materials processing: ceramics
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
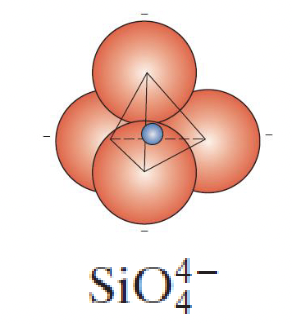
silicate ceramics describe __Si +__O, shape is ___
1, 4, tetrahedron (not a unit cell)
silicate ceramics are ____ charged, if not neutral, what is its charge?
negatively, -4
crystalline silica has a ____ structure with ___ melting points
network, high (due to Si-O interatomic bonding)
Silica glasses are ____ (fused silica) with a high degree of atomic randomness and same basic unit (NOT UNIT CELL) as silica
noncrystalline solids
network formers ex: B2O3 and GeO2
oxides than can form glassy/polyhedral oxide structures (similar to SiO2)
network modifiers ex: CaO and Na2O
do not form polyhedral networks, but cations are still incorporated
intermediates ex: TiO2 and Al2O3
are not network formers but substitute for Si
addition of these modifiers and intermediates -→ lowers the ____ and _____ of a glass
melting point and viscosity
cation–vacancy and a cation–interstitial pair
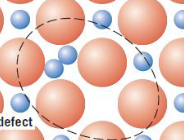
frenkel defect
a cation vacancy–anion vacancy pair (found in AX materials)
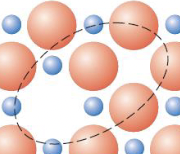
Schottky defect
measure of a ceramic material’s ability to resist fracture when a crack is present
fracture toughness
The degree of ionic character of the interatomic bonds in ceramics depends on the difference of ____
electronegativity of atoms (higher diff = more electronegative)
Carbon atoms in graphite are ___ hybridized, but are ____ hybridized in diamond
sp2, sp3
a state for ionic compounds wherein there is the exact ratio of cations to anions as predicted by the chemical formula
stoichiometry
The structure of a grinding wheel depends on the ______
spacing of grits
The grade of a grinding wheel depends on the amount of _____ holding abrasive grains in the wheel.
bonding agent
Typically small amounts of material are removed at high speed during grinding to produce…
fine swarf
_____ of a grinding wheel occurs when the porosities on the wheel surfaces become filled or clogged with chips from the workpiece
loading
glass forming operations occur between what two temperatures?
working and softening
powder particles are pressed together until pores form between them, the more it is pressed the smaller the pores get
sintering
what is the goal of sintering?
reduce porosity → increase mechanical properties
uses heat to relieve internal stresses
annealing
enhances strength of glass by intentionally inducing compressive residual surface stresses
glass tempering
larger ratio of Rc/Ra = ____ coordination #
higher (anions have more cation neighbors)
AmBnXp-Type Crystal Structures have ____ and ____ crystal structure
more than one cation type, perovskite
how is electroneutrality established in negatively charged layered silica?
2nd planar sheet with an excess of cations to bond to 1st sheets excess of anions
bonding within 2 layered silicate sheets are
strong and intermediate ionic-covalent
bonding between adjacent layered silicate sheets are
loosely bound to one another by weak van der Waals forces
is the ratio of cations to anions altered by the formation of either a Frenkel or a Schottky defect?
NO
as porosity increases, ____ and _____ decrease
elastic modulus and flexural strength
Material processed by heat treatment to produce fine-grained polycrystalline structure
glass-ceramic
what is the critical cooling rate for glass-ceramic (minimum rate so that entire product is only glass ceramic)?
