Chapter 5 (Tissues; the stuff on the white slides (if the slide has pics, the pics r here not the words gangalang ;))
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
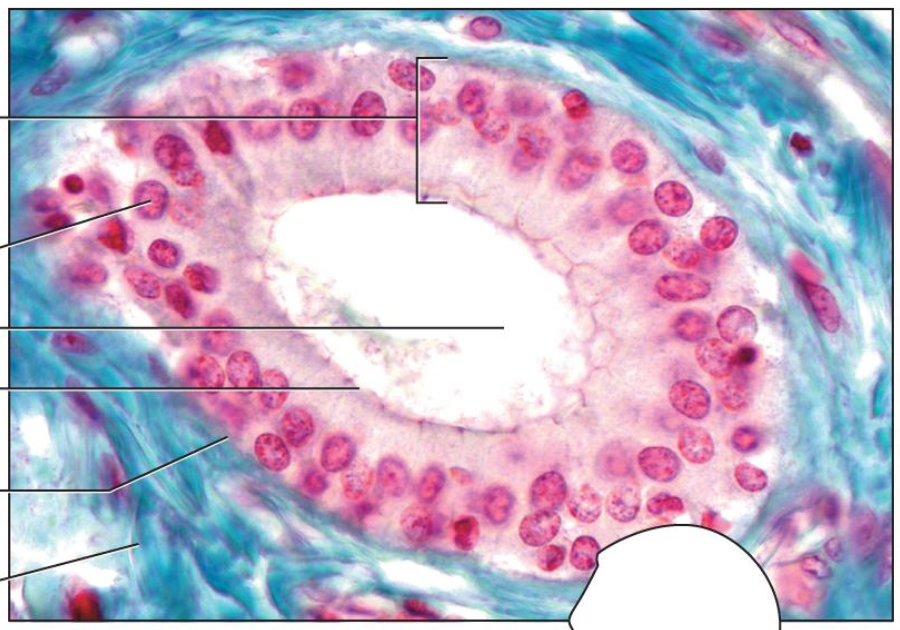
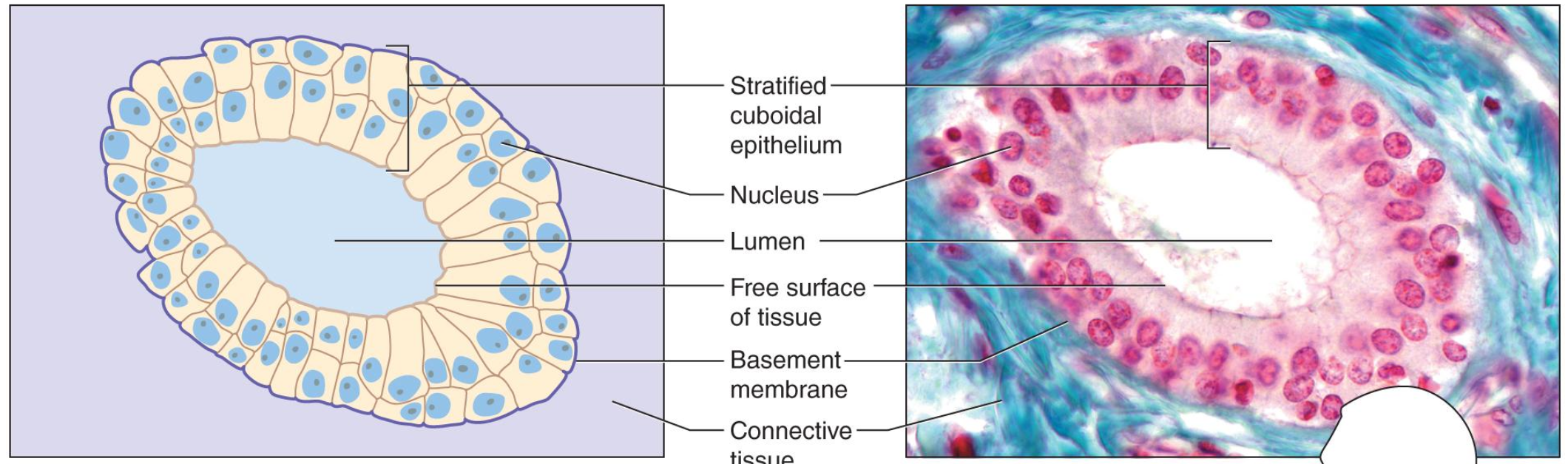
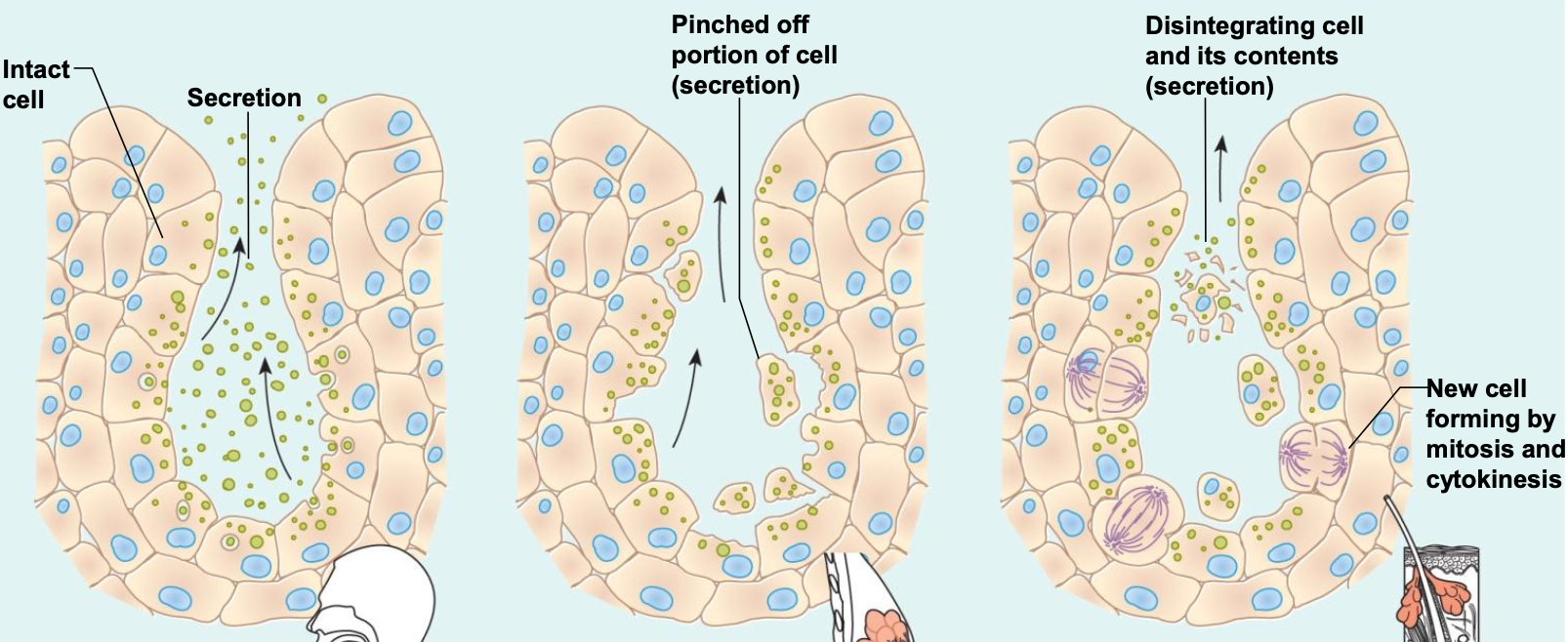
1 - merocrine gland
2 - apocrine gland
3 - holocrine gland
Types of Membranes
1 - Serous mMmbrane
inner lining & covering organs of thorax & abdomen to reduce friction
