Biotechnology
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Define Biotechnlogy
Biotechnology is the use of biological systems, processes and organisms in the creation of new products and technologies.
what are historical examples of biotechnology
selective breeding in agriculture
fermentation
traditional medicine
what are present application of biotechnology
polymerase Chain reactions
DNA sequencing
Cloning
transgenic organism
what are the benefits of medical biotechnology
Pharmaceuticals: Vaccines, Antibiotics, Stem cell treatments, bioinspired materials
Diagnostics: Biosensors
what are the benefits of environmental biotechnology
Agriculture —> transgenesis have been used to produce genetically modified crops, improving the plants’ ability to survive and often increasing their nutritional value.
what are the benefits of industrial biotechnology
biodegradable plastic, energy sources
what are the positive social and ethical uses of biotechnology
The fundamental aim of biotechnology is to improve peoples quality of life by meeting the growing needs of society.
- Genetic diversity: new arrangements of genes, increasing the diversity of traits, can have a positive impact upon the course of evolution —> as humans continue to recombine traits in order to best survive and thrive in our enviroments
Sustainable development goals —> e,g ending poverty and hunger, improving health and wellbeing, providing access to clean water and sanitation.
what are the concerns regarding social and ethical issues of biotechnology
- Regulations: regulating biotechnology to a global scale. This is because biotechnologies an their use will not only affect citizens but the world as a whole
Effect on biodiversity
Creation of monocultures: it is important that we do not rely so heavily on these favourable genes so as to wipe competitive alleles from species gene pools. We should continue to promote diverse agricultural practices (both of GMOs and “natural” crops), as variation is essential to species survival.
Horizontal gene transfer: refers to the acquisition of genetic information by transfer from a member of a different species. As traits escape into ecosystems, they may pose competition to other naturally occurring alleles. This may also lead to a reduction in biodiversity and loss of variation.
what are the three reproductive technologies
Artificial insemination
Artificial pollination
IVF
what is artificial insemination
Injection of semen through the cervix into the uterus without sexual intercourse for the purpose of achieving fertilisation

what are the advantages of artificial insemination
Humans can select desirable traits and forcibly combine them to hopefully produce offspring with desired characteristics.
May be used to synchronise both in the livestock industry, or avoid injuries during mating.
Allows for favourable genetic material to be sent around the world (common for race-horse breeding).
Conservation of a species – if a male is deceased
Many females can be inseminated by one male.
what the the disadvantages of artificial insemination
By selecting for the few traits, we perceive as desirable, we may limit genetic variation within a species. —> the main thing that leads to variation is the randomness of alleles and combination of genetics
An increase in homogenous populations may cause issues for species survival in the long term.
Can produce unwanted effects (undesirable traits passed on)
what is the definition of artificial pollination
When pollen (male plant gametes) is purposefully taken from one plant and placed on the stigma of another flower.

where is artificial pollination used
is agriculture, to influence the traits passed to subsequent generations of plants
what are the advantages of artificial pollination
In modern agriculture, it is used to ensure that all plants within a crop are pollinated and can produce fruit.
This increases crop yield and profitability
Used to create new species of plants with desirable characteristics.
what are the disadvantages of artificial pollination
It may create monocultures in which there is very little genetic variation. this may create species which are vulnerable to sudden environmental changes.
For example the Irish potatoes famine
Creation of monocultures also mean that natural varieties of plants are lost due to competition and biodiversity is reduced.
what is IVF
In Vitro Fertilisation: when an egg is fertilised by sperm outside the body, usually in a test tube (in vitro meaning in glass)
what is hybridisation
The crossbreeding of two genetically non-identical individuals
what is intraspecific hydridisation
hybridisation within species —> crossing parents of the same species (two dogs - cockapoo, goldendoodle)
what is interspecific
hybridisation between species —> crossing parents of different species - mule (half horse, half donkey) - results in infertile offspring
why is hybridisation used?
Selective breeding of parents with desirable traits to make their offspring better suited to the environment or to meet a use
Successful hybridisation results in hybrid vigour (as opposed to inbreeding)
what was the hybridisation of wheat
▪ Problem: The strain of English wheat was not suited to the Australian climate
▪ Solution:
▪ Indian wheat – drought tolerant and disease resistant
▪ Canadian Fife wheat – matured late and had good baking and milling properties
▪ By selecting offspring with desirable traits, the first commercially viable wheat strain was produced (Bob’s strain)
▪ By 1914, 22 of the 29 wheat varieties were Farrer’s
▪ Farrer contributed to our understanding that factors such as disease resistance, grain quality and maturing time in wheat can be inherited

