Ciulla: Immunohematology
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
C. Hematocrit too low
1. A woman wants to donate blood. Her
physical examination reveals the following:
weight—110 Ib, pulse—73 bpm,
blood pressure—125/75 mm Hg,
hematocrit—35%. Which of the following
exclusions applies to the prospective
donor?
A. Pulse too high
B. Weight too low
C. Hematocrit too low
D. Blood pressure too low
C. 454 mL
2. A potential donor has no exclusions, but
she weighs only 95 pounds. What is the
allowable amount of blood (including
samples) that can be drawn?
A. 367 mL
B. 378 mL
C. 454 mL
D. 473 mL
A. Blood could have transmitted hepatitis
(HBVorHCV)orHIV
3. Donors who have received blood or blood
products within 12 months of when they
desire to donate are deferred to protect the
recipient because the
A. Blood could have transmitted hepatitis
(HBVorHCV)orHIV
B. Blood may have two cell populations
C. Donor may not be able to tolerate the
blood loss
D. Donor red cell hemoglobin level may
be too low
D. Mild bacteremia
4. Which of the following conditions would
contraindicate autologous presurgical
donation?
A. Weight of 100 pounds
B. Age of 14 years
C. Hemoglobin of 12 g/dL
D. Mild bacteremia
D. Recipient of human growth hormone
5. Which of the following donors would be
deferred indefinitely?
A. History of syphilis
B. History of gonorrhea
C. Accutane® treatment
D. Recipient of human growth hormone
A. CMV
6. Which of the following viruses resides
exclusively in leukocytes?
A. CMV
B. HIV
C. HBV
D. HCV
C. May be used for pooled platelet
concentrate preparation
7. A donor indicates that he has taken
two aspirin tablets per day for the last
36 hours. The unit of blood
A. May not be used for pooled platelet
concentrate preparation
B. Should not be drawn until 36 hours
after cessation of aspirin ingestion
C. May be used for pooled platelet
concentrate preparation
D. May be used for red blood cells and
fresh-frozen plasma production, but
the platelets should be discarded
C. Properly dispose of unit by autoclaving
or incineration.
8. Which of the following best describes
what must be done with a unit of blood
drawn from a donor who is found to be at
high risk of contracting acquired immune
deficiency syndrome (AIDS)?
A. Hold unit in quarantine until donor
diagnosis is clarified.
B. Use the blood for research dealing
with AIDS.
C. Properly dispose of unit by autoclaving
or incineration.
D. Use the plasma and destroy the red
blood cells.
C. Plasma protein fraction (PPF)
9. Which of the following is least likely to
transmit hepatitis?
A. Cryoprecipitate
B. RBC
C. Plasma protein fraction (PPF)
D. Platelets
B. Test each donor in the pool for HCV
10. A pooled sera product from 16 donors has
a repeatedly positive nucleic acid test
(NAT) for HCV. The next action that
should be taken is to
A. Permanently exclude all the donors in
the pool
B. Test each donor in the pool for HCV
C. Label all the donors as HCV positive
D. Confirm the positive using recombinant
immunoblot assay (RIBA)
D. Antithrombin III
11. Although Cryoprecipitate has primarily
been used for treatment of hypofibrinogenemia
and hemophilia A, it contains
other blood proteins useful in the
treatment of coagulopathies. Which of the
following is not found in Cryoprecipitate?
A. Fibronectin
B. Factor XIII
C. Factor VIILvW
D. Antithrombin III
D. Platelets
12. Even though it is properly collected and
stored, which of the following will fresh frozen
plasma (FFP) not provide?
A. Factor V
B. FactorVIII
C. Factor IX
D. Platelets
C. Irradiate the RBCs before infusion
13. Blood needs to be prepared for intrauterine
transfusion of a fetus with severe
HDN. The red blood cell unit selected is
compatible with the mother's serum and
has been leuko-depleted. An additional
step that must be taken before transfusion
is to
A. Add pooled platelets and fresh-frozen
plasma
B. Check that the RBC group is consistent
with the father's
C. Irradiate the RBCs before infusion
D. Test the RBC unit with the neonate's
eluate
A. Maintaining ATP levels for red cell
viability
14. The addition of adenine in an anticoagulant-
preservative formulation aids in
A. Maintaining ATP levels for red cell
viability
B. Maintaining platelet function in stored
blood
C. Reducing the plasma K+ levels during
storage
D. Maintaining 2,3-BPG levels for
oxygen release to the tissues
D. Remove sufficient segments to
complete donor processing procedures
15. The pilot tubes for donor unit #3276 break
in the centrifuge. You should
A. Label the blood using the donor's
previous records
B. Discard the unit because processing
procedures cannot be performed
C. Discard the red cells and salvage the
plasma for fractionation
D. Remove sufficient segments to
complete donor processing procedures
C. 36%
16. A satellite bag containing 250 ml_ of fresh
plasma is selected for quality control of
cryoprecipitate production. Cryoprecipitate
is prepared according to standard operating
procedures. The final product has a total
volume of 10 ml_. The factor VIII assays are
1 ILJ/mL before and 9 ILJ/mL after preparation
.
What is the percent yield of factor VIII in
the final cryoprecipitate?
A. 11%
B. 25%
C. 36%
D. 80%
A. Yes
17. A satellite bag containing 250 ml_ of fresh
plasma is selected for quality control of
cryoprecipitate production. Cryoprecipitate
is prepared according to standard operating
procedures. The final product has a total
volume of 10 ml_. The factor VIII assays are
1 ILJ/mL before and 9 ILJ/mL after preparation.
Does this product meet AABB Standards
for cryoprecipitate production?
A. Yes
B. No; the percent recovery is too low.
C. No; the final factor VIII level is too low.
D. Data are insufficient to calculate.
D. 83%
18. A centrifuge used for platelet preparation has
been returned after major repair. A unit of whole
blood (450 mL; platelet count 200,000/ul_) is
selected for calibration of platelet production.
The platelet-rich plasma (PRP) contains 250 mL
with a platelet count of 300,000/uL. The final
platelet concentrate prepared from the PRP
contains 50 mL with a platelet count of
900,000/uL.
What is the percent yield of platelets in the
PRP from this unit?
A. 33%
B. 45%
C. 66%
D. 83%
D. 60%
19. A centrifuge used for platelet preparation has
been returned after major repair. A unit of whole
blood (450 mL; platelet count 200,000/ul_) is
selected for calibration of platelet production.
The platelet-rich plasma (PRP) contains 250 mL
with a platelet count of 300,000/uL. The final
platelet concentrate prepared from the PRP
contains 50 mL with a platelet count of
900,000/uL.
What is the percent yield of platelets in the
final product from the PRP?
A. 30%
B. 45%
C. 50%
D. 60%
B. No; the count on the final product is
too low.