100 C/min
why are glass-ceramics used in fabrication? what are some of its properties?
ease of fabrication, strength and resistance to thermal shock
failure modes of a grinding wheel:
______ of individual particles
______ in individual particles
______ between particles
attricious wear, microcracks, bond fracture
below the strain point, fracture will occur before…
the onset of plastic deformation
Bonding of ceramics tends to be either totally _____ or totally _____ or a combination of the two
ionic, covalent
what influences ionic crystal structure? (list 2)
magnitude of charge on each ion, relative size of cation and anion
what shows a stable crystal structure?
all anions are in contact with the cation
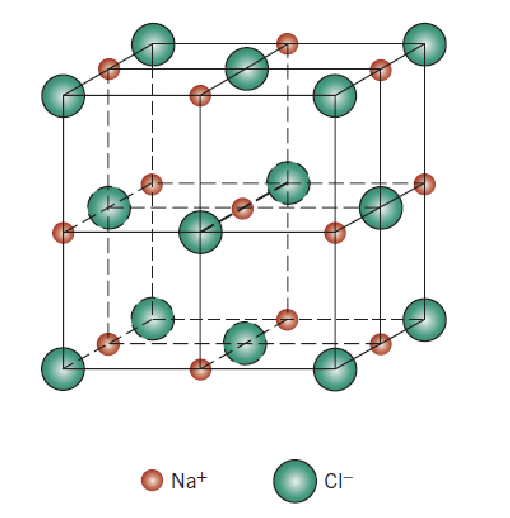
c
rock salt, 6
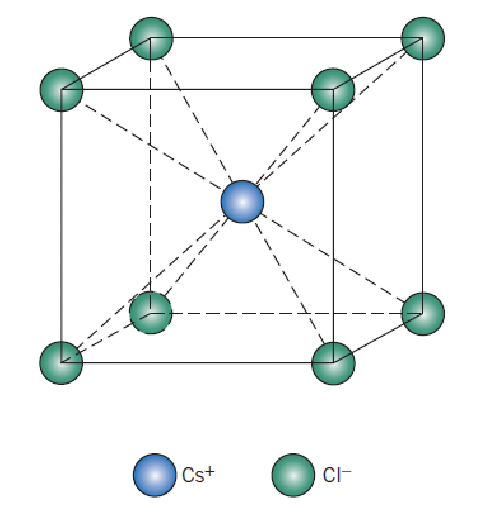
identify the crystal structure and coordination number
cesium chloride, 8 (cation)
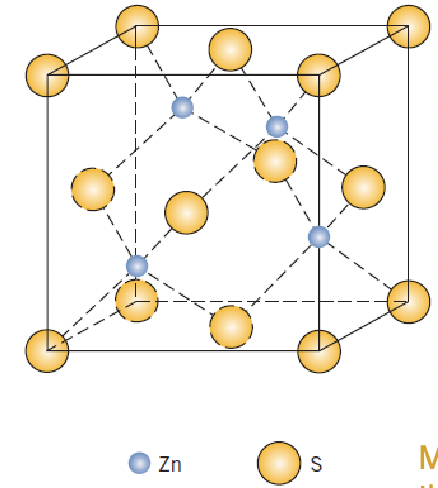
identify the crystal structure and coordination number, what type of atomic bonding is typically present here?
zinc blende, 4, covalent
AmXp-Type Crystal Structures have what notable properties, coordination number, and rc/ra ratio?
unequal charges on cation and anion, 8, 0.8
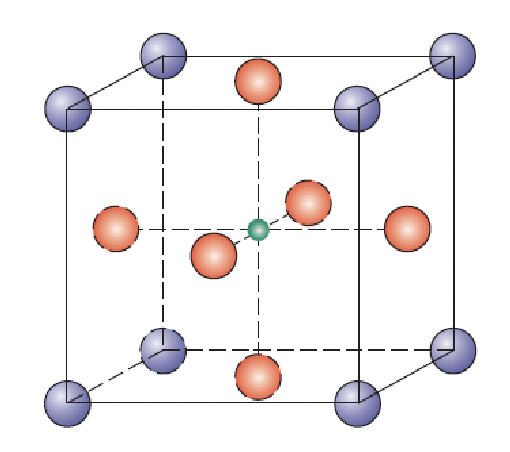
perovskite crystal structure
layers of covalently bonded carbon in hexagonal pattern, layers are held in a stack by ________ forces, who am i?
weak van der waals forces, graphite
repeating unit formula for layered silicates = _____
(Si2O5)^-2
are diamond and graphite considered a ceramic, polymer, or metal?
none, but sometimes graphite can be a ceramic
why do anions never have interstitial defects?