what is artificial selection
(the process by which humans choose which organisms to breed based on desired traits) —> alters populations
what is the artificial selection example of dairy cattle
Example: Bred for high milk yield. Dramatic increase in milk production per cow. Reduced lifespan and fertility. Increased susceptibility to disease due to narrowed gene pool and metabolic stress. |
what is the artificial selection example of domestic dogs
Example: Breeding for traits like small size in Chihuahuas or herding instincts in Border Collies. Increases frequency of desired traits (e.g. size, temperament, coat). Decreases genetic diversity within breeds. Increases risk of genetic disorders (e.g. hip dysplasia in German Shepherds, breathing issues in pugs) due to inbreeding. |
what is heterosis
Heterosis or hybrid vigor, on the other hand, is the tendency of outbred strains to exceed both inbred parents in fitness.
what is somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)
is a cloning technique where the nucleus from a body cell (somatic cell) is transferred into an egg cell (oocyte) that has had its own nucleus removed.
This reconstructed cell, now containing the somatic cell's DNA, can then be stimulated to develop into an embryo.
The resulting embryo can be used for reproductive cloning (creating a genetically identical copy of the donor) or for therapeutic cloning (generating stem cells for potential treatments).
what is a clone
an organism or cell, or group of organisms or cells, produced asexually from one ancestor or stock, to which they are genetically identical.
what are the three different types of cloning techniques
whole organism cloning
therapeutic cloning
gene cloning
what is whole organism cloning
also known as reproduction cloning, is the creation of a new molecular organism that is genetically identical to its parental organism. This occurs through somatic cell nuclear transfer.
what is the process for whole organism animal cloning
1. An adult cell (somatic cell) is removed from the organism you want to clone. This contains their genetic material
2. An unfertilised egg is removed from a donor organism. The DNA is removed from this egg – it is denucleated. (an empty vessel)
3. The denucleated egg and the stem cell are fused
4. The resulting cell is cultured so that it begins to divide and become an embryo
5. The embryo is implanted into a surrogate organism
6. The surrogate gives birth to an organism which is genetically identical to the donor.
why is a clone not strictly identical to the parent organism
as if mutations acquired in that cell will be passed down and mitochondria present in the cytoplasm of the donor egg contains DNA which is passed on to the cloned organism
what are different wats the clone whole plants
vegatative propagation —> done by taking a cutting of a plant
plant tissue culture —> taking little tiny pieces and plant them to grow many little clones
what is artificial twining / embryo twinning
Type of cloning that can divide an embryo and make many things grow – the early blastocyst is separated and then they become their own whole organism
Place that growing of cells into different surrogate cells – gives birth genetically identical animals
what does reproductive cloning mean
This term is used when the goal is to create a new, genetically identical organism from a single existing organism.
A genetically identical offspring is created from the somatic cells of another mature offspring
Technically this is asexual reproduction
why shouldnt somatic cell nuclear transfer be used in an agricultural setting
1. Low success rates: Many embryos fail to develop or result in unhealthy animals.
2. High costs: SCNT is expensive and requires advanced lab equipment and skilled technicians.
3. Ethical concerns: The process involves high embryo and animal loss, which raises welfare issues.
4. Limited genetic diversity: Cloning produces genetically identical animals, which can reduce resilience to disease and environmental changes.
5. Alternative methods exist: Traditional breeding and artificial insemination are more efficient, cost-effective, and accepted for improving livestock traits.
what are three applications of whole organism cloning
scientific research
agriculture
wildlife conservation
what does whole organism cloning do for scientific research?
- animal testing plays a key role in the development of drugs and medical devices
- Cloned animals produce reliable responses to drugs used in research
- Theoretically have the same reactions to the same drugs
- Shows the long and short consequences they would have on humans

what does whole organism cloning do in agricultre?
→ cloning allows desirable traits to be passed onto offspring
- Faster and more reliable than natural breeding
E.g tissue cultures enab;e the production of lots of genetically identical plants quickly

what does the application of whole organism cloning do to wildlife conservation?
→ cloning can be used to prevent to extinction of critically endangered species - e,g white rhinoceros
Cloning may be used to bring back species from extinction - e.g use of wolly mammoth DNA

