Bio 120 -Molecular Biology
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
What are genetic materials DNA features in relation to its structure DNA replication
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Characteristics of genetic materials
Replicates
Stores information (cells/body organisms)
Information Expression
Variation by mutation
What are the two constituents of the nucleus?
Proteins
Nucleic Acid
What two experiments confirmed that genetic material was DNA?
Prokaryotic bacterium transformation
The Hershey-Chase
Explain the Prokaryotic bacterium transformation experiment
A Streptococcus pneumoniae was injected into mice ( deadly)
Smooth Strain: had polysaccharides coat to protects himself from the host’s immune system
Rough Strain:no coating
the mice dies from S and survived from R
Heat killed S bacteria from temperature
Injected both types of cells into mouse with heat so they both die but mice survived
Explain The Hershey-Chase Experiments
Bacteriophage Infection
Used a T2 virus that infects bacteria. It has a outer protein coat that contained DNA
It infected the bacteria by injection from the legs
What are nucleic acids?
Polymers including DNA and RNA
Structure of nucleotide
nitrogenous base
pentose (a five carbon sugar)
phosphate group
What are the two types of nitrogen bases?
Purines
Pyrimidines
Purines consists of…
adenine
guanine
Pyrimidines consist of…
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracli (RNA)
Difference between nucleoside and nucleotide
Example:A
…side:adenosine
…tide:adenylic acid
How is the DNA sequence read/ polimerized?
From the 5’ end to the 3’end
What is the component of the 3’-end?
It contains a hydroxide
What is said about the amount of nitrogenous bases in the DNA?
Amount of A=T
Amount of C=G
What did the x-ray crystallography demonstrate?
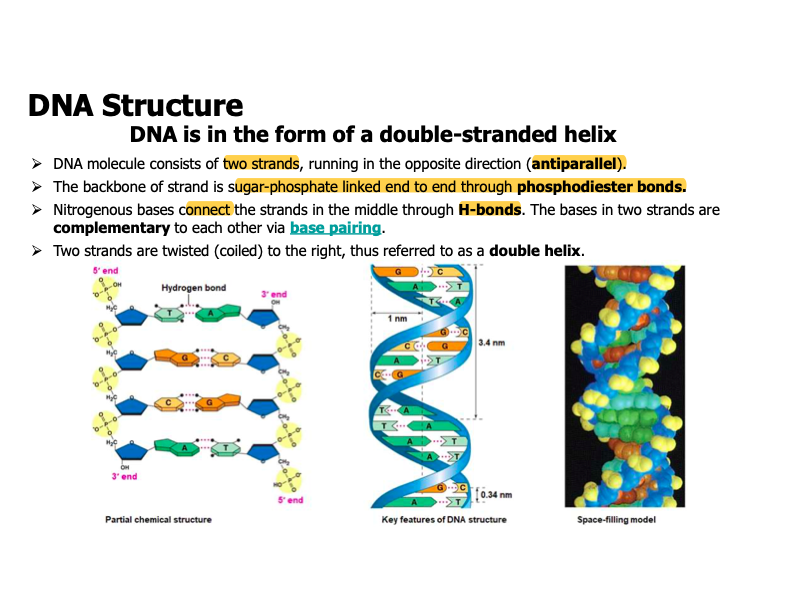
The DNA molecule is a helix
Nitogeous bases connect to stands in the middle though hydrogen bonds
_________________ connect to strands in the middle through hydrogen bonds.
Answer: Nitrogenous bases
What is the backbone of the DNA strand?
Sugar-phosphate linked end to end through through phosphodiester bonds
Describe the structure of RNA
Single strand polynucleotide
Uracil replaces thymine
Uses ribose ( two hydroxyl groups) instead of deoxyribose
What are the three types of RNA?
Messenger RNA
Transfer RNA
Ribosome RNA
What is a messenger RNA?
mRNA
Turns on protein synthesis information by carrying the transcription of genes to the ribosome
What is transfer RNA?
tRNA
Reads information/interprets from nucleic acid into protein language that recognizes specific codons for amino acid production
What is ribosome RNA?
rRNA
Most abundant type of RNA
Forms the structure of ribosomes with other proteins