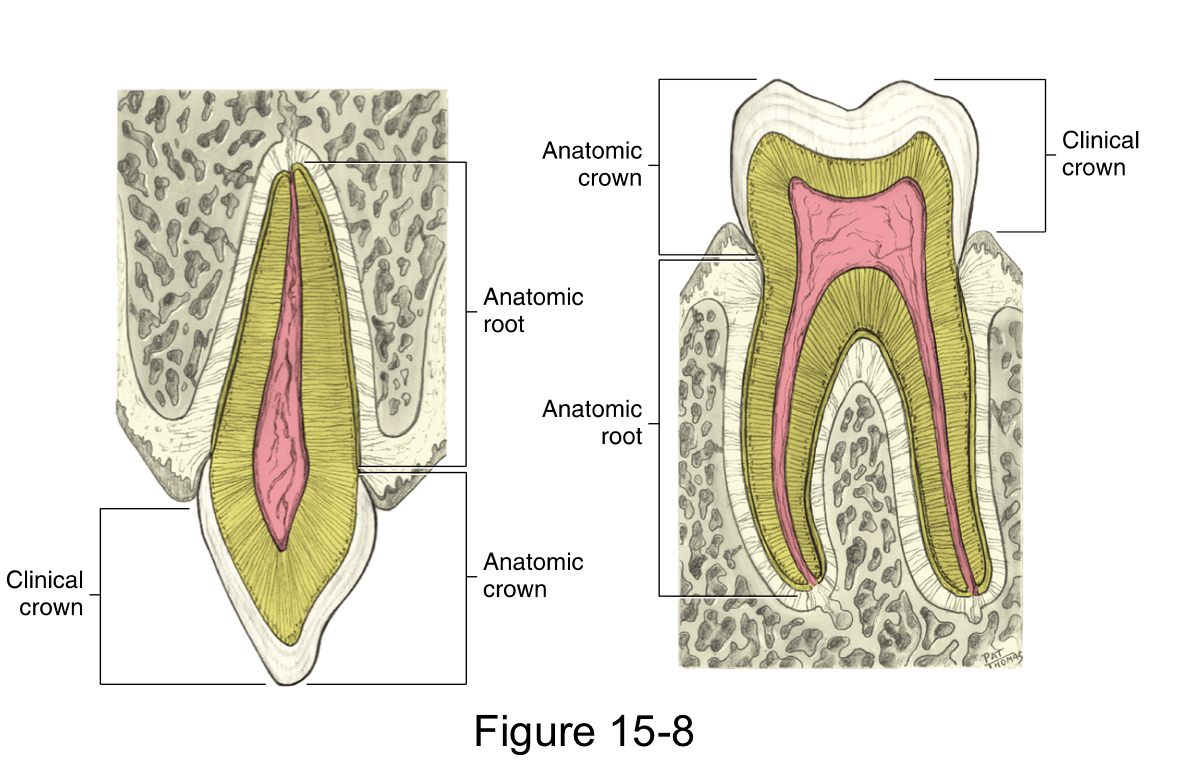
The clinical root
is the portion of the anatomical root that is visible in the oral cavity
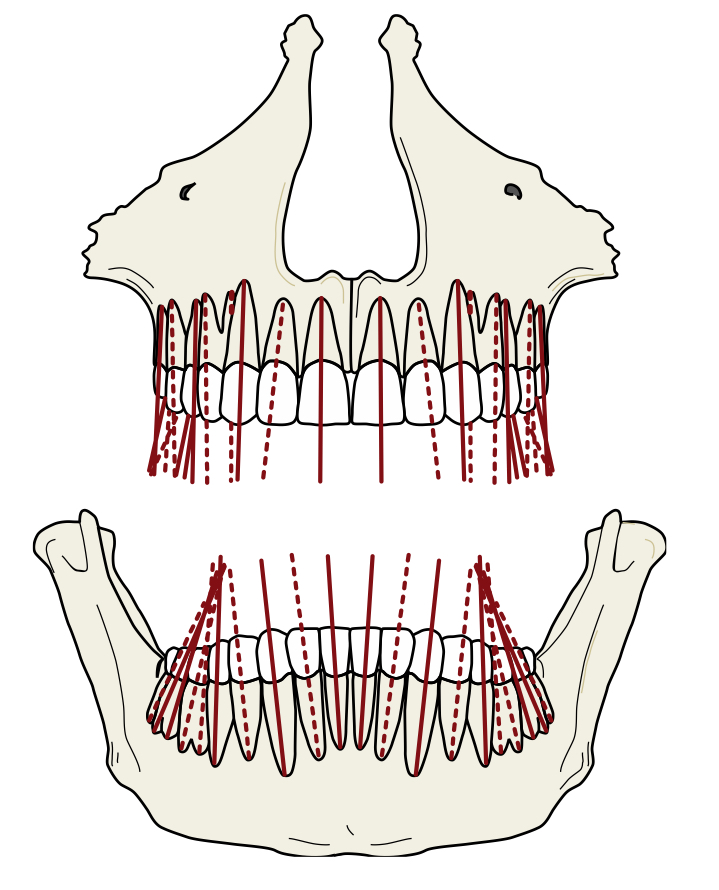
The root axis line
is an imaginary line representing the long axis of a tooth.