what is therapeutic cloning?
Cloning techniques developed in order to produce therapies for diseases. This involves the production of stem cells genetically identical to the donor which may be used to treat diseases such as diabetes and parkisons
does therapeutic cloning involve somatic cell nuclear transfer? and what is the process
yes.
▪ Therapeutic cloning involves somatic cell nuclear transfer, but instead of creating a baby, the early embryonic cells are cultured in special chemicals so that they form the type of cells required e.g. insulin producing cells for diabetics.
- A nucleaus containing genetic material is removed from a cell of the patient. This is inserted into a denucleated egg cell.
- This new cell then begins to divide.
- After a few days, the cell has divided into an embryo, and embryonic stem cells can be removed.
- These stem cells cultured in a specific way so that they remain in their undifferentiated state. – this is the creation of embryonic stem cell lines,
- These cells will be genetically identical to the cells of the patient whose DNA was used.
what is good about therapeutic cloning?
Good patient outcomes therapeutic cloning involves pluripotent stem cells that can grow and differtiate into any type of cell in the body, meaning that we can treat many kinds of diseases by replacing dysfunctional cells
There is no risk of immunological rejection the cloned cells are genetically identical to the patient, therefore they can be used without inducing an attack on transplanted cells
what is bad about therapeutic cloning?
Requires many attempts to create viable eggs. often, hundreds of attempts are required because the eggs fused with the somatic nuclei are not stable and often do not propagate
Ethical debates surrounding the use of egg cells and embryonic stem cells (even if artificially created)
what is gene cloning?
also known as molecular cloning, is the process of producing multiple copies of a specific DNA sequence, ultimately to produce multiple copies of an identical molecule.
what is recombinant dna
refers to DNA that has been broken and recombined This can be produced naturally in cells as a result of crossing over
what is the aim of gene cloning
The aims of gene cloning are to assemble recombinant DNA containing a gene of interest and then direct this DNA into a host organism which will replicate the gene and produce the target protein in large amounts.
what is the process whereby human insulin is cloned and produced by bacteria
1. A useful target gene is identified (insulin).
2. DNA sequence is synthesised
3. Plasmids (circular pieces of DNA) are isolated from bacteria. Both the bacterial plasmids and the DNA containing our target gene are treated using a restricted enzyme.
4. Complementary sticky ends of the target gene and the plasmid come together through base-pairing affinity. These are then annealed using DNA ligase. The two recombinant plasmids with the insulin gene inserted are now ready.
5. This new recombinant plasmid is re-inserted into host bacteria (transformation). The host bacteria expresses lots and lots of copies of the target gene, producing large amounts of the target protein (insulin)
6. This protein can then be extracted from the cells, the two side chains of insulin are combined, they are purified, and then used by humans.
what are the applications of gene cloning
Medicine: Producing insulin, growth hormones, vaccines.
Agriculture: Creating genetically modified (GM) crops with traits like pest resistance.
Research: Studying gene function, regulation, or mutations.
Industry: Producing enzymes used in food or cleaning products.
what are plasmids and their function in gene cloning
small, circular piece of DNA found in bacteria, separate from their chromosomal DNA. It can replicate independently and often carries useful genes, such as antibiotic resistance.
Function in gene cloning: Used as a vector to carry the gene of interest into a host cell.
what are restriction enzymes and their role in gene cloning
Also called restriction endonucleases, these are enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences.
Function: Used to cut both the gene of interest and the plasmid at matching sites, producing “sticky ends” or “blunt ends” that can be joined together.
what is recombinant plasmid
a plasmid that has been genetically engineered to include foreign DNA (the gene of interest). This new DNA combination allows the host organism to express or replicate the inserted gene.
what does the term monoculture mean
identical or very similar type of organism
what are advantages of monocultures
· Its predictable – what the traits are going to be
· More efficient – creating the same product and grow times, only have the look after it in that way, less pesticides – cost effective. Gorwing condition may be the same e.g medicine or feed, - treat them all the same way
· More time effieicient – to reproduce and grow the same
· Bread in traits that that farmer wants
what are disadvantages of monocultures
· Problem in the environment it wont be able to adapt to the changed environment
· Low genetic variation = resistance to environmental change and disease/pest which the plant has no built in genetic resistance against – could loose all of the organisks
· Possibility of breading unfavourable traits
· Reduce other biodiversity – natural product bread everywhere
what are the advantages of wholeorganism/reproductive cloning
· Predictability of genes and what you will get · Breeding/cloning favourable traits · Time and potentially cost effective and resource efficient (plants are easier though to clone reproductively than animals.. |
what are the disadvantages?
· Costly for animals
· Reduceds genetic variation/diversity
accidently profriration of unfavourable traits
what are the uses of it
· Conservation of endangered animals
· Crops and agriculture cuttings, plant tissues etc.
what are the uses of therapeutic cloning
· medicines
· stem cell therapy
· growth of hormones or medicine
medical procedure e.g hormone, medicines, biomoleclules, stem celld
what are the advantages of therapeutic cloning
· medical applications -> curing and helping previous uncurable diseases
· way to produce biomolecules without harming living creatures
what are the disadvantages of therapeutic cloning
· ethical concerns of being from a blastocyst
· significant ethical issues destructuion of embroyos that have the potential to grow into living organisms
· commodifying life business of selling parts of people
expensive, not easy access to the public