lines body cavities that DONT open to outside (omg if i’m serious, i wont open up)
secretes serous fluid
2 - Mucous Membrane
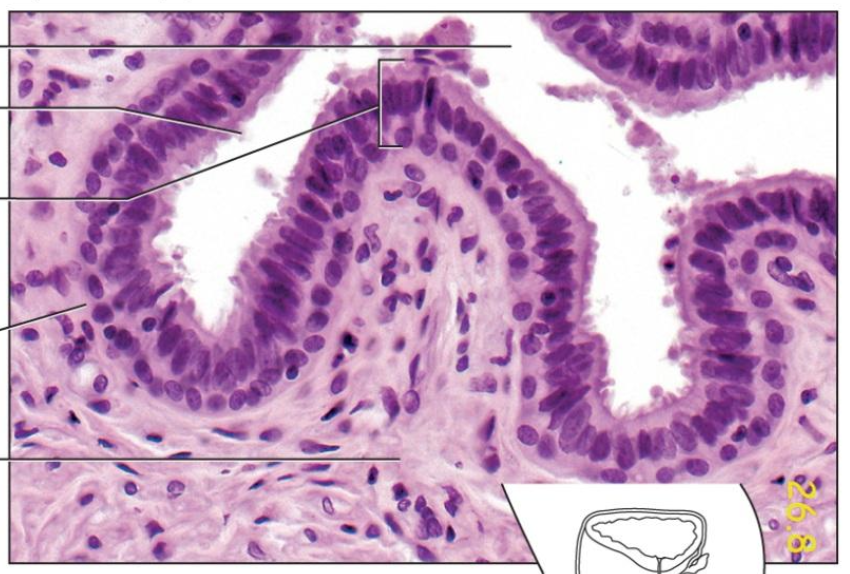
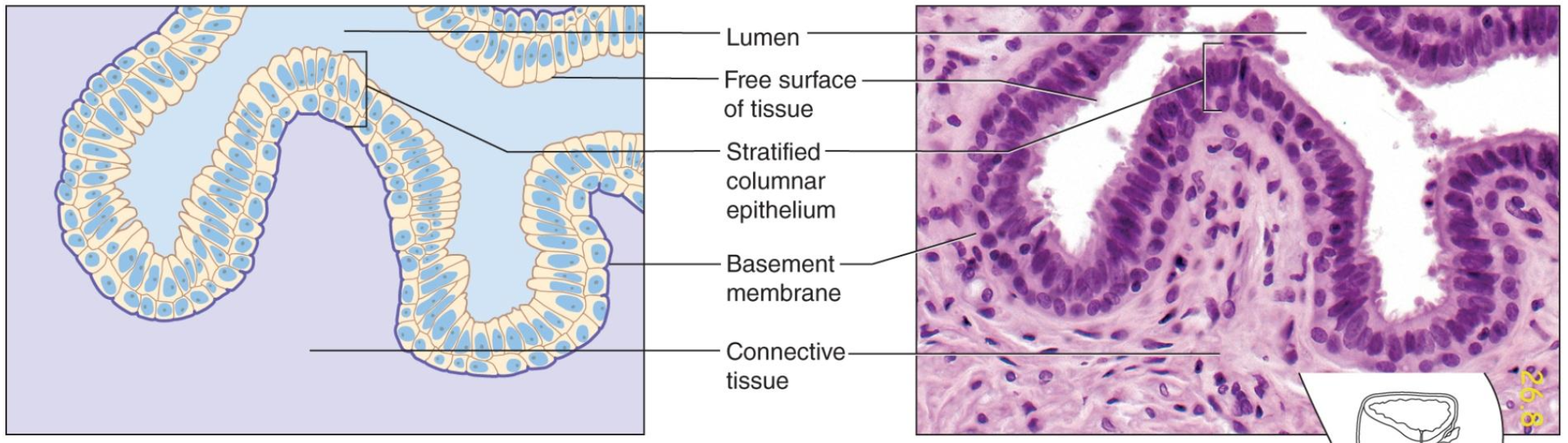
lining of digestive, respiratory, urinary & reproductive tracts
lines tubes/organs that DO open to outside
secretes mucus
3 - Cutaneous Membrane
covers body
skin
4 - Synovial Membrane
entirely connective tissue
lines joints