20. A centrifuge used for platelet preparation has
been returned after major repair. A unit of whole
blood (450 mL; platelet count 200,000/ul_) is
selected for calibration of platelet production.
The platelet-rich plasma (PRP) contains 250 mL
with a platelet count of 300,000/uL. The final
platelet concentrate prepared from the PRP
contains 50 mL with a platelet count of
900,000/uL.
Does this product meet AABB Standards
for platelet concentrate production?
A. Yes
B. No; the count on the final product is
too low.
C. No; the percentage recovery in the
PRP is too low.
D. Data are insufficient to calculate.
B. Increase the time and/or rpm for the
second spin
21. A centrifuge used for platelet preparation has
been returned after major repair. A unit of whole
blood (450 mL; platelet count 200,000/ul_) is
selected for calibration of platelet production.
The platelet-rich plasma (PRP) contains 250 mL
with a platelet count of 300,000/uL. The final
platelet concentrate prepared from the PRP
contains 50 mL with a platelet count of
900,000/uL.
The final product was prepared with a
PRP spin time of 2 minutes at 2500 rpm.
To increase the percent platelet yield in the
final product, one would
A. Increase the time and/or rpm for the
first spin
B. Increase the time and/or rpm for the
second spin
C. Decrease the time and/or rpm for the
first spin
D. Decrease the time and/or rpm for the
second spin
B. Red blood cell ability to release O2
decreases.
22. When 2,3-BPG levels drop in stored
blood, which of the following occurs as a
result?
A. Red blood cell K+ increases.
B. Red blood cell ability to release O2
decreases.
C. Plasma hemoglobin is stabilized.
D. ATP synthesis increases.
D. 72
23. The last unit of autologous blood for an
elective surgery patient should be
collected no later than ________
hours before surgery.
A. 24
B. 36
C. 48
D. 72
B. Patients with uncompensated anemia
24. For which of the following patients would
autologous donation not be advisable?
A. Patients with an antibody against a
high-incidence antigen
B. Patients with uncompensated anemia
C. Open heart surgery patients
D. Patients with multiple antibodies
C. HCV
25. It is generally asymptomatic but has a very
high carrier rate (70-80% have chronic
infections). About 10% of the carriers
develop cirrhosis or hepatocellular
carcinoma. These statements are most
typical of which of the following
transfusion-transmitted infections?
A. HAV
B. HBV
C. HCV
D. HEV
B. Increase in plasma K+
26. Biochemical changes occur during the
shelf life of stored blood. Which of the
following is a result of this "storage
lesion"?
A. Increase in pH
B. Increase in plasma K+
C. Increase in plasma Na+
D. Decrease in plasma hemoglobin
C. Notify the donor center that collected
the blood.
27. It has been determined that a patient has
posttransfusion hepatitis and received
blood from eight donors. There is nothing
to indicate that these donors may have
been likely to transmit hepatitis. What
action must be taken initially?
A. Defer all donors indefinitely from
further donations.
B. Repeat all hepatitis testing on a fresh
sample from each donor.
C. Notify the donor center that collected
the blood.
D. Interview all implicated donors.
C. 1-10°C
28. The temperature range for maintaining red
blood cells and whole blood during
shipping is
A. 0-4°C
B. 1-6°C
C. 1-10°C
D. 5-15°C
C. 5.5 X 10^10
29. Platelets play an important role in
maintaining hemostasis. One unit of donor
platelets derived from whole blood should
yield platelets.
A. 5.5 X 10^6
B. 5 X 10^8
C. 5.5 X 10^10
D. 5 X 10^10
C. Increase final plasma volume of
platelet concentrates.
30. The pH of four platelet concentrates is
measured on the day of expiration. The pH
and plasma volumes of the four units are
as follows: pH 6.0, 45 mL; pH 5.5, 38 mL;
pH 5.8, 40 mL; pH 5.7, 41 mL. What
corrective action is needed in product
preparation to meet AABB Standards for
platelet production?
A. No corrective action is necessary.
B. Recalibrate pH meter.
C. Increase final plasma volume of
platelet concentrates.
D. Decrease final plasma volume of
platelet concentrates.
C. Must be labeled with a 24-hour
expiration date
31. During preparation of platelet concentrate,
the hermetic seal of the primary bag is
broken. The red blood cells
A. Must be discarded
B. May be labeled with a 21-day
expiration date if collected in CPD
C. Must be labeled with a 24-hour
expiration date
D. May be glycerolized within 6 days and
stored frozen
D. Reviewed annually by an authorized
individual
32. The blood bank procedures manual must be
A. Revised annually
B. Revised after publication of each new
edition of AABB Standards
C. Reviewed prior to a scheduled
inspection
D. Reviewed annually by an authorized
individual
B. For 12 months
33. Previous records of patients' ABO and Rh
types must be immediately available for
comparison with current test results
A. For 6 months
B. For 12 months
C. For 10 years
D. Indefinitely
D. All the above
34. Which of the following weak D donor
units should be labeled Rh-positive?
A. Weak D due to transmissible genes
B. Weak D as position effect
C. Weak partial D
D. All the above
B. 80%, 5 X 10^6
35. In order to meet the current AABB
Standards for leukocyte reduction to
prevent HLA alloimmunization or CMV
transmission, the donor unit must retain at
least ________ of the original red
cells and leukocytes must be reduced to
less than ________ .
A. 85%, 5 X 10^8
B. 80%, 5 X 10^6
C. 75%, 5 X 10^5
D. 70%, 5 X 10^4
D. HBsAb
36. Which of the following tests is/are not
performed during donor processing?
A. ABO and Rh grouping
B. HBsAg
C. HIV-l-Ag
D. HBsAb
C. 45,000-75,000/uL
37. A 70-kg man has a platelet count of
15,000/uL, and there are no complicating
factors such as fever or HLA sensitization.
If he is given a platelet pool of 6 units,
what would you expect his posttransfusion
count to be?
A. 21,000-27,000/uL
B. 25,000-35,000/uL
C. 45,000-75,000/uL
D. 75,000-125,000/uL
A. Confirmation of ABO group and Rh
type of blood labeled D-negative
38. Which of the following tests on donor
red blood cells must be repeated by the
transfusing facility when the blood was
collected and processed by a different
facility?