too large, too much strain
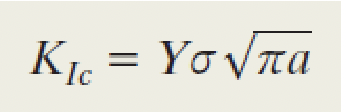
plane strain fracture toughness equation
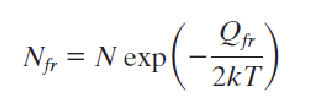
temperature dependence of defects
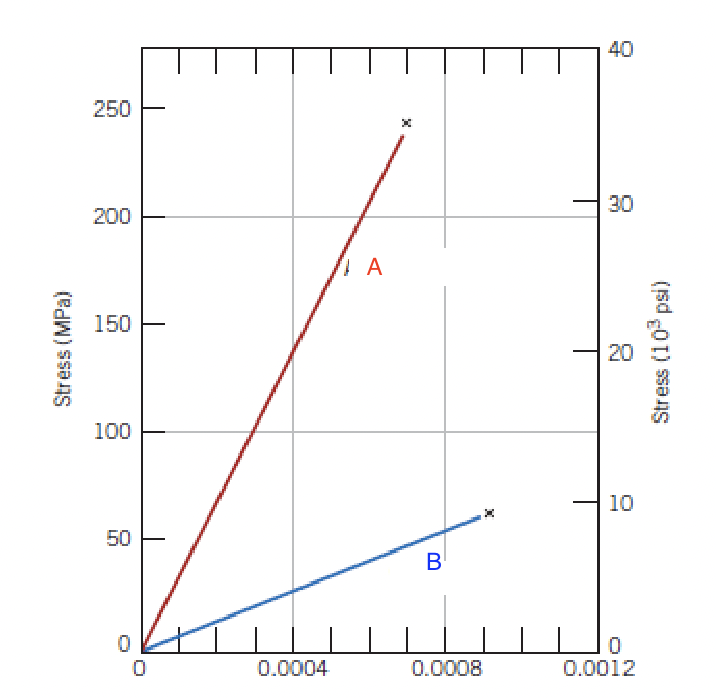
identify the materials
A=aluminum oxide B=glass
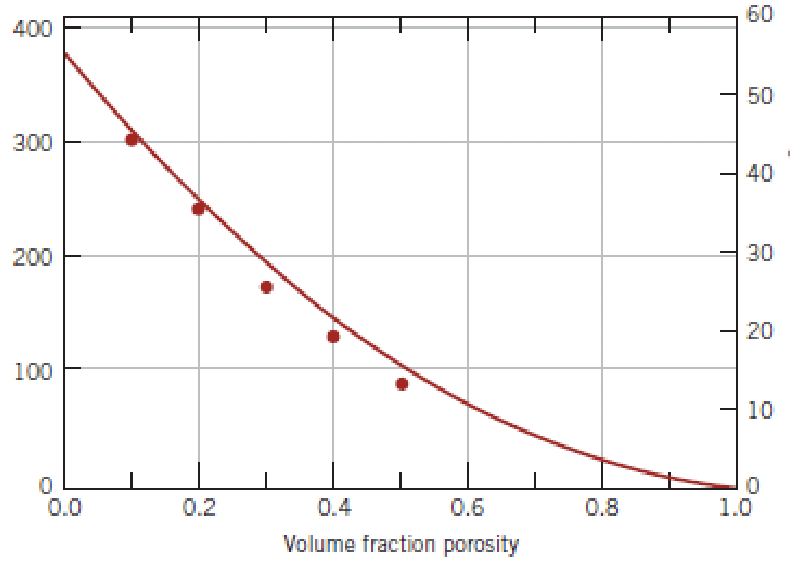
identify the y axis, what is the xmax?