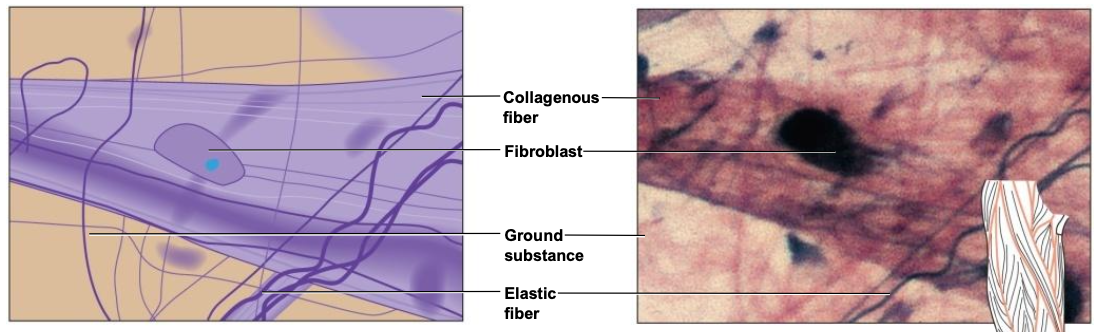
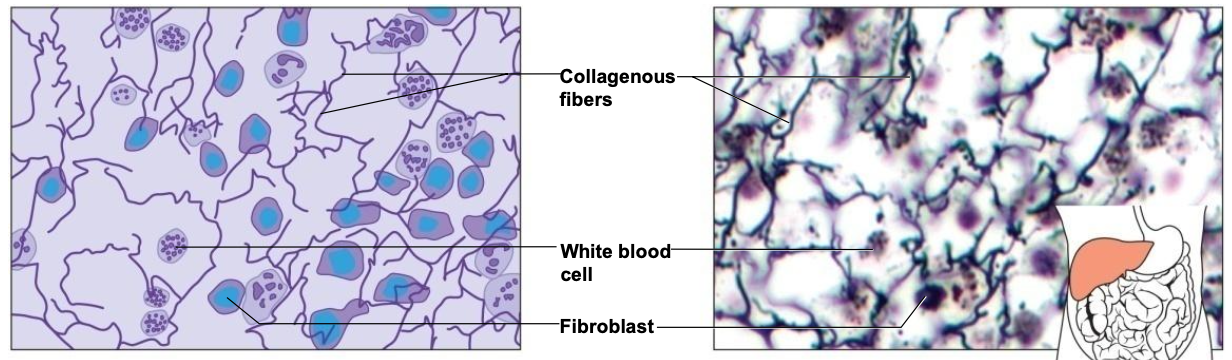
Connective Tissue Major Cell Types
1 - Fibroblast
most common cell
large
secretes ECM fibers
2 - Mast Cells
large cell
located near blood vessels
release heparin (anticoagulant)
release histamine (promotes inflammation)
3 - Macrophages
wandering cell
phagocytic
important in immunity & prevention of infection
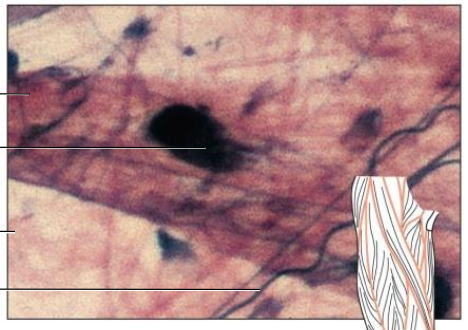
Connective Tissue Fibers