A. Confirmation of ABO group and Rh
type of blood labeled D-negative
B. Confirmation of ABO group and Rh
type
C. Weak D on D-negatives
D. Antibody screening
A. 1-6°C
39. Red blood cells (RBCs), liquid
A. 1-6°C
B. 20-24°C
C. -18°C or colder
D. -65°C or colder
D. -65°C or colder
40. Red blood cells, frozen
A. 1-6°C
B. 20-24°C
C. -18°C or colder
D. -65°C or colder
C. -18°C or colder
41. Fresh-frozen plasma
A. 1-6°C
B. 20-24°C
C. -18°C or colder
D. -65°C or colder
C. -18°C or colder
42. Cryoprecipitate
A. 1-6°C
B. 20-24°C
C. -18°C or colder
D. -65°C or colder
B. 20-24°C
43. Platelet concentrate
A. 1-6°C
B. 20-24°C
C. -18°C or colder
D. -65°C or colder
C. 35 days
44. Red blood cells in CPDA-1
A. 24 hours
B. 5 days
C. 35 days
D. 1 year
D. 1 year
45. Fresh-frozen plasma
A. 24 hours
B. 5 days
C. 35 days
D. 1 year
D. 1 year
46. Cryoprecipitate
A. 24 hours
B. 5 days
C. 35 days
D. 1 year
A. 24 hours
47. Fresh-frozen plasma, thawed
A. 24 hours
B. 5 days
C. 35 days
D. 1 year
B. 5 days
48. Platelet concentrate in PL-732 (with
agitation)
A. 24 hours
B. 5 days
C. 35 days
D. 1 year
A. 21 days
49. CPD (citrate phosphate dextrose)
A. 21 days
B. 35 days
C. 42 days
D. Not an approved anticoagulant
B. 35 days
50. CPDA-1 (citrate phosphate dextrose
adenine)
A. 21 days
B. 35 days
C. 42 days
D. Not an approved anticoagulant
C. 42 days
51. AS-l(Adsol®)
A. 21 days
B. 35 days
C. 42 days
D. Not an approved anticoagulant
D. Not an approved anticoagulant
52. EDTA
A. 21 days
B. 35 days
C. 42 days
D. Not an approved anticoagulant
D. Accept
53. A 65-year-old man whose birthday is
tomorrow
A. Defer temporarily
B. Defer for 12 months
C. Defer indefinitely
D. Accept
A. Defer temporarily
54. A 45-year-old woman who donated a unit
during a holiday appeal 54 days ago
A. Defer temporarily
B. Defer for 12 months
C. Defer indefinitely
D. Accept
C. Defer indefinitely
55. A 50-year-old man who had sex with
another man in 1980
A. Defer temporarily
B. Defer for 12 months
C. Defer indefinitely
D. Accept
D. Accept
56. A 25-year-old man who says he had
yellow jaundice right after he was born
A. Defer temporarily
B. Defer for 12 months
C. Defer indefinitely
D. Accept
D. Accept
57. An 18-year-old with poison ivy on his
hands and face
A. Defer temporarily
B. Defer for 12 months
C. Defer indefinitely
D. Accept
D. Accept
58. A woman who had a baby 2 months ago
A. Defer temporarily
B. Defer for 12 months
C. Defer indefinitely
D. Accept
D. Accept
59. A 35-year-old runner (pulse 46 bpm)
A. Defer temporarily
B. Defer for 12 months
C. Defer indefinitely
D. Accept
D. Transfusion not indicated
60. Patients with warm autoimmune
hemolytic anemia (AIHA) due to
a-methyldopa (Aldomet®) with
hemoglobins of 8.5 g/dL or above
A. Platelet concentrate
B. RBC
C. Leukocyte-reduced RBC
D. Transfusion not indicated
C. Leukocyte-reduced RBC
61 Patients requiring transfusion with RBC
that will not transmit cytomegalovirus
(CMV)
A. Platelet concentrate
B. RBC
C. Leukocyte-reduced RBC
D. Transfusion not indicated
B. RBC
62. Patients with normovolemic anemia
A. Platelet concentrate
B. RBC
C. Leukocyte-reduced RBC
D. Transfusion not indicated
A. Platelet concentrate
63. Patients who are thrombocytopenic
secondary to the treatment of acute
leukemia
A. Platelet concentrate
B. RBC
C. Leukocyte-reduced RBC
D. Transfusion not indicated
D. IgG and lgM
64. Most blood group antibodies are of what
immunoglobulin classes?
A. IgA and IgD
B. IgA and lgM
C. IgE and lgD
D. IgG and lgM
B. Father has one k gene and one K° gene
65.
Mother
K + k +
Father
K - k +
Child 1
K + k -
Child 2
K - k +
All other indications are that these
children are both the products of this
mating. Possible explanations for these
results would include
A. A dominant inhibitor gene has been
passed to child 1
B. Father has one k gene and one K° gene
C. Father has the McLeod phenotype
D. Mother has a cis-Kk gene
D. Group A1
66. Which of the following blood groups
reacts least strongly with an anti-H
produced in an A1B individual?
A. Group O
B. Group A2B
C. Group A2
D. Group A1
B. Two
67. How many genes encode the following Rh
antigens: D, C, E, c, e?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
C. Inheritance of hh genes
68. The test results could be due to:
A. Cold autoantibody
B. Inheritance of sese genes
C. Inheritance of hh genes
D. Rouleaux
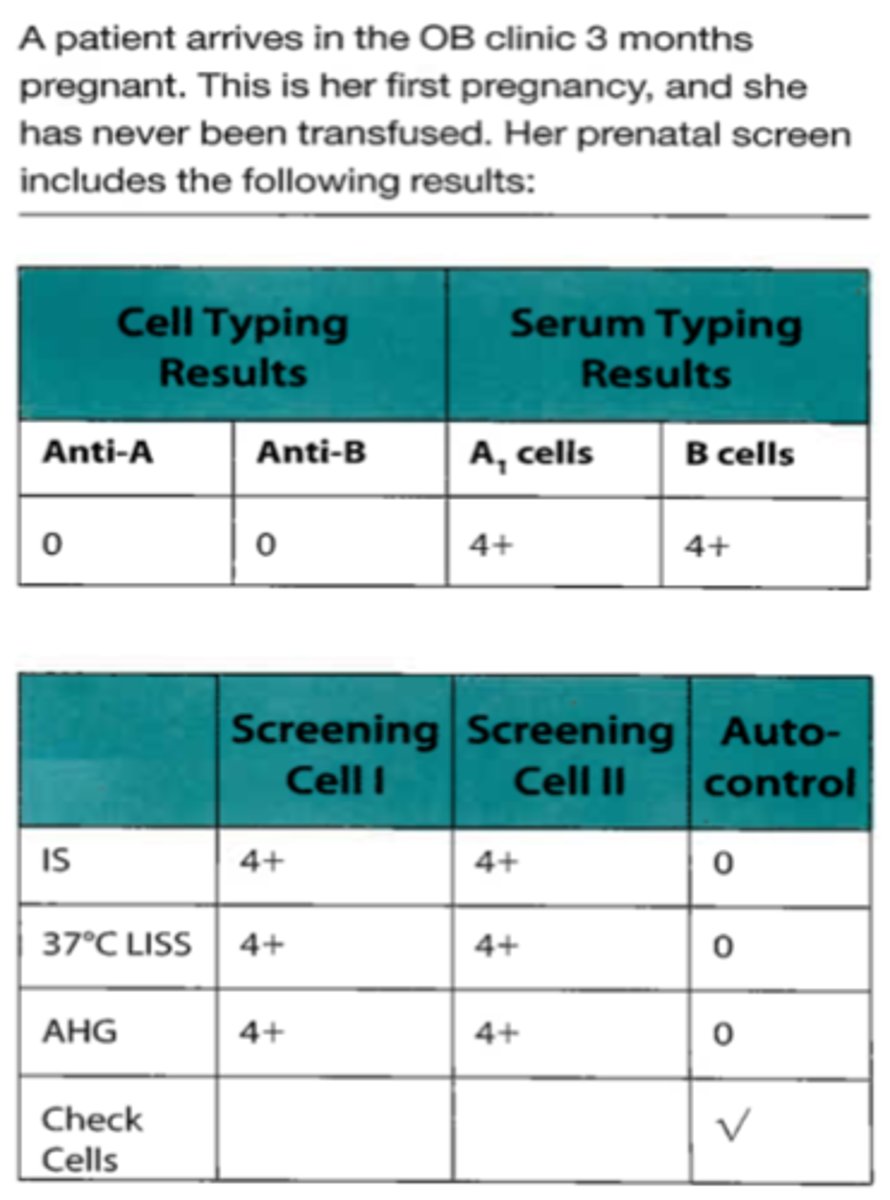
B. Oh phenotype
69. If the patient's RBCs were tested against anti-H lectin and did not react, this person would be identified as a(an):
A. Acquired B
B. Oh phenotype
C. Secretor
D. Subgroup of A
C. Lea substance
70. If a person has the genetic makeup Hh,
AO, LeLe, sese, what substance will be
found in the secretions?