Each tooth has how many surfaces?
Five
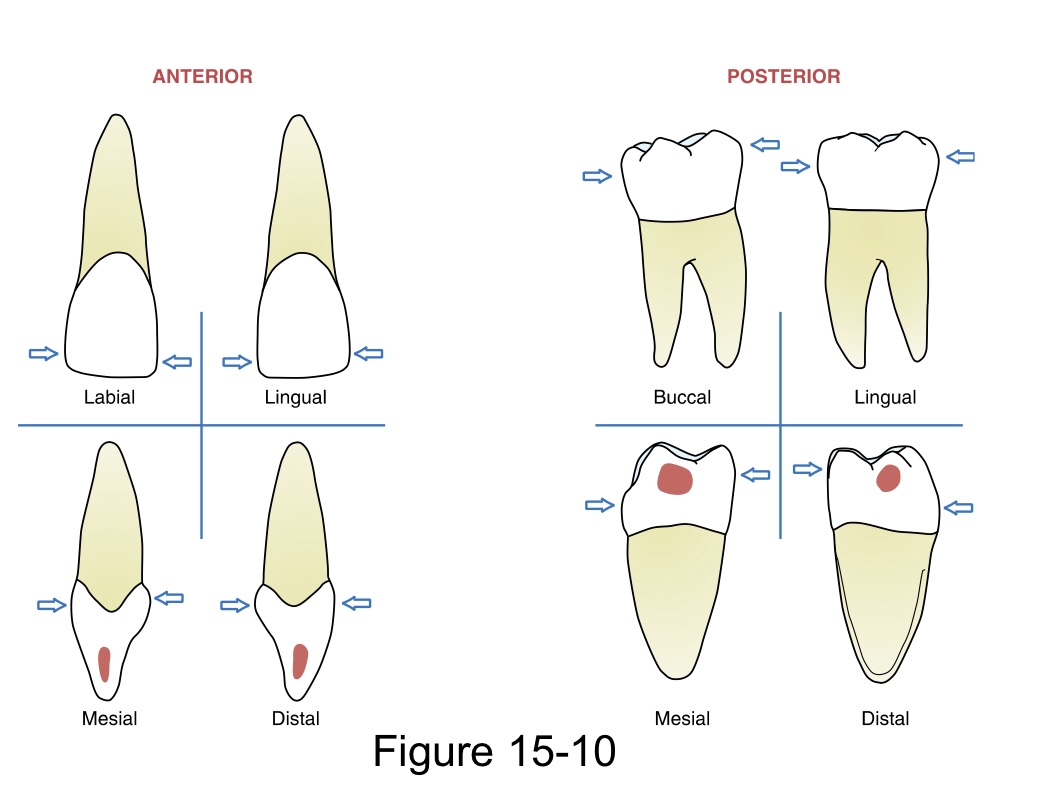
Facial surface
labial surface for anterior teeth
buccal surface for posterior teeth
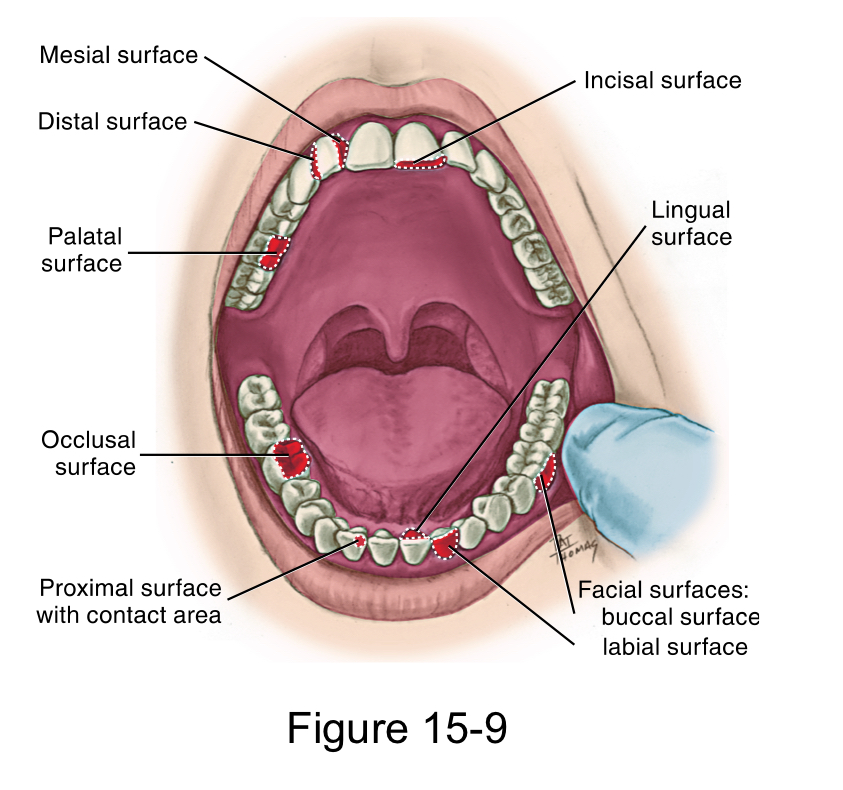