modulus of elasticity, 1
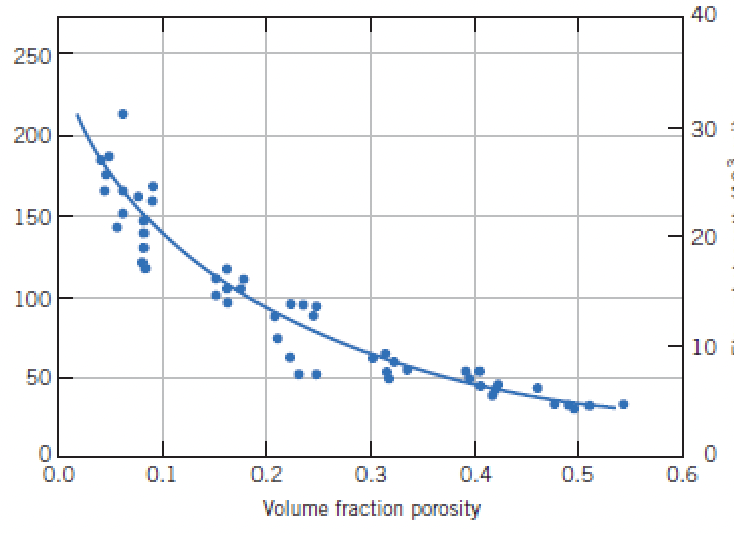
identify the y axis, what is xmax?
flexural strength, 0.55
Common applications for abrasives include ____, ____, ____, and _____
grinding, polishing, cutting, sharpening
Large number of cutting edges for abrasive particles, each removing very small amounts of material
grinding
the process of producing a true circle on a wheel that has become out of round
truing
the process of conditioning, producing sharp new edges on worn grains on the grinding surface of a wheel
dressing
dressing is necessary after the grinding wheel experiences ____ or becomes ____
attritious wear, loaded
what nucleating agent is typically added to shorten crystallization times?
TiO2
viscosity is ____ at ____ temperatures
higher, lower
does sintering involve melting?
no, occurs below the Tm
Which ceramic processing method involves compacting powders and heating them to improve strength?
powder processing and sintering
(T/F) Viscosity at the annealing point is lower than at the softening point, such that atomic diffusion occurs rapidly enough to relieve residual stresses within about 15 minutes at the annealing point.
false
(T/F) Viscosity is very high at the strain point, at which the material becomes so rigid that it will fracture before undergoing plastic deformation.
true
Which ceramic abrasive is known for being second only to diamond in hardness and is ideal for machining ferrous metals?
kaolinite
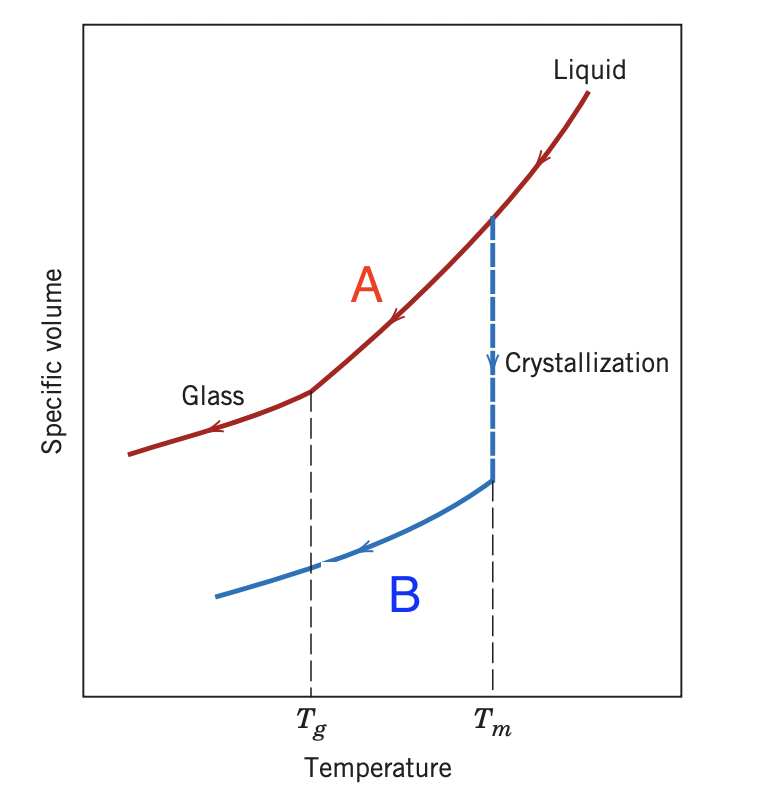
A=supercooled liquid B=crystalline solid