A. A substance
B. H substance
C. Lea substance
D. Leb substance
D. The patient's red cells give a negative
result, with a monoclonal anti-B
reagent lacking the ES-4 clone.
71. The following results were obtained when
typing a patient's blood sample.
Cell Typing
Results
Anti-A
4+
Anti-B
2 +
Serum Typing
Results
A, cells
0
B cells
4+
The tech suspects that this is a case of an
acquired B antigen. Which of the
following would support this suspicion?
A. A positive autocontrol test
B. Secretor studies show that the patient
is a nonsecretor.
C. A patient diagnosis of leukemia
D. The patient's red cells give a negative
result, with a monoclonal anti-B
reagent lacking the ES-4 clone.
B. A plant substance that chemically
reacts with certain RBC antigens
72. Lectins are useful in determining the
cause of abnormal reactions in blood bank
serology. These lectins are frequently
labeled as anti-H, anti-Ap etc. The nature
of these lectins is explained by which of
the following?
A. An early form of monoclonal antibody
produced in nonvertebrates
B. A plant substance that chemically
reacts with certain RBC antigens
C. Naturally occurring antibodies in
certain plants
D. The ability of plants to respond to
RBC antigens by antibody production
D. L-Fucose
73. Which of the following sugars must be
present on a precursor substance for A
and B antigenic activity to be expressed?
A. D-Galactose
B. N-Acetylgalactosamine
C. Glucose
D. L-Fucose
B. Complement
74. An antigen-antibody reaction alone
does not cause hemolysis. Which of the
following is required for red blood cell
lysis?
A. Albumin
B. Complement
C. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
(G6PD)
D. Antihuman globulin (AHG)
B. DCe/dce
75. A white female's red blood cells gave the
following reactions upon phenotyping:
D+ C+ E- c+ e+. Which of the
following is the most probable Rh
genotype?
A. DCe/Dce
B. DCe/dce
C. DCe/DcE
D. Dce/dCe
C. DCe/dcE
76. A black patient has the following Rh
phenotype: D+ C+ E+ c+ e+. Which of
the following genotypes is the least
probable?
A. DCE/dce
B. DCe/DcE
C. DCe/dcE
D. DcE/dCe
A. The antibody is anti-G.
77. An individual of the dee/dee genotype
given dCe/dce blood has an antibody
response that appears to be anti-C plus
anti-D. What is the most likely explanation
for this?
A. The antibody is anti-G.
B. The antibody is anti-partial D.
C. The antibody is anti-Cw.
D. The reactions were read incorrectly.
B. Anti-c
78. If a patient has the Rh genotype DCe/DCe
and receives a unit of red blood cells from
a DCe/dce individual, what Rh antibody
might the patient develop?
A. Anti-C
B. Anti-c
C. Anti-d
D. Anti-E
C. 50%
79. What percentage of this couple's offspring can be expected to be D-negative?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
