Ch. 14: The Costs of Production
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Profit
Total Revenue - Total Cost
Explicit cost
money paid in exchange for the item
Implicit cost
value of the owners time and resources used in production, opportunity cost
Accounting profit
TR - Explicit cost
Economic profit
TR - (explicit + implicit cost)
account for cost of capital
ATC =
total cost / quantity of output
fixed+var / quantity
AFC =
fixed cost / quantity of output
AVC =
variable cost / quantity of output
Diminishing marginal product explains why, as output increases, the production function gets ___ and the total-cost curve gets ____
flatter, steeper
Marginal cost
the amount that total cost rises when the firm increases production by 1 unit of output
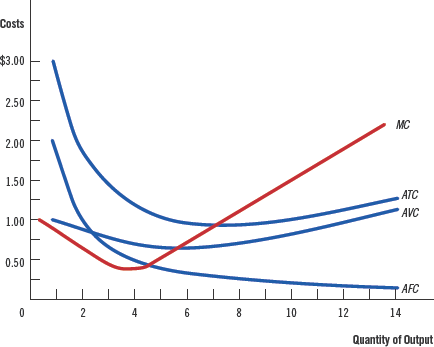
Cost curves for a typical firm
Marginal cost eventually rises with the quantity of output.
The average-total-cost curve is U-shaped.
The marginal-cost curve crosses the average-total-cost curve at the minimum of average total cost.
ATC in short and long run
In the long run, the firm is more flexible
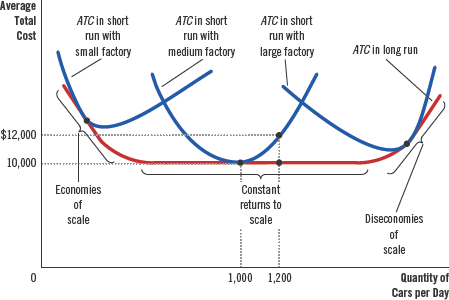
Economies of scale
As output increases, long run ATC declines
Diseconomies of scale
As output increases, long run ATC increases
Constant returns to scale
when long-run ATC does not vary with the level of output
In the short run,
capital is fixed and labor is variable
Marginal cost =
Δ in total cost / Δ in quantity
What does ATC tell us?
the cost of a typical unit of output if total cost is divided evenly over all the units produced
What does marginal cost tell us?
the increase in total cost that arises from producing an additional unit of output
What is the quantity at the bottom of the U-shape of the ATC?
efficient scale
When MC is less than ATC, average cost is ___
falling
When MC is greater than ATC, average cost is ___
rising