Lingual surface
palatal surface for maxillary teeth
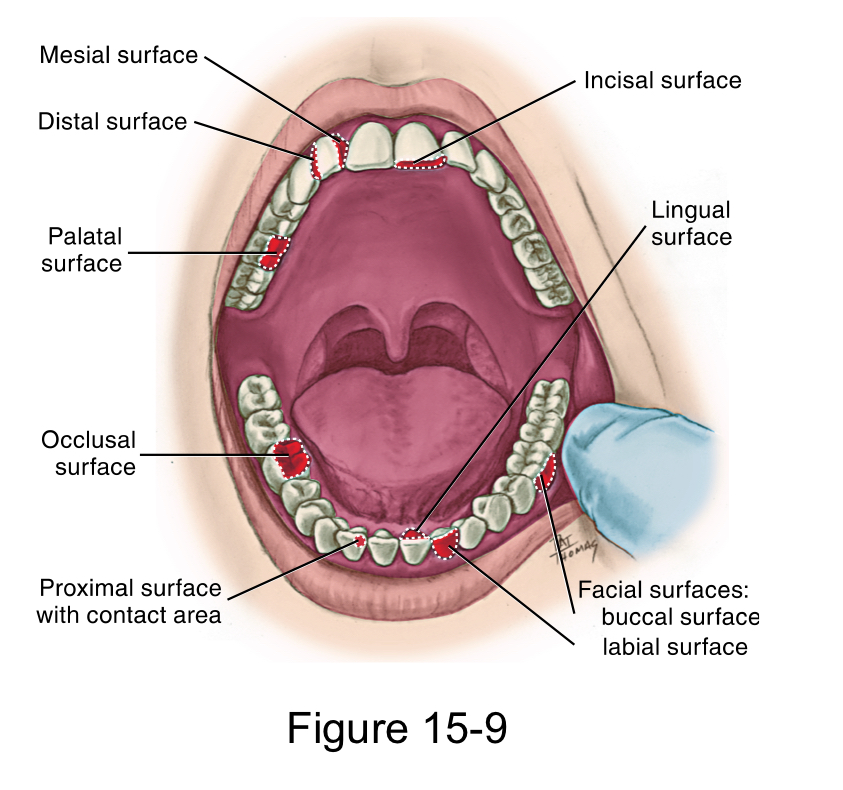
Masticatory surface
incisal surface for anterior teeth