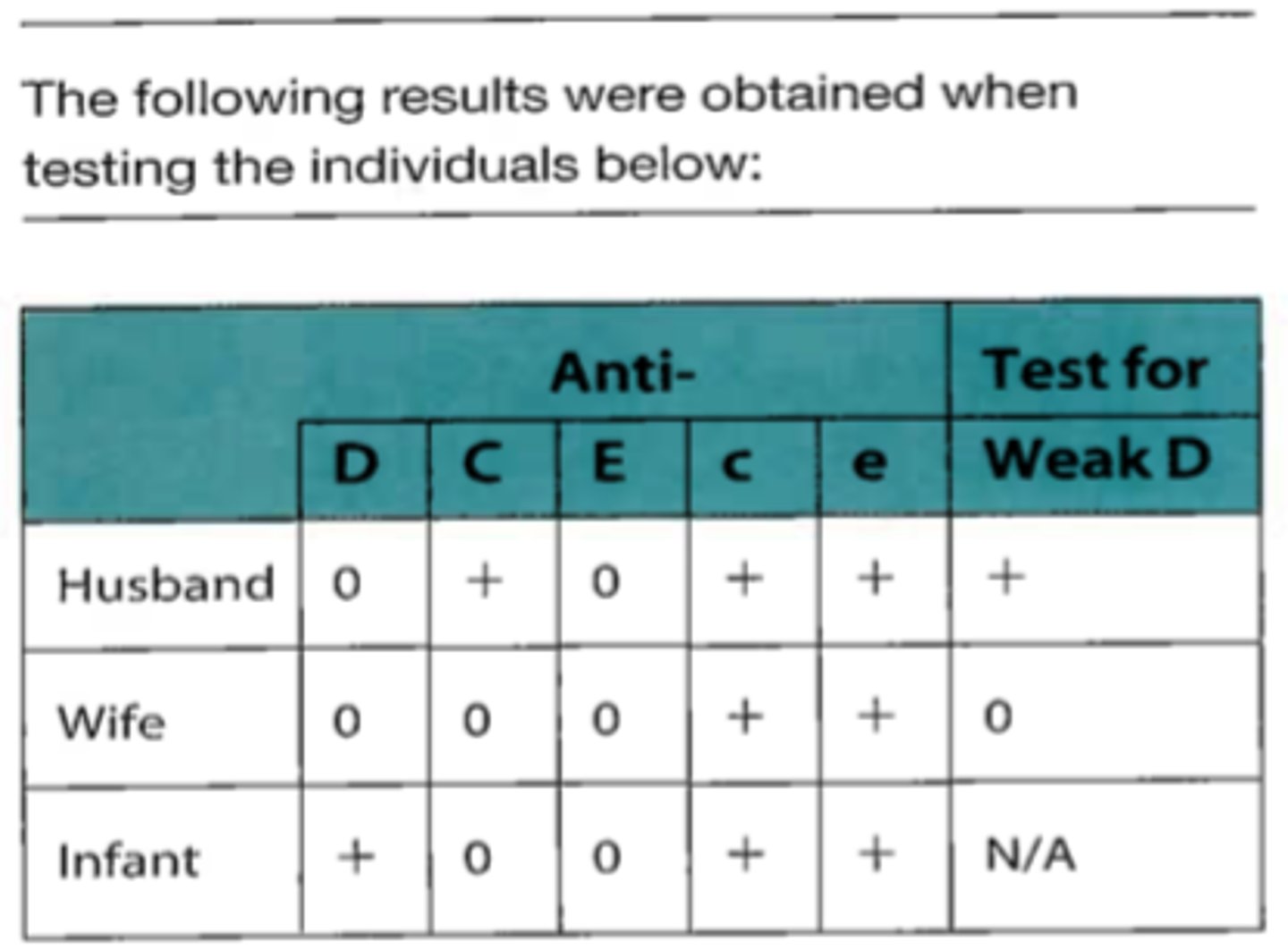
C. The husband cannot be excluded from being the infant's father.
80. Which of the following conclusions regarding the family typing is most likely?
A. The husband is not the infant's father.
B. The husband is proved to be the infant's father.
C. The husband cannot be excluded from being the infant's father.
D. The D typing on the infant is a false positive.
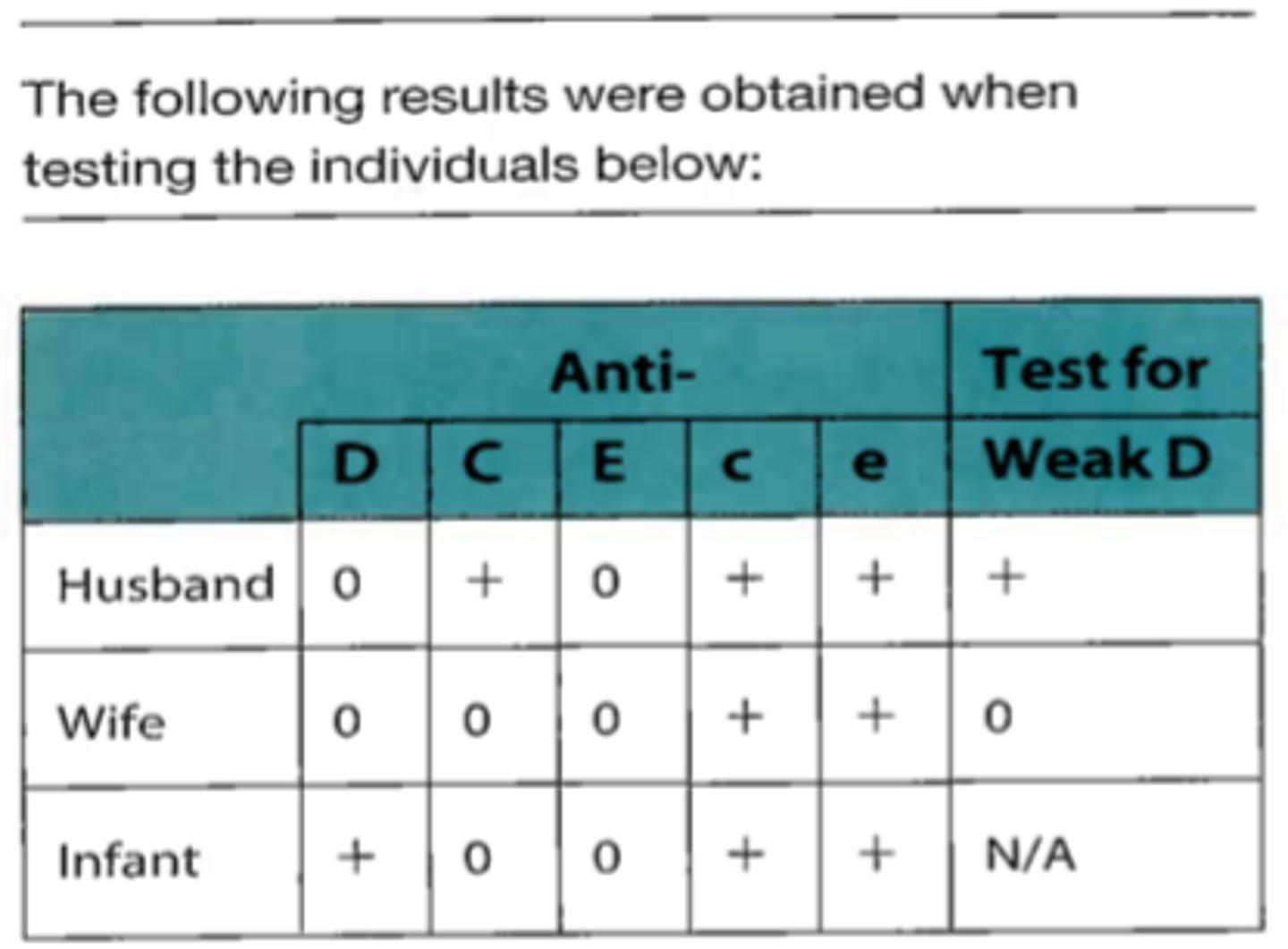
C. Wife
81. Which, if any, of these three individuals can make anti-D?
A. Husband
B. Husband and wife
C. Wife
D. None
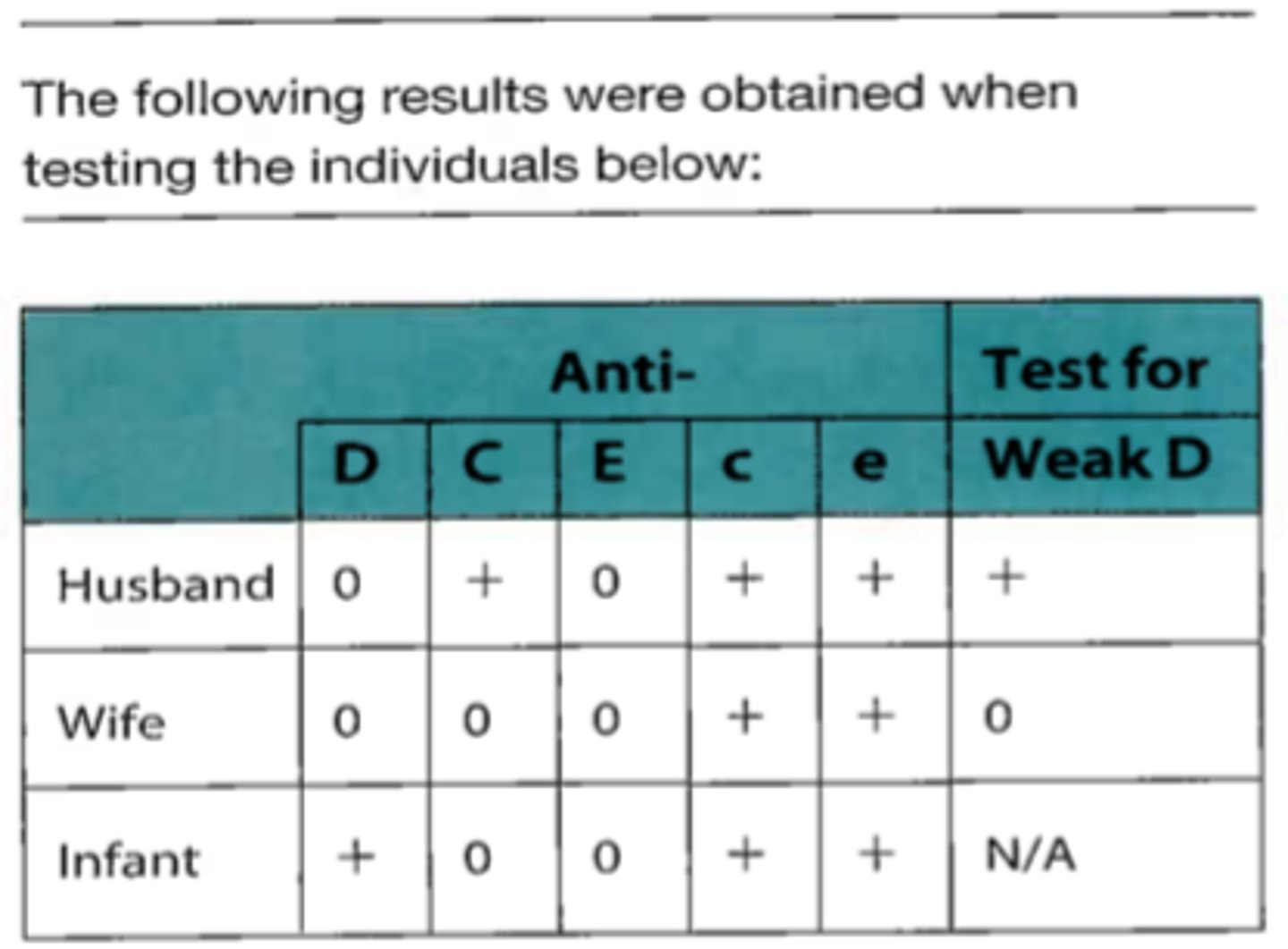
A. Partial D
82. If a D-positive person makes an anti-D,
this person is probably
A. Partial D
B. D-negative
C. Weak D as position effect
D. Weak D due to transmissible genes
A. People who lack the k antigen are rare
83. A serum containing anti-k is not frequently
encountered. This is because
A. People who lack the k antigen are rare
B. People who possess the k antigen are
rare
C. The k antigen is not a good immunogen
D. Kellnull people are rare
C. Anti-Jka
84. A victim of an auto accident arrives in the
emergency department (ED) as a transfer
from a hospital in a rural area. The patient
has been in that facility for several weeks
and has received several units of red blood
cells during that time. The ED resident
orders 2 units of RBCs for transfusion.
The sample sent to the blood bank is
centrifuged and the cell-serum interface
is not discernable. A subsequent sample
produces the same appearance. You would
suspect that the patient has
A. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
B. Anti-Fya
C. Anti-Jka
D. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
A. The Xga antigen has a higher
frequency in women than in men.
85. Which of the following is a characteristic
of the Xga blood group system?
A. The Xga antigen has a higher
frequency in women than in men.
B. The Xga antigen has a higher
frequency in men than in women.
C. The Xga antigen is enhanced by
enzymes.
D. Anti-Xga is usually a saline-reacting
antibody.
D. Testing a cell that is negative for the
antigen and one that is heterozygous
for the antigen
86. Testing needs to be done with an antiserum
that is rarely used. The appropriate
steps to take in using this antiserum
include following the manufacturer's
procedure and
A. Performing a cell panel to be sure that