1 - Collagenous Fibers
thick
composed of collagen
great tensile strength
abundant in dense connective tissue
hold structures tog
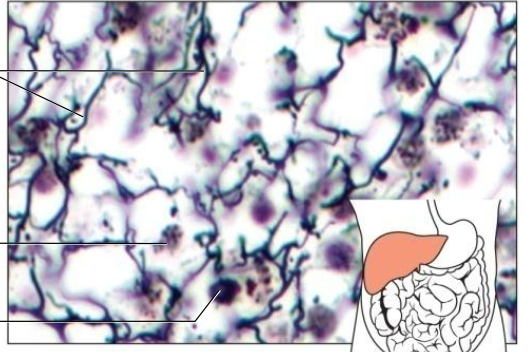
2 - Reticular Fibers
v thin collagenous fibers
highly branched
form delicate supportive networks
3 - Elastic Fibers
bundles of microfibrils embedded in elastin
elastic
Connective Tissues
- Loose Connective Tissue
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular
- Dense Connective Tissue
Dense regular
Dense irregular
Elastic
- Specialized Connective Tissue
Cartilage
Bone
Blood
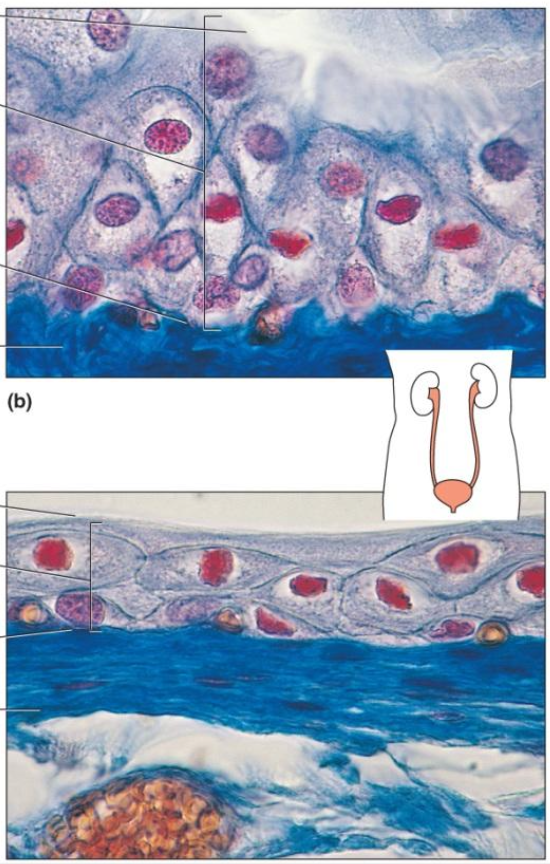
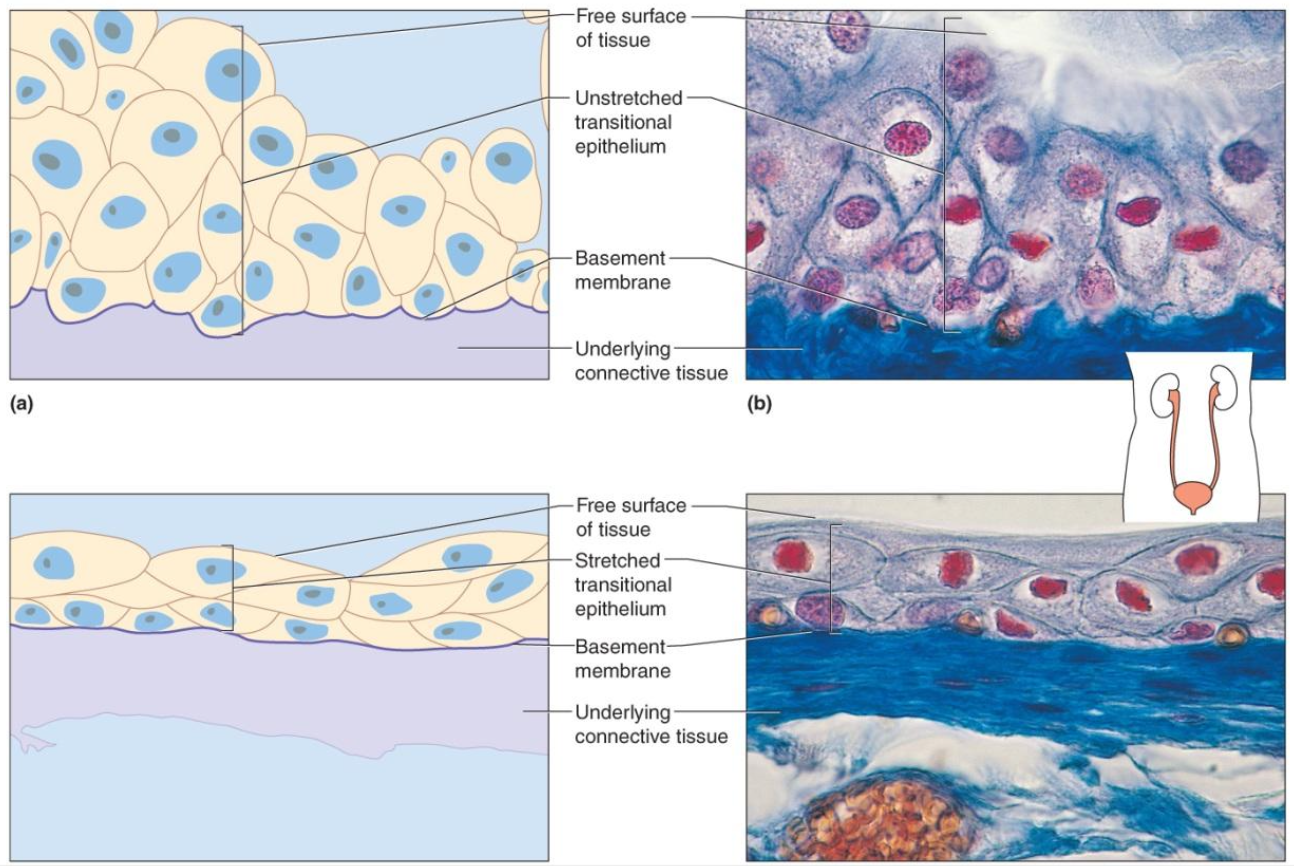
Glandular Epithelium — 2 Types
Composed of cells that are specialized to produce & secrete substances
2 Types:
Endocrine glands — secrete into body fluids or blood
Exocrine glands — secrete into ducts
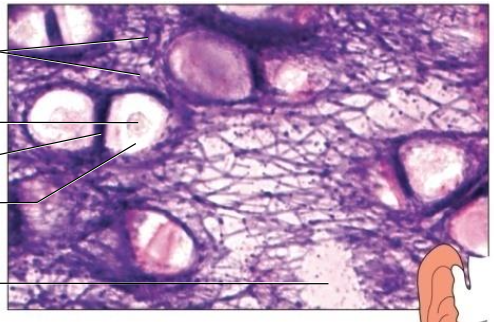
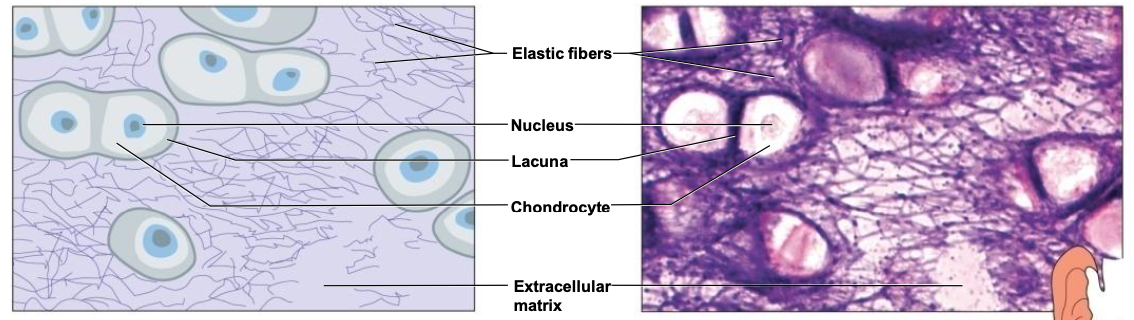