occlusal surface for posterior teeth
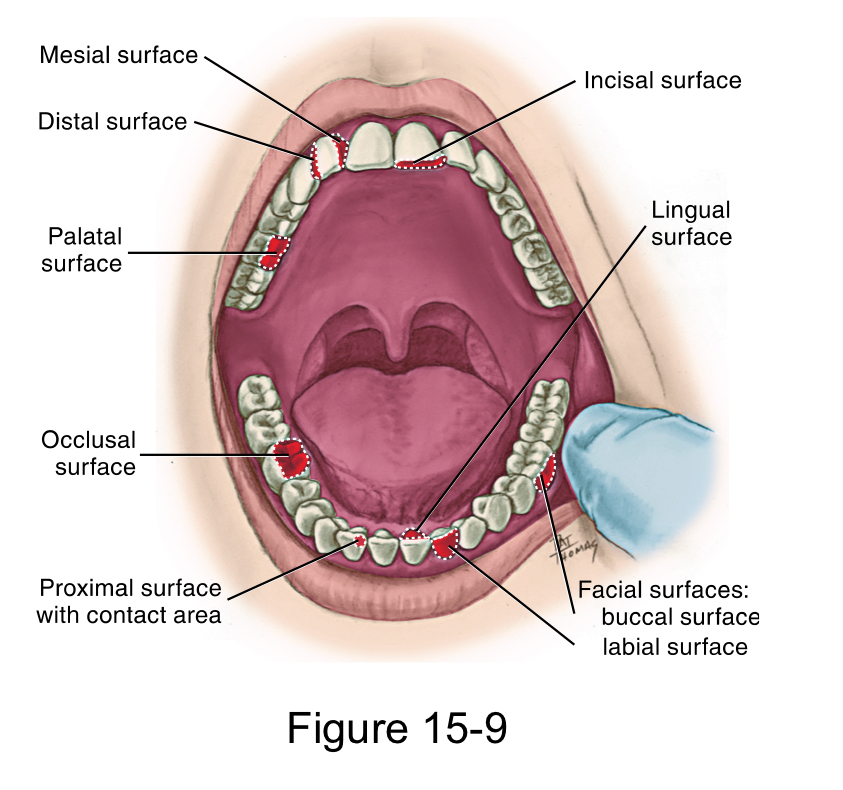
Mesial surface
closer to the midline
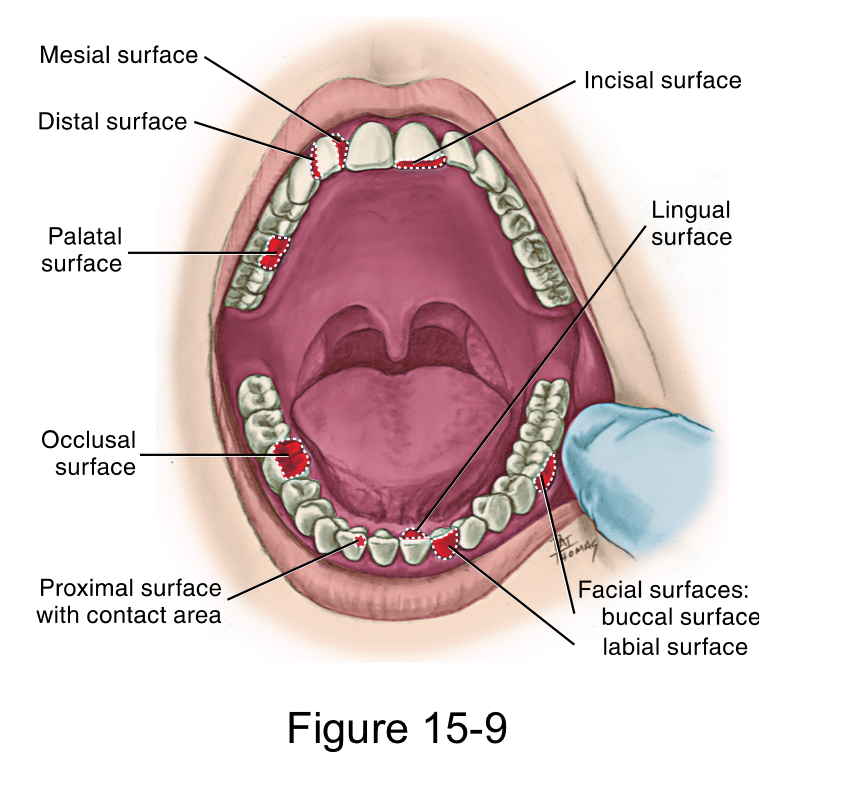
Distal surface
farther away from the midline.