the antiserum is performing correctly
B. Performing the testing on screen cells
C. Testing in duplicate to ensure the
repeatability of the results
D. Testing a cell that is negative for the
antigen and one that is heterozygous
for the antigen
D. Often implicated in delayed hemolytic
transfusion reactions
87. Which of the following is a characteristic
of Kidd system antibodies?
A. Usually IgM antibodies
B. Corresponding antigens are destroyed
by enzymes.
C. Usually strong and stable during
storage
D. Often implicated in delayed hemolytic
transfusion reactions
B. React well with enzyme-treated panel
cells
88. Which of the following statements is not
true of anti-Fya and anti-Fyb?
A. Are clinically significant
B. React well with enzyme-treated panel
cells
C. Cause hemolytic transfusion reactions
D. Cause a generally mild hemolytic
disease of the newborn
B. Anti-Cha and anti-Rga
89. Which of the following antibodies can be
neutralized with pooled human plasma?
A. Anti-Hy and anti-Ge: 1
B. Anti-Cha and anti-Rga
C. Anti-Coa and anti-Cob
D. Anti-Doa and anti-Jsb
D. Only occurs in Fy(a-b-) individuals
90. Which of the following statements is not
true about anti-U?
A. Is clinically significant
B. Is only found in black individuals
C. Only occurs in S-s- individuals
D. Only occurs in Fy(a-b-) individuals
B. Type the donor units for the E antigen
and crossmatch the E-negative units.
91. A patient had an anti-E identified in his
serum 5 years ago. His antibody screening
test is now negative. To obtain suitable
blood for transfusion, what is the best
procedure to use?
A. Type the patient for the E antigen as an
added part to the crossmatch procedure.
B. Type the donor units for the E antigen
and crossmatch the E-negative units.
C. Crossmatch donors with the patient's
serum and release the compatible units
for transfusion.
D. Perform the crossmatch with enzymetreated
donor cells, because enzymetreated
red cells react better with Rh
antibodies.
B. Fy(a+b+)
92. A patient's red blood cells are being typed
for the Fya antigen. Which of the following
is the proper cell type of choice for a
positive control of the anti-Fya reagent?
A. Fy(a+b-)
B. Fy(a+b+)
C. Fy(a-b+)
D. Fy(a-b-)
B. Anti-K
93. Which of the following antibodies has been
clearly implicated in transfusion reactions
and hemolytic disease of the newborn?