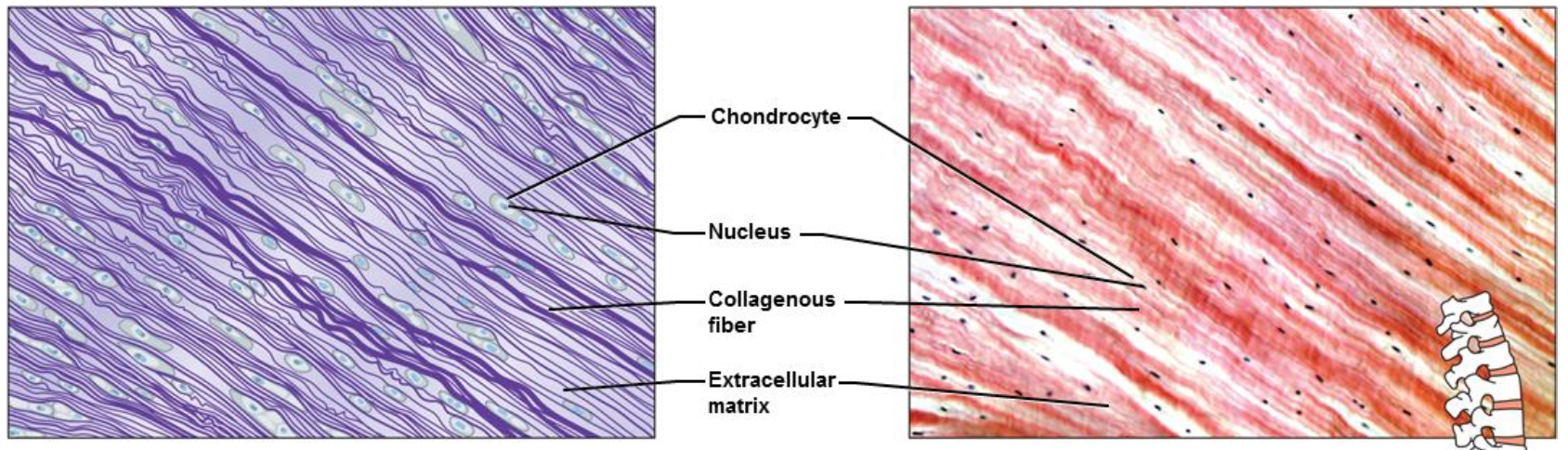
Connective Tissue Types - Cartilage
3 Types:
- Hyaline Cartilage
most abundant
fine collagenous fibers
ends of bones, nose & respiratory passages
- Elastic Cartilage
flexible bc of elastic fibers
external ear, larynx
- Fibrocartilage
v tough bc of many collagenous fibers
shock absorber
intervertebral discs, pads of knee & pelvic girdle
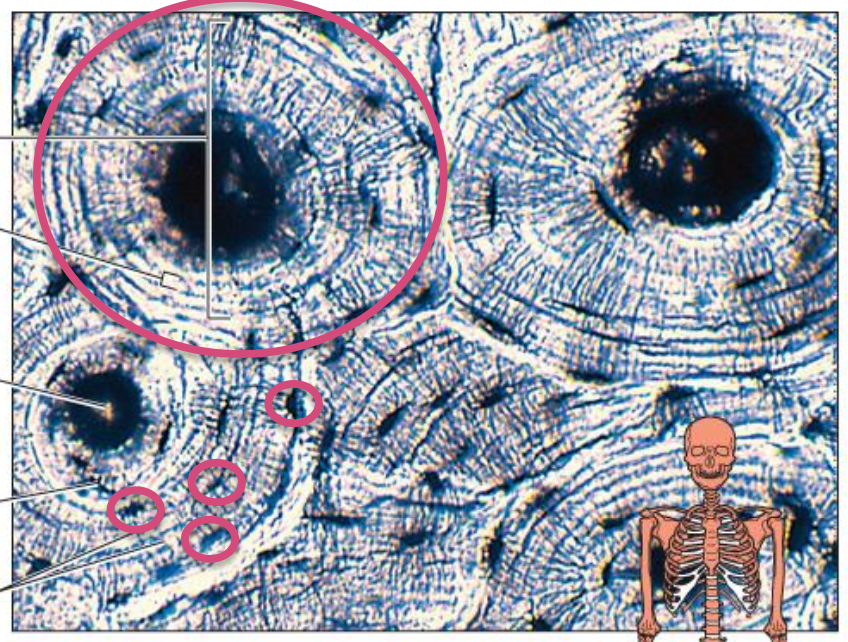
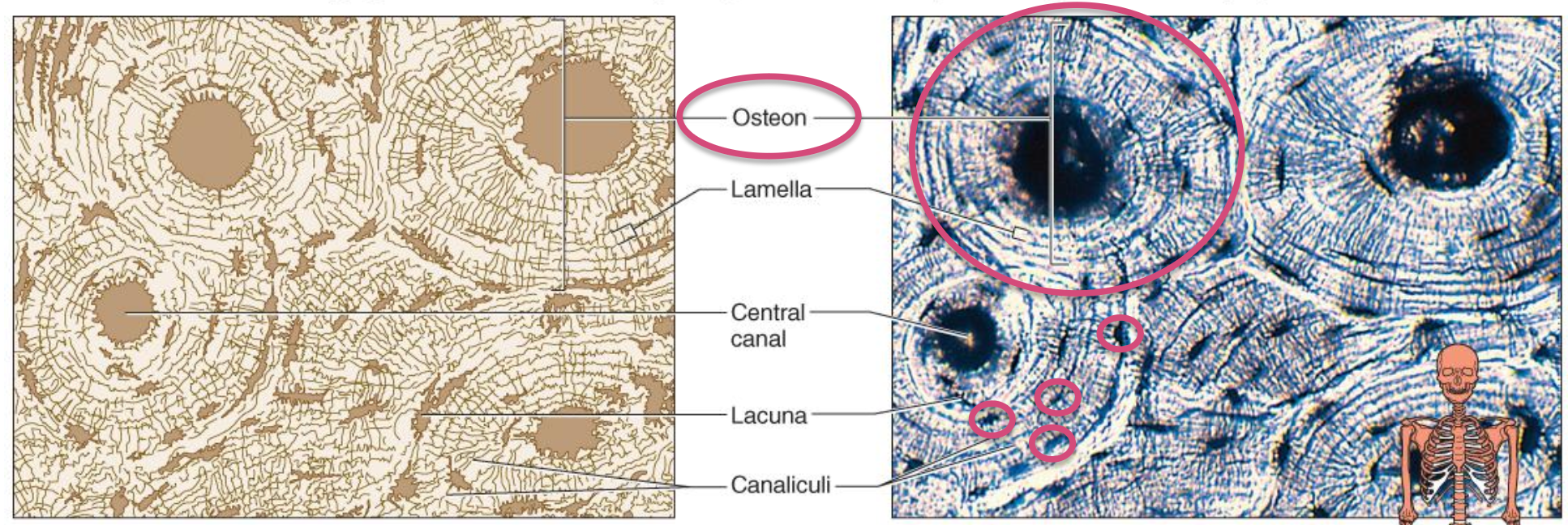