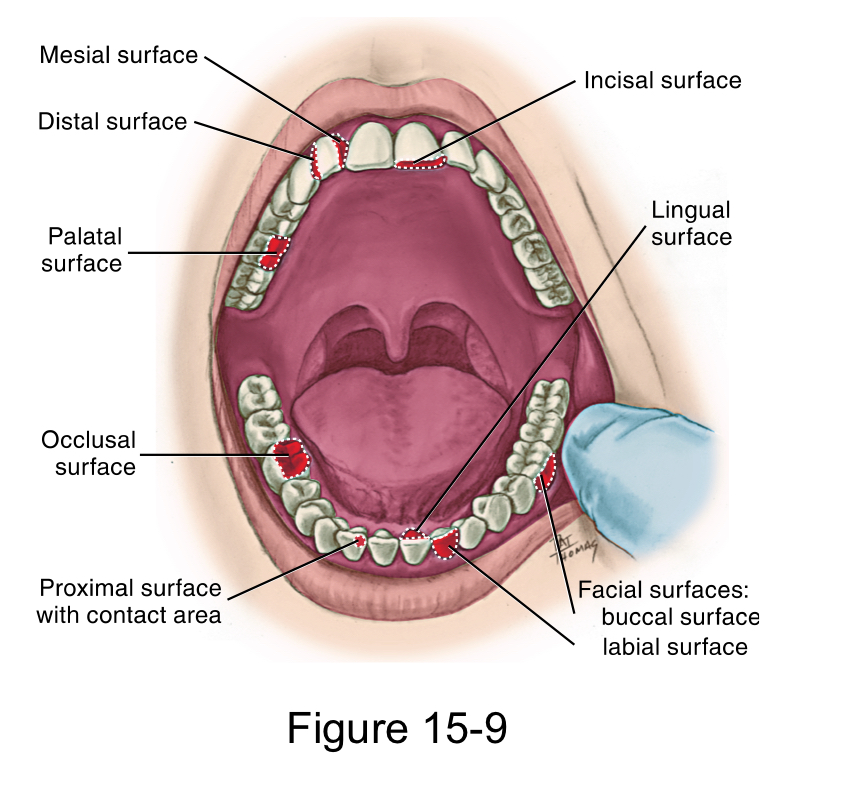
Both the Mesial and distal surface between adjacent teeth
Proximal Surfaces
is the area between adjacent tooth surfaces
interproximal Space
Contact area
is the area where the crowns of adjacent teeth in the same arch touch on each proximal surface.
The height of contour or crest of curvature
is the greatest elevation of the tooth either incisocervically or occlusocervically