A. Anti-I
B. Anti-K
C. Anti-Lea
D. Anti-N
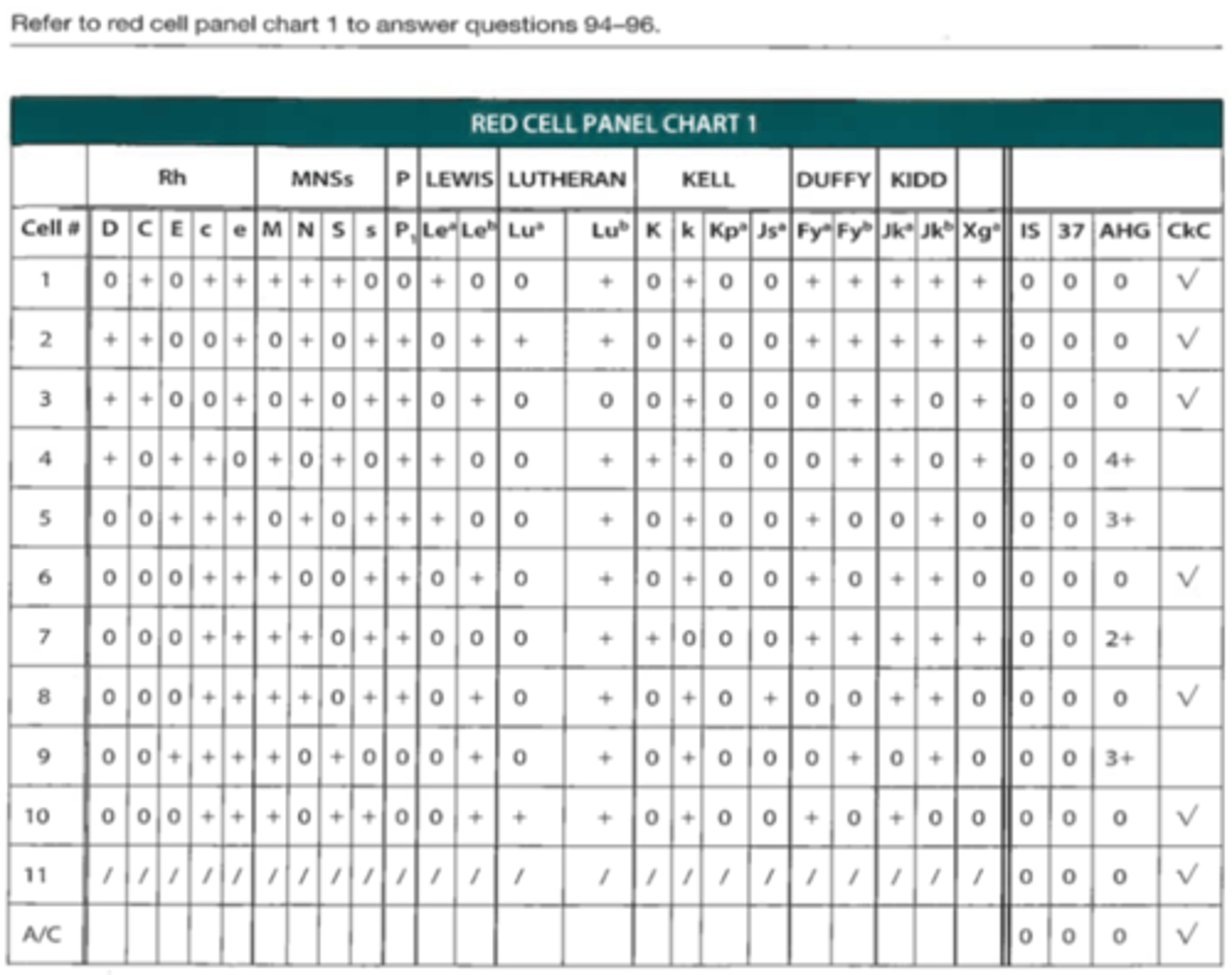
A. Anti-E, -K, -Kpa, -Jsa, -Jkb
94. Which of the following antibodies would require additional testing in order to be ruled out?
A. Anti-E, -K, -Kpa, -Jsa, -Jkb
B. Anti-E, -S, -Leb, -K, -Kpa, -Fya
C. Anti-E, -S, -Lea, -K, -Kpa, -Jsa, -Fya, -Jka
D. Anti-E, -Lea, -K, -Kpa, -Jsa, -Fyb, -Jka, -Jkb
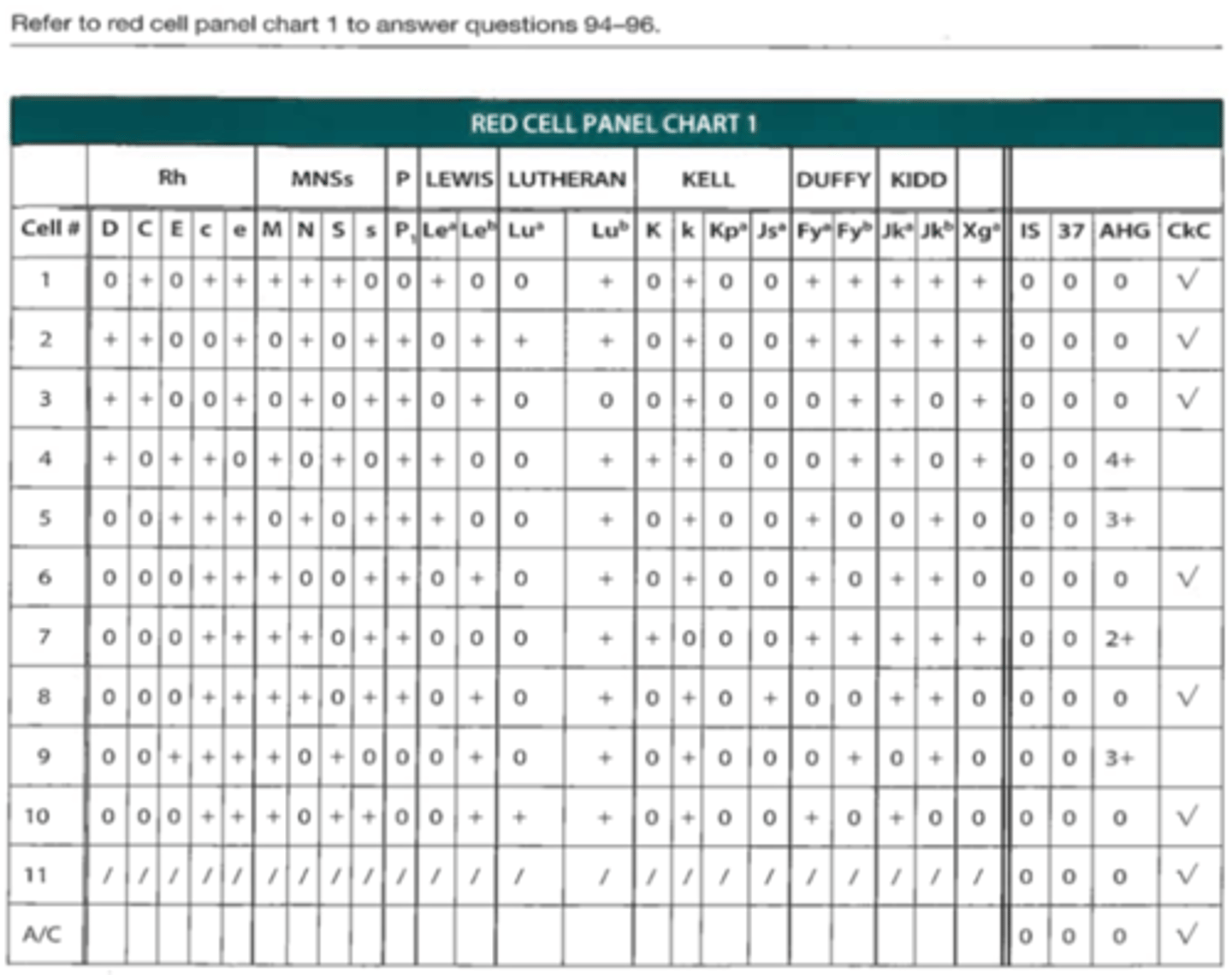
B. Anti-E and anti-K
95. The most likely antibody(ies) in the patient's serum is (are)
A. Anti-S and anti-E
B. Anti-E and anti-K
C. Anti-Fyb showing dosage
D. Anti-K, anti-Jsa, and anti-Lea
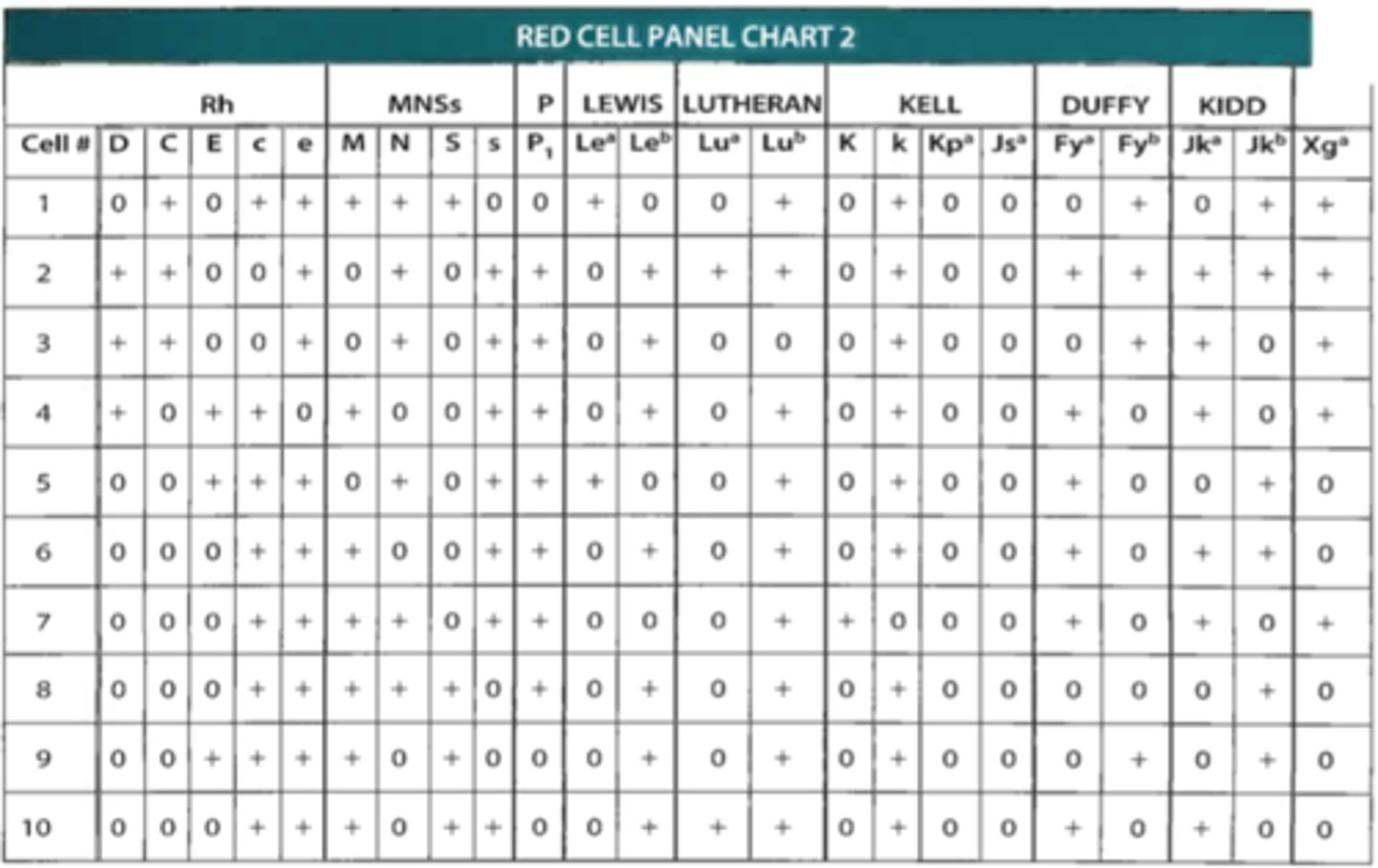
C. 1, 4, 7
96. From the cells in red cell panel chart 2, choose a selected cell panel to help identify the antibody(ies) in the patient described in question 95.
A. 1, 2, 5, 9, 10
B. 2, 6, 7, 10
C. 1, 4, 7
D. 2, 3, 4, 6, 9
C. Anti-Lea
97. Often when trying to identify a mixture of
antibodies, it is useful to neutralize one of
the known antibodies. Which one of the
following antibodies is neutralizable?
A. Anti-D
B. Anti-Jka
C. Anti-Lea
D. Anti-M
C. Anti-N
98. Which of the following antibodies does
not match the others in terms of optimal
reactive temperature?
A. Anti-Fya
B. Anti-Jkb
C. Anti-N
D. Anti-U
D. Enzyme panel
99. A recently transfused patient's serum has
a positive antibody screen. The panel
performed at IS, in LISS at 37°C, and at
AHG shows a strong anti-Fya and a weak
possible anti-C. To confirm the anti-C, you
would perform an
A. Elution
B. Absorption
C. Antigen typing
D. Enzyme panel
B. Gel test
100. The antiglobulin test does not require
washing or the addition of IgG-coated
cells in which of the following antibody
detection methods?
A. Solid-phase red cell adherence assays
B. Gel test
C. Affinity column technology
D. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) technique