Connective Tissue Types - Bone
rigid matrix with deposits of mineral salts & collagen
supports
protects
forms blood cells
attachment for muscles
skeleton
osteocytes in lacunae
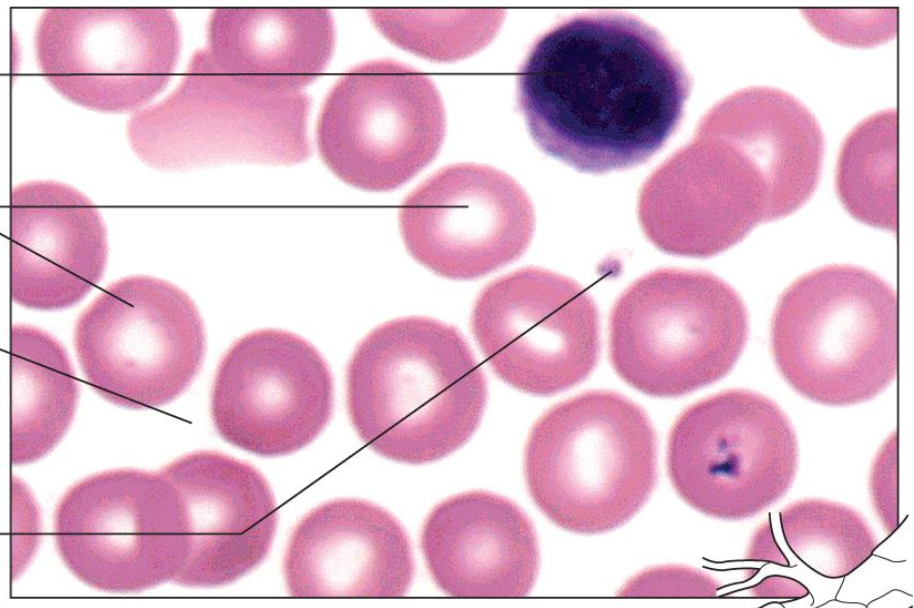
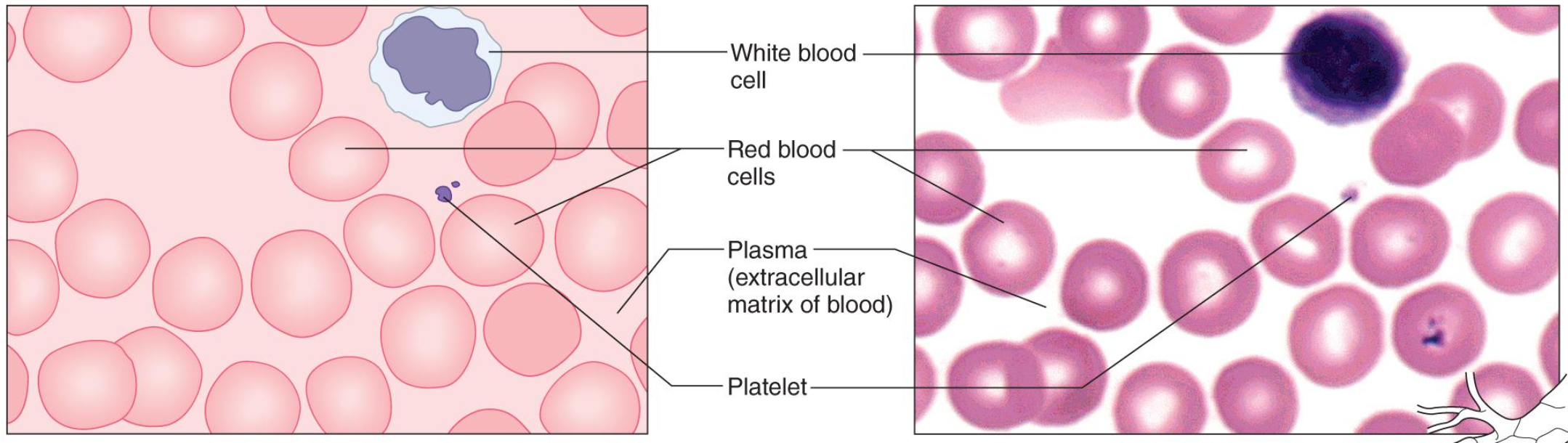
Connective Tissue Types - Blood
fluid matrix called plasma
RBCs & WBCs & platelets
transports & defends
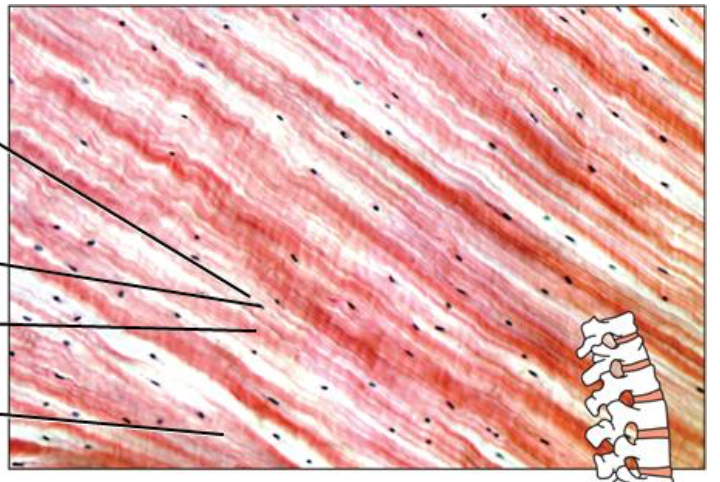
Muscle Tissue Types
3 Types:
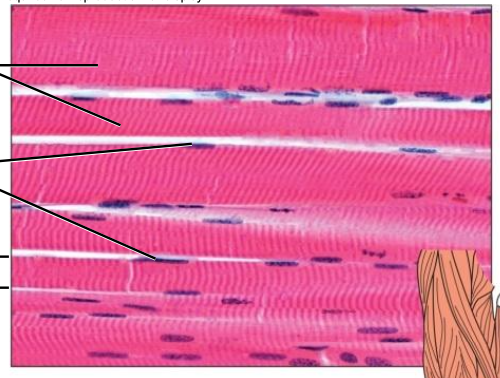
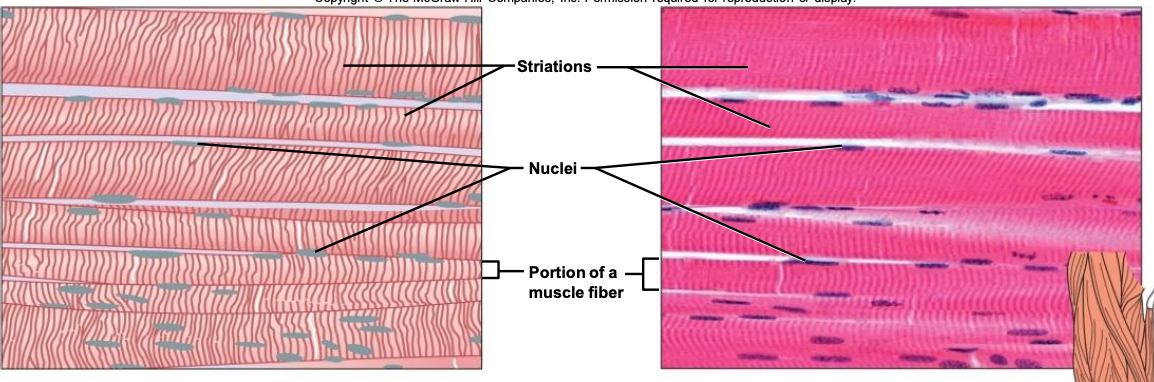
- Skeletal
attached to bones
voluntary
striated
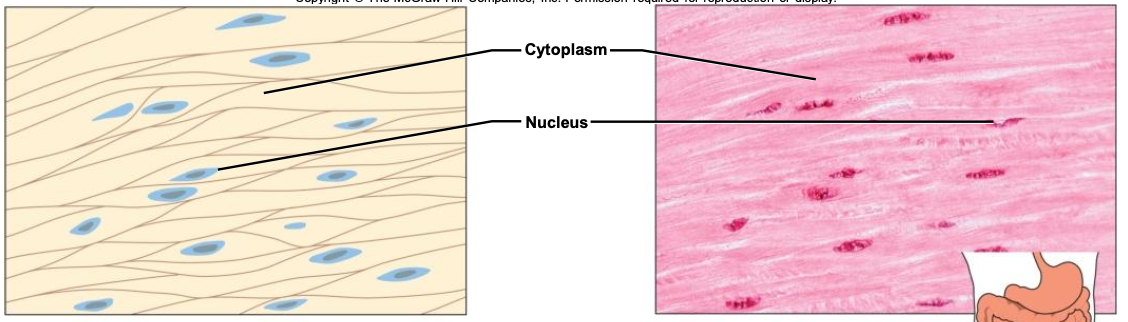
- Smooth
walls of organs
digestive tract & urinary bladder
walls of blood vessels
involuntary
non-striated
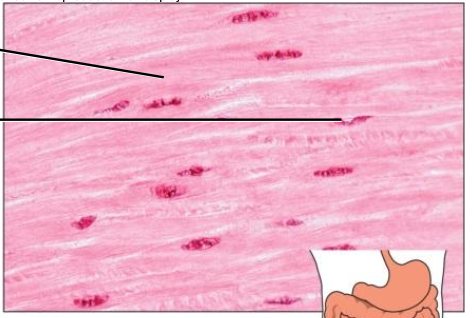
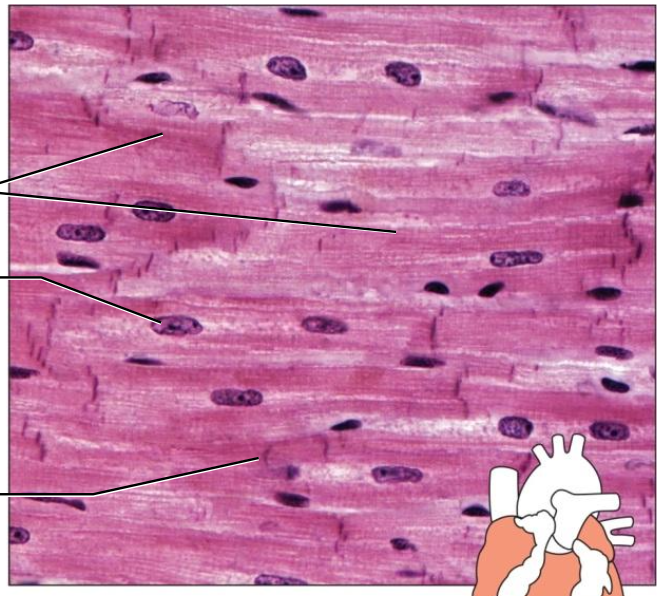
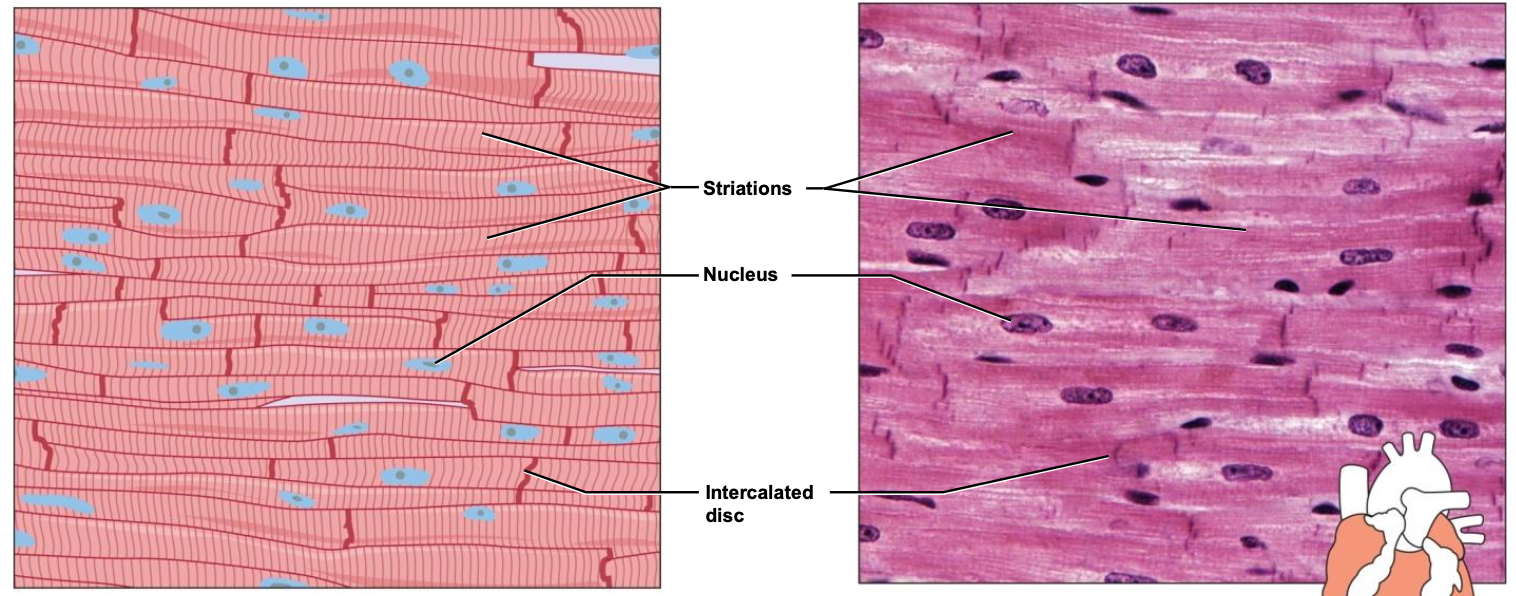
- Cardiac
heart wall
involuntary
striated
intercalated discs