what is recombinant DNA technology
Methods to join together DNA from two different species in order to produce new genetic combinations.
what are transgenic organism
taking gene from one organism and inserting it into the cells of a different animal
introduction of exogenous genetic material (from an external source) into a living organism. This is performed so that the organism exhibits a new trait and transfers this trait to its offspring

what are applications of transgenic organisms
▪ GM foods
▪ Disease and pest resistance
▪ Disease treatment – gene therapy
▪ Reproductive technology

what are examples of transgenic organisms
Golden rice Rice capable of producing beta-carotene (precursor to Vitamin A).
- Used to prevent nutritional blindness in third world countries
Transgenic cows A natural protein produced in the milk of transgenic cows like this one kills the bacteria that cause animal mastitis(bacterial infection) protects the livestock of cows
Transgenic Vaccines
Vaccine inserting part of pathogen/weakened pathogen into the body in order to provoke an immune response
immune system recognises foreign body, creates antibodies and cells which remember the pathogen when exposed to the full-strength pathogen, your body is equipped to respond.

what is gene therapy
The correction of genetic disorders by introducing normal, functional genes into cells.

· Has the potential to make lasting changes to an indivuals health, rather than just treating symptons
· Involves the insertion of a corrected, functioning gene into a defected one
- By introducing this healthy genetic material, the offspring of the cell of intresr will hopefully inherit this healthy gene, and therefore repair the genetic disorder.

what is the process of gene therapy
· A genetic cause of the disease is identified
· Cells involved in the disease are located
· Access to multiple copies of the normal gene
· Insertion of normal gene into the affected cells
potentially replace copies of defected genes with ‘regular’ genes
e.g cystic fibrosis, previouslt untreatable, they cant remove mucus from their lunds

how does gene therapy work
· Viral vectors are the most common method of delivery but non-viral methods are currently being trialled
· Direct injection of DNA
· Linking the normal gene to a molecule that binds to a receptor on the target cell
· Nanotechnology to make a liposome that carries the DNA
· Constructing an artificial chromosome containing a gene for insertion
· Once inside the cell, the gene must be incorporated into the cell’s DNA
· Silencing the gene

what is CRISPR
A gene editing system where point mutations are accurately introduced to genomes
· A guide RNA, containing the nucleotide sequence complementary to the gene you want to edit, bound to
· A cas9 endonuclease enzyme, which is able to cut DNA
Using this system, we can direct our gene editing tool to a specific part of a genome with very high accuracy, and with the same tool, cut and edit the gene of intrest. With CRISPR, we are able to insert, delete, or substitute up to 20 base pairs.
This technology has the potential to improve targeted gene therapy, reversing point mutations which cause diseases such as cystic fibrosis. In addition, its efficiency and relatively low cost make it a great tool for molecular biology research, improving gene cloning and production of transgenic species.
evaluate the techniques of genetic technologies and their benefits on agriculture, medicine and industry
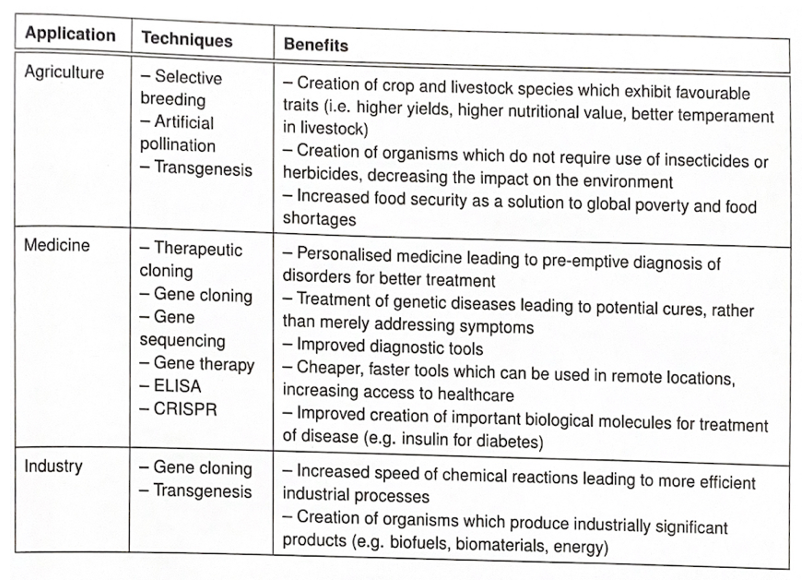
Evaluate the effect of biodiversity using biotechnology in agriculture