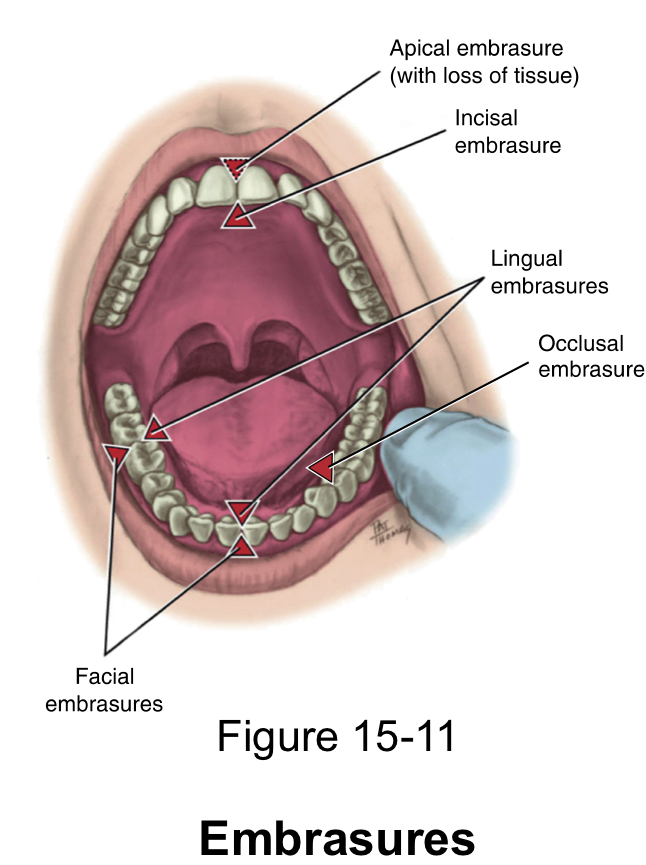
Embrasures
spaces that are formed next to the contact area when two teeth in the same arch contact
A line angle
is a line formed by the junction of two crown surfaces
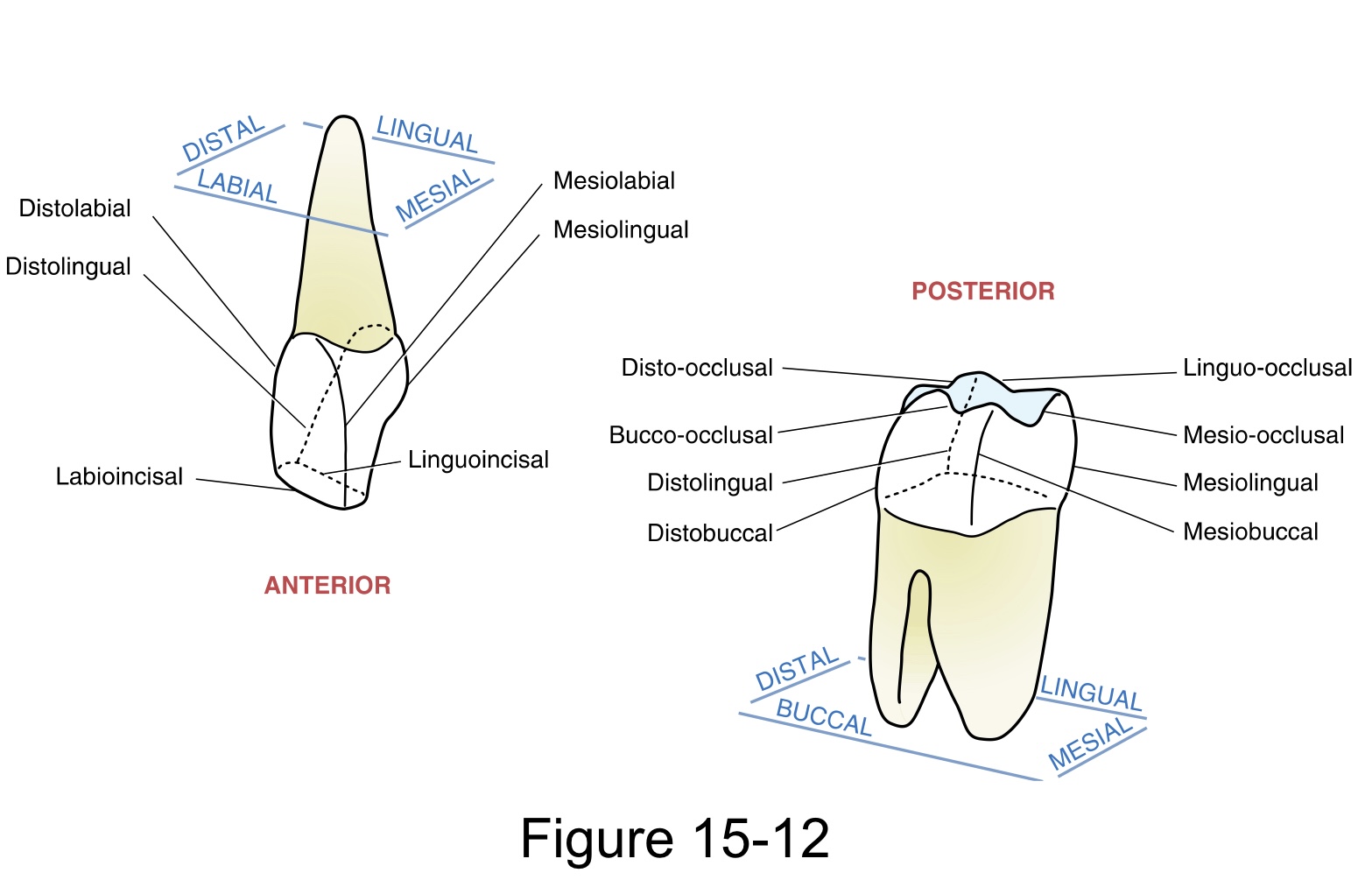
A point angle
is the junction of three crown surfaces
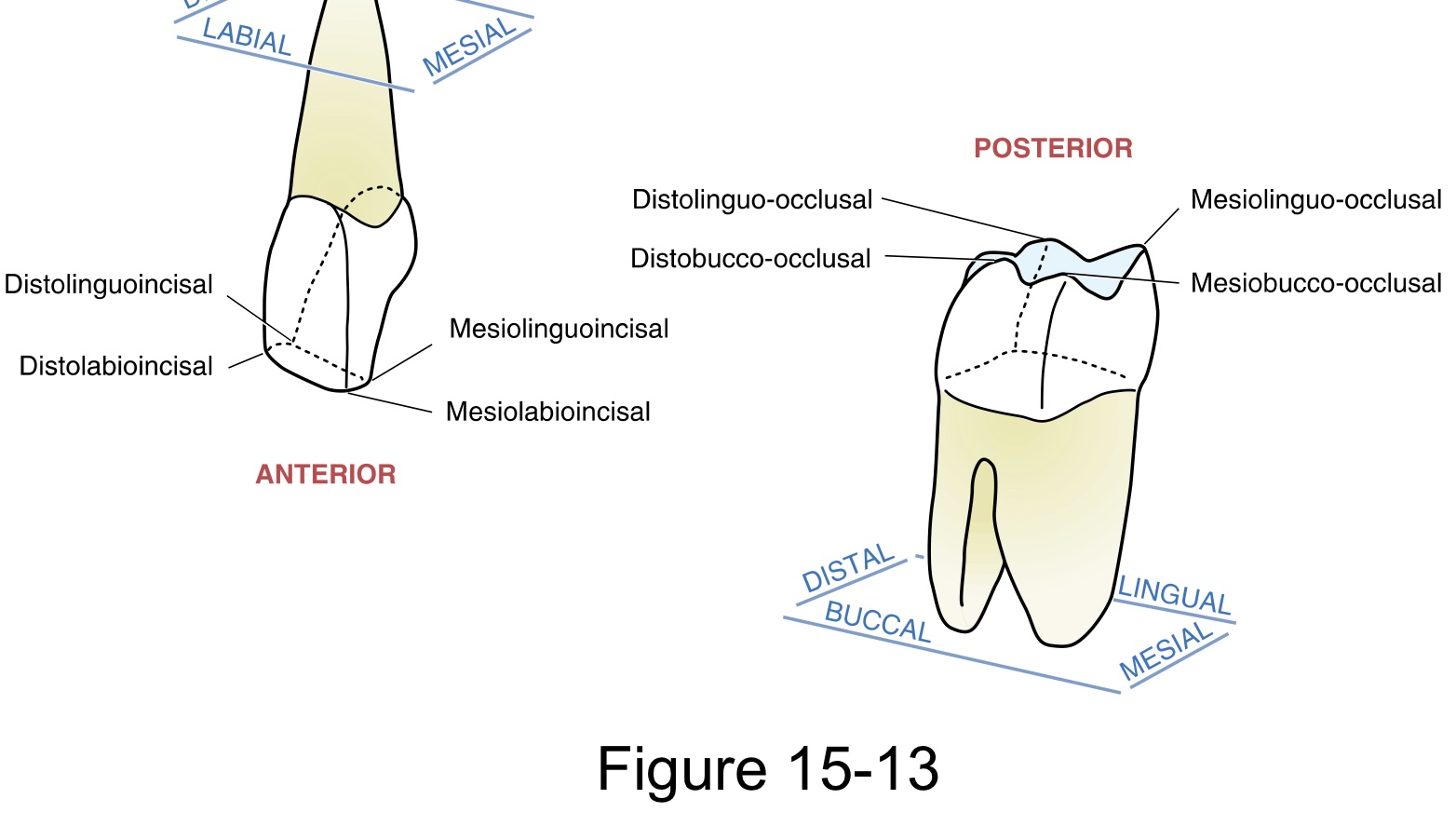
The accepted sequence when describing line angles or point angles is:
Mesial precedes distal; Labial/ buccal, lingual follow mesial or distal; and precede Incisal/ occlusal
Sextant
which further divide each dental arch into three parts according to the relationship to the midline.
Root concavities
These indentations in the root surface commonly occur on the proximal root surfaces of anteriors and posteriors and the buccal and lingual surfaces of molars.
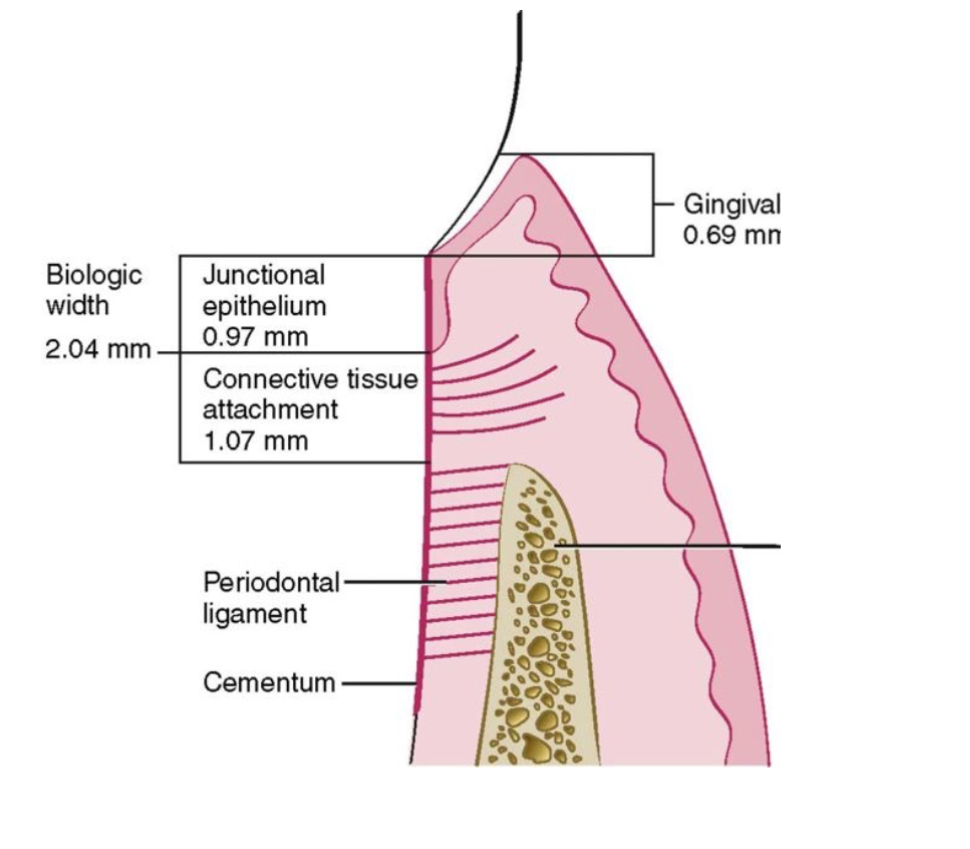
Biological width
The distance established by the junctional epithelium and connective tissue attachment to the root surface of a tooth.
Assessment for _____ can be made clinically by measuring the distance between the bone and the restoration margin using a periodontal probe.
Universal Numbering system (UNS)
This system is the most widely used in the United States for the designation of both dentitions, because it is adaptable to electronic data.
The permanent teeth are designated from each other in the UNS in consecutive arrangement as the patient is observed from in front by using the digits 1 through 32, starting with the maxillary right third molar, moving clockwise, and ending with the mandibular right third molar.
•When speaking about a certain tooth such as the permanent maxillary right
International Numbering System (INS)
the need for a system that can be used internationally, as well as by electronic data transfer
With this system, the teeth are designated from each other by using a two-digit code.
•The first digit of the code indicates the quadrant, and the second indicates the tooth’s position in this quadrant.
•the digits 1 through 4 are used for quadrants in a clockwise manner in the permanent dentition, and digits 5 through 8 are
Palmer Notation System
known as the Military Tooth Numbering System.
•In this system, the teeth are designated from each other with a right-angle symbol indicating the quadrants and arch, with the tooth number placed inside.
Dentition Period
primary, mixed, and permanent.
•Each patient should be assigned a _______ to allow for the most effective dental treatment for that period.
Succedaneous
the permanent teeth that replace the primary teeth, specifically the incisors, canines, and premolars.
Non Succedaneous
are the permanent teeth that do NOT replace any primary teeth.
what are the three dentition period, and how are they different from each other?
primary dentition period, mixed dentition period, permanent dentition period; primary period ends when the first permanent tooth erupts, a permanent mandibular first molar. the mixed dentition is when there is primary and permanent teeth and the permanent dentition period is when there are only permanent teeth.
Morphology
Means the shape, structure, and form of the teeth